usb主机控制器驱动
1、 tcc803x的usb2.0由两个模块组成:主从一体模块(dwc2)和主模块,主从一体模块里主部分集 成了echi、ohci两个主控制器,从部分集成了一个设备控制器。主模块里只集成了两个主控制 器:ehci和ohci。所以usb2.0里有两个echi两个ohci和一个设备控制器.
2、High-speed: 25Mbps~400Mbps(最大480Mbps) (高速)
Full-speed: 500Kbps~10Mbps(最大12Mbps) (全速)
Low-speed: 10Kbps~100Kbps(最大1.5Mbps) (低速)
3、USB主机控制器的类型有:OHCI和UHCI,EHCI,和xHCI
4、USB采用树形拓扑结构,主机侧和设备侧的USB控制器分别称为主机控制器(Host Controller) 和USB设备控制器(UDC),每条总线上只有一个主机控制器,负责协调主机和设备间的通信, 设备不能主动向主机发送任何消息。
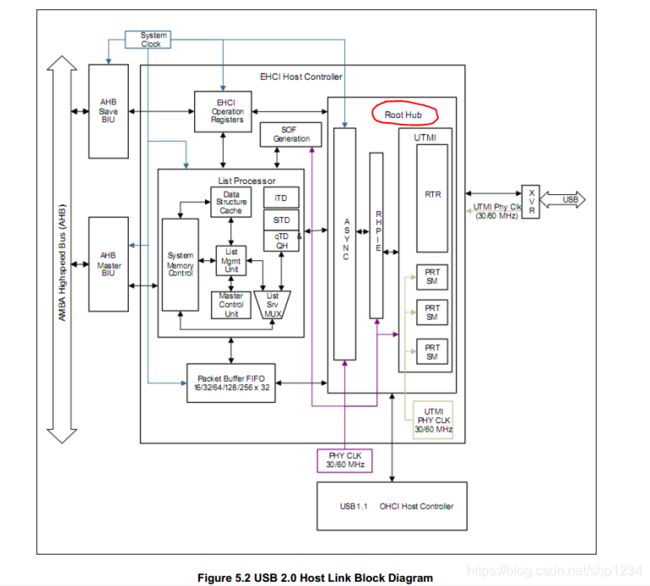
5、USB Host带有Root Hub,第一个USB设备就是根集线器(Root_hub),它控制连接到其上的整 个USB总线(其它的hub都只叫hub集线器)
6、usb主机控制器的块图:
7、usb主机控制器的代码分析(只分析usb2.0的dwc2模块中的两个主控制器):
a、设备树中对dwc2模块的设备描述:
dwc_otg: dwc_otg@11980000 {
compatible = "telechips,dwc2";
reg = <0x11980000 0xcfff 0x11900000 0x108 0x11940000 0x60>;
interrupts = , ;
clocks = <&clk_hsio HSIOBUS_USB20H>;
clock-names = "otg";
phy = <&dwc_otg_phy>;
phy-names = "usb2-phy";
telechips,mhst_phy = <&mhst_phy>;
status= "disabled";
};
其中reg属性中的寄存器地址分配说明:
b、dwc2代码分析:
b-1: drivers/usb/dwc2/params.c:
const struct of_device_id dwc2_of_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "telechips,dwc2" },
{},
};b-2: drivers/usb/dwc2/platform.c
static struct platform_driver dwc2_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = dwc2_driver_name,
.of_match_table = dwc2_of_match_table,
.pm = &dwc2_dev_pm_ops,
},
.probe = dwc2_driver_probe,
.remove = dwc2_driver_remove,
.shutdown = dwc2_driver_shutdown,
};
module_platform_driver(dwc2_platform_driver);注册dwc2_platform_driver平台驱动,如果在设备树中能够找到属性compatible=“telechips,dwc2”的设备节点,就调用 dwc2_driver_probe函数:
static int dwc2_driver_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct dwc2_hsotg *hsotg;
struct resource *res;
int retval;
hsotg = devm_kzalloc(&dev->dev, sizeof(*hsotg), GFP_KERNEL);
hsotg->dev = &dev->dev;
res = platform_get_resource(dev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
hsotg->regs = devm_ioremap_resource(&dev->dev, res);
hsotg->ehci_regs = dev->resource[1].start;
hsotg->ehci_regs_size = dev->resource[1].end - dev->resource[1].start + 1;
hsotg->ohci_regs = dev->resource[2].start;
hsotg->ohci_regs_size = dev->resource[2].end - dev->resource[2].start + 1;
dwc2_mux_hcd_init(hsotg);
}dwc2_driver_probe函数中通过调用platform_get_resource函数获取索引为0的寄存器地址空间(从寄存器地址分布上看即dwc2设备控制器的寄存器地址空间),然后经过地址重映射赋值给hsotg->regs。紧接着下面几行将dev->resource[1]和dev->resource[2] 分别表示的ehci和ohci主机控制器的寄存器地址空间赋值给hsotg->ehci_regs和hsotg->ohci_regs。最后调用dwc2_mux_hcd_init函数。
platform_get_resource函数,根据num索引返回对应的资源:
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int num)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < dev->num_resources; i++) {
struct resource *r = &dev->resource[i];
if (type == resource_type(r) && num-- == 0)
return r;
}
return NULL;
}dwc2_mux_hcd_init函数:
int dwc2_mux_hcd_init(struct dwc2_hsotg *hsotg)
{
struct usb_mux_hcd_device *usb_dev;
usb_dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct usb_mux_hcd_device), GFP_KERNEL);
start = (int)hsotg->ohci_regs;
size = (int)hsotg->ohci_regs_size;
