MongoDB - 1. 快速上手
《MongoDB - 1. 快速上手》
提示: 本材料只做个人学习参考,不作为系统的学习流程,请注意识别!!!
《MongoDB - 1. 快速上手》
- 《MongoDB - 1. 快速上手》
- 1 MongoDB相关概念
-
- 1.1 业务应用场景
- 1.2 MongoDB简介
- 1.3 体系结构
- 1.4 数据模型
- 1.5 MongoDB的特点
- 2 单机部署
-
- 2.1 Windows系统中的安装启动
- 2.2 Shell连接(mongo命令)
- 2.3 Compass-图形化界面客户端
- 2.4 Linux系统中的安装启动和连接
- 3 基本常用命令
-
- 3.1 案例需求
- 3.2 数据库操作
-
- 3.2.1 选择和创建数据库
- 3.2.2 数据库的删除
- 3.3 集合操作
-
- 3.3.1 集合的显式创建(了解)
- 3.3.2 集合的隐式创建
- 3.3.3 集合的删除
- 3.4 文档基本CRUD
-
- 3.4.1 文档的插入
- 3.4.2 文档的基本查询
- 3.4.3 文档的更新
- 3.4.4 删除文档
- 3.5 文档的分页查询
-
- 3.5.1 统计查询
- 3.5.2 分页列表查询
- 3.5.3 排序查询
- 3.6 文档的更多查询
-
- 3.6.1 正则的复杂条件查询
- 3.6.2 比较查询
- 3.6.3 包含查询
- 3.6.4 条件连接查询
- 3.7 常用命令小结
- 4 索引-Index
-
- 4.1 概述
- 4.2 索引的类型
-
- 4.2.1 单字段索引
- 4.2.2 复合索引
- 4.2.3 其他索引
- 4.3 索引的管理操作
-
- 4.3.1 索引的查看
- 4.3.2 索引的创建
- 4.3.3 索引的移除
- 4.4 索引的使用
-
- 4.4.1 执行计划
- 4.4.2 涵盖的查询
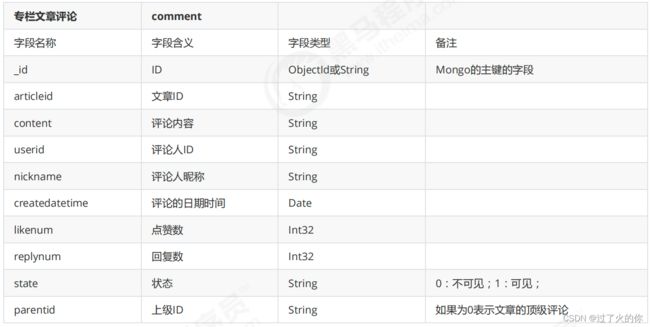
- 5 文章评论
-
- 5.1 需求分析
- 5.2 表结构分析
- 5.3 技术选型
-
- 5.3.1 mongodb-driver(了解)
- 5.3.2 SpringDataMongoDB
- 5.4 文章微服务模块搭建
- 5.5 文章评论实体类的编写
- 5.6 文章评论的基本增删改查
- 5.7 根据上级ID查询文章评论的分页列表
- 5.8 MongoTemplate实现评论点赞
1 MongoDB相关概念
1.1 业务应用场景
传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的“三高”需求以及应对Web2.0的网站需求面前,显得力不从心。
解释:“三高”需求:
- High performance - 对数据库高并发读写的需求。
- Huge Storage - 对海量数据的高效率存储和访问的需求。
- High Scalability && High Availability- 对数据库的高可扩展性和高可用性的需求。
而MongoDB可应对“三高”需求。
具体的应用场景如:
1)社交场景,使用 MongoDB 存储用户信息,以及用户发表的朋友圈信息,通过地理位置索引实现附近的人、地点等功能。
2)游戏场景,使用 MongoDB 存储游戏用户信息,用户的装备、积分等直接以内嵌文档的形式存储,方便查询、高效率存储和访问。
3)物流场景,使用 MongoDB 存储订单信息,订单状态在运送过程中会不断更新,以 MongoDB 内嵌数组的形式来存储,一次查询就能将
订单所有的变更读取出来。
4)物联网场景,使用 MongoDB 存储所有接入的智能设备信息,以及设备汇报的日志信息,并对这些信息进行多维度的分析。
5)视频直播,使用 MongoDB 存储用户信息、点赞互动信息等。
这些应用场景中,数据操作方面的共同特点是:
(1)数据量大
(2)写入操作频繁(读写都很频繁)
(3)价值较低的数据,对事务性要求不高
对于这样的数据,我们更适合使用MongoDB来实现数据的存储。
什么时候选择MongoDB
在架构选型上,除了上述的三个特点外,如果你还犹豫是否要选择它?可以考虑以下的一些问题:
- 应用不需要事务及复杂 join 支持
- 新应用,需求会变,数据模型无法确定,想快速迭代开发
- 应用需要2000-3000以上的读写QPS(更高也可以)
- 应用需要TB甚至 PB 级别数据存储
- 应用发展迅速,需要能快速水平扩展
- 应用要求存储的数据不丢失
- 应用需要99.999%高可用
- 应用需要大量的地理位置查询、文本查询
如果上述有1个符合,可以考虑 MongoDB,2个及以上的符合,选择 MongoDB 绝不会后悔。
思考:如果用MySQL呢?
