《Linux驱动:I2C驱动看这一篇就够了》
文章目录
- 一,前言
- 二,IIC驱动的体系架构
-
- 2.1 IIC核心
- 2.2 IIC适配器
-
- 2.2.1 适配器驱动资源的初始化和注册
- 2.2.2 IIC适配器里的通信方法
- 2.2.3 IIC适配器和IIC设备驱动的匹配
- 2.3 IIC设备驱动
-
- 2.3.1 IIC通用设备驱动
- 2.3.2 IIC通用设备驱动和IIC适配器的匹配
- 2.3.3 at24cxx的IIC设备驱动
- 2.3.4 at24cxx的IIC设备驱动和IIC适配器的匹配
- 三,应用程序和IIC设备的数据传输方式
- 四,和IIC设备进行一次数据传输的过程
-
- 4.1 通过IIC通用设备驱动进行数据传输
-
- 4.1.1 利用IIC通用设备驱动进行数据传输的函数调用过程
- 4.2 通过特定的IIC设备驱动进行数据传输
- 五,总结
一,前言
I2C(也写做IIC)总线支持设备之间的短距离通信,用于处理器和一些外围设备之间数据传输,它只需要两根信号线来就能完成数据传输,极大地简化了对硬件资源和PCB板布线空间的占用,所以它被EEPROM、时钟等设备与主控的接口中。前一篇简单分析下I2C协议,并且通过IO口模拟了I2C的数据传输,这一篇来分析下linux系统中的I2C协议的使用,分析Linux系统中I2C驱动的体系结构和工作方式。最后通过自行构建一个I2C设备驱动程序来了解I2C设备驱动开发的具体流程。
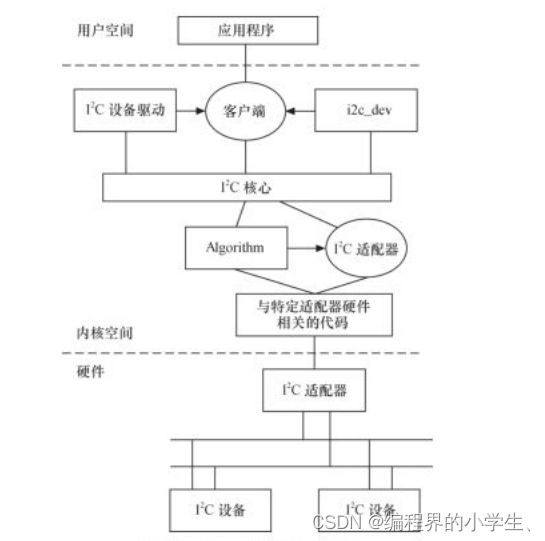
二,IIC驱动的体系架构
2.1 IIC核心
I2C核心向内核注册了I2C总线,同时创建了一个适配器类(/sys/class/i2c-adapter),以便于后面向I2C总线注册适配器时在该适配器类下创建适配器设备。在I2C核心中,提供了I2C适配器和I2C设备驱动的注册、注销方法。
通过 i2c_add_adapter 接口将I2C适配器注册到I2C总线中。
通过 i2c_add_driver 接口将I2C设备驱动注册到I2C总线中。
// linux-2.6.22.6/drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.dev_attrs = i2c_dev_attrs,
.match = i2c_device_match,
.uevent = i2c_device_uevent,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
.suspend = i2c_device_suspend,
.resume = i2c_device_resume,
};
struct class i2c_adapter_class = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "i2c-adapter",
.dev_attrs = i2c_adapter_attrs,
};
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
// 注册i2c总线
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
// 在/sys/class/下创建一个适配器类 /sys/class/i2c-adapter
return class_register(&i2c_adapter_class);
}
subsys_initcall(i2c_init);
2.2 IIC适配器
2.2.1 适配器驱动资源的初始化和注册
由于IIC总线控制器通常是在内存上的,所有它本身也连接在platform总线上,要通过paltform_driver 和paltform_device 的匹配来执行。在该paltform_driver 的probe函数中,通常完成两个工作。
- 初始化I2C适配器所使用的硬件资源,如申请i/o地址、中断号、时钟等。
- 通过i2c_add_adapter接口向I2C总线注册了一个适配器。
static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,
};
static struct s3c24xx_i2c s3c24xx_i2c = {
.lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(s3c24xx_i2c.lock),
.wait = __WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_INITIALIZER(s3c24xx_i2c.wait),
.tx_setup = 50,
.adap = {
.name = "s3c2410-i2c",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm,
.retries = 2,
.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON,
},
};
s3c24xx_i2c_probe ->
......
