TreeMap源码
介绍
- 如果我们希望Map可以保持key的大小顺序时,就需要利用TreeMap。
- 底层使用了红黑树,左子树总小于root,右子树总大于root,具有很好的平衡性,操作速度达到log(n)。
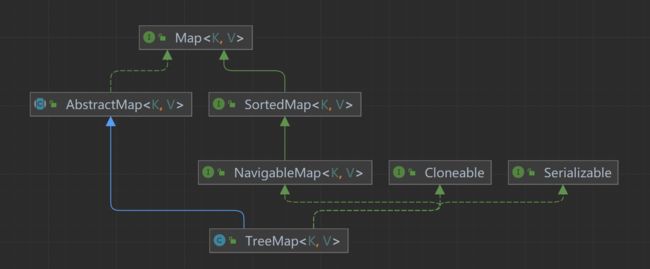
TreeMap 相比于HashMap多实现了了NavigableMap接口(也就是这个接口,决定了TreeMap与HashMap的不同:HashMap的key是无序的,TreeMap的key是有序的)。
TreeMap是非同步的
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
常量&变量
/**
* The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or
* null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys.
*
* @serial
* 定义key的排序规则
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* The number of entries in the tree
* 元素个数
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
* 一次操作所修改的元素个数
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
构造方法
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree map, using the natural ordering of its
* keys. All keys inserted into the map must implement the {@link
* Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such keys must be
* mutually comparable: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw
* a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and
* {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put a key into the
* map that violates this constraint (for example, the user attempts to
* put a string key into a map whose keys are integers), the
* {@code put(Object key, Object value)} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*/
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given
* comparator. All keys inserted into the map must be mutually
* comparable by the given comparator: {@code comparator.compare(k1,
* k2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys
* {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put
* a key into the map that violates this constraint, the {@code put(Object
* key, Object value)} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this map.
* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering} of the keys will be used.
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings as the given
* map, ordered according to the natural ordering of its keys.
* All keys inserted into the new map must implement the {@link
* Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such keys must be
* mutually comparable: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw
* a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and
* {@code k2} in the map. This method runs in n*log(n) time.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the keys in m are not {@link Comparable},
* or are not mutually comparable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings and
* using the same ordering as the specified sorted map. This
* method runs in linear time.
*
* @param m the sorted map whose mappings are to be placed in this map,
* and whose comparator is to be used to sort this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
内部类
Treemap的内部类和HashMap的内部类类似,大部分都是为了实现map需要返回视图的要求,或者迭代器的要求来实现的
SubMap
SubMap实现了SortMap接口的并拓展了AbstractMap的实现,但是SubMap没有实现任何方法全部都是抛出异常
/**
* This class exists solely for the sake of serialization
* compatibility with previous releases of TreeMap that did not
* support NavigableMap. It translates an old-version SubMap into
* a new-version AscendingSubMap. This class is never otherwise
* used.
*
* @serial include
*/
private class SubMap extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements SortedMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6520786458950516097L;
private boolean fromStart = false, toEnd = false;
private K fromKey, toKey;
private Object readResolve() {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(TreeMap.this,
fromStart, fromKey, true,
toEnd, toKey, false);
}
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { throw new InternalError(); }
public K lastKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
public K firstKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { throw new InternalError(); }
}
NavigableSubMap
对原TreeMap的一部分即子map进行操作,你的操作被限定在一定范围内,并且是直接影响到原map的,本质上就是在对原map树的相应节点进行操作,这就是NavigableSubMap实现的功能,也就是塑造一个特定范围的原map的视图,仍然是同一map,操作互相影响。
/**
* @serial include
*/
abstract static class NavigableSubMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2102997345730753016L;
/**
* The backing map.
* map的视图
*/
final TreeMap<K,V> m;
/**
* Endpoints are represented as triples (fromStart, lo,
* loInclusive) and (toEnd, hi, hiInclusive). If fromStart is
* true, then the low (absolute) bound is the start of the
* backing map, and the other values are ignored. Otherwise,
* if loInclusive is true, lo is the inclusive bound, else lo
* is the exclusive bound. Similarly for the upper bound.