答:相对MySQL,可以以更低的成本解决问题(包括学习、开发、运维等成本)
1.2 MongoDB简介
MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库,当初的设计就是用于简化开发和方便扩展,是NoSQL数据库产品中的一种。是最
像关系型数据库(MySQL)的非关系型数据库。
它支持的数据结构非常松散,是一种类似于 JSON 的格式叫BSON,所以它既可以存储比较复杂的数据类型,又相当的灵活。
MongoDB中的记录是一个文档,它是一个由字段和值对(field:value)组成的数据结构。MongoDB文档类似于JSON对象,即一个文档认
为就是一个对象。字段的数据类型是字符型,它的值除了使用基本的一些类型外,还可以包括其他文档、普通数组和文档数组。
1.3 体系结构
MySQL和MongoDB对比
| SQL术语/概念 | MongoDB术语/概念 | 解释/说明 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据记录行/文档 |
| column | field | 数据字段/域 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表连接,MongoDB不支持 | |
| 嵌入文档 | MongoDB通过嵌入式文档来替代多表连接 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
1.4 数据模型
MongoDB的最小存储单位就是文档(document)对象。文档(document)对象对应于关系型数据库的行。数据在MongoDB中以
BSON(Binary-JSON)文档的格式存储在磁盘上。
BSON(Binary Serialized Document Format)是一种类json的一种二进制形式的存储格式,简称Binary JSON。BSON和JSON一样,支持
内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,但是BSON有JSON没有的一些数据类型,如Date和BinData类型。
BSON采用了类似于 C 语言结构体的名称、对表示方法,支持内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,具有轻量性、可遍历性、高效性的三个特点,可
以有效描述非结构化数据和结构化数据。这种格式的优点是灵活性高,但它的缺点是空间利用率不是很理想。
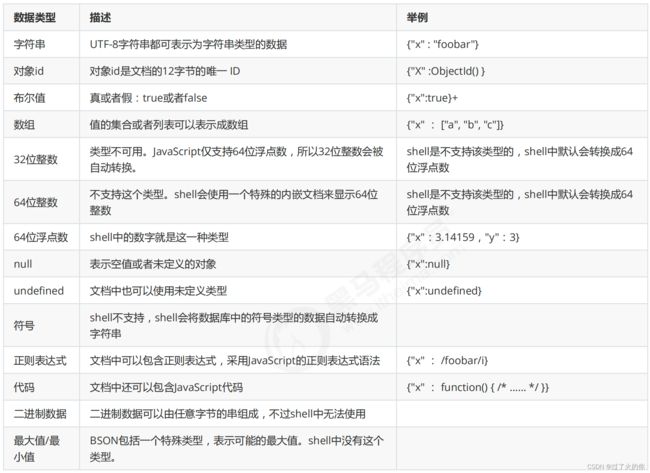
BSON中,除了基本的JSON类型:string,integer,boolean,double,null,array和object,mongo还使用了特殊的数据类型。这些类型包括
date,object id,binary data,regular expression 和code。每一个驱动都以特定语言的方式实现了这些类型,查看驱动的文档来获取详
细信息。
BSON数据类型参考列表:
提示:
shell默认使用64位浮点型数值。{“x”:3.14}或{“x”:3}。对于整型值,可以使用NumberInt(4字节符号整数)或NumberLong(8字节符
号整数),{“x”:NumberInt(“3”)}{“x”:NumberLong(“3”)}
1.5 MongoDB的特点
MongoDB主要有如下特点:
(1)高性能:
MongoDB提供高性能的数据持久性。特别是,对嵌入式数据模型的支持减少了数据库系统上的I/O活动。
索引支持更快的查询,并且可以包含来自嵌入式文档和数组的键。(文本索引解决搜索的需求、TTL索引解决历史数据自动过期的需求、地
理位置索引可用于构建各种 O2O 应用)
mmapv1、wiredtiger、mongorocks(rocksdb)、in-memory 等多引擎支持满足各种场景需求。
Gridfs解决文件存储的需求。
(2)高可用性:
MongoDB的复制工具称为副本集(replica set),它可提供自动故障转移和数据冗余。
(3)高扩展性:
MongoDB提供了水平可扩展性作为其核心功能的一部分。
分片将数据分布在一组集群的机器上。(海量数据存储,服务能力水平扩展)
从3.4开始,MongoDB支持基于片键创建数据区域。在一个平衡的集群中,MongoDB将一个区域所覆盖的读写只定向到该区域内的那些
片。
(4)丰富的查询支持:
MongoDB支持丰富的查询语言,支持读和写操作(CRUD),比如数据聚合、文本搜索和地理空间查询等。
(5)其他特点:如无模式(动态模式)、灵活的文档模型、
2 单机部署
2.1 Windows系统中的安装启动
第一步:下载安装包
MongoDB 提供了可用于 32 位和 64 位系统的预编译二进制包,你可以从MongoDB官网下载安装,MongoDB 预编译二进制包下载地址:
https://www.mongodb.com/download-center#community
根据上图所示下载 zip 包。
提示:版本的选择:MongoDB的版本命名规范如:x.y.z; y为奇数时表示当前版本为开发版,如:1.5.2、4.1.13; y为偶数时表示当前版本为稳定版,如:1.6.3、4.0.10; z是修正版本号,数字越大越好。
详情:http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/release-notes/#release-version-numbers
第二步:解压安装启动
将压缩包解压到一个目录中。
在解压目录中,手动建立一个目录用于存放数据文件,如 data/db
方式1:命令行参数方式启动服务
在 bin 目录中打开命令行提示符,输入如下命令:
mongod --dbpath=..\data\db
我们在启动信息中可以看到,mongoDB的默认端口是27017,如果我们想改变默认的启动端口,可以通过–port来指定端口。
为了方便我们每次启动,可以将安装目录的bin目录设置到环境变量的path中, bin 目录下是一些常用命令,比如 mongod 启动服务用的,
mongo 客户端连接服务用的。
方式2:配置文件方式启动服务
在解压目录中新建 config 文件夹,该文件夹中新建配置文件 mongod.conf ,内如参考如下:
storage:
#The directory where the mongod instance stores its data.Default Value is "\data\db" on Windows.
dbPath: D:\02_Server\DBServer\mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl-4.0.1\data
详细配置项内容可以参考官方文档:
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/configuration-options/
【注意】
1)配置文件中如果使用双引号,比如路径地址,自动会将双引号的内容转义。如果不转义,则会报错:
error-parsing-yaml-config-file-yaml-cpp-error-at-line-3-column-15-unknown-escape-character-d
解决:
a. 对 \ 换成 / 或 \
b. 如果路径中没有空格,则无需加引号。
2)配置文件中不能以Tab分割字段
解决:
将其转换成空格。
启动方式:
mongod -f ../config/mongod.conf
或
mongod --config ../config/mongod.conf
更多参数配置
systemLog:
destination: file
#The path of the log file to which mongod or mongos should send all diagnostic logging information
path: "D:/02_Server/DBServer/mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl-4.0.1/log/mongod.log"
logAppend: true
storage:
journal:
enabled: true
#The directory where the mongod instance stores its data.Default Value is "/data/db".
