【剑指offer专项突破版】链表篇——“C“
文章目录
- 前言
- 一.删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 细节分析
- 步骤
- 代码
- 二.链表中环的入口节点
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 写法①代码
- 写法②代码:
- 三.两个链表的第一个重合节点
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
- 四.反转链表
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 法①代码
- 法②代码
- 法③代码
- 五.链表中的两数相加
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
- 六.重排链表
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
- 七.回文链表
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
- 八. 展平多级双向链表
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
- 九.排序的循环链表
-
- 题目分析
- 思路分析
- 代码
前言
剑指offer专项突破版(力扣官网)——> 点击进入
本文所属专栏——>点击进入
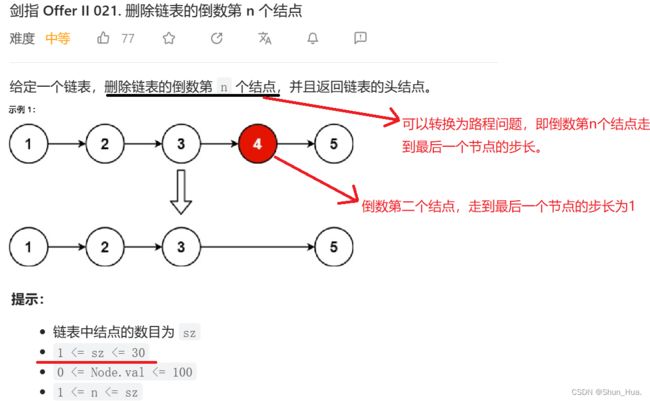
一.删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
题目分析
- 总结
数据格式——链表——结点数大于等于1,且n是符合要求的!
要求——删除链表的n个结点
返回——返回链表的头结点
思路分析
倒数第n个结点——>到最后一个结点的步长为n-1。到最后一个结点很容易,所以我们只需一个步长n-1距离即可,那么思路就很明显了,定义一个end指针走n-1步,再定义一个cur指针,从头节点开始跟end指针一块走,当end指针到最后一个结点(非空)时,这时cur与最后一个结点的距离为n-1,此时cur指向的不就是倒数第n个结点吗?
细节分析
1. 为了删除这个结点,我们还需要保存前一个节点。
2.当删除倒数第n个结点时,我们只能删除头结点,并将之指向下一个节点。
步骤
1.定义end指针,走n-1步停下来。
2.定义cur指针,跟end再一块走,直到end指向最后一个非空节点。
3.处理最后情况: 如果cur等于头指针,则进行头删操作;如果不等于则,cur前一个节点的下一个节点指向cur的下一个节点。然后释放cur节点。
代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n)
{
Node* end = head;
while(--n)
{
end = end->next;
}
Node* cur = head;
Node* prev = head;
while(end->next)
{
