Spring Security实现用户身份验证及权限管理
Spring Security简介
Spring Security是Spring生态的一个成员,提供了一套Web应用安全性的完整解决方案。
Spring Security 旨在以一种自包含的方式进行操作,因此你不需要在 Java 运行时环境中放置任何特殊的配置文件。这种设计使部署极为方便,因为可以将目标工件(无论是 JAR还是WAR)从一个系统复制到另一个系统,并且它可以立即工作。
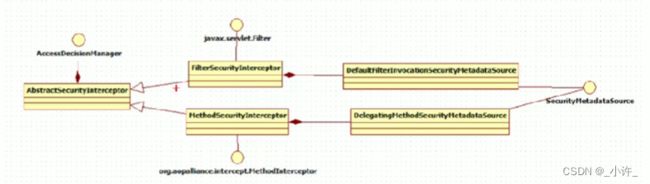
spring Security,这是一种基于 Spring AOP 和 Servlet 过滤器的安全框架。它提供全面的安全性解决方案,同时在 Web 请求级和方法调用级处理身份确认和授权。
spring sevurity提供了用户认证和授权,认证是只该用户是否可以访问该系统;授权是指该用户是否有权限执行相关操作。
Spring Security基本使用
Spring Security实际 上是基于Filter实现的,其底层为若干过滤器链。开发者所见到的 Spring Security 提供的功能,都是通过这些过滤器来实现的,这些过滤器按照既定的优先级排列,最终形成一个过滤器链。开发者也可以自定义过滤器,并通过@Order
注解去调整自定义过滤器在过滤器链中的位置。
过滤器不太了解的请移步Servlet与Filter两种方式实现身份验证和访问控制及其基本使用如下:
引入spring security依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
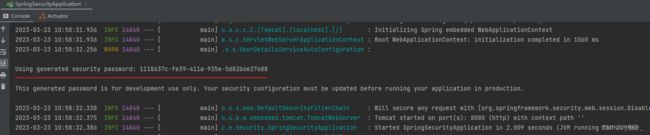
在配置过滤器的登录认证时,一般都配置所有路径,放行登录页面和逻辑,spring security也是,在启动后就会跳转到框架默认的登录界面,用户名是user密码在控制台:
实际开发中需要自定义登录页面,并且需要在数据库中查询用户信息,特殊的存在权限管理的还要分不同的角色,默认的一般无法满足要求,重写默认配置。只要导入了spring security依赖就会自动对接口进行保护。
用户认证
UserDetailsService
spring security提供了接口供开发者使用来定制相关登录时的用户认证逻辑,该接口为UserDetailsService。用户未实现该接口时spring security使用默认的配置即案例的登录效果。
在spring的项目中,基本都有两种实现方式配置类和配置文件,一个基于注解,一个基于xml配置文件;在spring boot项目中又多了一种方式是基于实现类的,因为spring boot都有默认的配置,只需要实现该类重写线管对象的方法覆盖默认的即可。
- 配置类更改默认配置
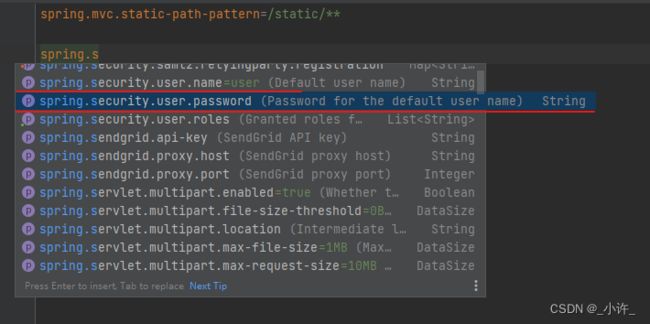
spring.security.user.name=xiaoxu
spring.security.user.password=xiaoxu
更改默认配置后,控制台就没有密码了
- 配置类实现,覆盖spring security默认的配置类
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("xiaoxu").password("xiaoxu").roles("admin");
}
}
上面的代码也是权限认证的,重写了
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的默认用户
使用配置文件都是修改默认的配置参数,但是使用配置类就必须重写默认配置在该行动中所使用到的其他类,如下,
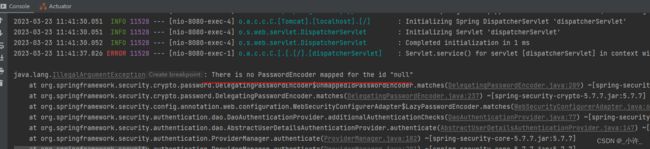
在重写了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter是没有实现默认的PasswordEncoder所以会报错。
PasswordEncoder
实现加密接口返回加密对象实例注入到IOC容器即可。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//密码加密
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String encode = passwordEncoder.encode("123");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("xiaoxu").password(encode).roles("admin");
}
//需要注意的是需要实现加密接口并调用,该方法返回一个加密对象
@Bean
PasswordEncoder encoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
BCryptPasswordEncoder是PasswordEncoder的一个实现类:

spring在启动时首先会找配置文件,再去找配置类,如果均没有就去找默认配类的实现类作为启动的配置,通过实现类也可以配置登录验证。
- 自定义实现类实现永固认证
实现类实现的用户权限认证,包括数据库用户名查询,密码加密,判断等。因此这里逻辑也需要覆盖默认的配置类,所以也需要重写配置类。
//重写配置类使用自定义UserDetailsService覆盖默认值
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//装配自定义的用户登录逻辑
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(encoder());
}
//密码加密工具类
@Bean
PasswordEncoder encoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
//自定义的角色验证
@Component("userDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsSevice implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
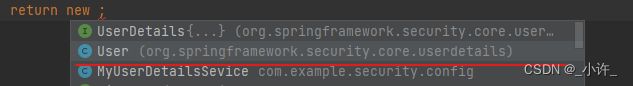
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//设置角色
