代码随想录刷题-哈希表(下)
本文是每天跟着代码随想录刷题时做的笔记,用来总结与复习。还差两道,明天补上
目录
350.两个数组的交集Ⅱ
202.快乐树
1.两数之和
454.四数相加
补上昨天的两题
15.三数之和
18.四数之和
今日总结
350.两个数组的交集Ⅱ
题目链接:350. 两个数组的交集 II - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:由于此题要求返回重复的数字,并且次数取两个数组中的最小值,因此可以先将两个数组进行排序,运用了双指针思想,指针移动策略是较小值指针追赶较大值指针,值相等存入结果数组。
class Solution {
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2){
Arrays.sort(nums1);
Arrays.sort(nums2);
int temp1 = 0;
int temp2 = 0;
int flag = 0;
// List ansList = new ArrayList<>();
int[] ansArr = new int[Math.min(nums1.length, nums2.length)];
while (temp1 < nums1.length && temp2 nums2[temp2]){
temp2++;
}else {
// ansList.add(nums1[temp1]);
ansArr[flag++] = nums1[temp1];
temp1++;
temp2++;
}
}
// int[] ansArr = new int[ansList.size()];
// for (int i = 0; i < ansList.size(); i++) {
// ansArr[i] = ansList.get(i);
// }
// return ansArr;
return Arrays.copyOfRange(ansArr, 0, flag);
}
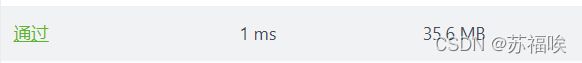
} 我第一次使用的是 List 动态存储结果,再将 List 转换为数组,与最优失之1ms
查看最优的答案,发现他使用了我以前没用过的方法 Arrays.copyOfRange(ansArr, 0, flag) 该方法可以从 [0, flag) 范围复制 ansArr 数组,使得时间比我快了 1ms
202.快乐树
题目链接:202. 快乐数 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:这题不难,主要就两点:①:获取一个整数每一位上的数字,在这里我使用了两种方法来获取;②:想到用 set 集合来判断是否出现了循环。
通过转化为字符串来获取
public int getSum(int n){
String str = n + "";
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int num = str.charAt(i) - '0';
sum += num * num;
}
return sum;
}通过取余再除10的方法
public int getSum(int n){
int sum = 0;
while (n > 0){
int temp = n % 10;
sum += temp * temp;
n = n / 10;
}
return sum;
}可以发现速度提升还是蛮大的
最终代码
public boolean isHappy(int n){
Set set = new HashSet<>();
while (!set.contains(n)){
if (n == 1){
return true;
}
set.add(n);
n = getSum(n);
}
return false;
}
public int getSum(int n){
int sum = 0;
while (n > 0){
int temp = n % 10;
sum += temp * temp;
n = n / 10;
}
return sum;
} 1.两数之和
题目链接:1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:二刷第一题。主要是遍历数组,用 target 减去每一次的值,判断结果是否为 map 的 key,如果是,则表明找到答案,不是则将该次所减值和他的下标作为 key-value 存储到 map 中
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target){
Map map = new HashMap<>();
int[] ansArr = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){
ansArr[0] = i;
ansArr[1] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
return ansArr;
}else {
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
}
return ansArr;
} 454.四数相加
题目链接:454. 四数相加 II - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:使用两次双重循环,第一次将前两个数组各元素相加的结果和各结果出现的次数作为 key-value 存储到 map 中,第二次用后两个数组各元素相加的相反数来查找 map 中是否有匹配的 key,如果有则其对应的 value 值就为该种情况符合题意的次数,将所有满足题意的 value 值相加即为结果。
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4){
Map map = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {
int sum = nums1[i] + nums2[j];
if (map.containsKey(sum)){
map.put(sum, map.get(sum) + 1);
}else {
map.put(sum, 1);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums3.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums4.length; j++) {
int flag = -(nums3[i] + nums4[j]);
if (map.containsKey(flag)){
count += map.get(flag);
}
}
}
return count;
} 补上昨天的两题
15.三数之和
题目链接:15. 三数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
不愧是通过率 34.3% 的题目,
思路:翻看题解思路,采用排序 + 双指针,先将数组排序,第一层循环就用 i 依次遍历数组,设定两个指针,left 初始指向 i 后面一位,right 初始指向数组末尾。在第二层循环中移动指针,如果 i、left、right对应位置上的数字相加 sum 小于 0 ,则要增大 sum 值即 left++;如果 sum 大于 0,则要减小 sum 值即 right--。然后还要考虑去重操作,三处地方:①:i 依次递增时出现值和前一位相同;②:left 递增时出现值与后一位相同;③:right 递减时出现值与前一位相同。
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List> ansList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (i > 0 && i < nums.length && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
i++;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum < 0) {
left++;
}else if (sum > 0) {
right--;
}else {
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(nums[i]);
ans.add(nums[left]);
ans.add(nums[right]);
ansList.add(ans);
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
left++;
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return ansList;
} 最后借用该题评论区里的一段话:
一题二写,三数之和,题解四瞅五瞄六瞧,水平还七上八下九流,十分辣鸡。
十推九敲,八种思路,用光七情六欲五感,在这里四覆三翻二挠,一拳爆屏。
18.四数之和
题目链接:18. 四数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路:在被三数之和折磨完后,又来四数之和,但有了三数之和的基础,做这题就很简单了。思路其实和三数之和差不多,区别就在于三数之和双指针的外层只有一次循环,而四数之和外层我用一个双重循环,来确定所有情况。设定一个 head 和 end 初始分别指向数组的开头和结尾,在一次双指针循环结束后将 head 后移,当 head 后移至不可能出现结果时,将 end 前移,head 重新回到数组开头。去重操作和三数之和一样,但是有四处地方:①:head 去重;②:end 去重;③、④:双指针去重。
public List> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List> ansList = new ArrayList<>();
int end = nums.length - 1;
while (end >= 3){
int head = 0;
while (head + 2 < end){
int left = head + 1;
int right = end - 1;
while (left < right){
int sum = nums[head] + nums[left] + nums[right] + nums[end];
if (sum < target){
left++;
}else if (sum > target){
right--;
}else {
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(nums[head]);
ans.add(nums[left]);
ans.add(nums[right]);
ans.add(nums[end]);
ansList.add(ans);
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]){
left++;
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]){
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
while (head < end && nums[head] == nums[head + 1]){
head++;
}
head++;
}
while (end >= 3 && nums[end] == nums[end - 1]){
end--;
}
end--;
}
return ansList;
} 今日总结
题目还好,思维不难
15、18题总结:打不败我的,终将会使我变得更强大