【Java算法题】剑指offer_数据结构之02树
前言
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj/ta?page=2&tpId=13&type=265
原定于5.27写完树部分的算法,但是未能如愿写完。现已经5.31,另外 “JZ37 序列化二叉树” HARD题目,暂时没写出来,后续再刷的时候会再写。
2. 树
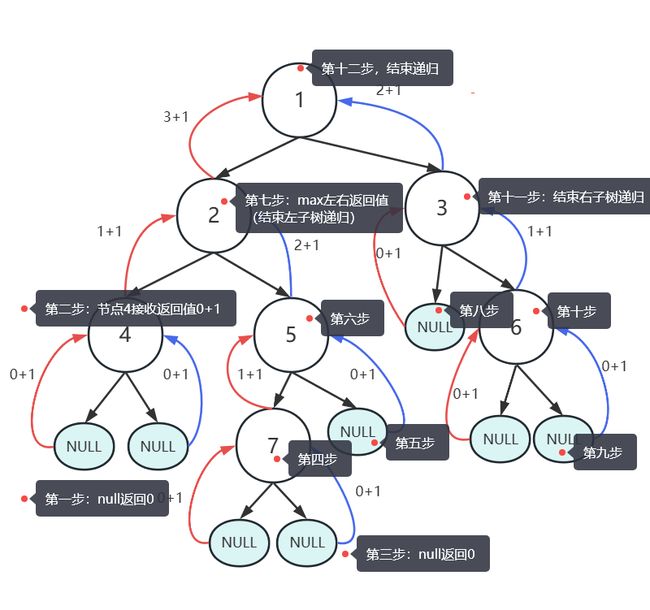
JZ55 二叉树的深度
思路:dep = max_deepth(left,right)+1,二叉树的深度为根节点到叶子节点,使用递归访问根节点的左孩子和右孩子,取最大值。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(TreeDepth(root.left),TreeDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
还可以用层次遍历,当前结点的左右孩子节点入队。记录队列大小,访问完的节点出队,访问完一层的时候深度+1。队列为空的时候,退出遍历。
JZ77 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
思路:使用队列进行层次遍历的应用,但是需要按照之字形访问,添加一个flag来操作。
import java.util.*;
/*
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> >();
TreeNode head = pRoot;
if(head==null){
return res;
}
// 队列存储,层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> temp = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
temp.offer(head); //根节点入队
TreeNode p;
boolean flag = true; //决定是否反转
while(!temp.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> row = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //记录二叉树的某一行
int n = temp.size();
flag = !flag;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
p = temp.poll(); //返回当前队列的节点
row.add(p.val);
if(p.left != null) // 当前节点的左右孩子不为空则添加到队列
temp.offer(p.left);
if(p.right != null)
temp.offer(p.right);
}
if(flag){ //奇数行不反转,偶数行反转
Collections.reverse(row);
}
res.add(row);
}
return res;
}
}
JZ54 二叉搜索树的第k个节点
思路:二叉搜索树的特点就是左节点<中间节点<右节点,利用中序遍历就可以生成一个升序的数组,那么利用一个count标记已访问的节点数,当count等于k的时候返回当前节点就行。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param proot TreeNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return int整型
*/
private int count = 0;
private int res = -1;
public int KthNode (TreeNode proot, int k) {
// write code here
if(proot == null)
return -1;
// 中序遍历
midOrder(proot,k);
return res;
}
public void midOrder(TreeNode p,int k ){
if(p == null || count > k){
return ;
}
midOrder(p.left,k);
count++;
if(count==k){
res = p.val; //记录第k个访问到的节点
}
midOrder(p.right,k);
}
}
JZ7 重建二叉树
思考:
- 利用前序遍历pre[0]确定根节点;
- 在中序遍历搜索根节点位置vin[i],确认左右子树;
- 递归:左子树传入pre[1:i+1]和vin[0,i] ,右子树传入pre[i+1,pre.length]和vin[i+1,vin.length]
Arrays.copyOfRange(int[] nums,int from,int to) 左开右闭复制数组
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] vin) {
int n = pre.length;
int m = vin.length;
if(n==0||m==0){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
if(vin[i] == pre[0]){ //找到中序遍历的根节点
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,i+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(vin,0,i));
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,i+1,n),Arrays.copyOfRange(vin,i+1,m));
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
JZ26 树的子结构
思路:考察的是二叉树先序遍历(仔细斟酌一下)