* 通过这6个变量来控制起始与结束边界。
*/
//(fromStart,lo,loInclusive)代表起点,若fromStart为true则为map的最左节点,即最小。
//若fromStart为false,lo为起点,是否包含lo由loInclusive决定。
//(toEnd, hi, hiInclusive)代表终点,规则与上面一样
final K lo, hi;
final boolean fromStart, toEnd;
final boolean loInclusive, hiInclusive;
NavigableSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
if (!fromStart && !toEnd) {
if (m.compare(lo, hi) > 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey > toKey");
} else {
if (!fromStart) // type check
m.compare(lo, lo);
if (!toEnd)
m.compare(hi, hi);
}
this.m = m;
this.fromStart = fromStart;
this.lo = lo;
this.loInclusive = loInclusive;
this.toEnd = toEnd;
this.hi = hi;
this.hiInclusive = hiInclusive;
}
// internal utilities
final boolean tooLow(Object key) {
if (!fromStart) {
int c = m.compare(key, lo);
if (c < 0 || (c == 0 && !loInclusive))
return true;
}
return false;
}
final boolean tooHigh(Object key) {
if (!toEnd) {
int c = m.compare(key, hi);
if (c > 0 || (c == 0 && !hiInclusive))
return true;
}
return false;
}
final boolean inRange(Object key) {
return !tooLow(key) && !tooHigh(key);
}
final boolean inClosedRange(Object key) {
return (fromStart || m.compare(key, lo) >= 0)
&& (toEnd || m.compare(hi, key) >= 0);
}
final boolean inRange(Object key, boolean inclusive) {
return inclusive ? inRange(key) : inClosedRange(key);
}
/*
* Absolute versions of relation operations.
* Subclasses map to these using like-named "sub"
* versions that invert senses for descending maps
*/
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowest() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
(fromStart ? m.getFirstEntry() :
(loInclusive ? m.getCeilingEntry(lo) :
m.getHigherEntry(lo)));
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighest() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
(toEnd ? m.getLastEntry() :
(hiInclusive ? m.getFloorEntry(hi) :
m.getLowerEntry(hi)));
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absCeiling(K key) {
if (tooLow(key))
return absLowest();
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getCeilingEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHigher(K key) {
if (tooLow(key))
return absLowest();
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getHigherEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absFloor(K key) {
if (tooHigh(key))
return absHighest();
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getFloorEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLower(K key) {
if (tooHigh(key))
return absHighest();
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getLowerEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
/** Returns the absolute high fence for ascending traversal */
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighFence() {
return (toEnd ? null : (hiInclusive ?
m.getHigherEntry(hi) :
m.getCeilingEntry(hi)));
}
/** Return the absolute low fence for descending traversal */
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowFence() {
return (fromStart ? null : (loInclusive ?
m.getLowerEntry(lo) :
m.getFloorEntry(lo)));
}
// Abstract methods defined in ascending vs descending classes
// These relay to the appropriate absolute versions
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest();
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest();
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key);
/** Returns ascending iterator from the perspective of this submap */
abstract Iterator<K> keyIterator();
abstract Spliterator<K> keySpliterator();
/** Returns descending iterator from the perspective of this submap */
abstract Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator();
// public methods
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.isEmpty() : entrySet().isEmpty();
}
public int size() {
return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.size() : entrySet().size();
}
public final boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return inRange(key) && m.containsKey(key);
}
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (!inRange(key))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key out of range");
return m.put(key, value);
}
public final V get(Object key) {
return !inRange(key) ? null : m.get(key);
}
public final V remove(Object key) {
return !inRange(key) ? null : m.remove(key);
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subCeiling(key));
}
public final K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subCeiling(key));
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subHigher(key));
}
public final K higherKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subHigher(key));
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subFloor(key));
}
public final K floorKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subFloor(key));
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subLower(key));
}
public final K lowerKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subLower(key));
}
public final K firstKey() {
return key(subLowest());
}
public final K lastKey() {
return key(subHighest());
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(subLowest());
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
return exportEntry(subHighest());
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subLowest();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
if (e != null)
m.deleteEntry(e);
return result;
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subHighest();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
if (e != null)
m.deleteEntry(e);
return result;
}
// Views
transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMapView;
transient EntrySetView entrySetView;
transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySetView;
public final NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
KeySet<K> nksv = navigableKeySetView;
return (nksv != null) ? nksv :
(navigableKeySetView = new TreeMap.KeySet<>(this));
}
public final Set<K> keySet() {
return navigableKeySet();
}
public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
}
public final SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
}
public final SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
return headMap(toKey, false);
}
public final SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
return tailMap(fromKey, true);
}
// View classes
abstract class EntrySetView extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
private transient int size = -1, sizeModCount;
public int size() {
if (fromStart && toEnd)
return m.size();
if (size == -1 || sizeModCount != m.modCount) {
sizeModCount = m.modCount;
size = 0;
Iterator<?> i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
size++;
i.next();
}
}
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> n = absLowest();
return n == null || tooHigh(n.key);
