#437 Path Sum III
Description
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Examples
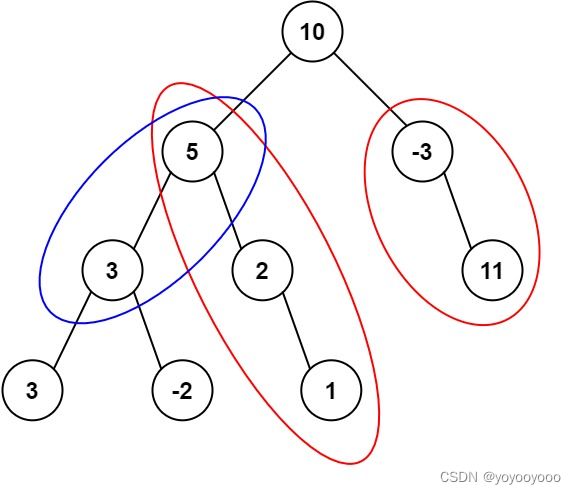
Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8
Output: 3
Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: 3
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 1000].
− 1 0 9 -10^9 −109 <= Node.val <= 1 0 9 10^9 109
-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
思路
第一种是把每个节点当作root往下测试,这种方法时间复杂度较高。
第二种就是类似于twoSum的方法,需要把一条路径上的sum都进行求和存档,但由于存在同一个sum可能有两条路径的情况(如 {1, 0, -1, 1} -> sum={1, 0, 0, 1}),需要在存储sum的同时,存储一下到达这个sum的路径条数有多少,所以用map而不是用set
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int answer = 0;
public void calPath(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (targetSum - root.val == 0)
answer ++;
calPath(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
calPath(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
public void calPath2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null)
return;
calPath(root, targetSum);
calPath2(root.left, targetSum);
calPath2(root.right, targetSum);
}
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
calPath2(root, targetSum);
return answer;
}
}
class Solution {
int count = 0;
// Sum, 和是这个Sum的路径个数
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
map.put(0,1);
traverse(root,0,targetSum);
return count;
}
public void traverse(TreeNode root, int currSum, int targetSum){
if(root == null)
return;
currSum+=root.val;
if(map.containsKey(currSum - targetSum) && map.get(currSum - targetSum) > 0)
count+=map.get(currSum - targetSum);
map.put(currSum,map.getOrDefault(currSum,0) + 1);
traverse(root.left, currSum, targetSum);
traverse(root.right, currSum, targetSum);
map.put(currSum,map.getOrDefault(currSum,0) - 1); // 只保存这条路径上的sum
}
}