// 时钟
i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c");
clk_enable(i2c->clk);
......
// i/o资源
i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, (res->end-res->start)+1,
pdev->name);
i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, (res->end-res->start)+1);
......
//中断
ret = request_irq(res->start, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED,
pdev->name, i2c);
......
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = &s3c24xx_i2c;
// 注册适配器
i2c_add_adapter(&i2c->adap)
......
2.2.2 IIC适配器里的通信方法
I2C适配器为后和它匹配的设备驱动提供通信方法,即数据传输的接口。主要是实现i2c_algorithm结构体的master_xfer 函数和 functionality函数。functionality函数用于返回algorithm所支持的通信协议。master_xfer 函数在I2C适配器上完成传递给它的i2c_msg数组中的每个IIC消息。
static u32 s3c24xx_i2c_func(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
return I2C_FUNC_I2C | I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_EMUL | I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING;
}
static int s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = (struct s3c24xx_i2c *)adap->algo_data;
int retry;
int ret;
for (retry = 0; retry < adap->retries; retry++) {
ret = s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(i2c, msgs, num);
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
return ret;
dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "Retrying transmission (%d)\n", retry);
udelay(100);
}
return -EREMOTEIO;
}
2.2.3 IIC适配器和IIC设备驱动的匹配
s3c24xx_i2c_probe ->
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = &s3c24xx_i2c;
// 注册适配器
i2c_add_adapter(&i2c->adap) ->
i2c_register_adapter(adapter) ->
......
// 将该注册的适配器加入到适配器链表中
list_add_tail(&adap->list, &adapters);
// 在 /sys/class/i2c-adapter设备类下创建一个设备
// /sys/class/i2c-adapter/i2c-0
sprintf(adap->dev.bus_id, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);
adap->dev.release = &i2c_adapter_dev_release;
adap->dev.class = &i2c_adapter_class;
res = device_register(&adap->dev);
// 从I2C设备驱动链表中,取出每一项驱动,执行驱动的attach_adapter接口,以匹配适配器和设备驱动
// IIC设备驱动链表由IIC设备驱动注册时设置。
list_for_each(item,&drivers) {
driver = list_entry(item, struct i2c_driver, list);
if (driver->attach_adapter)
/* We ignore the return code; if it fails, too bad */
// 调用IIC设备驱动的attach_adapter接口
driver->attach_adapter(adap);
}
......
2.3 IIC设备驱动
2.3.1 IIC通用设备驱动
实现了I2C适配器设备文件的功能,每一个IIC适配器都被分配一个设备。通过适配器访问设备时的主设备号都为89,次设备号为0~255。应用程序可以通过"/dev/i2c-%d"设备节点使用文件操作接口open()、write()、read()、ioctl()等来使用对应的IIC适配器访问某个I2C设备。
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = i2cdev_read,
.write = i2cdev_write,
.ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl,
.open = i2cdev_open,
.release = i2cdev_release,
};
static struct i2c_driver i2cdev_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "dev_driver",
},
.id = I2C_DRIVERID_I2CDEV,
.attach_adapter = i2cdev_attach_adapter,
.detach_adapter = i2cdev_detach_adapter,
.detach_client = i2cdev_detach_client,
};
#define I2C_MAJOR 89 /* Device major number */
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk(KERN_INFO "i2c /dev entries driver\n");
res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops);
if (res)
goto out;
// 创建/sys/class/i2c-dev
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev_class))