List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("role");
return new User("xiaoxu",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123"),auths);
}
}
需要注意的是从外部加载的只有
username这一个字符,密码被默认封装起来了。
实现了
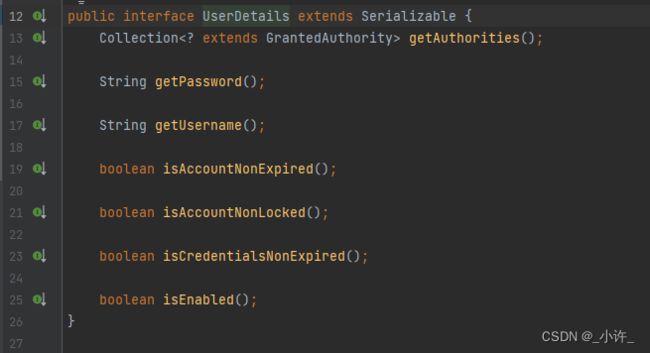
UserDetailsService接口的loadUserByUsername返回值是UserDetails,其源码如下
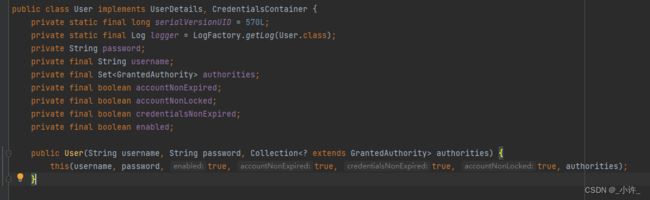
包含了用户名,密码等一些信息,返回值User是其一个实现类,其源码如下:
User又三个参数分别是用户名密码,角色,校色及一个集合且继承自GrantedAuthority这就意味着我们常见该集合必须使用继承类或者其实现类来创建包含角色信息的集合。正如代码所示使用AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("role")方法创建的集合。
通过实现接口的方式用途更广泛一些,一般也是用此方式实现数据库交互查询用户的账户,密码及角色信息。
下面是对用户验证的改造,使用查数据的方式:
- 引入数据库驱动的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.29version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.0.0version>
dependency>
- 配置数据库驱动信息datasource
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/account?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
- 数据库映射
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where user = #{user}")
List<User> userList(@Param("user") String user);
}
- 自定义安全配置类
//自定义配置类覆盖默认配置
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//装配自定义的用户登录逻辑
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(encoder());
}
//密码加密工具类
@Bean
PasswordEncoder encoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
- 实现用户认证的接口
@Component("userDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsSevice implements UserDetailsService {
//mapper层用户数据映射
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//代入用户名查询所有信息
List<com.example.security.pojo.User> users = userMapper.userList(username);
if(users.size() != 0){
//通过指定方法创建角色参数
List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(users.get(0).getRole());
//用户信息填入框架的User对象,由框架验证
return new User(username,new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(users.get(0).getPassword()),auths);
}else {
List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin");
return new User("admin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123"),auths);
}
}
}
这里的验证逻辑是代入用户名能查出数据就将正确的用户名和密码交给框架,由框架验证,未查出来就验证是否是超级管理员账户。
由于该框架只从外部加载了username一个数据,因此这里的查询逻辑是将用户名代入数据库查出用户所有信息,
UserDetailsService接口的loadUserByUsername的方法会自动识别设定密码,因此只需要将密码填入到返回的User的参数中即可。
自定义登录页面
spring security框架默认bootstrsp框架的登陆页面,登录成功后会直接跳转到根路径下,这样显然是不对的,需要跳转到主页面,或者定义的页面。
//省略实现接口等一些无关代码
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//省略过滤器代码
//配置默认登录页面成功跳转页面地址
http.formLogin().defaultSuccessUrl("/index");
}
配置登录成功的跳转的页面。configure 方法中是一个链式配置,当然也可以不用链式配置,每一个属性配置完毕后再从 http.重新开始写起。
http是一个链式配置,重写该方法后需要打开配置开关,如开启打开访问权限,不然会造成之前的登录验证被覆盖。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//authorizeRequests()方法表示开启权限配置
.authorizeHttpRequests()
//.anyRequest().authenticated()表示所有的请求都要认证之后才能访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
//配置默认登录页面成功跳转页面地址
.formLogin().defaultSuccessUrl("/index");
