MySQL数据库高级操作
MySQL数据库高级操作
- 准备工作:安装MySQL数据库
- 一、指定主键的另一种方式
- 二、克隆表
- 三、清空表,删除表内的所有数据
- 四、创建临时表
- 五、MySQL中6种常见的约束
- 六、创建外键约束
-
- 1、外键的定义
- 2、作用
- 3、主键表和外键表
- 4、主表和从表的操作原则和示范
- 七、数据库用户管理
-
- 1、新建用户
- 2、查看用户信息
- 3、重命名用户
- 4、删除用户
- 5、修改当前登录用户密码
- 6、修改其他用户密码
- 7、忘记 root 密码的解决办法
- 八、数据库用户授权
-
- 1、授予权限
- 2、查看权限
- 3、撤销权限
准备工作:安装MySQL数据库
create database client;
use client;
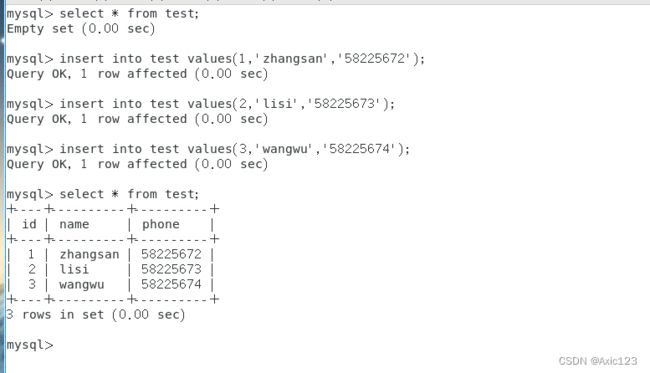
create table test (id int not null,name char(10) not null,phone varchar(18) not null unique key,primary key (id));
insert into test (id,name,phone) values (1,'zhangsan','58225672');
insert into test (id,name,phone) values (2,'lisi','58225673');
insert into test (id,name,phone) values (3,'wangwu','58225674');
select * from test;
一、指定主键的另一种方式
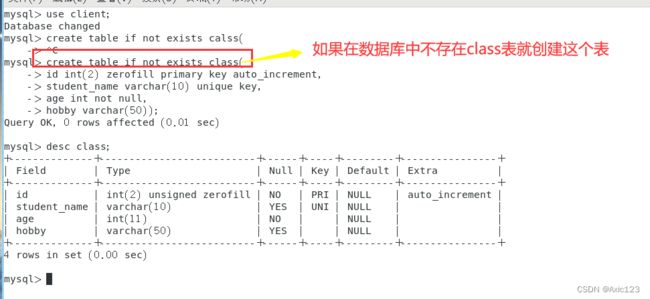
use client;
create table if not exists class (
id int(2) zerofill primary key auto_increment,
student_name varchar(10) not null,
age int not null unique key,
hobby varchar(50));
| if not exists | 表示检测要创建的表是否存在,如果不存在就创建表 |
|---|---|
| int(4) zerofill | 表示若数值不满4位数,则前面用“0”填充 |
| auto_increment | 表示此字段为自增长字段,即每条记录自动递增1,默认从1开始递增;自增长字段数据不可以重复;自增长字段必须是主键;如添加的记录数据没有指定此字段的值且添加失败也会自动递增一次 |
| unique key | 表示此字段唯一键约束,此字段数据不可以重复;一张表中只能有一个主键, 但是一张表中可以有多个唯一键 |
| not null | 表示此字段不允许为NULL |
二、克隆表
- 将数据表的数据记录复制到新的表中
方法一
create table 新表名 like 复制的表名; #复制格式,能够复制表的格式到新表,但是没有内容
insert into 新表名 select * from 复制的表名; #复制原表内容到新表
例:create table test2 like test;
show tables;
select * from test;
select * from test2;
insert into test2 select * from test;
select * from test2;
方法二
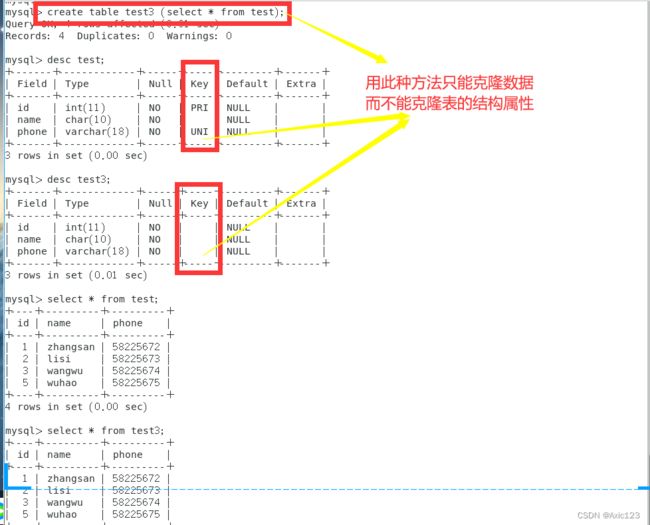
create table 新表名 (select * from 复制的表名)
例:create table test3 (select * from test);
desc test;
desc test3;
select * from test3;
这种方法会将oldtable中所有的内容都拷贝过来不过这种方法的一个最不好的地方就是新表中没有了旧表的primary key、Extra(auto_increment)等属性。
三、清空表,删除表内的所有数据
方法一:
delete from 表名;
#delete清空表后,返回的结果内有删除的记录条目;
delete工作时是一行一行的删除记录数据的;
如果表中有自增长字段,使用delete from 删除所有记录后,再次新添加的记录会从原来最大的记录 ID 后面继续自增写入记录
insert into class(student_name,age,hobby) values('zhangsan',22,'running');
delete from class;
insert into class(student_name,age,hobby) values('lisi',24,'running');
select * from class;
方法二:
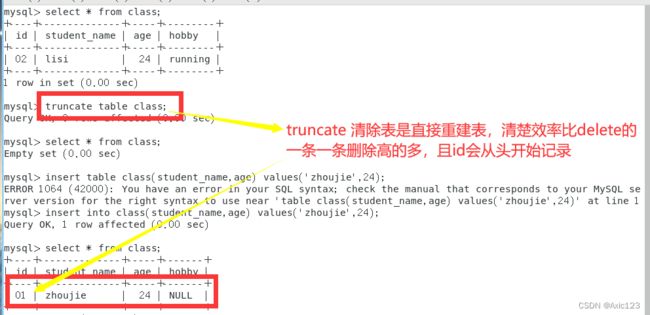
truncate table 表名;
例:select * from class;
truncate table class;
insert into class(student_name,age) values('zhoujie',24);
select * from class;
#TRUNCATE 清空表后,没有返回被删除的条目;
TRUNCATE 工作时是将表结构按原样重新建立,因此在速度上 TRUNCATE 会比 DELETE 清空表快;
使用 TRUNCATE TABLE 清空表内数据后,ID 会从 1 开始重新记录。
两个删除方法的对比
1、论删除速度而言:
- truncate 为直接摧毁重构
- delete 为逐条删除
- 因此 truncate > delete
2、就安全性而言:
- truncate 是不保留有记录的,不便于数据的恢复
- delete 因为有删除操作的每一个步骤,因此当误删的时候可以根据日志进行恢复操作
- 因此 delete 的安全性最好
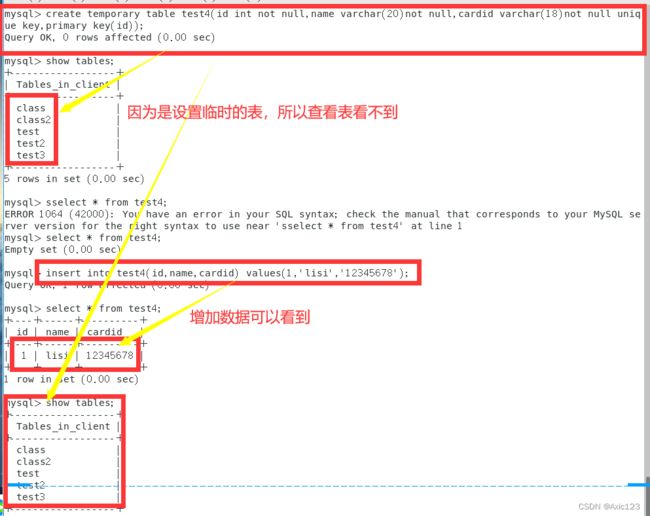
四、创建临时表
- 临时表创建成功之后,使用
show tables命令是看不到创建的临时表的,临时表会在连接退出后被销毁。 - 如果在退出连接之前,也可以可执行增删改查等操作,比如使用
