C++案例
目录
一、while循环猜数组
二、 水仙花数
三、for循环敲桌子游戏
四、9×9乘法表
五、一维数组--元素逆置
六、冒泡排序
七、封装一个函数--利用冒泡排序,实现对整型数组的升序排序
八、结构体嵌套结构体
九、结构体排序
一、while循环猜数组
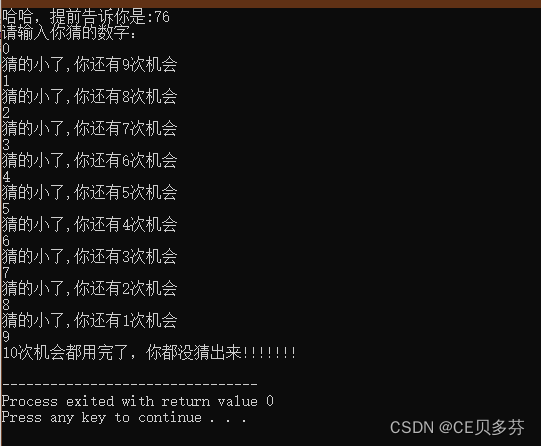
说明:随机一个100以内的数字,共10次机会,每次猜测都反馈偏大还是偏小,猜对后显示所用次数,10次机会用完后结束。
#include
#include
#include // 万能
#include
#include // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include // 保留小数位数
#include // 数学
#include // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int num = rand()%100+1;
cout<<"哈哈,提前告诉你是:"<>value;
if(value>num&&count<9)
{
count++;
cout<<"猜的大了,你还有"<<10-count<<"次机会"< 运行结果:
二、 水仙花数
说明:
水仙花数(Narcissistic number)也被称为超完全数字不变数(pluperfect digital invariant, PPDI)、自恋数、自幂数、阿姆斯壮数或阿姆斯特朗数(Armstrong number),水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和等于它本身。例如:1^3 + 5^3+ 3^3 = 153。
输出100~1000内的水仙花数。
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
for(int i=100;i<1000;i++){
a=i/100;
b=i/10%10;
c=i%10;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==i){
cout< 运行结果:
do-while循环
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
int num=100;
do{
a=num/100;
b=num/10%10;
c=num%10;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==num){
cout< 运行结果
三、for循环敲桌子游戏
说明:0~100内的数字,逢到7的倍数(7,14,21...)或者含有7的数字(17,27,37...)必须用敲桌子代替。
#include
#include
#include // 万能
#include
#include // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include // 保留小数位数
#include // 数学
#include // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
{
if(i>10)
{
if(i%7==0 || i/10==7 || i%10==7)
{
cout<<"敲桌子"< 运行结果:
四、9×9乘法表
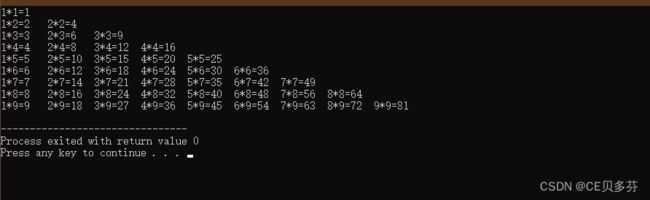
说明:就是我们从小背的9×9乘法表
#include
#include
#include // 万能
#include
#include // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include // 保留小数位数
#include // 数学
#include // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
for(int i=1;i<10;i++)
{
for( int j=1;j 运行结果:
五、一维数组--元素逆置
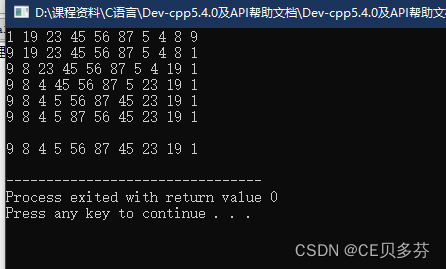
说明:将一维数组中的元素排序反转输出
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 元素逆置
int arr[10]={1,19,23,45,56,87,5,4,8,9};
int start=0;
int end=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
for(int i=0;i<=end/2;i++){
for(int j=0;j 运行结果:
方法二:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 元素逆置
int arr[10]={1,19,23,45,56,87,5,4,8,9};
int start=0;
int end=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);// 结束下标
while(start 运行结果:
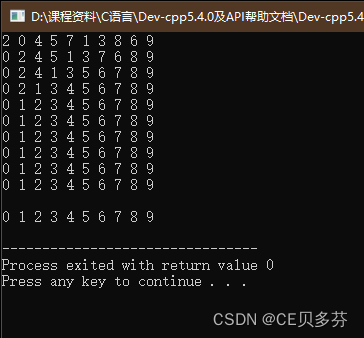
六、冒泡排序
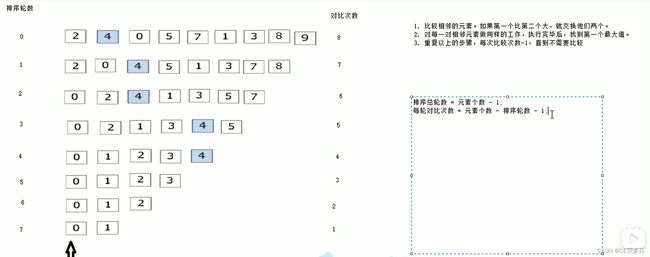
作用:最常用的排序算法,对数组内元素进行排序
过程:
- 比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个。
- 对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,执行完毕后,找到第一个最大值。
- 重复以上的步骤,每次比较次数-1,直到不需要比较
图示:
示例:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int arr[10]={2,4,0,5,8,7,1,3,9,6};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
for(int j=0;j<10-i-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
cout< 运行结果:
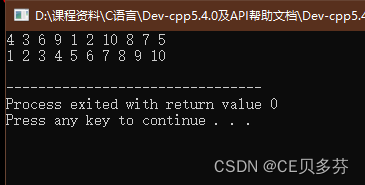
七、封装一个函数--利用冒泡排序,实现对整型数组的升序排序
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int *arr,int len)
{
for(int i=0;iarr[j+1]){
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
void printArr(int *arr,int len)
{
for(int i=0;i 运行结果:
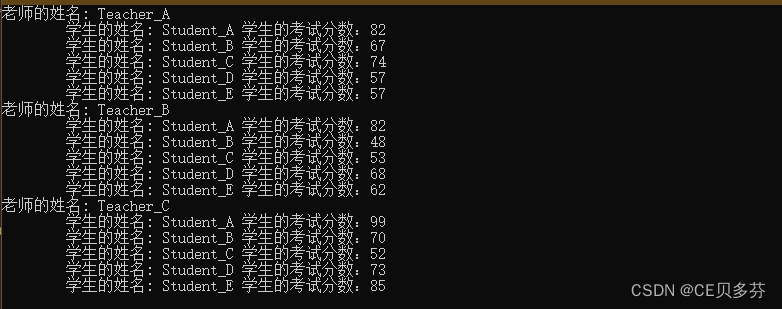
八、结构体嵌套结构体
说明:三个老师的结构体数组,下面带五个学生结构体数组,给五个学生打随机分数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct students {
string name;
int score;
};
struct teachers {
string name;
struct students student[5];
};
// 给老师和学生赋值函数
void space(struct teachers teacher[], int len)
{
string nameseed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
teacher[i].name = "Teacher_";
teacher[i].name += nameseed[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
teacher[i].student[j].name = "Student_";
teacher[i].student[j].name += nameseed[j];
int random = rand() % 61 + 40;
teacher[i].student[j].score = random;
}
}
}
void printinfo(struct teachers teacher[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "老师的姓名: " << teacher[i].name << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout << "\t学生的姓名: " << teacher[i].student[j].name
<< " 学生的考试分数:" << teacher[i].student[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
// 随机种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
teachers teacher[3];
int len = sizeof(teacher) / sizeof(teacher[0]);
space(teacher, len);
printinfo(teacher, len);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
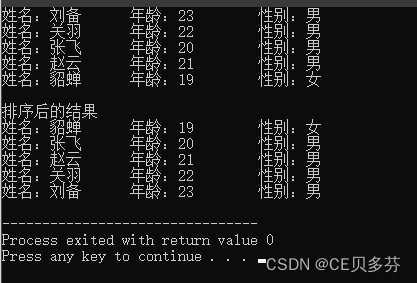
九、结构体排序
说明:
设计一个英雄的结构体,包括成员姓名,年龄,性别;创建结构体数组,数组中存放5名英雄。
通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照年龄进行升序排列,最终打印排序后的结果。
#include
using namespace std;
// 英雄结构体
struct Hero
{
string name; // 姓名
int age; // 年龄
string sex; // 性别
};
// 通过冒泡排序进行排序,按照年龄进行升序排列
void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArr[],int len)
{
for(int i=0;iheroArr[j+1].age){
struct Hero temp =heroArr[j];
heroArr[j]=heroArr[j+1];
heroArr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
// 输出函数
void printArr(struct Hero heroArr[],int len)
{
for(int i=0;i 运行结果: