SpringBoot基础
目录
一、SpringBoot简介
1.1 原有Spring优缺点分析
1.1.1 Spring的优点分析
1.1.2 Spring的缺点分析
1.2 SpringBoot的概述
1.2.1 SpringBoot解决上述Spring的缺点
1.2.2 SpringBoot的特点
1.2.3 SpringBoot的核心功能
二、SpringBoot快速入门
2.1 代码实现
2.2 快速入门解析
2.2.2 SpringBoot代码解析
2.2.3 SpringBoot工程热部署
编辑
三、SpringBoot原理分析
3.1 起步依赖原理分析
3.1.1 分析spring-boot-starter-parent
3.1.2 分析spring-boot-starter-web
3.2 自动配置原理解析
四、SpringBoot的配置文件
4.1 SpringBoot配置文件类型
4.1.1 SpringBoot配置文件类型和作用
4.1.2 application.yml配置文件
4.2 配置文件与配置类的属性映射方式
4.2.1 使用注解@Value映射
一、SpringBoot简介
1.1 原有Spring优缺点分析
1.1.1 Spring的优点分析
Spring是Java企业版(Java Enterprise Edition,JEE,也称J2EE)的轻量级代替品。无需开发重量级的Enterprise JavaBean(EJB),Spring为企业级Java开发提供了一种相对简单的方法,通过依赖注入和面向切面编程,用简单的Java对象(Plain Old Java Object,POJO)实现了EJB的功能。
1.1.2 Spring的缺点分析
虽然Spring的组件代码是轻量级的,但它的配置却是重量级的。一开始,Spring用XML配置,而且是很多XML配置。Spring 2.5引入了基于注解的组件扫描,这消除了大量针对应用程序自身组件的显式XML配置。Spring 3.0引入了基于Java的配置,这是一种类型安全的可重构配置方式,可以代替XML。
所有这些配置都代表了开发时的损耗。因为在思考Spring特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切换,所以编写配置挤占了编写应用程序逻辑的时间。和所有框架一样,Spring实用,但与此同时它要求的回报也不少。
除此之外,项目的依赖管理也是一件耗时耗力的事情。在环境搭建时,需要分析要导入哪些库的坐标,而且还需要分析导入与之有依赖关系的其他库的坐标,一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题就会严重阻碍项目的开发进度。
1.2 SpringBoot的概述
1.2.1 SpringBoot解决上述Spring的缺点
SpringBoot对上述Spring的缺点进行的改善和优化,基于约定优于配置的思想,可以让开发人员不必在配置与逻辑业务之间进行思维的切换,全身心的投入到逻辑业务的代码编写中,从而大大提高了开发的效率,一定程度上缩短了项目周期。
1.2.2 SpringBoot的特点
-
为基于Spring的开发提供更快的入门体验
-
开箱即用,没有代码生成,也无需XML配置。同时也可以修改默认值来满足特定的需求
-
提供了一些大型项目中常见的非功能性特性,如嵌入式服务器、安全、指标,健康检测、外部配置等
-
SpringBoot不是对Spring功能上的增强,而是提供了一种快速使用Spring的方式
1.2.3 SpringBoot的核心功能
-
起步依赖
起步依赖本质上是一个Maven项目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。
简单的说,起步依赖就是将具备某种功能的坐标打包到一起,并提供一些默认的功能。
-
自动配置
Spring Boot的自动配置是一个运行时(更准确地说,是应用程序启动时)的过程,考虑了众多因素,才决定Spring配置应该用哪个,不该用哪个。该过程是Spring自动完成的。
二、SpringBoot快速入门
2.1 代码实现
略
2.2 快速入门解析
2.2.2 SpringBoot代码解析
-
@SpringBootApplication:标注SpringBoot的启动类,该注解具备多种功能(后面详细剖析)
-
SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApplication.class) 代表运行SpringBoot的启动类,参数为SpringBoot启动类的字节码对象
2.2.3 SpringBoot工程热部署
我们在开发中反复修改类、页面等资源,每次修改后都是需要重新启动才生效,这样每次启动都很麻烦,浪费了大量的时间,我们可以在修改代码后不重启就能生效,在 pom.xml 中添加如下配置就可以实现这样的功能,我们称之为热部署。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
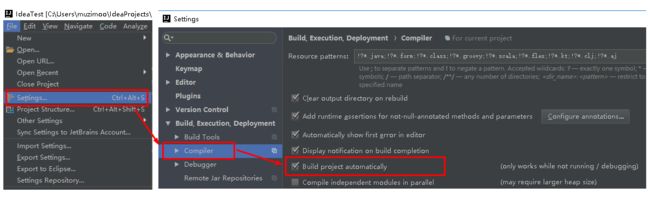
注意:IDEA进行SpringBoot热部署失败原因
出现这种情况,并不是热部署配置问题,其根本原因是因为Intellij IEDA默认情况下不会自动编译,需要对IDEA进行自动编译的设置,如下:
然后 Shift+Ctrl+Alt+/,选择Registry
三、SpringBoot原理分析
3.1 起步依赖原理分析
3.1.1 分析spring-boot-starter-parent
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-parent,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-parent的pom.xml,xml配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.0.1.RELEASE
../../spring-boot-dependencies
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-dependencies,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml,xml配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
5.15.3
2.7.7
1.9.63
2.4.0
1.8.13
3.9.1
4.0.6
2.1.4
3.0.0
1.7.11
... ... ...
