Vue Router 的使用
原文链接:https://note.noxussj.top/?source=sifo
项目中注入路由器
1.在项目中 src 目录下新建 router 目录,其中包含 index.js 路由主文件。
// src/router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import { routes } from './routes.js'
Vue.use(Router)
const router = new Router({
routes
})
export default router
2.新建 routes.js 路由表文件。
// src/router/routes.js
const routes = [
{
path: '/component1',
component: () => import('../components/Component1.vue')
},
{
path: '/component2',
component: () => import('../components/Component2.vue')
}
]
export { routes }
3.main.js 注册路由。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router/index.js'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
render: (h) => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
4.设置路由出口 router-view。
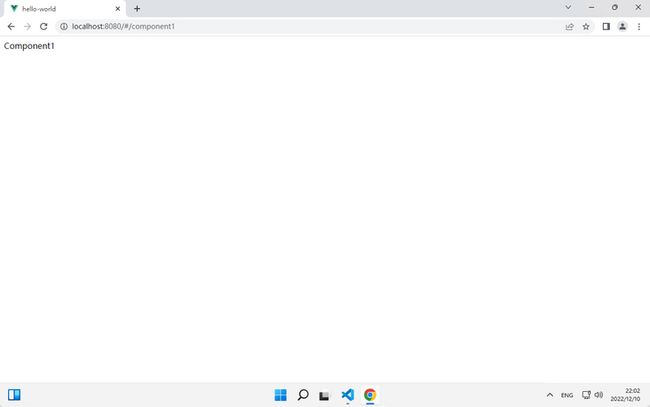
5.验证路由,在网页 url 中输入路由地址 /component1 就能够看到我们的页面了。
6.以上是路由的基本使用。
动态路由匹配
动态路由是指我们的路由后面携带了动态的参数,例如我有一个新闻详情页面,每个新闻详情页面展示的数据都不同,但是却又使用的是同一个组件。这种情况是可以使用动态路由。
基础案例
1.修改路由表,添加匹配动态参数的路由。这里写了两条路由规则代表,不传动态参数时候也能展示该组件,否则页面匹配不到是会空白的。
const routes = [
{
path: '/news',
component: () => import('../components/News.vue')
},
{
path: '/news/:id',
component: () => import('../components/News.vue')
}
]
export { routes }
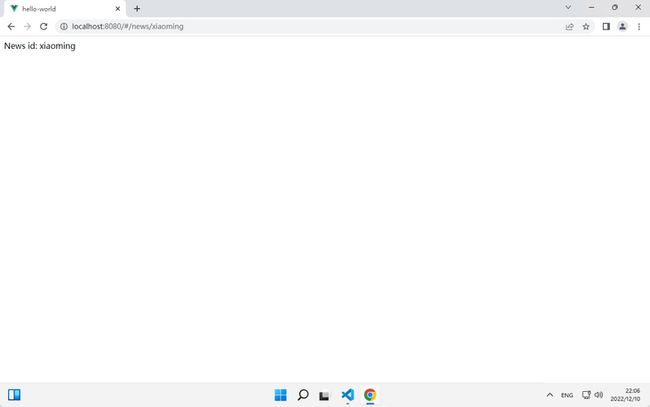
2.通过 $route 路由信息对象获取动态路由参数。
News id: {{ $route.params.id }}
3.验证路由。
嵌套路由
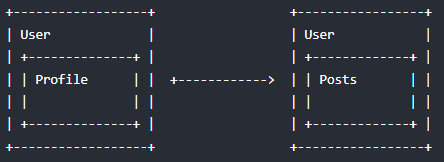
嵌套路由其实很简单,但是你思路没想通之前就会觉得很复杂。我们平时使用的页面切换的场景,基本上,一级路由就能实现了。但是实际上项目开发中会经常遇到多层路由的情况,也就是嵌套路由。举个例子,假设现在我不止有新闻页面,我还有一个用户主页面,但是我用户主页面里面又包含了两个子页面,分别是用户信息编辑页面,用户发布帖子页面。
基础案例
1.修改路由表,添加用户主页面路由(一级路由)、添加用户信息编辑页面(二级路由)、添加用户发布帖子页面(二级路由)。
// src/routes.js
const routes = [
{
path: '/user',
component: () => import('../components/user/MyIndex.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'profile',
component: () => import('../components/user/MyProfile.vue')
},
{
path: 'posts',
component: () => import('../components/user/MyPosts.vue')
}
]
}
]
export { routes }
2.设置二级路由出口 router-view,因为一级的我们已经设置过了。你要记住,你用到了多少层级路由嵌套,就要设置对应的路由出口,路由出口代表匹配到的组件,会替换掉 router-view 进行展示的。
// components/user/index.vue
user
3.验证路由,可以发现 router-view 标签被组件替换掉了。
4.再替换另外一个路由地址,效果依然是正常的。
编程式导航
在上面的所有案例中,我们都是通过手动替换浏览器地址栏中的路径,从而达到切换路由的效果。那么有没有办法通过 JavaScript 代码的方式进行切换呢?
基础案例
1.在 App.vue 页面中通过 $router 路由操作对象中的 push 方法进行路由切换,请记住是 $router ,而不是 $route,这两者是有区别的。一个是操作路由用的,一个是获取路由信息用的。
2.这里就不验证了,小伙伴们可以自己尝试。
3.另外通过路由器操作对象 $router 的 go 方法是可以实现路由的前进、后退操作的。$router.go(1) 代表前进一步,$router.go(-1) 代表后退一步。
重定向
重定向是需要通过路由表进行配置的,重定向的作用就是当用户访问 /a 路由时,URL 将会被替换成 /b,然后匹配路由为 /b。
基础案例
1.配置路由表,添加重定向。
// src/router/routes.js
const routes = [
{
path: '/user',
redirect: '/news',
component: () => import('../components/user/index.vue')
},
{
path: '/news',
component: () => import('../components/News.vue')
}
]
export { routes }
2.验证路由,我们尝试访问 /user ,看看实际上是不是直接变成了访问 /news 路由。不仅 url 变成了 /news ,展示的路由组件,应该也是 /news 的。小伙伴们需要自行验证一下。
别名
别名其实和重定向很类似,也很容易混淆。例如 /a 路由的别名是 /b,意味着,当用户访问 /b 时,URL 会保持为 /b,但是路由匹配则为 /a,就像用户访问 /a 一样。
1.配置路由表,添加别名。
const routes = [
{
path: '/user',
alias: '/news',
component: () => import('../components/user/index.vue')
}
]
export { routes }
2.验证路由,我们尝试访问 /news,URL 中应该会保持显示为 /news,但是实际上渲染的组件应该是 /user。
HTML5 History 模式
Vue Router 默认是 hash 模式 —— 使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。hash 模式代表 URL 后面有个 # 符号。在传统模式中,我们都是利用 # 来实现锚点功能的。
如果不想要很丑的 hash,我们可以用路由的 history 模式,这种模式充分利用 history.pushState API 来完成 URL 跳转而无须重新加载页面。
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes
})
当你使用 history 模式时,URL 就像正常的 url,例如 http://yoursite.com/user/id 也好看!