SPI FLASH Fatfs文件系统移植
一.FATFS文件系统简介
FATFS是面向小型嵌入式系统的FAT文件系统。他由C语言编写并且独立与底层I/O介质。支持的内核有:8051,PLC,ARV,ARM等。FATFS支持FAT12,FAT16,FAT32等文件系统格式。
官网链接
二.FATFS源码文件结构
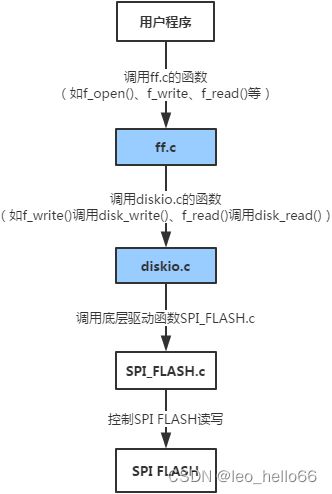
- diskio.c:包含底层存储介质的操作函数,需要与硬件设备适配移植。主要是在这个文件里调用用户实现的底层驱动函数,如SPI读写falsh的操作函数;
- diskio.h:为diskio.c文件的函数原型声明和各个宏定义;
- ff.c:Fatfs核心文件,通过调用diskio.c的底层操作函数实现文件的读写等操作。该文件独立于底层介质操作文件,移植系统时不需要修改。
- ff.h:相关文件和文件夹的结构体定义。
- ffconf.h:用于fatfs的功能配置,通过宏实现条件编译,修改相应宏定义的值即可实现功能的裁剪。如,需要支持简体中文,长文件名等。
三.函数调用流程
四.移植说明
修改diskio.c文件,这个文件里的函数主要有已下几个函数需要实现:
获取当前的驱动的状态:
DSTATUS disk_status(BYTE pdrv )
初始化当前驱动的硬件设备:
DSTATUS disk_initialize(BYTE pdrv)
从当前驱动中读取某块连续的扇区数据:
DRESULT disk_read(
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE buff, / Data buffer to store read data /
LBA_t sector, / Start sector in LBA /
UINT count / Number of sectors to read */
)
将数据写入当前驱动的某块扇区:
DRESULT disk_write(
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE buff, / Data to be written /
LBA_t sector, / Start sector in LBA /
UINT count / Number of sectors to write */
)
获取当前驱动的一些信息:
DRESULT disk_ioctl(
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0…) /
BYTE cmd, / Control code */
void buff / Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
ff.h相关的几个重要的宏定义
#define _USE_MKFS 1 // 格式化选择
#define _CODE_PAGE 936 // 语言选择
#define _USE_LFN 2 // 长文件名支持
#define _VOLUMES 2 // 物理设备数量
#define _MIN_SS 512 // 指定扇区的最小值
#define _MAX_SS 4096 // 指定扇区的最大值
五.测试demo
FATFS fs;
FIL fp;
BYTE fatfs_buffer[FF_MAX_SS] = {0};
UINT bw;
BYTE write_buf[] = "my name is leo";
BYTE read_buf[sizeof(write_buf)];
UINT br;
char filename[] = "SPI0:test.txt";
void test(void)
{
FRESULT res; /* 文件操作结果 */
res = f_mount(&fs, "SPI0:", 1);
if (res == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM)
{
printf("[%s:%d] not find filesystem \r\n", __func__, __LINE__);
/* 格式化 */
res = f_mkfs("SPI0:", 0, fatfs_buffer, sizeof(fatfs_buffer));
if (res == FR_OK)
{
/* 格式化后,先取消挂载 */
res = f_mount(NULL, "SPI0:", 1);
/* 重新挂载 */
res = f_mount(&fs, "SPI0:", 1);
if (res == FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d]format flash ok\r\n", __func__, __LINE__);
}
}
else
{
printf("[%s:%d]format falsh filed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
}
else if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] mount flash filesystem failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
else
{
printf("[%s:%d] mount flash system ok\r\n", __func__, __LINE__);
}
res = f_open(&fp, "SPI0:test.txt", FA_READ | FA_WRITE | FA_CREATE_ALWAYS);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] open test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
res = f_close(&fp);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] close test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
res = f_open(&fp, "SPI0:test.txt", FA_WRITE | FA_OPEN_EXISTING);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] open test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
res = f_write(&fp, write_buf, sizeof(write_buf), &bw);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] write test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
res = f_close(&fp);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] close test.txt failed(%s)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
// // 读之前需要打开文件:只读权限(文件存在就读取)
res = f_open(&fp, filename, FA_READ | FA_OPEN_EXISTING);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] open test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
res = f_read(&fp, read_buf, sizeof(write_buf), &br);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] read test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
printf("read_buf = %s\r\n", read_buf);
res = f_close(&fp);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("[%s:%d] close test.txt failed(%d)\r\n", __func__, __LINE__, res);
while (1)
;
}
}
移植好的链接