usb_dev->ohci_dev = dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev(hsotg, true, start, size);
start = (int)hsotg->ehci_regs;
size = hsotg->ehci_regs_size;
usb_dev->ehci_dev = dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev(hsotg, false, start, size);
} dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev 函数:
struct platform_device *dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev(struct dwc2_hsotg *hsotg, bool ohci,
u32 res_start, u32 size){
struct platform_device *hci_dev;
struct resource hci_res[2];
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
hci_res[0].start = res_start;
hci_res[0].end = res_start + size - 1;
hci_res[0].flags = IORESOURCE_MEM;
hci_res[1].start = hsotg->ehci_irq;
hci_res[1].flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ;
platform_device_add_resources(hci_dev, hci_res,ARRAY_SIZE(hci_res));
hci_dev = platform_device_alloc(ohci ? "ohci-mux" :"ehci-mux" , 0);
hci_dev->dev.parent = hsotg->dev;
platform_device_add(hci_dev);
}dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev函数根据ehci和ohci主控制器不同的地址空间资源分别创建名为“ehci-mux”和“ehci-mux”平台设备(即主控制器设备),然后加入到设备链表中,等待匹配某个驱动,调用相应的probe函数。
b-3:这里只分析ohci-mux对应的平台驱动:
drivers/usb/host/ohci-platform.c:
static const struct platform_device_id ohci_platform_table[] = {
{ "ohci-mux", 1 },
{ }
};
static struct platform_driver ohci_platform_driver = {
.id_table = ohci_platform_table,
.probe = ohci_platform_probe,
.remove = ohci_platform_remove,
.shutdown = usb_hcd_platform_shutdown,
.driver = {
.name = "ohci-platform",
.pm = &ohci_platform_pm_ops,
.of_match_table = ohci_platform_ids,
}
};前面dwc2_create_mux_hcd_pdev 函数创建了名为“ohci-mux”的平台设备(控制器设备),与这里注册的ohci_platform_driver平台驱动匹配,调用ohci_platform_probe函数:
static int ohci_platform_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
struct resource *res_mem;
struct ohci_hcd *ohci;
hcd = usb_create_hcd(&ohci_platform_hc_driver, &dev->dev,
dev_name(&dev->dev));
err = usb_add_hcd(hcd, irq, IRQF_SHARED);
}ohci_platform_probe函数中主要看usb_create_hcd和usb_add_hcd这两个函数,这两函数分别是创建和添加struct usb_hcd结构体变量。hcd即host controller driver,主要描述主控制器设备和主控制器的数据传输。ohci_platform_hc_driver是struct hc_driver变量,是hcdi接口,封装了对相应主控制器(struct usb_hcd)的操作。
usb_create_hcd函数:
struct usb_hcd *usb_create_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,struct device *dev,
const char *bus_name){
return __usb_create_hcd(driver, dev, dev, bus_name, NULL);
}__usb_create_hcd函数:
struct usb_hcd *__usb_create_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,struct device *sysdev,
struct device *dev, const char *bus_name,struct usb_hcd *primary_hcd)
{
struct usb_hcd *hcd;
hcd = kzalloc(sizeof(*hcd) + driver->hcd_priv_size, GFP_KERNEL);
usb_bus_init(&hcd->self);
hcd->self.controller = dev;
hcd->self.sysdev = sysdev;
hcd->self.bus_name = bus_name;
init_timer(&hcd->rh_timer);
hcd->rh_timer.function = rh_timer_func;
hcd->rh_timer.data = (unsigned long) hcd;
hcd->driver = driver;
hcd->speed = driver->flags & HCD_MASK;