dbPath: "D:/02_Server/DBServer/mongodb-win32-x86_64-2008plus-ssl-4.0.1/data"
net:
#bindIp: 127.0.0.1
port: 27017
setParameter:
enableLocalhostAuthBypass: false
2.2 Shell连接(mongo命令)
在命令提示符输入以下shell命令即可完成登陆
mongo
或
mongo --host=127.0.0.1 --port=27017
查看已经有的数据库
>show databases
退出mongodb
exit
更多参数可以通过帮助查看:
mongo --help
提示:
MongoDB javascript shell是一个基于javascript的解释器,故是支持js程序的。
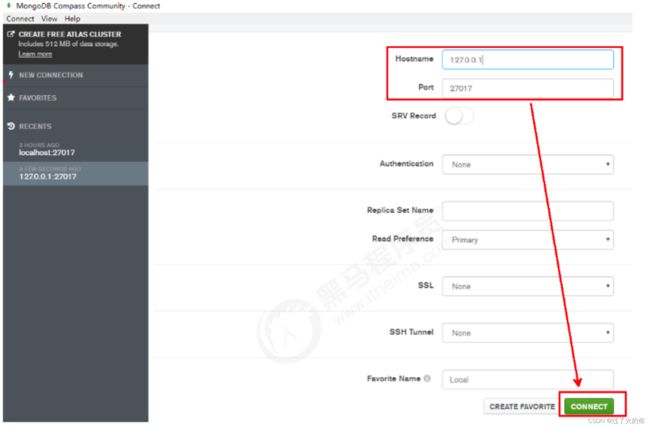
2.3 Compass-图形化界面客户端
到MongoDB官网下载MongoDB Compass,
地址:https://www.mongodb.com/download-center/v2/compass?initial=true
如果是下载安装版,则按照步骤安装;如果是下载加压缩版,直接解压,执行里面的 MongoDBCompassCommunity.exe 文件即可。
在打开的界面中,输入主机地址、端口等相关信息,点击连接:
2.4 Linux系统中的安装启动和连接
目标:在Linux中部署一个单机的MongoDB,作为生产环境下使用。
提示:和Windows下操作差不多。
步骤如下:
(1)先到官网下载压缩包 mongod-linux-x86_64-4.0.10.tgz 。
(2)上传压缩包到Linux中,解压到当前目录:
tar -xvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.10.tgz
(3)移动解压后的文件夹到指定的目录中:
mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.10 /usr/local/mongodb
(4)新建几个目录,分别用来存储数据和日志:
#数据存储目录
mkdir -p /mongodb/single/data/db
#日志存储目录
mkdir -p /mongodb/single/log
(5)新建并修改配置文件
vi /mongodb/single/mongod.conf
配置文件的内容如下:
[root@bobohost single]# /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongod -f /mongodb/single/mongod.conf
about to fork child process, waiting until server is ready for connections.
forked process: 90384
child process started successfully, parent exiting
注意:
如果启动后不是 successfully ,则是启动失败了。原因基本上就是配置文件有问题。
通过进程来查看服务是否启动了:
[root@bobohost single]# ps -ef |grep mongod
root 90384 1 0 8月26 ? 00:02:13 /usr/local/mongdb/bin/mongod -f /mongodb/single/mongod.conf
(7)分别使用mongo命令和compass工具来连接测试。
提示:如果远程连接不上,需要配置防火墙放行,或直接关闭linux防火墙
#查看防火墙状态
systemctl status firewalld
#临时关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
#开机禁止启动防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld
(8)停止关闭服务
停止服务的方式有两种:快速关闭和标准关闭,下面依次说明:
(一)快速关闭方法(快速,简单,数据可能会出错)
目标:通过系统的kill命令直接杀死进程:
杀完要检查一下,避免有的没有杀掉。
#通过进程编号关闭节点
kill -2 54410
【补充】
如果一旦是因为数据损坏,则需要进行如下操作(了解):
1)删除lock文件:
rm -f /mongodb/single/data/db/*.lock
2)修复数据:
/usr/local/mongdb/bin/mongod --repair --dbpath=/mongodb/single/data/db
(二)标准的关闭方法(数据不容易出错,但麻烦):
目标:通过mongo客户端中的shutdownServer命令来关闭服务
主要的操作步骤参考如下:
//客户端登录服务,注意,这里通过localhost登录,如果需要远程登录,必须先登录认证才行。
mongo --port 27017
//#切换到admin库
use admin
//关闭服务
db.shutdownServer()
3 基本常用命令
3.1 案例需求
存放文章评论的数据存放到MongoDB中,数据结构参考如下:
数据库:articledb
3.2 数据库操作
3.2.1 选择和创建数据库
选择和创建数据库的语法格式:
use 数据库名称
如果数据库不存在则自动创建,例如,以下语句创建 spitdb 数据库:
use articledb
查看有权限查看的所有的数据库命令
show dbs
或
show databases
注意: 在 MongoDB 中,集合只有在内容插入后才会创建! 就是说,创建集合(数据表)后要再插入一个文档(记录),集合才会真正创建。
查看当前正在使用的数据库命令
db
MongoDB 中默认的数据库为 test,如果你没有选择数据库,集合将存放在 test 数据库中。
另外:
数据库名可以是满足以下条件的任意UTF-8字符串。
- 不能是空字符串(“”)。
- 不得含有’ '(空格)、.、$、/、\和\0 (空字符)。
- 应全部小写。
- 最多64字节。
有一些数据库名是保留的,可以直接访问这些有特殊作用的数据库。
- admin: 从权限的角度来看,这是"root"数据库。要是将一个用户添加到这个数据库,这个用户自动继承所有数据库的权限。一些特
定的服务器端命令也只能从这个数据库运行,比如列出所有的数据库或者关闭服务器。 - local: 这个数据永远不会被复制,可以用来存储限于本地单台服务器的任意集合
- config: 当Mongo用于分片设置时,config数据库在内部使用,用于保存分片的相关信息。
3.2.2 数据库的删除
MongoDB 删除数据库的语法格式如下:
db.dropDatabase()
提示:主要用来删除已经持久化的数据库
3.3 集合操作
集合,类似关系型数据库中的表。
可以显示的创建,也可以隐式的创建。
3.3.1 集合的显式创建(了解)
基本语法格式:
db.createCollection(name)
参数说明:
- name: 要创建的集合名称
例如:创建一个名为 mycollection 的普通集合。
db.createCollection("mycollection")
查看当前库中的表:show tables命令
show collections
或
show tables
集合的命名规范:
- 集合名不能是空字符串""。
- 集合名不能含有\0字符(空字符),这个字符表示集合名的结尾。
- 集合名不能以"system."开头,这是为系统集合保留的前缀。
- 用户创建的集合名字不能含有保留字符。有些驱动程序的确支持在集合名里面包含,这是因为某些系统生成的集合中包含该字符。除
非你要访问这种系统创建的集合,否则千万不要在名字里出现$。
3.3.2 集合的隐式创建
当向一个集合中插入一个文档的时候,如果集合不存在,则会自动创建集合。
详见 文档的插入 章节。
提示:通常我们使用隐式创建文档即可。
3.3.3 集合的删除
集合删除语法格式如下:
db.collection.drop()
或
db.集合.drop()
返回值
如果成功删除选定集合,则 drop() 方法返回 true,否则返回 false。
例如:要删除mycollection集合
db.mycollection.drop()
3.4 文档基本CRUD
文档(document)的数据结构和 JSON 基本一样。
所有存储在集合中的数据都是 BSON 格式。
3.4.1 文档的插入
(1)单个文档插入
使用insert() 或 save() 方法向集合中插入文档,语法如下:
db.collection.insert(
<document or array of documents>,
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)
参数:
【示例】
要向comment的集合(表)中插入一条测试数据:
db.comment.insert({"articleid":"100000","content":"今天天气真好,阳光明 媚","userid":"1001","nickname":"Rose","createdatetime":new Date(),"likenum":NumberInt(10),"state":null})
提示:
1)comment集合如果不存在,则会隐式创建
2)mongo中的数字,默认情况下是double类型,如果要存整型,必须使用函数NumberInt(整型数字),否则取出来就有问题了。
3)插入当前日期使用 new Date() 4)插入的数据没有指定 _id ,会自动生成主键值
5)如果某字段没值,可以赋值为null,或不写该字段。
执行后,如下,说明插入一个数据成功了。
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
注意:
- 文档中的键/值对是有序的。
- 文档中的值不仅可以是在双引号里面的字符串,还可以是其他几种数据类型(甚至可以是整个嵌入的文档)。 3. MongoDB区分类型和大小写。
- MongoDB的文档不能有重复的键。
- 文档的键是字符串。除了少数例外情况,键可以使用任意UTF-8字符。
文档键命名规范:
- 键不能含有\0 (空字符)。这个字符用来表示键的结尾。
- .和$有特别的意义,只有在特定环境下才能使用。
- 以下划线"_"开头的键是保留的(不是严格要求的)。
(2)批量插入
语法:
db.collection.insertMany(
[ <document 1> , <document 2>, ... ],
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)
参数:
批量插入多条文章评论:
db.comment.insertMany([
{"_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"我们不应该把清晨浪费在手机上,健康很重要,一杯温水幸福你我 他。","userid":"1002","nickname":"相忘于江湖","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08- 05T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"我夏天空腹喝凉开水,冬天喝温开水","userid":"1005","nickname":"伊人憔 悴","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"我一直喝凉开水,冬天夏天都喝。","userid":"1004","nickname":"杰克船 长","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"专家说不能空腹吃饭,影响健康。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯 撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"研究表明,刚烧开的水千万不能喝,因为烫 嘴。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08- 06T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1"}
]);
提示:
插入时指定了 _id ,则主键就是该值。
如果某条数据插入失败,将会终止插入,但已经插入成功的数据不会回滚掉。
因为批量插入由于数据较多容易出现失败,因此,可以使用try catch进行异常捕捉处理,测试的时候可以不处理。如(了解):
try {
db.comment.insertMany([
{"_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"我们不应该把清晨浪费在手机上,健康很重要,一杯温水幸福你我 他。","userid":"1002","nickname":"相忘于江湖","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08- 05T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"我夏天空腹喝凉开水,冬天喝温开水","userid":"1005","nickname":"伊人憔 悴","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"我一直喝凉开水,冬天夏天都喝。","userid":"1004","nickname":"杰克船 长","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"专家说不能空腹吃饭,影响健康。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯 撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"研究表明,刚烧开的水千万不能喝,因为烫 嘴。","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08- 06T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1"}
]);
} catch (e) {
print (e);
}
3.4.2 文档的基本查询
查询数据的语法格式如下:
db.collection.find(<query>, [projection])
参数:
(1)查询所有
如果我们要查询spit集合的所有文档,我们输入以下命令
db.comment.find()
或
db.comment.find({})
这里你会发现每条文档会有一个叫_id的字段,这个相当于我们原来关系数据库中表的主键,当你在插入文档记录时没有指定该字段,
MongoDB会自动创建,其类型是ObjectID类型。
如果我们在插入文档记录时指定该字段也可以,其类型可以是ObjectID类型,也可以是MongoDB支持的任意类型。
如果我想按一定条件来查询,比如我想查询userid为1003的记录,怎么办?很简单!只 要在find()中添加参数即可,参数也是json格式,如
下:
db.comment.find({userid:'1003'})
如果你只需要返回符合条件的第一条数据,我们可以使用findOne命令来实现,语法和find一样。
如:查询用户编号是1003的记录,但只最多返回符合条件的第一条记录:
db.comment.findOne({userid:'1003'})
(2)投影查询(Projection Query):
如果要查询结果返回部分字段,则需要使用投影查询(不显示所有字段,只显示指定的字段)。
如:查询结果只显示 _id、userid、nickname :
>db.comment.find({userid:"1003"},{userid:1,nickname:1})
{ "_id" : "4", "userid" : "1003", "nickname" : "凯撒" }
{ "_id" : "5", "userid" : "1003", "nickname" : "凯撒" }
默认 _id 会显示。
如:查询结果只显示 、userid、nickname ,不显示 _id :
>db.comment.find({userid:"1003"},{userid:1,nickname:1,_id:0})
{ "userid" : "1003", "nickname" : "凯撒" }
{ "userid" : "1003", "nickname" : "凯撒" }
再例如:查询所有数据,但只显示 _id、userid、nickname :
>db.comment.find({},{userid:1,nickname:1})
3.4.3 文档的更新
更新文档的语法:
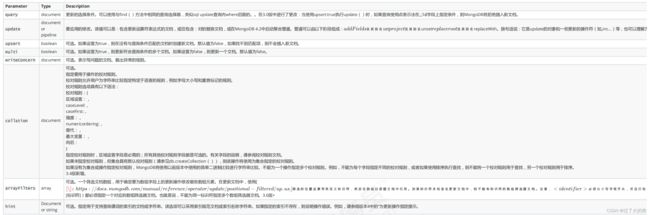
db.collection.update(query, update, options)
//或
db.collection.update(
<query>,
<update>,
{
upsert: <boolean>,
multi: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
arrayFilters: [ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
hint: <document|string> // Available starting in MongoDB 4.2
}
)
参数:
提示:
主要关注前四个参数即可。
【示例】
(1)覆盖的修改
如果我们想修改_id为1的记录,点赞量为1001,输入以下语句:
db.comment.update({_id:"1"},{likenum:NumberInt(1001)})
执行后,我们会发现,这条文档除了likenum字段其它字段都不见了
(2)局部修改
为了解决这个问题,我们需要使用修改器$set来实现,命令如下:
我们想修改_id为2的记录,浏览量为889,输入以下语句:
db.comment.update({_id:"2"},{$set:{likenum:NumberInt(889)}})
这样就OK啦。
(3)批量的修改
更新所有用户为 1003 的用户的昵称为 凯撒大帝 。
//默认只修改第一条数据
db.comment.update({userid:"1003"},{$set:{nickname:"凯撒2"}})
//修改所有符合条件的数据
db.comment.update({userid:"1003"},{$set:{nickname:"凯撒大帝"}},{multi:true})
提示:如果不加后面的参数,则只更新符合条件的第一条记录
(3)列值增长的修改
如果我们想实现对某列值在原有值的基础上进行增加或减少,可以使用 $inc 运算符来实现。
需求:对3号数据的点赞数,每次递增1
db.comment.update({_id:"3"},{$inc:{likenum:NumberInt(1)}})
3.4.4 删除文档
删除文档的语法结构:
db.集合名称.remove(条件)
以下语句可以将数据全部删除,请慎用
db.comment.remove({})
如果删除_id=1的记录,输入以下语句
db.comment.remove({_id:"1"})
3.5 文档的分页查询
3.5.1 统计查询
统计查询使用count()方法,语法如下:
db.collection.count(query, options)
参数:
可选项暂时不使用。
【示例】
(1)统计所有记录数:
统计comment集合的所有的记录数:
db.comment.count()
(2)按条件统计记录数:
例如:统计userid为1003的记录条数
db.comment.count({userid:"1003"})
提示:
默认情况下 count() 方法返回符合条件的全部记录条数。
3.5.2 分页列表查询
可以使用limit()方法来读取指定数量的数据,使用skip()方法来跳过指定数量的数据。
基本语法如下所示:
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().limit(NUMBER).skip(NUMBER)
如果你想返回指定条数的记录,可以在find方法后调用limit来返回结果(TopN),默认值20,例如:
db.comment.find().limit(3)
skip方法同样接受一个数字参数作为跳过的记录条数。(前N个不要),默认值是0
db.comment.find().skip(3)
分页查询:需求:每页2个,第二页开始:跳过前两条数据,接着值显示3和4条数据
//第一页
db.comment.find().skip(0).limit(2)
//第二页
db.comment.find().skip(2).limit(2)
//第三页
db.comment.find().skip(4).limit(2)
3.5.3 排序查询
sort() 方法对数据进行排序,sort() 方法可以通过参数指定排序的字段,并使用 1 和 -1 来指定排序的方式,其中 1 为升序排列,而 -1 是用
于降序排列。
语法如下所示:
db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().sort({KEY:1})
或
db.集合名称.find().sort(排序方式)
例如:
对userid降序排列,并对访问量进行升序排列
db.comment.find().sort({userid:-1,likenum:1})
提示:
skip(), limilt(), sort()三个放在一起执行的时候,执行的顺序是先 sort(), 然后是 skip(),最后是显示的 limit(),和命令编写顺序无关。
3.6 文档的更多查询
3.6.1 正则的复杂条件查询
MongoDB的模糊查询是通过正则表达式的方式实现的。格式为:
db.collection.find({field:/正则表达式/})
或
db.集合.find({字段:/正则表达式/})
提示:正则表达式是js的语法,直接量的写法。
例如,我要查询评论内容包含“开水”的所有文档,代码如下:
db.comment.find({content:/开水/})
如果要查询评论的内容中以“专家”开头的,代码如下:
db.comment.find({content:/^专家/})
3.6.2 比较查询
<, <=, >, >= 这个操作符也是很常用的,格式如下:
db.集合名称.find({ "field" : { $gt: value }}) // 大于: field > value
db.集合名称.find({ "field" : { $lt: value }}) // 小于: field < value
db.集合名称.find({ "field" : { $gte: value }}) // 大于等于: field >= value
db.集合名称.find({ "field" : { $lte: value }}) // 小于等于: field <= value
db.集合名称.find({ "field" : { $ne: value }}) // 不等于: field != value
示例:查询评论点赞数量大于700的记录
db.comment.find({likenum:{$gt:NumberInt(700)}})
3.6.3 包含查询
包含使用$in操作符。 示例:查询评论的集合中userid字段包含1003或1004的文档
db.comment.find({userid:{$in:["1003","1004"]}})
不包含使用$nin操作符。 示例:查询评论集合中userid字段不包含1003和1004的文档
db.comment.find({userid:{$nin:["1003","1004"]}})
3.6.4 条件连接查询
我们如果需要查询同时满足两个以上条件,需要使用$and操作符将条件进行关联。(相 当于SQL的and) 格式为:
$and:[ { },{ },{ } ]
示例:查询评论集合中likenum大于等于700 并且小于2000的文档:
db.comment.find({$and:[{likenum:{$gte:NumberInt(700)}},{likenum:{$lt:NumberInt(2000)}}]})
如果两个以上条件之间是或者的关系,我们使用 操作符进行关联,与前面 and的使用方式相同 格式为:
$or:[ { },{ },{ } ]
示例:查询评论集合中userid为1003,或者点赞数小于1000的文档记录
db.comment.find({$or:[ {userid:"1003"} ,{likenum:{$lt:1000} }]})
3.7 常用命令小结
选择切换数据库:use articledb
插入数据:db.comment.insert({bson数据})
查询所有数据:db.comment.find();
条件查询数据:db.comment.find({条件})
查询符合条件的第一条记录:db.comment.findOne({条件})
查询符合条件的前几条记录:db.comment.find({条件}).limit(条数)
查询符合条件的跳过的记录:db.comment.find({条件}).skip(条数)
修改数据:db.comment.update({条件},{修改后的数据}) 或db.comment.update({条件},{$set:{要修改部分的字段:数据})
修改数据并自增某字段值:db.comment.update({条件},{$inc:{自增的字段:步进值}})
删除数据:db.comment.remove({条件})
统计查询:db.comment.count({条件})
模糊查询:db.comment.find({字段名:/正则表达式/})
条件比较运算:db.comment.find({字段名:{$gt:值}})
包含查询:db.comment.find({字段名:{$in:[值1,值2]}})或db.comment.find({字段名:{$nin:[值1,值2]}})
条件连接查询:db.comment.find({$and:[{条件1},{条件2}]})或db.comment.find({$or:[{条件1},{条件2}]})
4 索引-Index
4.1 概述
索引支持在MongoDB中高效地执行查询。如果没有索引,MongoDB必须执行全集合扫描,即扫描集合中的每个文档,以选择与查询语句
匹配的文档。这种扫描全集合的查询效率是非常低的,特别在处理大量的数据时,查询可以要花费几十秒甚至几分钟,这对网站的性能是非
常致命的。
如果查询存在适当的索引,MongoDB可以使用该索引限制必须检查的文档数。