- 因为空树不是任何树的子树,先判断B树是否为空
- 当A树为空节点,但是B树不为空的时候,B树不是A的子树
- 当A树为空节点,B树为空,则B树为A的子树
- 每次递归从比较A树当前节点开始,判断是否与B树一致,同步先序遍历
- A树自己再前序遍历进入子节点,当作子树起点再与B树同步遍历。
以上任意一种情况满足即可。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null || root2 == null){ //空树不是任何树的子树
return false;
}
if(isSame(root1,root2)){ //判断是否相等
return true;
}else{
return HasSubtree(root1.left,root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
}
public boolean isSame(TreeNode head1, TreeNode head2){
if(head2 == null){ //遍历树B完成
return true; //B为A的子树
}else if(head1 == null){
return false; //遍历树A完成,B不是子树
}
if(head1.val != head2.val){ //当前节点不相等
return false;
}
// 当前节点相等,进入下一节点比较,所有节点相等返回true
boolean flag1 = isSame(head1.left,head2.left);
boolean flag2 = isSame(head1.right,head2.right);
return flag1&&flag2;
}
}
JZ27 二叉树的镜像
思路:考察后序遍历
访问当前节点的左右节点,将两个值交换
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pRoot TreeNode类
* @return TreeNode类
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
//空树返回
if(pRoot == null){
return null;
}
//递归子树
TreeNode left = Mirror(pRoot.left);
TreeNode right = Mirror(pRoot.right);
//交换
pRoot.left = right;
pRoot.right = left;
return pRoot;
}
}
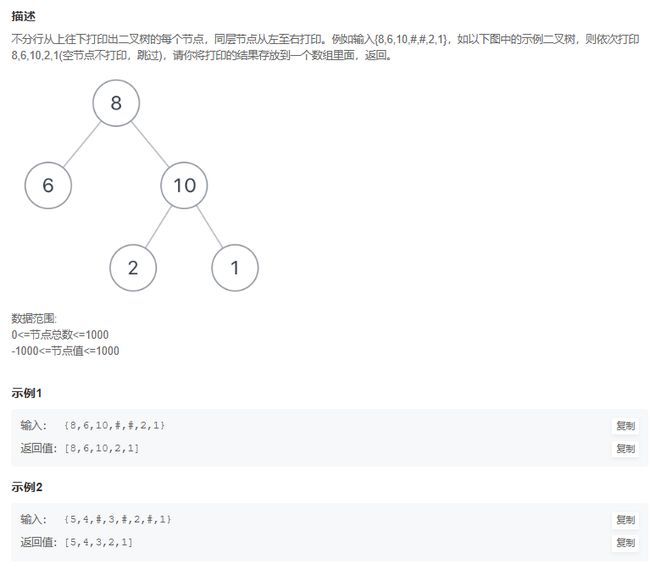
JZ32 从上往下打印二叉树
思路:广度遍历(层次遍历),使用队列保存当前层的节点信息,访问一个节点则存入数组中。
import java.util.*;
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
//层次遍历
ArrayList<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){ //空则返回空
return nums;
}
//创建队列存储节点
Queue<TreeNode> t = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p;
t.offer(root); //根节点入队
while(!t.isEmpty()){
int n = t.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
p = t.poll(); //删除并返回队头元素
nums.add(p.val);
if(p.left != null){
t.offer(p.left);
}
if(p.right != null){
t.offer(p.right);
}
}
}
return nums;
}
}
JZ33 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
思路:
二叉搜索树的特点就是左子树<中间节点<右子树
- 找到左右子树分界点,记录索引值mid
- 如果mid==-1,说明没有右子树,直接判定为true
- 若有右子树,判断右子树合不合法,即看数值是不是都小于root
- 递归检查左右子树
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence.length==0){
return false;
}
return order(sequence,0,sequence.length-1);
}
public boolean order(int[] sequence,int left, int right){
if(left >= right) return true;
int root = sequence[right]; //根节点为最后一个元素
// 找到左右子树的分界点,第一个大于根节点的元素位置
int mid = -1;
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
if(sequence[i]>root){
mid = i;
break;
}
}
if(mid == -1) return true; //只有左子树,直接判定true
// 判断右子树合不合法
for(int i=mid;i<right;i++){
if(sequence[i]<root){ //右子树存在小于root的元素则为false
return false;
}
}
return order(sequence,left,mid-1) && order(sequence,mid,right-1);
}
}
一个待解决的BUG:
小白发问,这个代码面对{4,6,7,5}时运行错误,应该如何修正呢?出错的点在于处理右子树{6,7}时,order(seq,1,2)=>mid=0 没有该子树没有右子树,但是因为mid=0,还是会运行下面的右子树合法判断。
我将mid初始化为-1,额外添加了if(mid==-1) return true; 还有别的方法改进吗?