goto out_unreg_chrdev;
res = i2c_add_driver(&i2cdev_driver);
if (res)
goto out_unreg_class;
return 0;
out_unreg_class:
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
out_unreg_chrdev:
unregister_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c");
out:
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: Driver Initialisation failed\n", __FILE__);
return res;
}
2.3.2 IIC通用设备驱动和IIC适配器的匹配
static struct i2c_driver i2cdev_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "dev_driver",
},
.id = I2C_DRIVERID_I2CDEV,
.attach_adapter = i2cdev_attach_adapter,
.detach_adapter = i2cdev_detach_adapter,
.detach_client = i2cdev_detach_client,
};
i2c_dev_init ->
// 注册IIC设备驱动,匹配每个适配器进而为每个匹配到的适配器在 /sys/class/i2c-dev设备类下创建适配器设备
i2c_add_driver(&i2cdev_driver) ->
i2c_register_driver ->
// 将IIC设备驱动添加到驱动链表中
list_add_tail(&driver->list,&drivers);
// 从IIC适配器链表中,取出每一个适配器,调用IIC设备驱动提供的attach_adapter接口
list_for_each_entry(adapter, &adapters, list) {
driver->attach_adapter(adapter); // 即 调用i2cdev_attach_adapter
}
// 调用i2cdev_attach_adapter
i2cdev_attach_adapter
// 在 /sys/class/i2c-dev设备类下创建适配器设备 /sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-%d
// 同时会以I2C_MAJOR为主设备号,次设备号0~255,在/dev/下生成 /dev/i2c-%d设备节点
i2c_dev->dev = device_create(i2c_dev_class, &adap->dev,
MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, adap->nr),
"i2c-%d", adap->nr);
res = device_create_file(i2c_dev->dev, &dev_attr_name);
2.3.3 at24cxx的IIC设备驱动
为某个特定的IIC设备的构建的IIC设备驱动,通常在提供的attach_adapter 接口调用I2C核心提供的i2c_probe接口,同时提供一个设备探测成功后调用的函数"at24cxx_detect"给到i2c_probe,在i2c_probe中会去探测某个设备地址的设备是否存在,如果存在便调用at24cxx_detect。通常来说为某个特定的IIC设备去构建IIC设备驱动、针对平台硬件资源构建IIC适配器便是IIC驱动相关开发所需要做的工作,IIC核心相关、IIC总线驱动相关的部分,系统中一般已经存在。
static struct i2c_driver at24cxx_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "at24cxx",
},
.attach_adapter = at24cxx_attach,
.detach_client = at24cxx_detach,
};
static int at24cxx_attach(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)
{
return i2c_probe(adapter, &addr_data, at24cxx_detect);
}
static int at24cxx_detect(struct i2c_adapter *adapter, int address, int kind)
{
printk("at24cxx_detect\n");
/* 构构一个i2c_client结构体: 以后收改数据时会用到它 */
at24cxx_client = kzalloc(sizeof(struct i2c_client), GFP_KERNEL);
at24cxx_client->addr = address;
at24cxx_client->adapter = adapter;
at24cxx_client->driver = &at24cxx_driver;
strcpy(at24cxx_client->name, "at24cxx");
i2c_attach_client(at24cxx_client);
// 注册一个IIC设备的驱动,提供file_operations接口
major = register_chrdev(0, "at24cxx", &at24cxx_fops);
// 创建一个设备类/sys/class/at24cxx,并在该设备类下创建一个设备/sys/class/at24cxx/at24cxx
// 以 major为主设备号,次设备号0~255,生成/dev/at24cxx设备节点,供应用程序使用
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "at24cxx");
class_device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "at24cxx"); /* /dev/at24cxx */
return 0;
}
static int at24cxx_init(void)
{
i2c_add_driver(&at24cxx_driver);
return 0;
}
static unsigned short ignore[] = { I2C_CLIENT_END };
static unsigned short normal_addr[] = { 0x50, I2C_CLIENT_END }; /* 地址值是7位 */
static struct i2c_client_address_data addr_data = {
.normal_i2c = normal_addr, /* 要发出S信号和设备地址并得到ACK信号,才能确定存在这个设备 */
.probe = ignore,
.ignore = ignore,
