Linux /proc/kcore详解(一)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、/proc/kcore
-
- 1.1 简介
- 1.2 x86_64内存空间布局
- 1.3 elf core格式
- 二、 readelf 读取/proc/kcore
- 三、 Linux 读取/proc/kcore
- 总结
- 参考资料
前言
环境:
Linux发行版:centos 7.6
linux内核版本: 3.10.0
硬件平台:intel x86_64
一、/proc/kcore
1.1 简介
/proc/kcore是一个动态的内核文件,包含了系统运行中内核的所有数据(内核当前状态的映像),以 ELF core file 格式存储,与大多数/proc/目录下的文件不同的是:kcore显示了一个大小,该值以字节为单位。
它由内核在 fs/proc/kcore.c 中创建,并允许从用户空间读取所有内核虚拟内存空间,通过ls -l 展示它的大小是一个非常大数字,但是它根本不占用任何磁盘空间:与 /proc 中的所有其他文件一样,它的内容是由内核在读取文件时动态生成的,并且只能以root权限读取。

可以看出/proc/kcore显示一个非常大的数字:128T,2^47次方,也就是整个内核虚拟地址空间(x86_64的内核虚拟地址空间为128T:0xFFFF800000000000 ~ 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF)

1.2 x86_64内存空间布局
对于 intel x86_64 :
Complete virtual memory map with 4-level page tables(使用4级页表完成虚拟内存映射)
x86_64体系结构定义了一个 64 位的虚拟地址。 当前支持的是 48 位和 57 位虚拟地址。 位 63 到最高有效位是符号扩展的。如果您将它们解释为无符号,这会导致用户空间和内核地址之间出现空洞。
我当前的Intel x86_64机器支持的虚拟地址:48 位虚拟地址
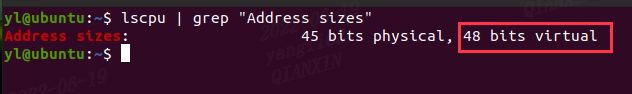
对于 4-level page tables, Linux支持48 位虚拟地址(仅使用低48位,高16位做扩展),其支持的 2^48次方 = 256T,内核虚拟地址空间和用户虚拟地址空间各是128T。
用户虚拟地址空间:0x0000000000000000 ~ 0x00007FFFFFFFFFFF
内核虚拟地址空间:0xFFFF800000000000 ~ 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
其余的都是unused space,hole。
/proc/kcore就是代表着这0xFFFF800000000000 ~ 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF。
====================================================
Complete virtual memory map with 4-level page tables
====================================================
========================================================================================================================
Start addr | Offset | End addr | Size | VM area description
========================================================================================================================
| | | |
0000000000000000 | 0 | 00007fffffffffff | 128 TB | user-space virtual memory, different per mm
__________________|____________|__________________|_________|___________________________________________________________
| | | |
0000800000000000 | +128 TB | ffff7fffffffffff | ~16M TB | ... huge, almost 64 bits wide hole of non-canonical
| | | | virtual memory addresses up to the -128 TB
| | | | starting offset of kernel mappings.
__________________|____________|__________________|_________|___________________________________________________________
|
| Kernel-space virtual memory, shared between all processes:
____________________________________________________________|___________________________________________________________
| | | |
ffff800000000000 | -128 TB | ffff87ffffffffff | 8 TB | ... guard hole, also reserved for hypervisor
ffff880000000000 | -120 TB | ffff887fffffffff | 0.5 TB | LDT remap for PTI
ffff888000000000 | -119.5 TB | ffffc87fffffffff | 64 TB | direct mapping of all physical memory (page_offset_base)
ffffc88000000000 | -55.5 TB | ffffc8ffffffffff | 0.5 TB | ... unused hole
ffffc90000000000 | -55 TB | ffffe8ffffffffff | 32 TB | vmalloc/ioremap space (vmalloc_base)
ffffe90000000000 | -23 TB | ffffe9ffffffffff | 1 TB | ... unused hole
ffffea0000000000 | -22 TB | ffffeaffffffffff | 1 TB | virtual memory map (vmemmap_base)
ffffeb0000000000 | -21 TB | ffffebffffffffff | 1 TB | ... unused hole
ffffec0000000000 | -20 TB | fffffbffffffffff | 16 TB | KASAN shadow memory
__________________|____________|__________________|_________|____________________________________________________________
|
| Identical layout to the 56-bit one from here on:
____________________________________________________________|____________________________________________________________
| | | |
fffffc0000000000 | -4 TB | fffffdffffffffff | 2 TB | ... unused hole
| | | | vaddr_end for KASLR
fffffe0000000000 | -2 TB | fffffe7fffffffff | 0.5 TB | cpu_entry_area mapping
fffffe8000000000 | -1.5 TB | fffffeffffffffff | 0.5 TB | ... unused hole
ffffff0000000000 | -1 TB | ffffff7fffffffff | 0.5 TB | %esp fixup stacks
ffffff8000000000 | -512 GB | ffffffeeffffffff | 444 GB | ... unused hole
ffffffef00000000 | -68 GB | fffffffeffffffff | 64 GB | EFI region mapping space
ffffffff00000000 | -4 GB | ffffffff7fffffff | 2 GB | ... unused hole
ffffffff80000000 | -2 GB | ffffffff9fffffff | 512 MB | kernel text mapping, mapped to physical address 0
ffffffff80000000 |-2048 MB | | |
ffffffffa0000000 |-1536 MB | fffffffffeffffff | 1520 MB | module mapping space
ffffffffff000000 | -16 MB | | |
FIXADDR_START | ~-11 MB | ffffffffff5fffff | ~0.5 MB | kernel-internal fixmap range, variable size and offset
ffffffffff600000 | -10 MB | ffffffffff600fff | 4 kB | legacy vsyscall ABI
ffffffffffe00000 | -2 MB | ffffffffffffffff | 2 MB | ... unused hole
__________________|____________|__________________|_________|___________________________________________________________
1.3 elf core格式
在用file命令查看:
file /proc/kcore
它在内部具有 ELF 核心转储文件的格式(ELF 类型 4/ET_CORE)。 这意味着它与崩溃进程的核心文件具有相同的格式; 但它不是在崩溃时捕获单个进程的(静态)状态,而是提供整个系统状态的实时视图。
ELF 类型 4/ET_CORE:表示是elf文件格式的第四种类型。
其它三种格式: .o文件(ET_REL)、.so文件(ET_DYN)、exe文件(ET_EXEC)
ET_CORE:通过gdb 调试就能恢复到故障现场。
/proc/kcore 是把当前系统的内存模拟成一个 elf core 文件,可以使用gdb 对当前系统进行在线调试,来查看运行中系统的当前状态。
有了/proc/kcore和当前版本的带有debug信息的vmlinux ,gdb(crash)可以用来检查任何内核数据结构的当前状态。
// include/uapi/linux/elf.h
/* These constants define the different elf file types */
#define ET_REL 1 /* Relocatable file */
#define ET_EXEC 2 /* Executable file */
#define ET_DYN 3 /* Shared object file */
#define ET_CORE 4 /* Core file */
elf core 文件格式简图:
elf core 文件是程序运行时的状态,只有 segment 信息,没有 section 信息。
1、PT_NOTE。这个是 elf core 中新增的 segment,记录了解析 memory 区域的关键信息。PT_NOTE segment 被分成了多个 elf_note结构,其中 NT_PRSTATUS 类型的记录了复位前 CPU 的寄存器信息,NT_TASKSTRUCT 记录了进程的 task_struct 信息。
/*
* Notes used in ET_CORE. Architectures export some of the arch register sets
* using the corresponding note types via the PTRACE_GETREGSET and
* PTRACE_SETREGSET requests.
*/
#define NT_PRSTATUS 1
#define NT_PRFPREG 2
#define NT_PRPSINFO 3
#define NT_TASKSTRUCT 4
#define NT_AUXV 6
2、PT_LOAD。每个 segemnt 用来记录一段 memory 区域,并记录了这段 memory 对应的物理地址、虚拟地址和长度。
elf core 文件的大部分内容用 PT_LOAD segemnt 来记录 memeory 信息。
二、 readelf 读取/proc/kcore
readelf - Displays information about ELF files.
(1)
-h
--file-header
显示文件开头的 ELF header 中包含的信息:
readelf -h /proc/kcore
linux 内核中elf header数据结构如下:
// include/uapi/linux/elf.h
#define EI_NIDENT 16
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf64_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf64_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf64_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf64_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf64_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf64_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf64_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf64_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf64_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf64_Ehdr;
(2)
-l
--program-headers
--segments
显示文件 segment headers 中包含的信息
readelf -l /proc/kcore
PT_NOTE 程序头包含附加信息,例如线程的寄存器、与每个 VMA 关联的文件等。
程序头中的 PT_LOAD 条目描述了进程的虚拟内存区域 (VMA)。
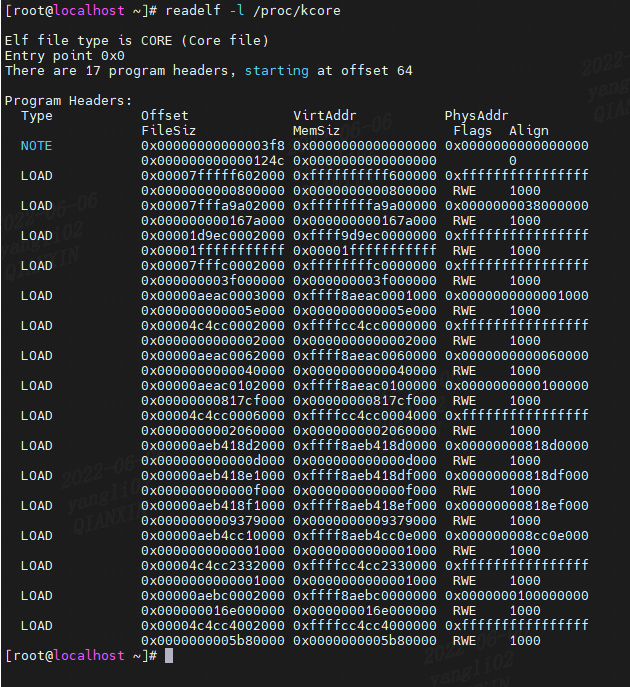
注意:
PT_NOTE segment 的 VirtAddr、PhysAddr和MemSiz都是0。
PT_LOAD segment 的 FileSiz、MemSiz 总是相等的,这也说明/proc/kcode是内存中文件,不存在于磁盘中。
linux 内核中程序头表数据结构如下:
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word p_type; /* Segment type */
Elf64_Word p_flags; /* Segment flags */
Elf64_Off p_offset; /* Segment file offset */
Elf64_Addr p_vaddr; /* Segment virtual address */
Elf64_Addr p_paddr; /* Segment physical address */
Elf64_Xword p_filesz; /* Segment size in file */
Elf64_Xword p_memsz; /* Segment size in memory */
Elf64_Xword p_align; /* Segment alignment */
} Elf64_Phdr;
(3)
-n
--notes
如果有,则显示 NOTE段和/或节的内容(elf core显示NOTE段的内容):
readelf -n /proc/kcore
/*
* Notes used in ET_CORE. Architectures export some of the arch register sets
* using the corresponding note types via the PTRACE_GETREGSET and
* PTRACE_SETREGSET requests.
*/
#define NT_PRSTATUS 1
#define NT_PRFPREG 2
#define NT_PRPSINFO 3
#define NT_TASKSTRUCT 4
#define NT_AUXV 6
三、 Linux 读取/proc/kcore
对 /proc/kcore 虚拟文件的每次读取访问都由 Linux 内核中的函数 read_kcore 处理。如果读访问包括ELF头、程序头或ELF notes,则会动态生成它们并返回给用户。否则,该函数将匹配要读取到虚拟内存地址的文件偏移量,并将内容复制过来。
// fs/proc/kcore.c
/*
* read from the ELF header and then kernel memory
*/
static ssize_t
read_kcore(struct file *file, char __user *buffer, size_t buflen, loff_t *fpos)
{
......
}
static const struct file_operations proc_kcore_operations = {
.read = read_kcore,
.open = open_kcore,
.llseek = default_llseek,
};
总结
这是/proc/kcore解析第一部分,主要是/proc/kcore简介以及readelf读取/proc/kcore文件的描述。
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/pwl999/article/details/118418242
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/x86/x86_64/mm.txt
https://schlafwandler.github.io/posts/dumping-/proc/kcore/
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/286088470
https://lief-project.github.io/doc/latest/tutorials/12_elf_coredump.html
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/proc.5.html