hcd->product_desc = (driver->product_desc) ? driver->product_desc :"USB Host Controller";
return hcd;
}struct usb_hcd的结构体:
struct usb_hcd {
struct usb_bus self;
const char *product_desc;
struct timer_list rh_timer;
const struct hc_driver *driver;
struct usb_phy *usb_phy;
unsigned long hcd_priv[0] __attribute__ ((aligned(sizeof(s64))));
};hcd_priv是元素个数为0的数组,即标签,标示着紧挨着struct usb_hcd结构体下面的地址,用于扩展内存使用。
struct usb_bus的结构:
struct usb_bus {
struct device *controller; /* host/master side hardware */
struct device *sysdev; /* as seen from firmware or bus */
int busnum; /* Bus number (in order of reg) */
const char *bus_name; /* stable id (PCI slot_name etc) */
int devnum_next; /* Next open device number in
struct usb_devmap devmap; /* device address allocation map */
struct usb_device *root_hub; /* Root hub */
};__usb_create_hcd函数创建一个struct usb_hcd的变量,并对该变量初始化。self的结构体是struct usb_bus,一条总线对应着一个主控制器,一个主控制器对应着一个总线,hcd->self.controller指向该usb总线对应的主控制器,也就是我们这里的平台设备,struct usb_hcd的变量通过self成员的controller成员间接指向主控制器设备,所以说struct usb_hcd描述主控制器信息是没问题的。hcd->self.sysdev也指向平台设备,从usb总线角度看,靠向系统端的设备就是主控制器设备。
usb_bus_init函数,初始化相关成员:
void usb_bus_init (struct usb_bus *bus)
{
memset (&bus->devmap, 0, sizeof(struct usb_devmap));
bus->devnum_next = 1;
bus->root_hub = NULL;
bus->busnum = -1;
}再来看看usb_add_hcd函数:
int usb_add_hcd(struct usb_hcd *hcd,unsigned int irqnum, unsigned long irqflags)
{
struct usb_device *rhdev;
struct usb_phy *phy = usb_get_phy_dev(hcd->self.sysdev, 0);
usb_register_bus(&hcd->self);
rhdev = usb_alloc_dev(NULL, &hcd->self, 0);
hcd->self.root_hub = rhdev;
register_root_hub(hcd);
}从usb_add_hcd函数来看,一是寻找有没有struct usb_phy,二是注册总线,三是分配一个struct usb_device的结构体变量,我们知道,主控制器上有一个root_hub,root_hub本质上就是一个usb设备,所以hcd->self.root_hub指向这个rhdev。四是注册root_hub。
usb_get_phy_dev函数:
struct usb_phy *usb_get_phy_dev(struct device *dev, u8 index)
{
struct usb_phy *phy = NULL;
phy = __usb_find_phy_dev(dev, &phy_bind_list, index);
return phy;
}__usb_find_phy_dev函数:
struct usb_phy *__usb_find_phy_dev(struct device *dev,struct list_head *list, u8 index)
{
struct usb_phy_bind *phy_bind = NULL;
/*第一个list是函数里的list形参,第二个list是phy_bind的list成员*/
list_for_each_entry(phy_bind, list, list)
if (!(strcmp(phy_bind->dev_name, dev_name(dev))) && phy_bind->index == index) {
if (phy_bind->phy)
return phy_bind->phy;
}
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
}对usb_get_phy_dev函数层层剥下来,该函数的作用是从phy_bind_list链表里寻找索引为0的struct usb_phy的东西,但是由于从未向phy_bind_list链表里添加东西,导致该链表是空,所以返回为-ENODEV。
usb_register_bus函数:
int usb_register_bus(struct usb_bus *bus){
busnum = idr_alloc(&usb_bus_idr, bus, 1, USB_MAXBUS, GFP_KERNEL);
bus->busnum = busnum;
}所谓的注册总线,就是随机分配一个编号。
usb_alloc_dev函数:
struct usb_device *usb_alloc_dev(struct usb_device *parent,struct usb_bus *bus,
unsigned port1){
struct usb_device *dev;
struct usb_hcd *usb_hcd = bus_to_hcd(bus);
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
//root_hub没有父设备了,所以parent设NULL,所以不会去判断第三个条件