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence.length==0){
return false;
}
return order(sequence,0,sequence.length-1);
}
public boolean order(int[] sequence,int left, int right){
if(left >= right) return true;
int root = sequence[right]; //根节点为最后一个元素
// 找到左右子树的分界点,第一个大于根节点的元素位置
int mid = 0;
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
if(sequence[i]>root){
mid = i;
break;
}
}
// 判断右子树合不合法
for(int i=mid;i<right;i++){
if(sequence[i]<root){ //右子树存在小于root的元素则为false
return false;
}
}
return order(sequence,left,mid-1) && order(sequence,mid,right-1);
}
}
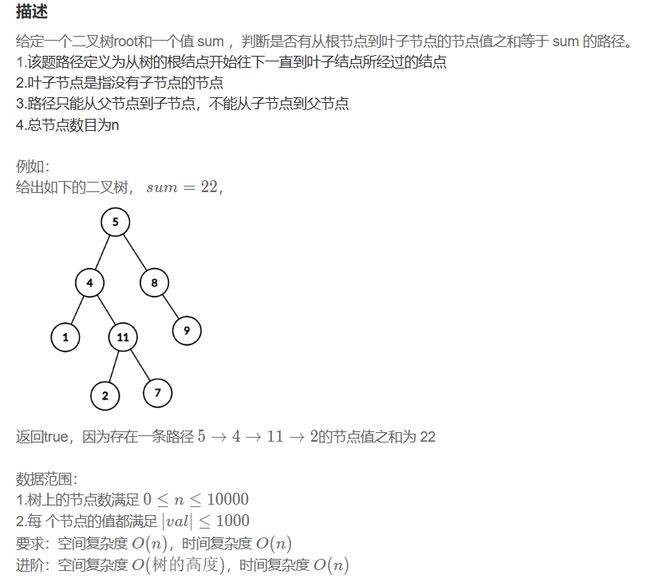
JZ82 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
思路:检查根节点到叶子节点是否有满足条件的路径,那么就需要从根节点遍历。采用先序遍历的思想,每遍历一个就将sum减去该节点值。首先判断该节点是否为空,空则不是路径;其次检查该节点是否为叶子节点,且sum减去该节点值为0,那么该条路径满足要求。递归检查左右子树是否有满足要求的路径,任意一条满足即可。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param sum int整型
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
if(root == null) //检查该节点是否为空,空则不是路径
return false;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && sum-root.val==0){
//检查是不是为叶子节点,且sum-该节点值是否等于0
return true;
}
//检查左子树或右子树
return hasPathSum(root.left,sum-root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right,sum-root.val);
}
}
可以用深度优先搜索(dfs)
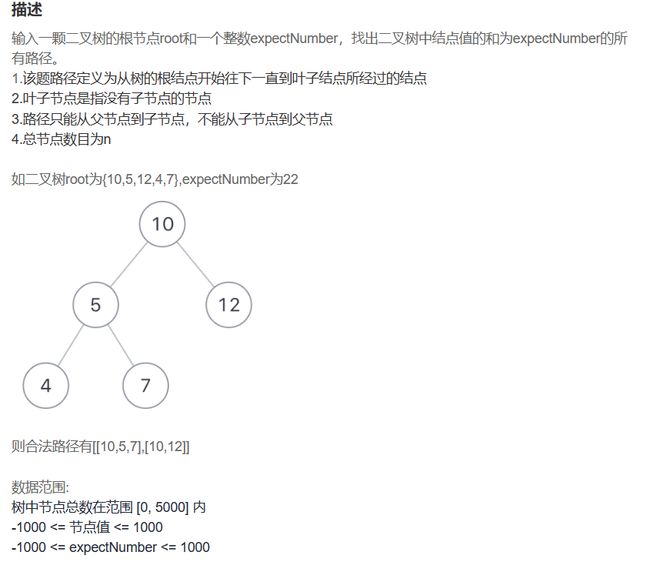
JZ34 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(二)
思路:从根节点开始遍历,当前路径path记录路径,当前的目标值减去该节点值,如果满足叶子节点和值==0的要求则满足路径要求,加入到输出数组res中。递归左右子树,找寻是否存在满足要求的路径。
import java.util.*;
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
private Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int expectNumber) {
if(root==null){ //该节点为空,直接输出来所有路径
return res;
}
path.push(root.val);//加入该节点到路径数组中
expectNumber -= root.val;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null && expectNumber==0){
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path)); //找到一条满足的路径,加入到res中
}
FindPath(root.left,expectNumber); //左子树、右子树查找
FindPath(root.right,expectNumber);
path.pop();//清空当前路径数组
return res;
}
}
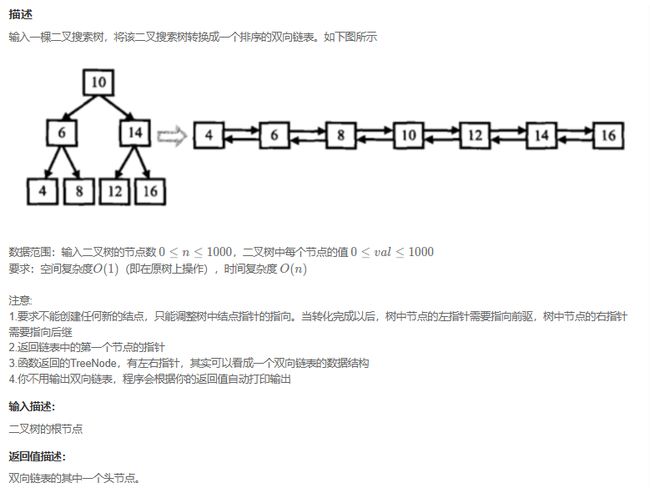
JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表
思路:
- 想到了中序遍历,创建两个指针(head指向双链表表头,pre指向当前遍历的前一个节点);
- 首先,递归到最左找到叶子节点(递归出口就是节点为空则返回),也就可以初始化(if pre==null)双链表表头head和pre;