索引是特殊的数据结构,它以易于遍历的形式存储集合数据集的一小部分。索引存储特定字段或一组字段的值,按字段值排序。索引项的排
序支持有效的相等匹配和基于范围的查询操作。此外,MongoDB还可以使用索引中的排序返回排序结果。
官网文档:https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/indexes/
了解:
MongoDB索引使用B树数据结构(确切的说是B-Tree,MySQL是B+Tree)
4.2 索引的类型
4.2.1 单字段索引
MongoDB支持在文档的单个字段上创建用户定义的升序/降序索引,称为单字段索引(Single Field Index)。
对于单个字段索引和排序操作,索引键的排序顺序(即升序或降序)并不重要,因为MongoDB可以在任何方向上遍历索引。
4.2.2 复合索引
MongoDB还支持多个字段的用户定义索引,即复合索引(Compound Index)。
复合索引中列出的字段顺序具有重要意义。例如,如果复合索引由 { userid: 1, score: -1 } 组成,则索引首先按userid正序排序,然后
在每个userid的值内,再在按score倒序排序。
4.2.3 其他索引
地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)、文本索引(Text Indexes)、哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)。
地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)
为了支持对地理空间坐标数据的有效查询,MongoDB提供了两种特殊的索引:返回结果时使用平面几何的二维索引和返回结果时使用球面
几何的二维球面索引。
文本索引(Text Indexes)
MongoDB提供了一种文本索引类型,支持在集合中搜索字符串内容。这些文本索引不存储特定于语言的停止词(例如“the”、“a”、“or”),
而将集合中的词作为词干,只存储根词。
哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)
为了支持基于散列的分片,MongoDB提供了散列索引类型,它对字段值的散列进行索引。这些索引在其范围内的值分布更加随机,但只支
持相等匹配,不支持基于范围的查询。
4.3 索引的管理操作
4.3.1 索引的查看
说明:
返回一个集合中的所有索引的数组。
语法:
db.collection.getIndexes()
提示:该语法命令运行要求是MongoDB 3.0+
【示例】
查看comment集合中所有的索引情况
> db.comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
}
]
结果中显示的是默认 _id 索引。
默认_id索引:
MongoDB在创建集合的过程中,在 _id 字段上创建一个唯一的索引,默认名字为 id ,该索引可防止客户端插入两个具有相同值的文
档,您不能在_id字段上删除此索引。
注意:该索引是唯一索引,因此值不能重复,即 _id 值不能重复的。在分片集群中,通常使用 _id 作为片键。
4.3.2 索引的创建
说明:
在集合上创建索引。
语法:
db.collection.createIndex(keys, options)
参数:
options(更多选项)列表:
提示:
注意在 3.0.0 版本前创建索引方法为 db.collection.ensureIndex() ,之后的版本使用了 db.collection.createIndex() 方法,
ensureIndex() 还能用,但只是 createIndex() 的别名。
【示例】
(1)单字段索引示例:对 userid 字段建立索引:
> db.comment.createIndex({userid:1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
参数1:按升序创建索引
可以查看一下:
> db.comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
},{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"userid" : 1
},
"name" : "userid_1",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
}
]
索引名字为userid_1
compass查看:
(2)复合索引:对 userid 和 nickname 同时建立复合(Compound)索引:
> db.comment.createIndex({userid:1,nickname:-1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"ok" : 1
}
查看一下索引:
> db.comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"userid" : 1
},
"name" : "userid_1",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"userid" : 1,
"nickname" : -1
},
"name" : "userid_1_nickname_-1",
"ns" : "articledb.comment"
}
]
compass中:
4.3.3 索引的移除
说明:可以移除指定的索引,或移除所有索引
一、指定索引的移除
语法:
db.collection.dropIndex(index)
参数:
【示例】
删除 comment 集合中 userid 字段上的升序索引:
> db.comment.dropIndex({userid:1})
{ "nIndexesWas" : 3, "ok" : 1 }
查看已经删除了。
二、所有索引的移除
语法:
db.collection.dropIndexes()
【示例】
删除 spit 集合中所有索引。
> db.comment.dropIndexes() {
"nIndexesWas" : 2,
"msg" : "non-_id indexes dropped for collection",
"ok" : 1
}
提示: _id 的字段的索引是无法删除的,只能删除非 _id 字段的索引
4.4 索引的使用
4.4.1 执行计划
分析查询性能(Analyze Query Performance)通常使用执行计划(解释计划、Explain Plan)来查看查询的情况,如查询耗费的时间、是
否基于索引查询等。
那么,通常,我们想知道,建立的索引是否有效,效果如何,都需要通过执行计划查看。
语法:
db.collection.find(query,options).explain(options)
【示例】
查看根据userid查询数据的情况:
db.comment.find({userid: "1003"}).explain()
{
"queryPlanner": {
"plannerVersion": 1,
"namespace": "articledb.comment",
"indexFilterSet": false,
"parsedQuery": {
"userid": {
"$eq": "1003"
}
},
"winningPlan": {
"stage": "COLLSCAN",
"filter": {
"userid": {
"$eq": "1003"
}
},
"direction": "forward"
},
"rejectedPlans": []
},
"serverInfo": {
"host": "9ef3740277ad",
"port": 27017,
"version": "4.0.10",
"gitVersion": "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok": 1
}
关键点看: “stage” : “COLLSCAN”, 表示全集合扫描
下面对userid建立索引
> db.comment.createIndex({userid:1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
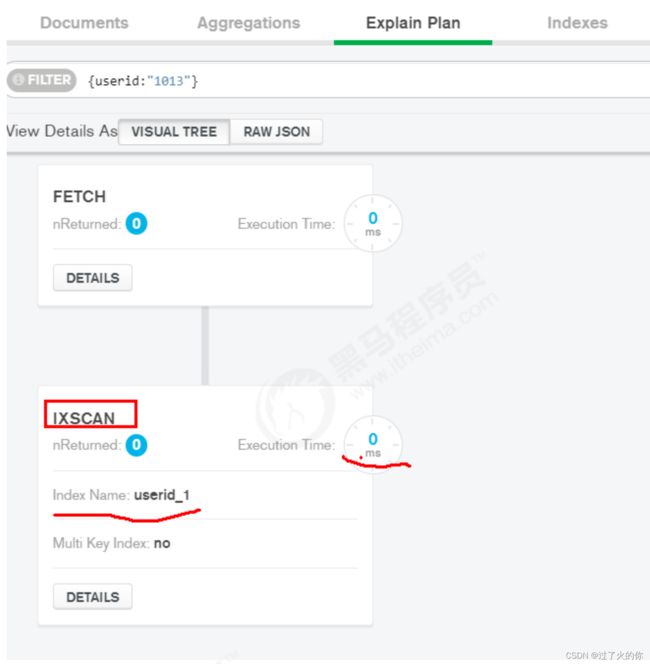
再次查看执行计划:
db.comment.find({
userid: "1013"
}).explain() {
"queryPlanner": {
"plannerVersion": 1,
"namespace": "articledb.comment",
"indexFilterSet": false,
"parsedQuery": {
"userid": {
"$eq": "1013"
}
},
"winningPlan": {
"stage": "FETCH",
"inputStage": {