if (usb_hcd->driver->alloc_dev && parent &&!usb_hcd->driver->alloc_dev(usb_hcd, dev)){}
device_initialize(&dev->dev);
dev->dev.bus = &usb_bus_type;
dev->dev.type = &usb_device_type;
usb_enable_endpoint(dev, &dev->ep0, false);
dev->can_submit = 1;
if (unlikely(!parent)) {
dev->devpath[0] = '0';
dev->dev.parent = bus->controller;
device_set_of_node_from_dev(&dev->dev, bus->sysdev);
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "usb%d", bus->busnum);
root_hub = 1;
}
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "%d-%s", bus->busnum, dev->devpath);
}从usb_alloc_dev函数中可以看出,其作用就是创建分配一个struct usb_device结构体,并对该结构体初始化。其中usb_enable_endpoint函数使能usb端点(这里是端点0),用于usb通信,待会usb会通过该端点发送设备描述符信息。
usb_enable_endpoint函数:
void usb_enable_endpoint(struct usb_device *dev, struct usb_host_endpoint *ep,
bool reset_ep){
//我们并没有对ep0的相关字段赋值,ep0的相关字段都是0.
int epnum = usb_endpoint_num(&ep->desc); //获取端点编号
int is_out = usb_endpoint_dir_out(&ep->desc); //判断是否是输出
int is_control = usb_endpoint_xfer_control(&ep->desc); //判断是否是控制传输
if (is_out || is_control) //如果是控制传输,端点编号为0,输入输出端点都要设置
dev->ep_out[epnum] = ep;
if (!is_out || is_control)
dev->ep_in[epnum] = ep;
ep->enabled = 1;
}device_set_of_node_from_dev函数:
void device_set_of_node_from_dev(struct device *dev, const struct device *dev2)
{
of_node_put(dev->of_node);
dev->of_node = of_node_get(dev2->of_node);
dev->of_node_reused = true;
}该函数的作用是dev使用dev2的of_node。
register_root_hub函数:
int register_root_hub(struct usb_hcd *hcd)
{
struct device *parent_dev = hcd->self.controller;
struct usb_device *usb_dev = hcd->self.root_hub;
usb_dev->devnum =1; //表示root_hub的设备编号是1
usb_dev->bus->devnum_next = devnum + 1;
memset (&usb_dev->bus->devmap.devicemap, 0,sizeof usb_dev->bus->devmap.devicemap);
set_bit (devnum, usb_dev->bus->devmap.devicemap); //表示将devicemap第devnum位置1
usb_get_device_descriptor(usb_dev, USB_DT_DEVICE_SIZE); //获取设备描述符
usb_new_device (usb_dev);
}register_root_hub函数,顾名思义,就是注册root_hub设备,先是对自身初始化,然后获取设备描述符,最后把自己当普通usb设备给注册了。
usb_get_device_descriptor函数:
int usb_get_device_descriptor(struct usb_device *dev, unsigned int size)
{
struct usb_device_descriptor *desc;
desc = kmalloc(sizeof(*desc), GFP_NOIO);
usb_get_descriptor(dev, USB_DT_DEVICE, 0, desc, size);
memcpy(&dev->descriptor, desc, size);//将获取到的设备描述符复制给dev->descriptor
kfree(desc);
}获取设备描述符。
usb_new_device函数:
int usb_new_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
usb_enumerate_device(udev);
udev->dev.devt = MKDEV(USB_DEVICE_MAJOR,(((udev->bus->busnum-1) * 128)
+ (udev->devnum-1))); //设备号
announce_device(udev);
device_add(&udev->dev);
}注册usb设备,先是枚举(这里枚举获取的pid、vid等用于设备驱动匹配的id使用),然后加入到设备设备链表中。
usb_enumerate_device函数:
int usb_enumerate_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
struct usb_hcd *hcd = bus_to_hcd(udev->bus);
usb_get_configuration(udev); //获取配置描述符
udev->product = usb_cache_string(udev, udev->descriptor.iProduct); //获取产品号
udev->manufacturer = usb_cache_string(udev,udev->descriptor.iManufacturer);//制造商