- 然后,pRootOfTree指向最左子树的中间节点,双向连接pre和pRootOfTree(pre.right=pRootOfTree; pRootOfTree.left=pre;),更新pre节点到当前遍历的pRootOfTree(pre=pRootOfTree);
- 最后,递归进入右子树,重复操作。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode head = null; //头节点
public TreeNode pre = null; // 当前节点的前一节点
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null){
return null; //中序递归,叶子节点为空则返回
}
//左边最小值
Convert(pRootOfTree.left);
if(pre == null){
head = pRootOfTree; //双向链表的头节点
pre = pRootOfTree;
}else{ //建立连接,当前节点与上一个节点
pre.right = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.left = pre;
pre = pRootOfTree; //当前节点变为前一节点
}
Convert(pRootOfTree.right);
return head;
}
}
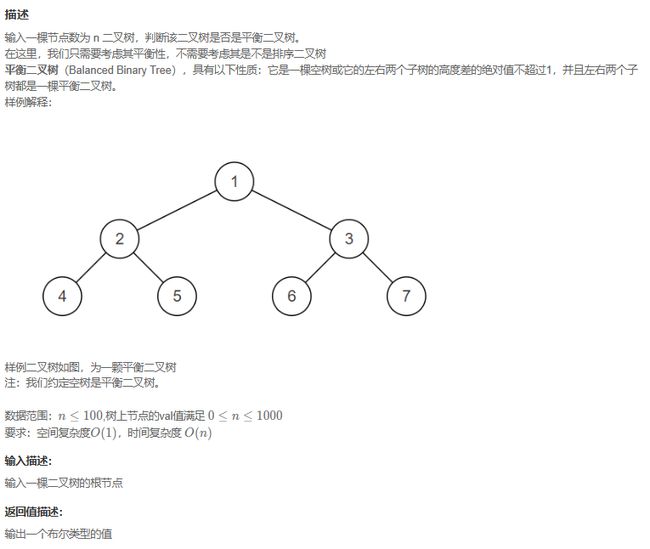
JZ79 判断是不是平衡二叉树
思路:DFS方法
- 递归左子树和右子树,如果为null则返回true,证明该子树为平衡树。
- 计算左右子树高度差(递归实现,参考JZ55 二叉树的深度),如果高度差小于2则为true
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){ //空树是平衡二叉树
return true;
}
boolean left = IsBalanced_Solution(root.left);
boolean right = IsBalanced_Solution(root.right);
return left && right && Math.abs(deepth(root.left)-deepth(root.right))<2;
}
public int deepth(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(deepth(root.left),deepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
JZ8 二叉树的下一个结点
思路:
- 当前节点有右子树: 下一节点为当前节点的右子树的最左下节点
- 当前节点无右子树:
- 当前节点是其父亲节点的左孩子:下一节点为父亲节点
- 当前节点是其父亲节点的右孩子:向上找当前节点的父亲节点的父亲节点,直到当前节点为父亲节点的左子树,返回该父亲节点为当前节点的下一节点
- 否则为NULL
/*
public class TreeLinkNode {
int val;
TreeLinkNode left = null;
TreeLinkNode right = null;
TreeLinkNode next = null;
TreeLinkNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {
//1.该节点有右孩子,下一节点为其右子树的最左下的节点
if(pNode.right!=null){
TreeLinkNode rchild = pNode.right;
//找最左下的节点
while(rchild.left != null){
rchild = rchild.left;
}
return rchild;
}
//2.该节点无右孩子,当前节点是其父亲节点的左孩子,下一节点为其父亲节点
if(pNode.next!=null && pNode.next.left == pNode){
return pNode.next;
}
//3.该节点无右孩子,当前节点是其父亲节点的右孩子,
// 往上找父亲节点的父亲节点,直到当前节点为父亲节点的左子树,返回这个父亲节点
if(pNode.next != null && pNode == pNode.next.right){
TreeLinkNode father = pNode.next; //往上面找
while(father.next!=null && father.next.right==father){
father = father.next;
}
return father.next;
}
return null;
}
}
JZ28 对称的二叉树
思路:比较外侧节点和内侧节点
https://www.programmercarl.com/0101.%E5%AF%B9%E7%A7%B0%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91.html#%E9%80%92%E5%BD%92%E6%B3%95