end = end->next;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//分析情况,看是否需要修改头结点
if(cur==head)
{
head = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
free(cur);
return head;
}
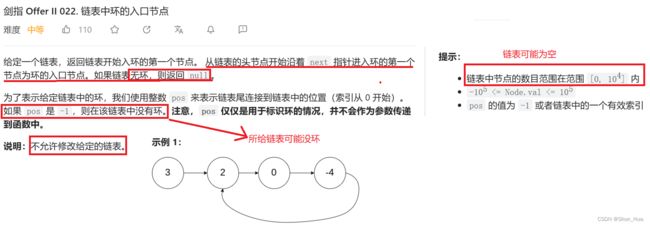
二.链表中环的入口节点
题目分析
- 总结
数据格式——可能是环形链表也可能不是环形链表。
要求——找到入环节点。
返回值——入环节点。
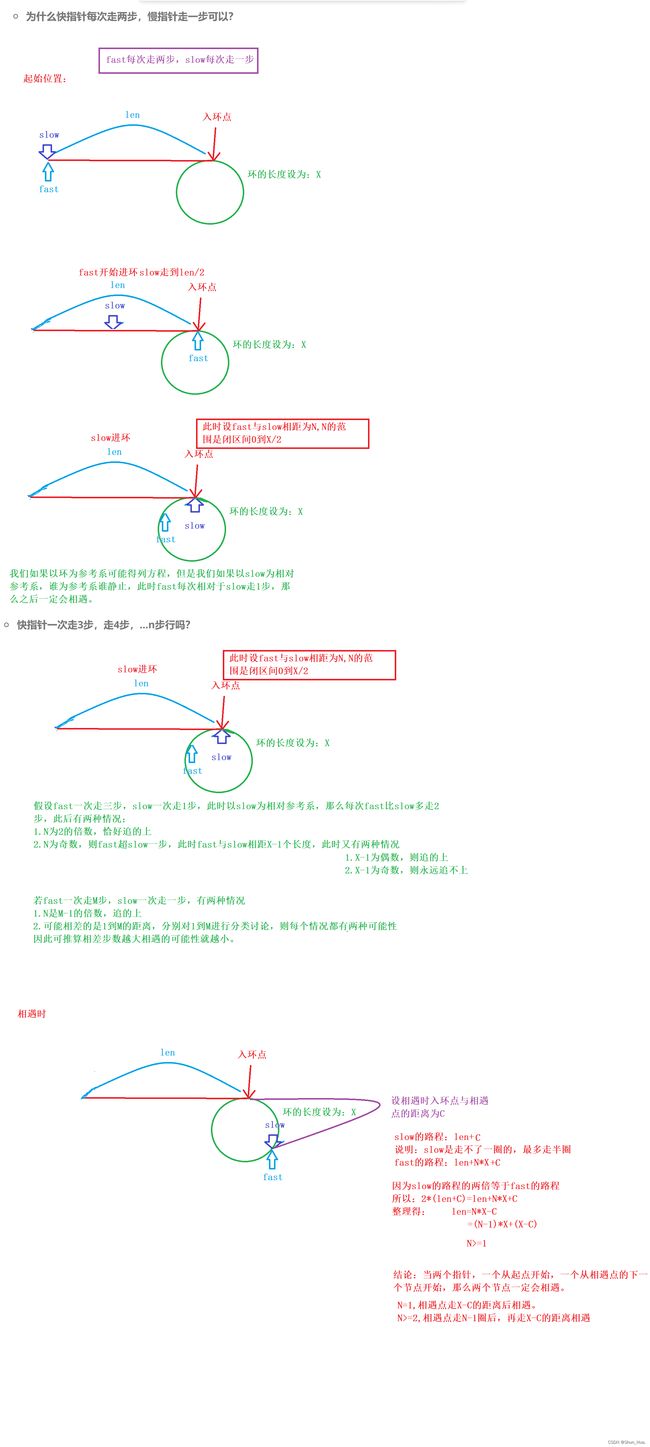
思路分析
写法①代码
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head,* slow = head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
struct ListNode* start = fast;
struct ListNode* begin = head;
while(start!=begin)
{
begin = begin->next;
start = start->next;
}
return start;
}
}
return NULL;
}
写法②代码:
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* fast = head->next;
Node* slow = head;
while(fast&&fast->next&&fast!=slow)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
if(fast==NULL||fast->next==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* begin = fast->next;
Node* start = head;
while(begin!=start)
{
begin = begin->next;
start = start->next;
}
return begin;
}
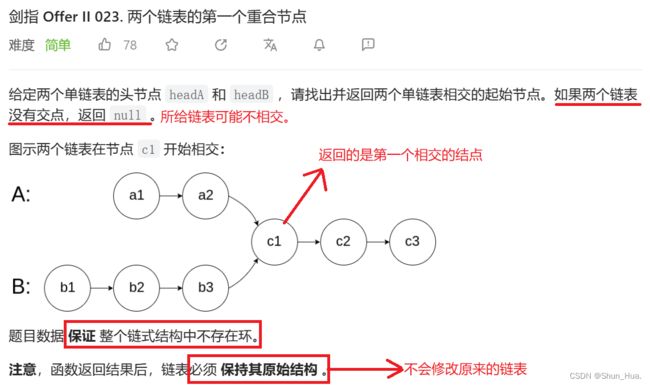
三.两个链表的第一个重合节点
题目分析
- 总结
1.数据——所给两个链表,可能不相交,但不存在环。
2.要求——找到第一个相交的结点。
3.返回值——第一个相交的结点。
思路分析
代码
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
int len_A = 0,len_B = 0;
struct ListNode* A = headA,*B = headB;
while(A||B)
{
if(A)
{
A = A->next;
len_A++;
}
if(B)
{
B = B->next;
len_B++;
}
}
A = headA;
B = headB;
int k =abs(len_B-len_A);
//长度对齐
while(k--)
{
if(len_A>len_B)
{
A= A->next;
}
else
{
B = B->next;
}
}
while(A!=B)
{
A = A->next;
B = B->next;
}
//如果没有相交节点,则最后结果为空时,相等也会结束循环
return A;
}
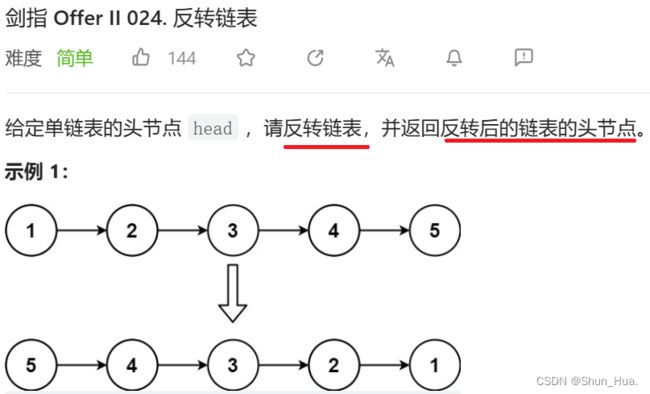
四.反转链表
题目分析
- 总结
数据——单链表
要求——反转整个链表
返回——反转后链表的头结点
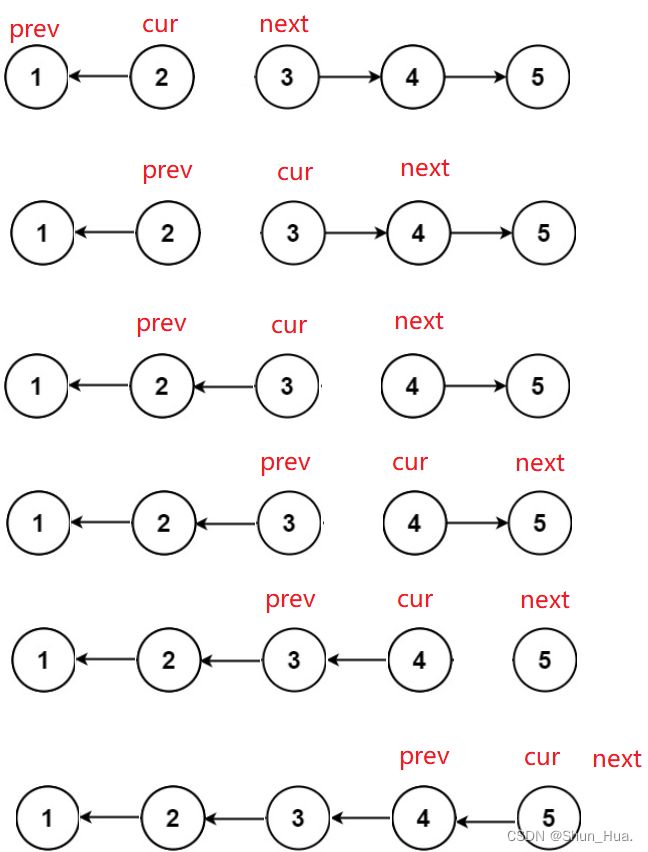
思路分析
法①代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
//在原链表的基础上进行操作
//首先我们知道链表需要反转的条件是有两个或两个以上的结点
if(head&&head->next)
{
//我们需要换方向的话需要三个指针
//当前的需要改变方向的两个指针
Node* cur = head->next;
Node* prev = head;
Node* next = cur->next;
while(cur)
{
if(prev==head)
{
prev->next = NULL;
}
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
if(next)
{
next = next->next;
}
}
return prev;
}
else
{
//这里只有一个结点直接返回头结点即可
return head;
}
}
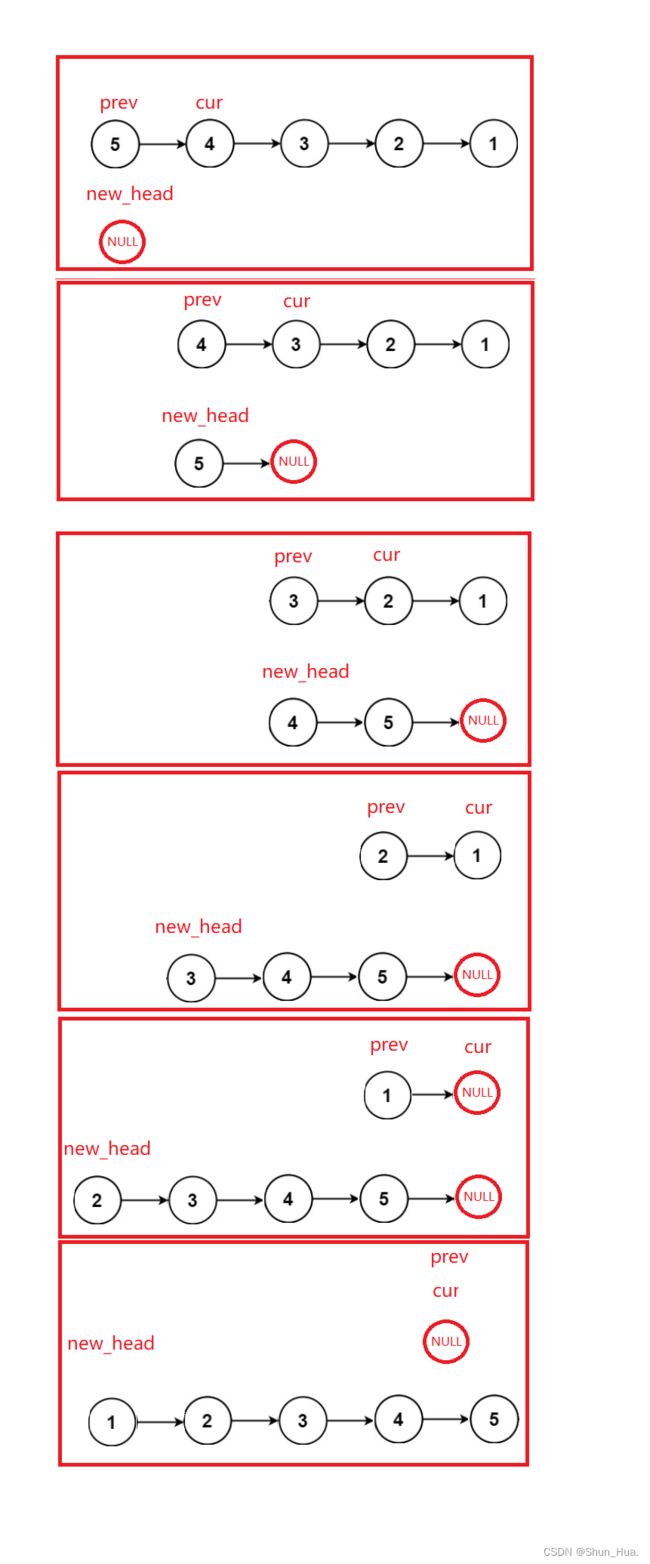
法②代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
Node* prev = head;
Node* new_head = NULL;
while(cur)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
prev->next = new_head;
new_head =prev;
}
return new_head;
}
方法三:
反转链表问题可以不断拆解为,反转前一个结点和剩余结点,以此类推最终反转整个链表,不过需要注意的是第一次反转的一个空结点和头结点,最后一次反转遇到空节点,直接返回最后一个非空节点即可。
法③代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
Node* reverse(Node* cur,Node* next,Node* new_head)
{
if(next&&next->next)
{
new_head = reverse(next,next->next,new_head);
}
if(next&&next->next==NULL)
{
new_head = next;
}
if(next)
{
next->next = cur;
}
return new_head;