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
if (!inRange(key))
return false;
TreeMap.Entry<?,?> node = m.getEntry(key);
return node != null &&
valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue());
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
if (!inRange(key))
return false;
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key);
if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(),
entry.getValue())) {
m.deleteEntry(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Iterators for SubMaps
*/
abstract class SubMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> next;
final Object fenceKey;
int expectedModCount;
SubMapIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
fenceKey = fence == null ? UNBOUNDED : fence.key;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null && next.key != fenceKey;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = predecessor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
final void removeAscending() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// deleted entries are replaced by their successors
if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
next = lastReturned;
m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
}
final void removeDescending() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
}
}
final class SubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
SubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(first, fence);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
public void remove() {
removeAscending();
}
}
final class DescendingSubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(last, fence);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return prevEntry();
}
public void remove() {
removeDescending();
}
}
// Implement minimal Spliterator as KeySpliterator backup
final class SubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K>
implements Spliterator<K> {
SubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(first, fence);
}
public K next() {
return nextEntry().key;
}
public void remove() {
removeAscending();
}
public Spliterator<K> trySplit() {
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
if (hasNext()) {
action.accept(next());
return true;
}
return false;
}
public long estimateSize() {
return Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.DISTINCT | Spliterator.ORDERED |
Spliterator.SORTED;
}
public final Comparator<? super K> getComparator() {
return NavigableSubMap.this.comparator();
}
}
final class DescendingSubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K>
implements Spliterator<K> {
DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(last, fence);
}
public K next() {
return prevEntry().key;
}
public void remove() {
removeDescending();
}
public Spliterator<K> trySplit() {
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
if (hasNext()) {
action.accept(next());
return true;
}
return false;
}
public long estimateSize() {
return Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.DISTINCT | Spliterator.ORDERED;
}
}
}
常用方法
put
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
*
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
* 如果key存在的话,old value被替换,否则新建一个节点,然后做红黑树的平衡操作
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
//根节点
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//根节点为空 创建根节点
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
//compare的比较结果
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
// 自定义key大小比较器
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
//对红黑树进行遍历搜索 查找key要插入的位置
do {
//当前遍历到的节点
parent = t;
//插入的key 与当前节点的key比价
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//小于 遍历左子节点
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//大于 遍历右子节点
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//相等,该节点存在,替换并返回
return t.setValue(value);
//结束条件 遍历到的节点t为null
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//不存在则新建结点插入
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//红黑树平衡调整
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
fixAfterInsertion
/** From CLR */
//新增节点后对红黑树的调整方法
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
//新插入的节点颜色 为红色
x.color = RED;
//保证新加入节点x不是根节点或者x的父节点不是红色
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
//x的父节点是祖父节点的左孩子
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
//获得父节点的兄弟节点
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
//如果x的父节点是红色
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
//将x的父节点设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//x的父节点的兄弟节点设置为黑色
setColor(y, BLACK);
//将x的祖父节点设置为红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//将x指向祖父节点,如果x的祖父节点的父节点是红色,按照上面的步奏继续循环
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
//x的父节点是祖父节点的右孩子
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
//左旋父节点
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
//x的父节点设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//x的祖父节点设置为红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//右旋x的祖父节点
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
// 最后将根节点设置为黑色,不管当前是不是红色,反正根节点必须是黑色
root.color = BLACK;
}
rotateLeft
/**
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-- / \
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*/
/** From CLR */
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
//节点p的右孩子
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
//r的左孩子设为p的右孩子
p.right = r.left;
// 如果r的左孩子非空,将"p"设为"r的左孩子的父亲"
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
// 将"p的父亲"设为"y的父亲"
r.parent = p.parent;
// 如果"p的父亲"是空节点,则将r设为根节点
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
// 如果p是它父节点的左孩子,则将r设为"p的父节点的左孩子"
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
// 如果p是它父节点的左孩子,则将r设为"p的父节点的左孩子"
p.parent.right = r;
// 将"p"设为"r的左孩子"
r.left = p;
// 将"p的父节点"设为"r"
p.parent = r;
}
}
rotateRight
/**
* 对红黑树的节点进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行右旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-- / \
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
/** From CLR */
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
// 取得要选择节点p的左孩子
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
// 将"l的右孩子"设为"p的左孩子"
p.left = l.right;
// 如果"l的右孩子"不为空的话,将"p"设为"l的右孩子的父亲"
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
// 将"p的父亲"设为"l的父亲"
l.parent = p.parent;
// 如果"p的父亲"是空节点,则将l设为根节点
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
// 如果p是它父节点的右孩子,则将l设为"p的父节点的右孩子"
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
//如果p是它父节点的左孩子,将l设为"p的父节点的左孩子"
else p.parent.left = l;
// 将"p"设为"l的右孩子"
l.right = p;
// 将"l"设为"p父节点"
p.parent = l;
}
}
get
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key} compares
* equal to {@code k} according to the map's ordering, then this
* method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns {@code null}.