"stage": "IXSCAN",
"keyPattern": {
"userid": 1
},
"indexName": "userid_1",
"isMultiKey": false,
"multiKeyPaths": {
"userid": []
},
"isUnique": false,
"isSparse": false,
"isPartial": false,
"indexVersion": 2,
"direction": "forward",
"indexBounds": {
"userid": ["[\"1013\", \"1013\"]"]
}
}
},
"rejectedPlans": []
},
"serverInfo": {
"host": "9ef3740277ad",
"port": 27017,
"version": "4.0.10",
"gitVersion": "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok": 1
}
关键点看: “stage” : “IXSCAN” ,基于索引的扫描
compass查看:
4.4.2 涵盖的查询
Covered Queries
当查询条件和查询的投影仅包含索引字段时,MongoDB直接从索引返回结果,而不扫描任何文档或将文档带入内存。 这些覆盖的查询可以
非常有效。

更多:https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/core/query-optimization/#read-operations-covered-query
【示例】
> db.comment.find({userid:"1003"},{userid:1,_id:0})
{ "userid" : "1003" }
{ "userid" : "1003" }
> db.comment.find({userid: "1003"}, {userid: 1,_id: }).explain()
{
"queryPlanner": {
"plannerVersion": 1,
"namespace": "articledb.comment",
"indexFilterSet": false,
"parsedQuery": {
"userid": {
"$eq": "1003"
}
},
"winningPlan": {
"stage": "PROJECTION",
"transformBy": {
"userid": 1,
"_id": 0
},
"inputStage": {
"stage": "IXSCAN",
"keyPattern": {
"userid": 1
},
"indexName": "userid_1",
"isMultiKey": false,
"multiKeyPaths": {
"userid": []
},
"isUnique": false,
"isSparse": false,
"isPartial": false,
"indexVersion": 2,
"direction": "forward",
"indexBounds": {
"userid": ["[\"1003\", \"1003\"]"]
}
}
},
"rejectedPlans": []
},
"serverInfo": {
"host": "bobohost.localdomain",
"port": 27017,
"version": "4.0.10",
"gitVersion": "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok": 1
}
Compass中:
5 文章评论
5.1 需求分析
某头条的文章评论业务如下:
文章示例参考:早晨空腹喝水,是对还是错?
需要实现以下功能:
1)基本增删改查API
2)根据文章id查询评论
3)评论点赞
5.2 表结构分析
数据库:articledb
5.3 技术选型
5.3.1 mongodb-driver(了解)
mongodb-driver是mongo官方推出的java连接mongoDB的驱动包,相当于JDBC驱动。我们通过一个入门的案例来了解mongodb-driver
的基本使用。
官方驱动说明和下载:http://mongodb.github.io/mongo-java-driver/
官方驱动示例文档:http://mongodb.github.io/mongo-java-driver/3.8/driver/getting-started/quick-start/
5.3.2 SpringDataMongoDB
SpringData家族成员之一,用于操作MongoDB的持久层框架,封装了底层的mongodb-driver。
官网主页: https://projects.spring.io/spring-data-mongodb/
5.4 文章微服务模块搭建
(1)搭建项目工程article,pom.xml引入依赖:
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>cn.itcastgroupId>
<artifactId>articleartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodbartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
(2)创建application.yml
spring:
#数据源配置
data:
mongodb:
# 主机地址
host: 192.168.40.141
# 数据库
database: articledb
# 默认端口是27017
port: 27017
#也可以使用uri连接
#uri: mongodb://192.168.40.134:27017/articledb
(3)创建启动类
cn.itcast.article.ArticleApplication
package cn.itcast.article;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ArticleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ArticleApplication.class, args);
}
}
(4)启动项目,看是否能正常启动,控制台没有错误。
5.5 文章评论实体类的编写
创建实体类 创建包cn.itcast.article,包下建包po用于存放实体类,创建实体类
cn.itcast.article.po.Comment
package cn.itcast.article.po;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Field;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
/*** 文章评论实体类 */
//把一个java类声明为mongodb的文档,可以通过collection参数指定这个类对应的文档。
//@Document(collection="mongodb 对应 collection 名")
// 若未加 @Document ,该 bean save 到 mongo 的 comment collection
// 若添加 @Document ,则 save 到 comment collection
@Document(collection = "comment")//可以省略,如果省略,则默认使用类名小写映射集合
// 复合索引
// @CompoundIndex( def = "{'userid': 1, 'nickname': -1}")
public class Comment implements Serializable {
//主键标识,该属性的值会自动对应mongodb的主键字段"_id",如果该属性名就叫“id”,则该注解可以省略,否则必须写
@Id
private String id;//主键
// 该属性对应mongodb的字段的名字,如果一致,则无需该注解
@Field("content")
private String content;//吐槽内容
private Date publishtime;//发布日期 //添加了一个单字段的索引
@Indexed
private String userid;//发布人ID
private String nickname;//昵称
private LocalDateTime createdatetime;//评论的日期时间
private Integer likenum;//点赞数
private Integer replynum;//回复数
private String state;//状态
private String parentid;//上级ID
private String articleid;
//getter and setter.....