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
return reverse(NULL,head,NULL);
}
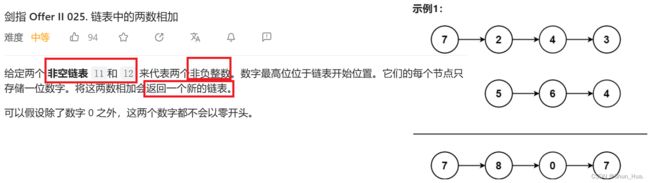
五.链表中的两数相加
题目分析
- 总结
数据格式——非空链表。
要求——将链表的值进行相加。
返回——一个新链表。
思路分析
代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
Node* reverselist(Node* head)
{
Node* prev = head;
Node* cur = head;
Node* new_head = NULL;
while(cur)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
prev->next = new_head;
new_head = prev;
}
return new_head;
}
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2)
{
Node* head1 = reverselist(l1);
Node* head2 = reverselist(l2);
Node* sum_head = NULL;
int carry = 0;
while(head1||head2)
{
int sum = (head1 != NULL ? head1->val : 0)\
+(head2 != NULL ? head2->val : 0) + carry;
int cur = sum%10;
carry = sum/10;
Node* NewNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
NewNode->val = cur;
NewNode->next = sum_head;
sum_head = NewNode;
head1 = head1 != NULL ? head1->next : NULL;
head2 = head2 != NULL ? head2->next : NULL;
}
if(carry)
{
Node* NewNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
NewNode->val = carry;
NewNode->next = sum_head;
sum_head = NewNode;
}
return sum_head;
}
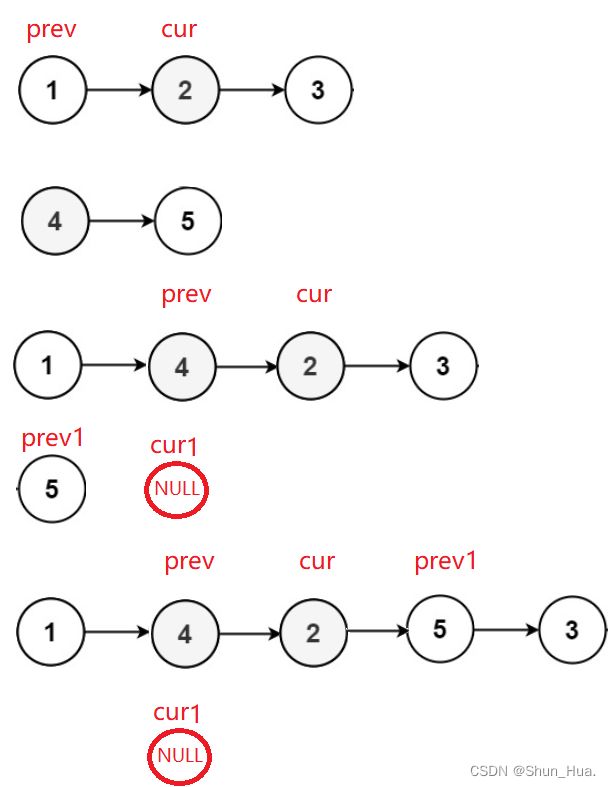
六.重排链表
题目分析
思路分析
代码
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
Node* prev = head;
Node* new_head = NULL;
while(cur)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
prev->next = new_head;
new_head =prev;