* (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
*
A return value of {@code null} does not necessarily
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V get(Object key) {
//获取key对应的entry
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
getEntry
/**
* Returns this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map
* does not contain an entry for the key.
*
* @return this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map
* does not contain an entry for the key
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
* log(n)
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
// 如果比较器为空,只是用key作为比较器查询
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
// 取得root节点
Entry<K,V> p = root;
//遍历红黑树找到相同的元素返回 从root节点开始查找,根据比较器判断是在左子树还是右子树
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
getEntryUsingComparator
用key作为比较器查询
/**
* Version of getEntry using comparator. Split off from getEntry
* for performance. (This is not worth doing for most methods,
* that are less dependent on comparator performance, but is
* worthwhile here.)
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
remove
/**
* Removes the mapping for this key from this TreeMap if present.
*
* @param key key for which mapping should be removed
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
//找到对应的节点对象
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
//删除节点
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
deleteEntry
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
//元素个数减1
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
//如果被删除的节点p的左孩子和右孩子都不为空,则寻找替代节点
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
// 查找p的替代节点 (后继节点)
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
//replacement为替代节点p的继承者 p的左孩子存在则用p的左孩子替代,否则用p的右孩子
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
//如果上面的if有两个孩子不通过--------------这里表示要删除的节点只有一个孩子
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
// 将p的父节点拷贝给替代节点
replacement.parent = p.parent;
// 如果替代节点p的父节点为空,也就是p为跟节点,则将replacement设置为根节点
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
// 如果替代节点p是其父节点的左孩子,则将replacement设置为其父节点的左孩子
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
// 如果替代节点p是其父节点的左孩子,则将replacement设置为其父节点的右孩子
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
//将替代节点p的left、right、parent的指针都指向空,即解除前后引用关系(相当于将p从树种摘除),使得gc可以回收
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
// 如果替代节点p的颜色是黑色,则需要调整红黑树以保持其平衡
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
// 如果要替代节点p没有父节点,代表p为根节点,直接删除即可
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
// 判断进入这里说明替代节点p没有孩子--------------这里表示没有孩子则直接删除
// 如果p的颜色是黑色,则调整红黑树
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
// 下面删除替代节点p
if (p.parent != null) {
// 解除p的父节点对p的引用
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
// 解除p对p父节点的引用
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
successor
查找要删除节点的替代节点
/**
* Returns the successor of the specified Entry, or null if no such.
* 宏观上讲,TreeMap通过对红黑树进行中序遍历保证其迭代输出是有序的。迭代器
* 的next方法会调用successor取得后继。
*/
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
//有右子树的结点,后继结点是右子树的“最左结点”,
// 因为最左子树就是右子树的最小结点
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
//若右子树为空,寻找当前结点所在左子树的第一个祖先结点
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
//保证左子树,即父结点的右子树不指向它
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
fixAfterDeletion
/** From CLR */
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
//保证要删除节点x不是跟节点,并且是黑色(根节点和红色不需要调整)
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
// 如果要删除节点x是其父亲的左孩子
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
// 取出要删除节点x的兄弟节点
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
// 如果删除节点x的兄弟节点是红色
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
// 将x的兄弟节点颜色设置为黑色
setColor(sib, BLACK);
// 将x的父节点颜色设置为红色
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
// 左旋x的父节点
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
// 将sib重新指向旋转后x的兄弟节点 ,进入else的步奏
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
// 如果x的兄弟节点的两个孩子都是黑色
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// 将兄弟节点的颜色设置为红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// 将x的父节点指向x,如果x的父节点是黑色,需要将x的父节点整天看做一个节点继续调整
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
// 如果x的兄弟节点右孩子是黑色,左孩子是红色
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// 将x的兄弟节点的左孩子设置为黑色
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
// 将x的兄弟节点设置为红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// 右旋x的兄弟节点
rotateRight(sib);
// 将sib重新指向旋转后x的兄弟节点
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
//如果x的兄弟节点右孩子是红色
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
//将x的父节点设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
// 将x的兄弟节点的右孩子设置为黑色
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
// 左旋x的父节点
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
// 达到平衡,将x指向root,退出循环
x = root;
}
// 如果要删除节点x是其父亲的右孩子
} else { // symmetric
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}