}
在上面代码中先开启过滤器,对所有请求都过滤,未开启就不会跳转到登录页面。配置登录成功后的跳转页面 /index,这样登录成功后就不会返回根路径。
配置登录成功跳转目录的方法由两个
defaultSuccessUrl和successForwardUrl,它们的区别是前者在访问的是否为参数配置的页面进行跳转。例如,在访问 http://localhost:8080/hello时,defaultSuccessUrl配置额index,那么将会返回到hello,uri的优先级高;successForwardUrl无论地址栏输入的是什么都会返回配置的参数的资源。
有时候需要订制登陆页面,也需要在配置类中配置:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//authorizeRequests()方法表示开启权限配置
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.antMatchers("/static/*")
//.anyRequest().authenticated()表示所有的请求都要认证之后才能访问
.permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
//配置默认登录页面成功跳转页面地址
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/static/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index");
}
.antMatchers("/static/*")需要放行/static目录,不然返回的页面的uri标识符也会被拦截。.loginPage("/static/login.html")设置返回的页面,覆盖默认配置;.loginProcessingUrl("/login")配置为请求登录的地址。
- 配置类重写默认跳转页面
SpringSecurityConfig.confifigure(HttpSecurity http)中使用 loginPage("/login/page") 指定前往自定义的登录页面认证请求
实现的配置类有众多的方法,其中confifigure方法是对放行权限和用户管理的,因此接口也主要是实现该方法:
![]()
接口的实现类中可重写三个方法,只是参数不一样,方法过滤器器限制的范围不同,HttpSecurity范围更广,这里也重写该方法。AuthenticationManagerBuilder是登录时对用户认证。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig2 extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//装配自定义的用户登录逻辑
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
//用户认证实现
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(encoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//authorizeRequests()方法表示开启权限配置
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.antMatchers("/static/*")
//.anyRequest().authenticated()表示所有的请求都要认证之后才能访问
.permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
//配置默认登录页面成功跳转页面地址
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/static/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index");
}
//密码加密工具类
@Bean
PasswordEncoder encoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
该类重写了多个configure会使第一个失效,造成无法登录。

需要注意的是表单传递的参数必须是username与password,不然就会登陆失败:
<form action="/index" method="get">
Username: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
<button type="submit">提交button>
form>
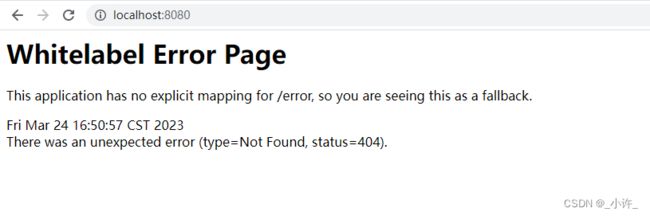
这里一直登不上且报错302,如下:

这是由于过滤器链的放行配置错误造成的,代码时配的过滤器所有请求,登录表单未实现状态记录,需要使用框架代理认证,记录会话状态,不然会出现登录页面的循环。配置如下:
HttpSecurity.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
<form action="/doLogin" method="post" class="form">
Username: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
<button type="submit">提交button>
form>
/doLogin可以定义为任意地址,更多细节移步Spring Security配置访问权限在登录页循环并报错302
总结
-
Spring Security 定义了
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter抽象类供用户自定义过滤器规则。 -
Spring Security 中定义了 UserDetails 接口来规范开发者自定义的用户对象,其一般实现类为
UserDetailsService,用户身份验证。 -
使用
PasswordEncoder接口加密密码。 -
过滤器规则的配置。
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter抽象类的抽象方法configure(HttpSecurity http)可以自定义过滤规则。更多细节移步https://www.jianshu.com/c/cba5438e553e感谢作者!@怪诞140819