}
return new_head;
}
void reorderList(struct ListNode* head)
{
//找到中间结点
Node* fast = head;
Node* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//此时slow即为中间结点
//反转slow后面的链表
Node* head1 = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
head1 = reverseList(head1);
//head1链表插在head的前半个链表中
Node *prev = head;
Node* cur = head;
Node* cur1 = head1;
Node* prev1 = head1;
while(cur&&cur1)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
prev1 = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
prev->next = prev1;
prev1->next = cur;
}
return head;
}
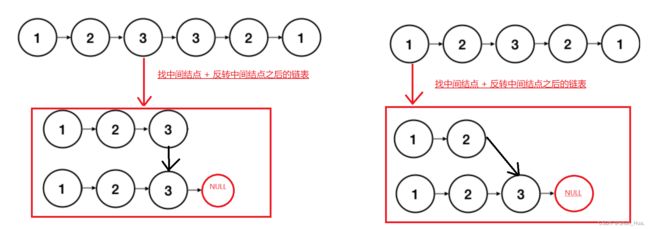
七.回文链表
题目分析
思路分析
找到中间结点,然后让中间结点及其以后的结点进行逆转,再进行判断即可。
代码
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
struct ListNode* new_head = NULL;
while(cur)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
prev->next = new_head;
new_head = prev;
}
return new_head;
}
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head)
{
//找到中心结点
struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head,*prev = head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
prev = slow;
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
struct ListNode* new_head = slow;
//进行后半部分链表的反转工作
new_head = reverseList(new_head);
struct ListNode* begin = head;
//判断是否是回文
while(new_head&&begin)
{
if(new_head->val!=begin->val)
{
return false;
}
new_head = new_head->next;
begin = begin->next;
}