//.forces = forces, /* 强制认为存在这个设备 */
};
2.3.4 at24cxx的IIC设备驱动和IIC适配器的匹配
at24cxx_init ->
i2c_add_driver ->
i2c_register_driver ->
// 将IIC设备驱动添加到驱动链表中
list_add_tail(&driver->list,&drivers);
// 从IIC适配器链表中,取出每一个适配器,调用IIC设备驱动提供的attach_adapter接口
list_for_each_entry(adapter, &adapters, list) {
driver->attach_adapter(adapter); // 即 调用at24cxx_attach
}
at24cxx_attach ->
i2c_probe(adapter, &addr_data, at24cxx_detect) ->
// 对每个设备地址执行
i2c_probe_address(adapter,address_data->probe[i + 1],-1, found_proc) ->
// 判断之前适配器中是否已经有该I2C设备连接了
i2c_check_addr(adapter, addr)
// 去探测这个设备地址的设备
i2c_smbus_xfer(adapter, addr, 0, 0, 0,I2C_SMBUS_QUICK, NULL) ->
i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated(adapter,addr,flags,read_write,command,size,data) ->
i2c_transfer(adapter, msg, num)
adap->algo->master_xfer(adap,msgs,num) ->
// 以i2c-s3c2410.c的适配器为例
s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(i2c, msgs, num)->
// 向某设备地址传输一个msg
s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, msgs);
// 等待设备的ACK回应,在s3c24xx_i2c_master_complete会唤醒该wait,并赋值i2c->msg_idx
timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, i2c->msg_num == 0, HZ * 5);
ret = i2c->msg_idx; // 返回ACK的值
// 设备有ACK回应则调用found_proc,即at24cxx_detect函数
found_proc(adapter, addr, kind);
at24cxx_detect中
设置了i2c_client结构体,记录了I2C设备的设备地址、匹配的适配器等信息
注册了一个字符设备,提供了file_operations接口,以供应用程序使用
创建设备类、设备、生成设备节点,以供应用程序使用
三,应用程序和IIC设备的数据传输方式
应用程序一般通过两种方式和i2c设备进行数据传输
- 应用程序通过通用设备驱动(i2c-dev)的设备节点"/dev/i2c-0"和某个i2c设备进行数据传输。
应用程序打开"/dev/i2c-0"节点,使用其file_operations接口(open、read、write、ioctl、close)和某IIC设备进行数据传输。
- 构建某个i2c设备的设备驱动程序,创建该i2c设备的设备节点(“/dev/at24cxx”),然后应用程序通过该i2c设备的设备节点和该i2c设备进行数据传输。
应用程序打开"/dev/at24cxx"节点,使用其file_operations接口(open、read、write、ioctl、close)和某IIC设备进行数据传输。
四,和IIC设备进行一次数据传输的过程
进行一次数据传输操作,IIC设备地址为0x50。
4.1 通过IIC通用设备驱动进行数据传输
#include 4.1.1 利用IIC通用设备驱动进行数据传输的函数调用过程
IIC通用设备驱动注册了一个字符设备,提供了file_operations 接口(open\read\write\ioctl等),并创建了一个设备节点“/dev/i2c-0”。
open("/dev/i2c-0", O_RDWR) // 即 i2cdev_open
adap = i2c_get_adapter(i2c_dev->adap->nr); // 获取驱动对应的适配器
client = kzalloc(sizeof(*client), GFP_KERNEL); // 申请并设置struct i2c_client 结构体
client->driver = &i2cdev_driver;
/* registered with adapter, passed as client to user */
client->adapter = adap;
file->private_data = client;
ioctl(fd,I2C_SLAVE,0x50) -> // 即 i2cdev_ioctl
case I2C_SLAVE:
client->addr = arg; // 设置从设备地址
read(fd, buf, 1) -> // 即 i2cdev_read
i2c_master_recv ->
i2c_transfer
adap->algo->master_xfer // 以下和上面分析的探测某设备地址的设备一致
write(fd, buf, 1) -> // 即 i2cdev_write
i2c_master_send ->
i2c_transfer
adap->algo->master_xfer // 以下和上面分析的探测某设备地址的设备一致
4.2 通过特定的IIC设备驱动进行数据传输
#include 五,总结
通常来说为某个特定的IIC设备去构建IIC设备驱动、针对平台硬件资源构建IIC适配器便是IIC驱动相关开发所需要做的工作,IIC核心相关、IIC总线驱动相关的部分,系统中一般已经存在。
构建IIC设备驱动一般需要做的工作
- 设置struct i2c_driver结构体,提供attach_adapter、detach_client接口。
- 在attach_adapter 中调用 i2c_probe接口,去探测某设备地址的设备,并提供设备探测存在后调用的函数at24cxx_detect,在该函数中设置struct i2c_client。
- 还需在at24cxx_detect函数中(即设备探测成功后),实现IIC设备所对应类型的具体驱动,比如说本例中为字符设备,便注册了字符设备驱动、创建了字符设备节点等。
构建IIC适配器一般需要做的工作
- 提供IIC适配器的硬件驱动,探测、初始化IIC适配器(比如申请IIC的i/o地址和中断号)、驱动CPU控制的IIC控制器从硬件上产生各种信号以及处理IIC中断等。
- 提供IIC适配器的algorithm,即提供master_xfer 接口以及functionality接口,IIC设备驱动将调用对应适配器的master_xfer 接口进行数据传输。