drop table语句手动直接删除临时表。 - 同时,临时表也无法创建外键。
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE 表名 (字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...][,PRIMARY KEY (主键名)]);
例:create temporary table test4 (id int not null,name varchar(20) not null,cardid varchar(18) not null unique key,primary key (id));
show tables;
insert into test4 values (1,'haha','12345');
select * from test4;
五、MySQL中6种常见的约束
| 主键约束 | primary key |
|---|---|
| 外键约束 | foreign key |
| 非空约束 | not null |
| 唯一约束 | unique key |
| 默认值约束 | default |
| 自增约束 | auto_increment |
六、创建外键约束
1、外键的定义
- 外键的定义:如果同一个属性字段x在表一中是主键,而在表二中不是主键,则字段x称为表二的外键。
2、作用
- 创建外键约束的作用:保证数据的完整性和一致性
3、主键表和外键表
- 以公共关键字作为主键的表为主键表(父表、主表)
- 以公共关键字作为外键的表为外键表(从表、外表)
- 注意:与外键关联的主表的字段必须设置为主键,要求从表不能是临时表,主从表的字段具有相同的数据类型、字符长度和约束
4、主表和从表的操作原则和示范
- (1)首先创建两张表,并且其中一张表的字段和另一张表的主键相同==
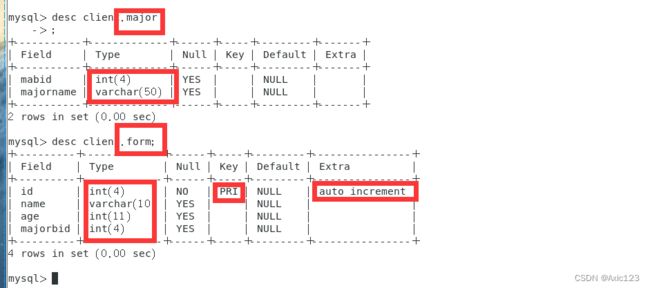
例:create table major (mabid int(4),majorname varchar(50));
create table form (id int(4) primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10),age int(4),majorbid int(4));
alter table major add constraint primary key(mabid);
alter table form add constraint foreign key(majorbid) references major (mabid);
- (2)向表内添加数据内容
例:添加数据记录
insert into major(mabid ,majorname) values (1,'mathematics');
insert into major(mabid ,majorname) values (2,'english');
insert into major(mabid ,majorname) values (3,'medicine');
insert into major(mabid ,majorname) values (4,'law');
insert into form() values (1,'mike',22,2);
insert into form() values (2,'nacy',20,1);
insert into form() values (3,'david',25,4);
- (3)为主表添加主键约束,并为从表添加外键
alter table major add constraint primary key(mabid);
alter table form add constraint foreign key(majorbid) references major (mabid);
#为主表 major 添加一个主键约束。主键名建议以“PK_”开头 ( 在用命令查看时是不会显示主键名的)
#为从表 form 表添加外键,并将 form 表的 majorbid 字段和 major 表的 mapid 字段建立外键关联。外键名建议以“FK_”开头。 ( 在用命令查看时是可以显示外键名的)
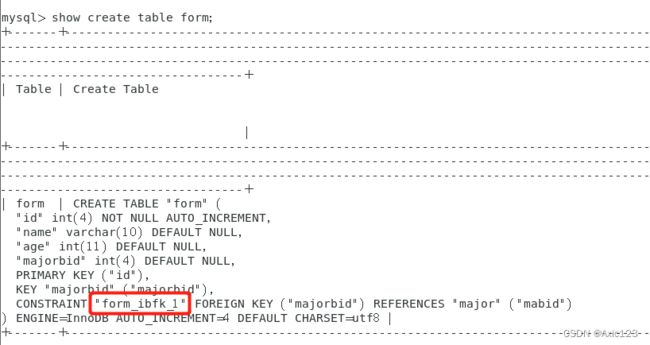
- (4)查看结构情况显示外键关联
show create table major;
show create table form;
- (5)插入数据(先主表,再从表)
insert into form values(4,‘yami’,24.6);
insert into form values(4,‘yami’,24.8);
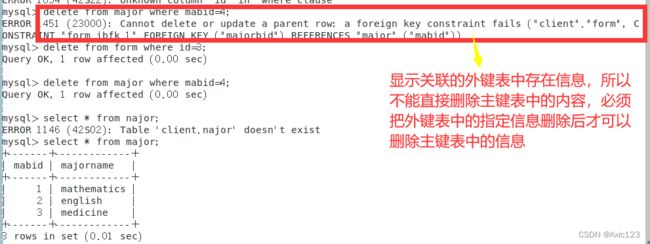
- (6)删除数据记录(先从表,后主表)
delete from major where mabid=4;
delete from form where id=3;
delete from major where mabid=4;
select * from najor;
注:如果要删除外键约束字段
先删除外键约束,再删除外键名
show create table form;
alter table form drop foreign key form_ibfk_1;
七、数据库用户管理
1、新建用户
create user '用户名'@'来源地址' [identified by [password] '密码'];
用户名:指定将创建的用户名
来源地址:指定新创建的用户可在哪些主机上登录,可使用IP地址、网段、主机名的形式,本地用户可用localhost,允许任意主机登录
可用通配符%
可使用通配符 %
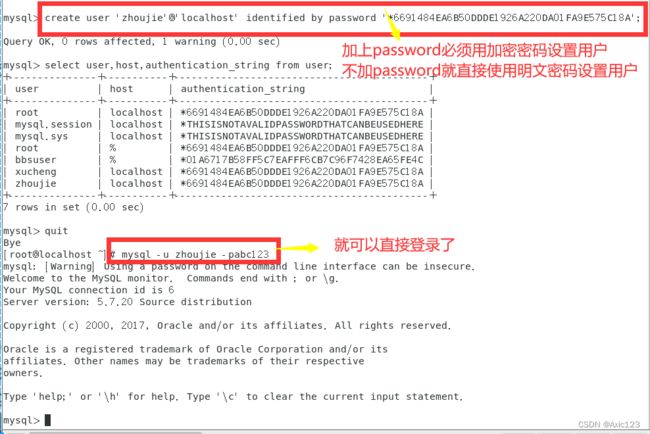
密码:若使用明文密码,直接输入’密码’,插入到数据库时由Mysql自动加密;
若使用加密密码,需要先使用SELECT PASSWORD(‘密码’); 获取密文,再在语句中添加 PASSWORD ‘密文’;
若省略“IDENTIFIED BY”部分,则用户的密码将为空(不建议使用)
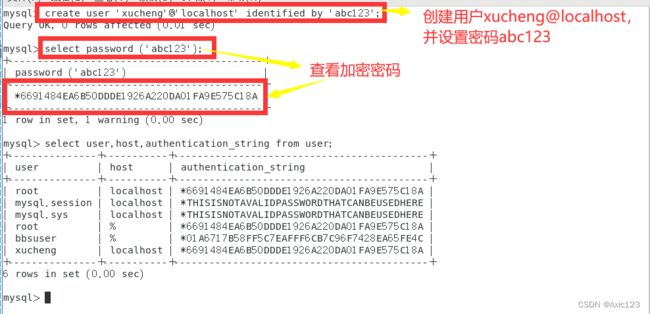
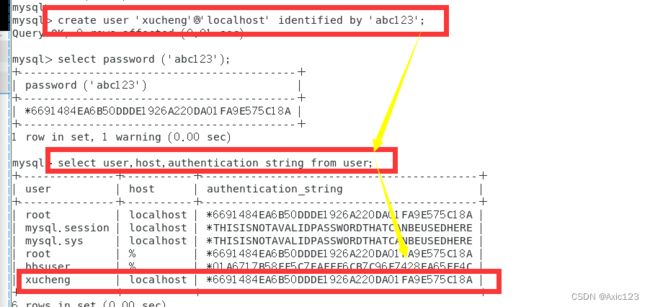