return true;
}
八. 展平多级双向链表
题目分析
- 总结
数据——多级双向链表
要求——将此种链表展平
返回——头结点
思路分析
代码
Node* flatten(Node* head)
{
Node* head1 = head;
while(head1)
{
Node* child = head1->child;
Node* child_end = NULL;
Node* prev = child;
if(child)
{
child_end = child;
while(child_end)
{
prev = child_end;
child_end = child_end->next;
}
if(head1->next)
{
head1->next->prev = prev;
prev->next = head1->next;
child->prev = head1;
head1->next = child;
}
else
{
child->prev = head1;
head1->next = child;
}
//展平操作
head1->child = NULL;
}
head1 = head1->next;
}
return head;
}
九.排序的循环链表
题目分析
思路分析
1.当所给链表为空时,这时我们需要自己把插入结点,构造成环,即自己指向自己,并返回构造的结点。
2.当所给链表不为空时,我们需要找到最大最小结点,并且判断插入结点的值是否大于最大的结点值。
3. 继续处理找到第一个大于等于插入值的结点,同时保存此节点的前一个节点。将插入结点插入在两节点之间。
4. 返回头结点。
代码
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* insert(struct Node* head, int insertVal)
{
Node* inser = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
inser->val = insertVal;
//处理为空的情况
if(head == NULL)
{
inser->next = inser;
return inser;
}
else
{
//找到最大和最小节点
Node* max = head;
Node* min = head->next;
while(min->val >= max->val && min!=head)
{
min = min->next;
max = max->next;
}
//处理插入结点大于等于最大节点的情况
if(inser->val >= max->val)
{
inser->next = min;
max->next = inser;
}
else
{
//找到大于等于inser的第一个节点
Node* prev = max;
Node* cur = min;
while(inser->val > cur->val)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = inser;
inser->next = cur;
}
}
return head;
}