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Date getPublishtime() {
return publishtime;
}
public void setPublishtime(Date publishtime) {
this.publishtime = publishtime;
}
public String getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(String userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getNickname() {
return nickname;
}
public void setNickname(String nickname) {
this.nickname = nickname;
}
public LocalDateTime getCreatedatetime() {
return createdatetime;
}
public void setCreatedatetime(LocalDateTime createdatetime) {
this.createdatetime = createdatetime;
}
public Integer getLikenum() {
return likenum;
}
public void setLikenum(Integer likenum) {
this.likenum = likenum;
}
public Integer getReplynum() {
return replynum;
}
public void setReplynum(Integer replynum) {
this.replynum = replynum;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getParentid() {
return parentid;
}
public void setParentid(String parentid) {
this.parentid = parentid;
}
public String getArticleid() {
return articleid;
}
public void setArticleid(String articleid) {
this.articleid = articleid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" + "id='" + id + '\'' + ", content='" + content + '\'' + ", publishtime=" + publishtime + ", userid='" + userid + '\'' + ", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' + ", createdatetime=" + createdatetime + ", likenum=" + likenum + ", replynum=" + replynum + ", state='" + state + '\'' + ", parentid='" + parentid + '\'' + ", articleid='" + articleid + '\'' + '}';
}
}
说明:
索引可以大大提升查询效率,一般在查询字段上添加索引,索引的添加可以通过Mongo的命令来添加,也可以在Java的实体类中通过注解添加。
1)单字段索引注解 @Indexed
org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed.class
声明该字段需要索引,建索引可以大大的提高查询效率。
Mongo命令参考:
db.comment.createIndex({"userid":1})
2)复合索引注解@CompoundIndex
org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.CompoundIndex.class
复合索引的声明,建复合索引可以有效地提高多字段的查询效率。
Mongo命令参考:
db.comment.createIndex({"userid":1,"nickname":-1})
5.6 文章评论的基本增删改查
(1)创建数据访问接口 cn.itcast.article包下创建dao包,包下创建接口
cn.itcast.article.dao.CommentRepository
package cn.itcast.article.dao;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
//评论的持久层接口
public interface CommentRepository extends MongoRepository<Comment, String> {
}
(2)创建业务逻辑类 cn.itcast.article包下创建service包,包下创建类
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentService
package cn.itcast.article.service;
import cn.itcast.article.dao.CommentRepository;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
//评论的业务层
@Service
public class CommentService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
/*** 保存一个评论 * @param comment */
public void saveComment(Comment comment) {
//如果需要自定义主键,可以在这里指定主键;如果不指定主键,MongoDB会自动生成主键
// 设置一些默认初始值。。。
// 调用dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/*** 更新评论 * @param comment */
public void updateComment(Comment comment) {
//调用dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/*** 根据id删除评论 * @param id */
public void deleteCommentById(String id) {
//调用dao
commentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
/*** 查询所有评论 * @return */
public List<Comment> findCommentList() {
//调用dao
return commentRepository.findAll();
}
/*** 根据id查询评论 * @param id * @return */
public Comment findCommentById(String id) {
//调用dao
return commentRepository.findById(id).get();
}
}
(3)新建Junit测试类,测试保存和查询所有:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
package cn.itcast.article.service;
import cn.itcast.article.ArticleApplication;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
//测试评论的业务层
//SpringBoot的Junit集成测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
//SpringBoot的测试环境初始化,参数:启动类
@SpringBootTest(classes = ArticleApplication.class)
public class CommentServiceTest {
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
/*** 保存一个评论 */
@Test
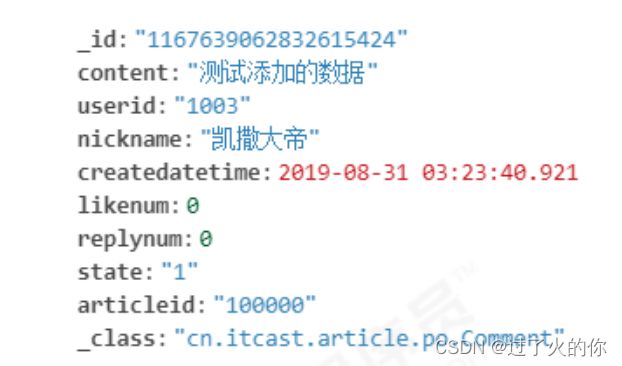
public void testSaveComment() {
Comment comment = new Comment();
comment.setArticleid("100000");
comment.setContent("测试添加的数据");
comment.setCreatedatetime(LocalDateTime.now());
comment.setUserid("1003");
comment.setNickname("凯撒大帝");
comment.setState("1");
comment.setLikenum(0);
comment.setReplynum(0);
commentService.saveComment(comment);
}
/*** 查询所有数据 */
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
List<Comment> list = commentService.findCommentList();
System.out.println(list);
}
/**
* 测试根据id查询
*/
@Test
public void testFindCommentById() {
Comment comment = commentService.findCommentById("5d6a27b81b8d374798cf0b41");
System.out.println(comment);
}
}
添加结果:
5.7 根据上级ID查询文章评论的分页列表
(1)CommentRepository新增方法定义
//根据父id,查询子评论的分页列表
Page<Comment> findByParentid(String parentid, Pageable pageable);
(2)CommentService新增方法
/**
* 根据父id查询分页列表
* @param parentid
* @param page
* @param size
* @return
*/
public Page<Comment> findCommentListPageByParentid(String parentid,int page,int size){
return commentRepository.findByParentid(parentid,PageRequest.of(page-1,size));
}
(3)junit测试用例:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
/**
* 测试根据父id查询子评论的分页列表
**/
@Test
public void testFindCommentListPageByParentid(){
Page<Comment> pageResponse = commentService.findCommentListPageByParentid("3", 1, 2);
System.out.println("----总记录数:"+pageResponse.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("----当前页数据:"+pageResponse.getContent());
}
(4)测试
使用compass快速插入一条测试数据,数据的内容是对3号评论内容进行评论。
----总记录数:1
----当前页数据:
[Comment{id='33', content='你年轻,火力大', publishtime=null, userid='1003', nickname='凯撒大帝', createdatetime=null, likenum=null, replynum=null, state='null', parentid='3', articleid='100001'}]
5.8 MongoTemplate实现评论点赞
我们看一下以下点赞的临时示例代码: CommentService 新增updateThumbup方法
/**
* 点赞-效率低
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentThumbupToIncrementingOld(String id){
Comment comment = CommentRepository.findById(id).get();
comment.setLikenum(comment.getLikenum()+1);
CommentRepository.save(comment);
}
以上方法虽然实现起来比较简单,但是执行效率并不高,因为我只需要将点赞数加1就可以了,没必要查询出所有字段修改后再更新所有字段。(蝴蝶效应)
我们可以使用MongoTemplate类来实现对某列的操作。
(1)修改CommentService
//注入MongoTemplate
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
/**
* 点赞数+1
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentLikenum(String id){
//查询对象
Query query=Query.query(Criteria.where("_id").is(id));
//更新对象
Update update=new Update();
//局部更新,相当于$set
// update.set(key,value)
//递增$inc
// update.inc("likenum",1);
update.inc("likenum");
//参数1:查询对象
//参数2:更新对象
//参数3:集合的名字或实体类的类型Comment.class
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,"comment");
}
(2)测试用例:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
/**
* 点赞数+1
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateCommentLikenum(){
//对3号文档的点赞数+1
commentService.updateCommentLikenum("3");
}
执行测试用例后,发现点赞数+1了: