Android Handler被弃用,那么以后怎么使用Handler,或者类似的功能
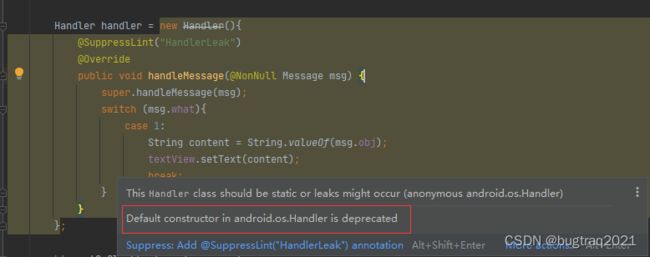
Android API30左右,Android应用在使用传统写法使用Handler类的时候会显示删除线,并提示相关的方法已经被弃用,不建议使用。
Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what){
case 1:
String content = String.valueOf(msg.obj);
textView.setText(content);
break;
}
}
};Android studio中的显示和建议:
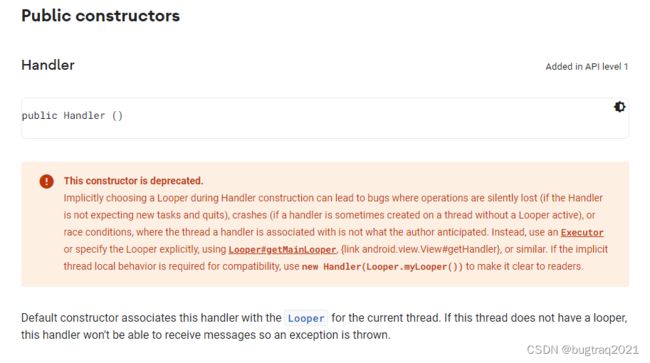
看下官方API关于此处的解释:
简要说就是如果在实例化Handler的时候不提供Looper, 可能导致操作丢失(Handler 没有预估到新任务并已退出)、App崩溃的bug(Handler有时候创建一个线程,但没有运行的Looper),亦或者race情况下,造成处理错误。
所以作者弃用了这部分内容。
那以后如何用Handler,或者相关功能挺好用的,有没有替代功能呢?
通常,Android 应用程序使用主线程来处理 UI 任务和输入事件。因此,在此主线程上执行任何长时间运行的任务都可能导致应用程序冻结和无响应。 该主线程将 UI 事件或消息收集到队列 ( MessageQueue) 中,然后使用Looper类的实例对其进行处理。默认情况下,主线程已经准备好了Looper 。
但意外总是有的,那应该怎么处理?
1。仍然用Handler
弃用的不是Handler, 而上Handler的两个构造方法:
Handler()Handler(Handler.Callback)
上面两个构造方法在某些情况下会发生弃用理由里面的bug,但是,并不是整个Handler类被弃用了,还可以用其他的构造方法来构造Handler对象。
安卓建议采用如下方法来替代:
- 使用 Executor
- 明确指定Looper 。
使用Looper.getMainLooper()定位并使用主线程的Looper- 如果又想在其他线程,又想要不出bug,请使用
new Handler(Looper.myLooper(), callback) 或者 new Handler(Looper.myLooper())两个构造方法。
public Handler(@NonNull Looper looper) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stub!");
}
public Handler(@NonNull Looper looper, @Nullable Handler.Callback callback) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stub!");
}2。仍然使用Handler的方法
2.1 在主线程内运行。
val mainHandler = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post {
System.out.println("Thread : " + Thread.currentThread().name)
}
/* prints
I/System.out: Thread : main */2.2 在当前线程运行Handler
val mainHandler = Handler(Looper.myLooper()).post {
System.out.println("Thread : " + Thread.currentThread().name)
}2.3 明确指出使用某线程的Looper
val handlerThread = HandlerThread("HandlerThread");
handlerThread.start();
val backgroundHandler = Handler(handlerThread.looper).post {
println("Thread : " + Thread.currentThread().name)
handlerThread.quitSafely();
}
/* prints
I/System.out: Thread : HandlerThread */2.4 从主线程内新建一个线程handler线程
// Create a handler to execute in the background thread
val backgroundHandler = Handler(handlerThread.getLooper(), Handler.Callback() {
// Your code logic goes here.
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post {
System.out.println("Thread : " + Thread.currentThread().name)
// update UI
}
return true
}
})3。使用 Executor
3.1 在主线程内运行 Executor
val mainExecutor: Executor = ContextCompat.getMainExecutor(this)
// Execute a task in the main thread
mainExecutor.execute(Runnable {
// You code logic goes here.
})3.2 新建后台线程运行 Executor
val backgroundExecutor: ScheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()
// Execute a task in the background thread.
backgroundExecutor.execute {
// background code
backgroundExecutor.shutdown();
}
// Execute a task in the background thread after 5 seconds.
backgroundExecutor.schedule({
// background code
backgroundExecutor.shutdown();
}, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)