例:create user 'xucheng'@'localhost' identified by 'abc123';
select password('abc123');
create user 'zhoujie'@'localhost' identified by password '*6691484EA6B50DDDE1926A220DA01FA9E575C18A';
mysql -u zhoujie -pabc123
2、查看用户信息
创建后的用户保存在 mysql 数据库的 user 表里
use mysql ; #切换到mysql数据库中
select User,authentication_string,Host from user; #不区分大小写
3、重命名用户
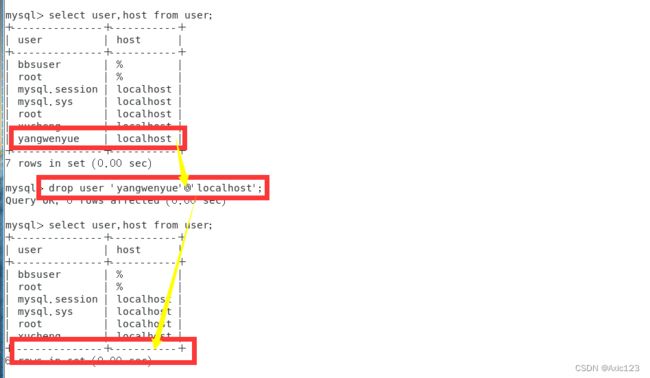
rename user 'wangxin'@'localhost' to 'yangwenyue'@'localhost';
select user,host from user;
4、删除用户
drop user 'yangwenyue'@'localhost';
select user,host from user;
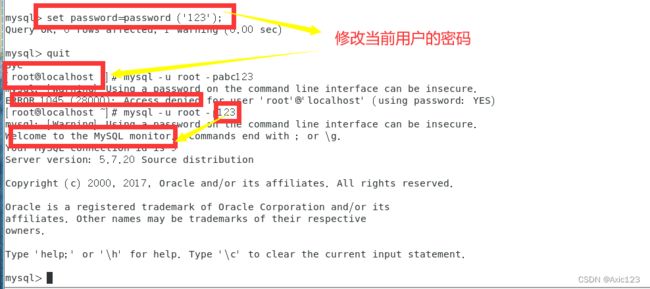
5、修改当前登录用户密码
set password = password('123');
quit
mysql -u root -p123
6、修改其他用户密码
set password for 'xucheng'@'localhost' =password('123123');
select password('123123');
select user,host,authentication_string from user;
7、忘记 root 密码的解决办法
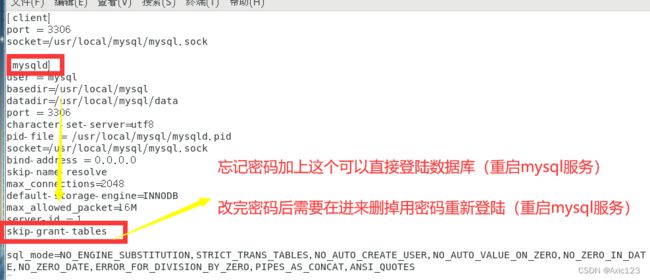
(1)修改 /etc/my.cnf 配置文件,不使用密码直接登录到 mysql
vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables #添加,使登录mysql不使用授权表
systemctl restart mysqld
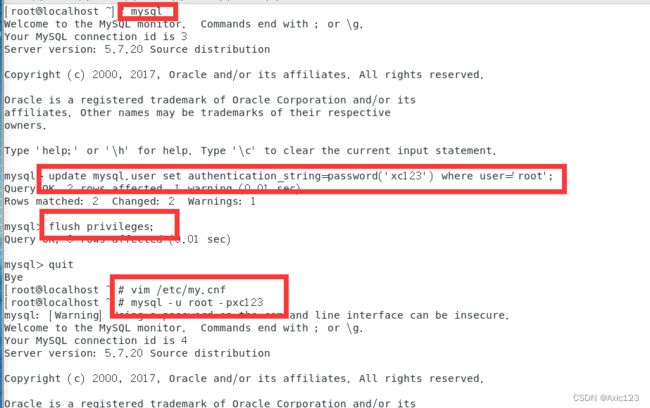
mysql #直接登录
(2)使用 update 修改 root 密码,刷新数据库
update mysql.user set authentication_string = password('xc123') where user='root';
flush privileges;
quit
再把 /etc/my.cnf 配置文件里的 skip-grant-tables 删除,并重启 mysql 服务。
mysql -u root -pxc123
八、数据库用户授权
1、授予权限
grant 语句:专门用来设置数据库用户的访问权限。当指定的用户名不存在时,grant 语句将会创建新的用户;当指定的用户名存在时,grant 语句用于修改用户信息。
grant 提权
