Netty实战(十四)
WebSocket协议(二)
- 一、初始化 ChannelPipeline
- 二、引导
- 三、加密
一、初始化 ChannelPipeline
我们之前说过为了将 ChannelHandler 安装到 ChannelPipeline 中,需要扩展了ChannelInitializer,并实现 initChannel()方法。
下面我们演示一下:
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
/**
* Author: lhd
* Data: 2023/6/12
* Annotate: 初始化 ChannelPipeline
*/
public class ChatServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final ChannelGroup group;
public ChatServerInitializer(ChannelGroup group) {
this.group = group;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//将所有需要的ChannelHandler 添加到 ChannelPipeline 中
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(64 * 1024));
pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler(group));
}
}
我们对于 initChannel()方法的调用,安装所有必需的 ChannelHandler 来设置该新注册的 Channel 的 ChannelPipeline。那么我们安装的这些ChannelHandler 有什么用呢?
| ChannelHandler | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| HttpServerCodec | 将字节解码为 HttpRequest、HttpContent 和 LastHttpContent。并将 HttpRequest、HttpContent 和 LastHttpContent 编码为字节 |
| ChunkedWriteHandler | 写入一个文件的内容 |
| HttpObjectAggregator | 将一个 HttpMessage 和跟随它的多个 HttpContent 聚合为单个 FullHttpRequest 或者 FullHttpResponse(取决于它是被用来处理请求还是响应)。安装了这个之后,ChannelPipeline 中的下一个 ChannelHandler 将只会收到完整的 HTTP 请求或响应 |
| HttpRequestHandler | 处理 FullHttpRequest(那些不发送到/ws URI 的请求) |
| WebSocketServerProtocolHandler | 按照 WebSocket 规范的要求,处理 WebSocket 升级握手、PingWebSocketFrame 、PongWebSocketFrame 和CloseWebSocketFrame |
| TextWebSocketFrameHandler | 处理 TextWebSocketFrame 和握手完成事件 |
Netty 的 WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 处理了所有委托管理的 WebSocket帧类型以及升级握手本身。如果握手成功,那么所需的 ChannelHandler 将会被添加到ChannelPipeline中,而那些不再需要的ChannelHandler 则将会被移除。
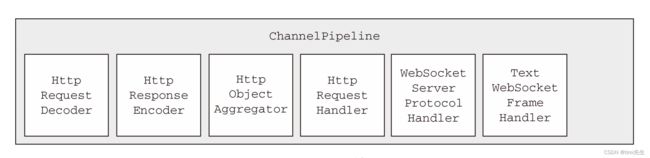
WebSocket 协议升级之前的 ChannelPipeline 的状态如下图所示。这代表了刚刚被ChatServerInitializer 初始化之后的 ChannelPipeline。
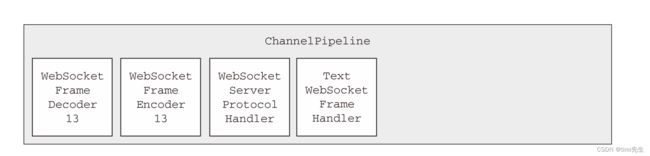
WebSocket 协议升级完成之后,WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 将会把 HttpRequestDecoder 替换为 WebSocketFrameDecoder,把 HttpResponseEncoder 替换为WebSocketFrameEncoder。为了性能最大化,它将移除任何不再被 WebSocket 连接所需要的ChannelHandler。其中也包括 HttpObjectAggregator 和 HttpRequestHandler
下图展示了上面操作完成之后的ChannelPipeline,Netty目前支持 4个版本的WebSocket协议,它们每个都具有自己的实现类。Netty将会根据客户端/浏览器所支持的版本 ,自动地选择正确版本WebSocketFrameDecoder和WebSocketFrameEncoder。
二、引导
我们来写一个引导服务器:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.DefaultChannelGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.ImmediateEventExecutor;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* Author: lhd
* Data: 2023/6/12
* Annotate:
*/
public class ChatServer {
//创建 DefaultChannelGroup,其将保存所有已经连接的WebSocket Channe
private final ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(ImmediateEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
private final EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
private Channel channel;
//引导服务器
public ChannelFuture start(InetSocketAddress address) {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(createInitializer(channelGroup));
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(address);
future.syncUninterruptibly();
channel = future.channel();
return future;
}
//创建 ChatServerInitialize
protected ChannelInitializer<Channel> createInitializer(ChannelGroup group) {
return new ChatServerInitializer(group);
}
//处理服务器关闭,并释放所有的资源
public void destroy() {
if (channel != null) {
channel.close();
}
channelGroup.close();
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Please give port as argument");
System.exit(1);
}
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
final ChatServer endpoint = new ChatServer();
ChannelFuture future = endpoint.start(new InetSocketAddress(port));
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
endpoint.destroy();
}
});
future.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
}
}
三、加密
处理好服务器后,下一步就是测试和加密,测试我们之前说过这里不再多说。
这里的加密有两步,一是为 ChannelPipeline 加密,二是为 ChatServer 添加加密。
ChannelPipeline 加密:
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.SslContext;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.SslHandler;
/**
* Author: lhd
* Data: 2023/6/12
* Annotate:为 ChannelPipeline 添加加密
*/
public class SecureChatServerInitializer extends ChatServerInitializer {
private final SslContext context;
public SecureChatServerInitializer(ChannelGroup group, SslContext context) {
super(group);
this.context = context;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
//调用父类的initChannel()方法
super.initChannel(ch);
SSLEng.ine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc());
engine.setUseClientMode(false);
// 将SslHandler 添加到ChannelPipeline 中
ch.pipeline().addFirst(new SslHandler(engine));
}
}
ChatServer 添加加密
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.SslContext;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.util.SelfSignedCertificate;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* Author: lhd
* Data: 2023/6/12
* Annotate:
*/
public class SecureChatServer extends ChatServer {//SecureChatServer 扩展 ChatServer 以支持加密
private final SslContext context;
public SecureChatServer(SslContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
protected ChannelInitializer<Channel> createInitializer(ChannelGroup group) {
//返回之前创建的 SecureChatServerInitializer 以启用加密
return new SecureChatServerInitializer(group, context);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Please give port as argument");
System.exit(1);
}
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
SelfSignedCertificate cert = new SelfSignedCertificate();
SslContext context = SslContext.newServerContext(cert.certificate(), cert.privateKey());
final SecureChatServer endpoint = new SecureChatServer(context);
ChannelFuture future = endpoint.start(new InetSocketAddress(port));
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
endpoint.destroy();
}
});
future.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
}
}