比较的是二叉树的左右节点,确定递归终止条件:
- 左节点为空,右节点不为空,不对称
- 左节点不为空,右节点为空,不对称
- 左右节点都为空,对称
- 左右节点不为空,数值不相等,不对称
左右节点不为空,数值相等,进入递归: - 比较二叉树外侧是否对称:传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子
- 比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子
- 如果左右都对称就返回true ,有一侧不对称就返回false
/*
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if(pRoot==null) return true;
return compare(pRoot.left,pRoot.right);
}
boolean compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
if(left==null && right!=null){
return false;
}else if(left!=null && right==null){
return false;
}else if(left==null && right==null){
return true;
}else if(left.val != right.val){
return false;
}
return compare(left.right,right.left) && compare(left.left,right.right);
}
}
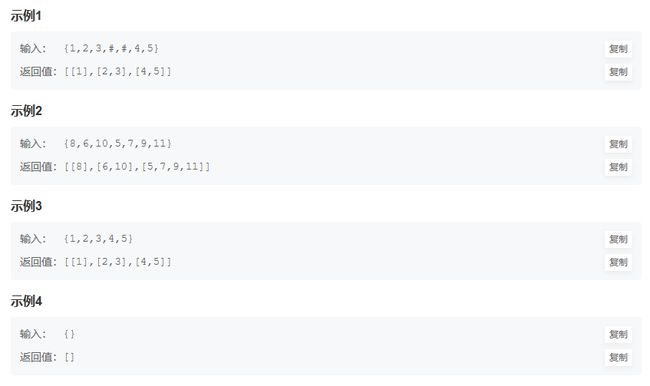
JZ78 把二叉树打印成多行
思路:层次遍历
使用队列,遍历一层的节点入队,出队输出到一维数组里面。
import java.util.*;
/*
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> >();
if(pRoot==null){
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p;
queue.offer(pRoot);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> num = new ArrayList<Integer>(queue.size()); //创建行数组
int n = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
p = queue.poll();
num.add(p.val);
if(p.left != null){
queue.offer(p.left);
}
if(p.right != null){
queue.offer(p.right);
}
}
res.add(num);
}
return res;
}
}
JZ84 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(三)

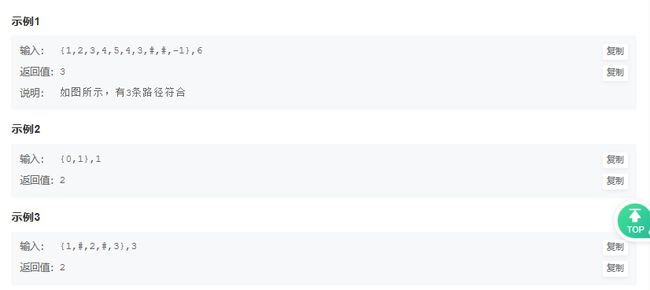
思路:从任意节点出发寻找路径,因此需要遍历二叉树,使用前序遍历选取起始节点。查找路径也需要往下遍历,每遍历一个节点,sum减去该节点的值。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param sum int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int res = 0;
//以某节点为根查询满足要求的路径数
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int sum){
if(root==null){
return;
}
if(sum==root.val){ //符合目标值
res++;
}
dfs(root.left,sum-root.val); //减去当前节点值,进入子节点继续寻找
dfs(root.right,sum-root.val);
}
//以每个节点为根查询路径
public int FindPath (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
if(root == null) return res;
//以某节点为跟的路径数
dfs(root,sum);
//以某子节点为新根
FindPath(root.left,sum);
FindPath(root.right,sum);
return res;
}
}
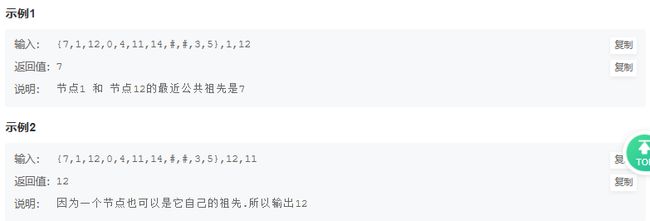
JZ86 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先


思路:需要从下往上遍历所有的节点,用后序遍历可以满足从下往上找的要求。
- 确认递归函数返回值以及参数:
int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2)
- 确认终止条件:此处为某节点的值等于o1或者o2时返回root.vall,或者root为null则返回-1;
if(root == null) return -1;
if(root.val == o1 || root.val == o2 ) return root.val;
- 确认单层递归逻辑:分为三种情况
a. 两个值都在当前节点的左子树,公共祖先就在左子树;
b. 两个值都在当前节点的右子树,公共祖先就在右子树;
c. 在当前节点的一左一右,公共祖先为当前节点(root)。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param o1 int整型
* @param o2 int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) { //后序遍历
if(root == null) return -1;
if(root.val == o1 || root.val == o2 ) return root.val;
int left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,o1,o2);
int right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,o1,o2);
if(left==-1){ //不在左子树,则在右子树
return right;
}
if(right==-1){ //不在右子树,找左子树
return left;
}
return root.val; //一个在左,一个在右,root就是公共祖先
}
}
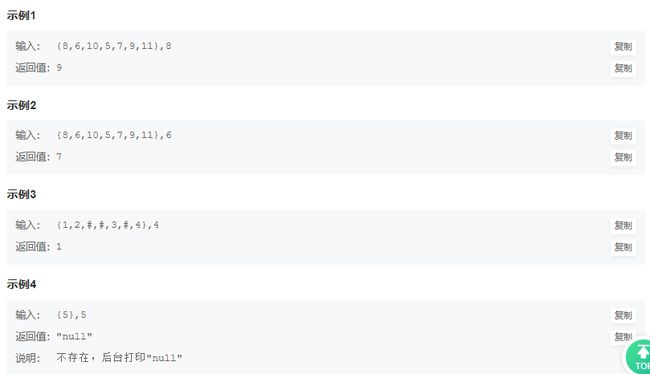
JZ68 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param p int整型
* @param q int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
// write code here
ArrayList<Integer> path1 = getPath(root,p);
ArrayList<Integer> path2 = getPath(root,q);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<path1.size() && i<path2.size();i++){
int x = path1.get(i);
int y = path2.get(i);
if(x==y){
res = path1.get(i);
}else{
break;
}
}
return res;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> getPath(TreeNode root,int target){
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
TreeNode node = root;
while(node.val!= target){
path.add(node.val);
if(node.val<target){
node=node.right;
}else if(node.val>target){
node=node.left;
}
}
path.add(node.val); //加入相等的节点
return path;
}
}
- 二叉树递归的方法和《JZ86》相同
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param p int整型
* @param q int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
// write code here
if(root==null) return -1;
if(root.val == p || root.val == q) return root.val;
int left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
int right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left==-1){
return right;
}
if(right==-1){
return left;
}
return root.val;
}
}
3. 队列 & 栈
【Java算法题】剑指offer_数据结构之03队列&栈