grant 权限列表 on 数据库名 .表名 to '用户名'@'来源地址' [identified by '密码'];
- 权限列表:用于列出授权使用的各种数据库操作,以逗号进行分隔,如 “select,insert,update” 。使用 “all” 表示所有权限,可授权执行任何操作。
- 数据库名.表名:用于指定授权操作的数据库和表的名称,其中可以使用通配符 * 。lucien.* 表示授权操作的对象为lucien数据库中的所有表。
- ‘用户名@来源地址’:用于指定用户名称和允许访问的客户机地址,即谁能连接、能从哪里连接。来源地址可以是域名、IP 地址,还可以使用 “%” 通配符,表示某个区域或网段内的所有地址,如 “%.lucien.com” 、“192.168.184.%” 等。
- identified by:用于设置用户连接数据库时所使用的密码字符串。在新建用户时,若省略 “identified by” 部分, 则用户的密码将为空。
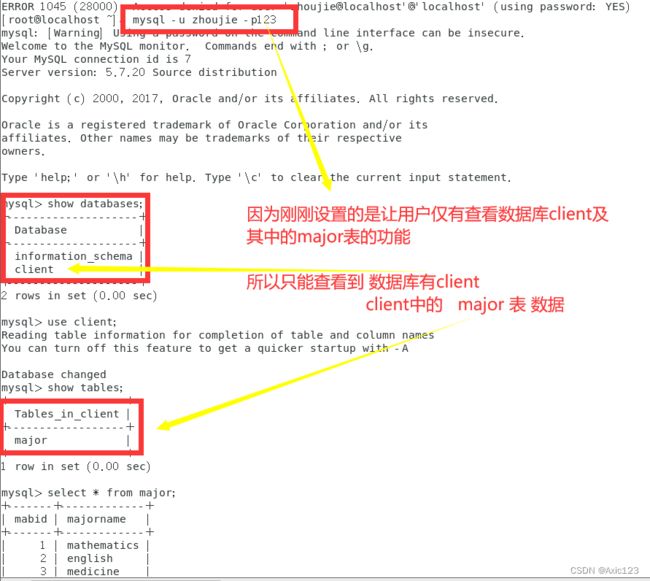
#允许用户wangwu在本地查询 CLASS 数据库中所有表的数据记录,但禁止查询其他数据库中的表的记录。
例:
grant select on client.major to 'zhoujie'@'localhost' identified by '123';
quit;
mysql -u zhoujie -p123
show databases;
use client;
show tables;
select * from major;
#允许用户wangwu在本地远程连接 mysql ,并拥有所有权限。
quit;
mysql -u root -pxc123
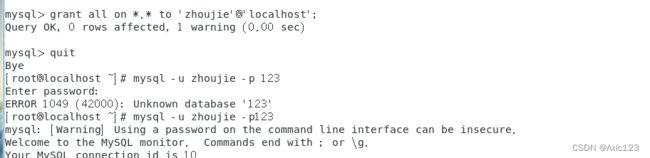
grant all privileges on *.* to 'zhoujie'@'localhost' ;
flush privileges;
quit
mysql -u zhoujie -p123
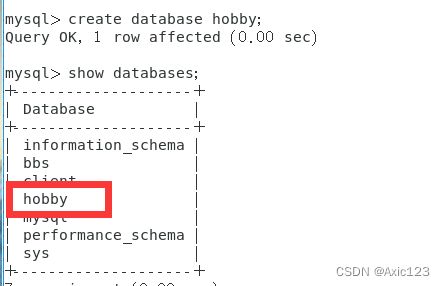
create database SCHOOL;
2、查看权限
show grants for 用户名@来源地址;
例:show grants for 'zhoujie'@'localhost';
3、撤销权限
revoke 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 from 用户名@来源地址;
例:quit;
mysql -u root -pxc123
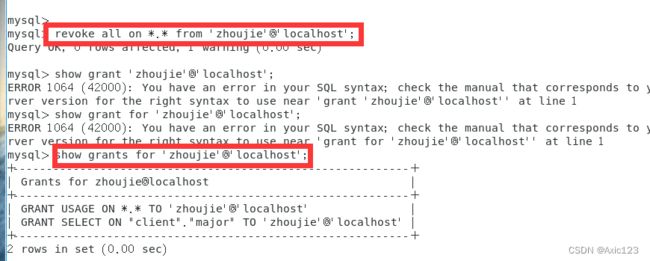
revoke all on *.* from 'zhoujie'@'localhost';
revoke select on client.major from 'zhoujie'@'localhost';
show grants for 'zhoujie'@'localhost';
#USAGE权限只能用于数据库登陆,不能执行任何操作;USAGE权限不能被回收,即 REVOKE 不能删除用户。
flush privileges;