- 数据库认证,用户信息认证。
- 注册功能要与
PasswordEncoder的加密方式一致。
最后就是获取会话信息了,例如登录后要显示XXX登录系统,就需要从会话取得用户:
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
SecurityContextHolder对象获取上下文连接SecurityContextHolder.getContext(),上下文连接获取认证信息SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()。最后再从认证信息获取用户信息即可。
可以通过配置管理会话
会话生命周期
清楚会话需要的工作:
- HttpSession无效
- 清楚
SecurityContextHolder - 消除会话跳转登录页面

退出消除会话也不需要开发者来完成,均有框架来完成,就行登录时创建会话一样,只需要配置一个代理的接口即可,控制器也不需要实现该接口。如下:
@RequestMapping("/main")
public String getMain(){
return "static/index.html";
}
WebMvcConfigurer采用JavaBean的形式来代替传统的xml配置文件形式进行针对框架个性化定制,相当于web.xml。早期版本使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter。SpringBoot 2.0 后,该类被标记为@Deprecated(弃用)。官方推荐直接实现WebMvcConfigurer或者直接继承WebMvcConfigurationSupport。
权限认证
用户的角色管理不同的权限,不同角色看到的页面不同,能够访问的资源也不同,spring security为开发者提供了完整的框架供用户使用。其中主要包括Web授权认证,方法认证。
web授权
通过获取的角色信息限定用户可以访问的url,如下:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**","/role/**","/user/**").hasAuthority("admin")
.antMatchers("/role/**","/user/**").hasAuthority("role")
.antMatchers("/user/**").authenticated() //配置相应角色必须要有权限访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/static/login.html")
//会话状态代理接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/static/index.html")
.successForwardUrl("/main")
.failureUrl("/static/login.html")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
//自定义退出配置
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/quit")
.logoutSuccessUrl("/static/login.html");
}
重点是这几个配置:
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**","/role/**","/user/**").hasAuthority("admin")
.antMatchers("/role/**","/user/**").hasAuthority("role")
.antMatchers("/user/**").authenticated() //配置相应角色必须要有权限访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.antMatchers("/role/**","/user/**").hasAuthority("role")所标识的意义是具有role角色的用户可以访问/role,/user地址。.authenticated() 表示需要认证。
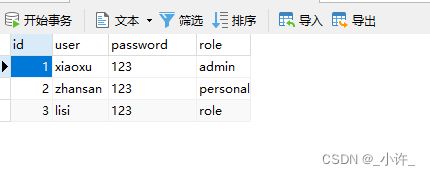
数据库表的数据如下:
UserDetailsService接口的实现类如下:
@Component("userDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsSevice implements UserDetailsService {
//mapper层用户数据映射
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//代入用户名查询所有信息
List<com.example.security.pojo.User> users = userMapper.userList(username);
if(users.size() != 0){
//通过指定方法创建角色参数
List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(users.get(0).getRole());
//用户信息填入框架的User对象,由框架验证
return new User(username,new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(users.get(0).getPassword()),auths);
}else {
List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin");
return new User("admin",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123"),auths);
}
}
}
控制器查看用户信息
@RequestMapping("/who")
@ResponseBody
public String getRole(){
//获取认证上下文连接