udev->serial = usb_cache_string(udev, udev->descriptor.iSerialNumber);//序列号
//usb_detect_interface_quirks(udev);
}announce_device函数:
void announce_device(struct usb_device *udev)
{
show_string(udev, "Product", udev->product);
show_string(udev, "Manufacturer", udev->manufacturer);
show_string(udev, "SerialNumber", udev->serial);
}show_string函数:
void show_string(struct usb_device *udev, char *id, char *string)
{
dev_info(&udev->dev, "[INFO][USB] %s: %s\n", id, string);
}至此,root_hub就注册完毕,root_hub满足hub.c驱动的struct usb_device_id条件中的一个,从而调用hub_probe函数,这个后面细说。
b-4、usb设备、驱动匹配过程:
代码位置:usb/core/driver.c
说明:
设备:usb_new_device注册usb设备时,会通过获取usb的设备描述符获取pid、vid等信息。
驱动:定义struct usb_device_id变量,设置pid、vid等信息。
设备驱动通过struct usb_device_id进行匹配。
usb_device_match函数:
int usb_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct usb_interface *intf;
struct usb_driver *usb_drv;
const struct usb_device_id *id;
intf = to_usb_interface(dev);
usb_drv = to_usb_driver(drv);
id = usb_match_id(intf, usb_drv->id_table);
if (id)
return 1;
.........
}usb_match_id函数:
struct usb_device_id *usb_match_id(struct usb_interface *interface,
const struct usb_device_id *id) {
for(; id->idVendor || id->idProduct || id->bDeviceClass ||id->bInterfaceClass
|| id->driver_info; id++) {
if (usb_match_one_id(interface, id))
return id;
}
}usb_match_one_id函数:
/* returns 0 if no match, 1 if match */
int usb_match_one_id(struct usb_interface *interface,const struct usb_device_id *id)
{
struct usb_host_interface *intf;
struct usb_device *dev;
intf = interface->cur_altsetting;
dev = interface_to_usbdev(interface);
if (!usb_match_device(dev, id))
return 0;
return usb_match_one_id_intf(dev, intf, id);
}usb_match_device函数:
int usb_match_device(struct usb_device *dev, const struct usb_device_id *id)
{
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR) &&
id->idVendor != le16_to_cpu(dev->descriptor.idVendor))
return 0;
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT) &&
id->idProduct != le16_to_cpu(dev->descriptor.idProduct))
return 0;
return 1;
}usb_match_one_id_intf函数:
/* returns 0 if no match, 1 if match */
int usb_match_one_id_intf(struct usb_device *dev,struct usb_host_interface *intf,const struct usb_device_id *id){
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_CLASS) &&
(id->bInterfaceClass != intf->desc.bInterfaceClass))
return 0;
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_SUBCLASS) &&
(id->bInterfaceSubClass != intf->desc.bInterfaceSubClass))
return 0;
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_PROTOCOL) &&
(id->bInterfaceProtocol != intf->desc.bInterfaceProtocol))
return 0;
if ((id->match_flags & USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_NUMBER) &&
(id->bInterfaceNumber != intf->desc.bInterfaceNumber))
return 0;
return 1;
}附:
1、usb设备连接后开机不识别:
USB OTG规范的SRP和HNP协议-SilkWomILinx-ChinaUnix博客
开机vbus就上电,等到insmod usb驱动初始化时,由于较长时间没有通信,usb总线挂起,导致不能枚举usb设备,这时需要vbus断电后延迟100ms再上电,确保B-device SRP B1+B4即低电平阶段的完成。
2、参考文章:linux设备驱动之USB主机控制器驱动分析-zhuqing_739-ChinaUnix博客