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//获取认证用户名信息
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User user = (org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User) principal;
String username = user.getUsername();
return username;
}

如GIF所示,role角色的用户只能访问admin以下的权限。
配置规则的顺序非常重要,具体或则更为苛刻的权限在前。对角色的授权应该在全部资源之前。
方法授权
在spring boot2.0中,除了使用http.authorizeRequests()对web资源授权外还支持服务层方法的安全性支持。通过注解@PreAuthorize,PostAuthorize,@Secured。
@secured
在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的实现类开启该注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
然后再方法上添加该注解就会限制对该方法的访问,注解不同的参数控制不同的访问权限。@Secured注解可以指定一个字符串数组参数作为value的值,表示当前用户具备这些角色中的任何一个角色即可满足授权条件。
注解不支持表达式,而且需要注意的是这里匹配的字符串需要添加前缀“ROLE_“。
IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY匿名访问
ROLE_XXX具有XXX权限的允许访问
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
public void addUser(){
//超级用户权限
}
//也可以一次放行多个权限
@Secured({"ROLE_ADMIN","ROLE_USER"})
public User getUserByName(String name){
//...
return User;
}
总结:
- 需要在WebSecuirtyConfig添加配置
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
}
- 方法上放行权限
@Secured({"ROLE_user","ROLE_admin"})
//如下对控制器的配置
@GetMapping("/add")
@Secured("ROLE_admin","ROLE_角色名")
public boolean addUser(){
return true;
}
@PreAuthorize
配置类启动该注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)
方法上添加授权注解
//多个角色授权
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('权限名1','权限名2','权限名1')")
//单个角色授权
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('权限名')")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('personal','admin')")
//角色授权
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_角色名')")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ROLE_角色名','ROLE_角色名')")
该注解支持Spring EL表达式
//同时拥有私人和管理员两种权限
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('personal') AND hasRole('admin')")
@PostAuthorize(" returnObject!=null && returnObject.username == authentication.name")
@PostAuthorize
@PostAuthorize 注解是在方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限,Spring EL 提供 返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取返回的对象returnObject。
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)的时候,@PostAuthorize可以使用
@GetMapping("/helloUser")
@PostAuthorize(" returnObject!=null && returnObject.username == authentication.name")
public User helloUser() {
Object pricipal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
User user;
if("anonymousUser".equals(pricipal)) {
user = null;
}else {
user = (User) pricipal;
}
return user;
}
Spring表达式语言—SpringEL,SpEL是一种强大,简洁的装配Bean的方式,他可以通过运行期间执行的表达式将值装配到我们的属性或构造函数当中也可以调用JDK中提供的静态常量,获取外部Properties文件中的的配置。
SpringEL的使用和EL表达式的使用非常相似,EL表达式在JSP页面更方便的获取后台中的值,而SpringEL就是为了更方便获取Spring容器中的Bean的值.
EL使用${},而SpringEL使用#{}进行表达式的声明。
@RolesAllowed
@RolesAllowed 也是 JSR-250 提供的注解,可以添加在方法上或者类上,当添加在类上时,表示该注解对类中的所有方法生效;如果类上和方法上都有该注解,并且起冲突,则以方法上的注解为准。
另外还有@PreFilter、@PostFilter用的比较少。