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot
2.0.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-test
2.0.1.RELEASE
... ... ...
org.jetbrains.kotlin
kotlin-maven-plugin
${kotlin.version}
org.jooq
jooq-codegen-maven
${jooq.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.0.1.RELEASE
... ... ...
从上面的spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml中我们可以发现,一部分坐标的版本、依赖管理、插件管理已经定义好,所以我们的SpringBoot工程继承spring-boot-starter-parent后已经具备版本锁定等配置了。所以起步依赖的作用就是进行依赖的传递。
3.1.2 分析spring-boot-starter-web
按住Ctrl点击pom.xml中的spring-boot-starter-web,跳转到了spring-boot-starter-web的pom.xml,xml配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starters
2.0.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
2.0.1.RELEASE
Spring Boot Web Starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
2.0.1.RELEASE
compile
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-json
2.0.1.RELEASE
compile
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
2.0.1.RELEASE
compile
org.hibernate.validator
hibernate-validator
6.0.9.Final
compile
org.springframework
spring-web
5.0.5.RELEASE
compile
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
5.0.5.RELEASE
compile
从上面的spring-boot-starter-web的pom.xml中我们可以发现,spring-boot-starter-web就是将web开发要使用的spring-web、spring-webmvc等坐标进行了“打包”,这样我们的工程只要引入spring-boot-starter-web起步依赖的坐标就可以进行web开发了,同样体现了依赖传递的作用。
3.2 自动配置原理解析
按住Ctrl点击查看启动类MySpringBootApplication上的注解@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApplication.class);
}
}注解@SpringBootApplication的源码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class[] exclude() default {};
... ... ...
}其中,
@SpringBootConfiguration:等同与@Configuration,既标注该类是Spring的一个配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration:SpringBoot自动配置功能开启
按住Ctrl点击查看注解@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
... ... ...
}其中,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
按住Ctrl点击查看AutoConfigurationImportSelector源码
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
... ... ...
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
}
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
return configurations;
}
其中,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法的作用就是从META-INF/spring.factories文件中读取指定类对应的类名称列表
spring.factories 文件中有关自动配置的配置信息如下:
... ... ...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
... ... ...上面配置文件存在大量的以Configuration为结尾的类名称,这些类就是存有自动配置信息的类,而SpringApplication在获取这些类名后再加载
我们以ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration为例来分析源码:
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
... ... ...
}
其中,
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) 代表加载ServerProperties服务器配置属性类
进入ServerProperties.class源码如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
/**
* Server HTTP port.
*/
private Integer port;
/**
* Network address to which the server should bind.
*/
private InetAddress address;
... ... ...
}其中,
prefix = "server" 表示SpringBoot配置文件中的前缀,SpringBoot会将配置文件中以server开始的属性映射到该类的字段中。映射关系如下:
四、SpringBoot的配置文件
4.1 SpringBoot配置文件类型
4.1.1 SpringBoot配置文件类型和作用
SpringBoot是基于约定的,所以很多配置都有默认值,但如果想使用自己的配置替换默认配置的话,就可以使用application.properties或者application.yml(application.yaml)进行配置。
SpringBoot默认会从Resources目录下加载application.properties或application.yml(application.yaml)文件
其中,application.properties文件是键值对类型的文件,之前一直在使用,所以此处不在对properties文件的格式进行阐述。除了properties文件外,SpringBoot还可以使用yml文件进行配置,下面对yml文件进行讲解。
4.1.2 application.yml配置文件
4.1.2.1 yml配置文件简介
YML文件格式是YAML (YAML Aint Markup Language)编写的文件格式,YAML是一种直观的能够被电脑识别的的数据数据序列化格式,并且容易被人类阅读,容易和脚本语言交互的,可以被支持YAML库的不同的编程语言程序导入,比如: C/C++, Ruby, Python, Java, Perl, C#, PHP等。YML文件是以数据为核心的,比传统的xml方式更加简洁。
YML文件的扩展名可以使用.yml或者.yaml。
4.1.2.2 yml配置文件的语法
4.1.2.2.1 配置普通数据
-
语法: key: value
-
示例代码:
-
name: haohao
-
注意:value之前有一个空格
4.1.2.2.2 配置对象数据
-
语法:
key:
key1: value1
key2: value2
或者:
key: {key1: value1,key2: value2}
-
示例代码:
-
person:
name: haohao
age: 31
addr: beijing#或者
person: {name: haohao,age: 31,addr: beijing}
-
注意:key1前面的空格个数不限定,在yml语法中,相同缩进代表同一个级别
-
字符串默认不用加上单引号或双引号:
“”:双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想要表示的意思
name:"zhangsan \n lisi";输出:张三 换行 lisi
单引号:会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
'':单引号;会转义特殊字符串,特殊字符串最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name:"zhangsan \n lisi";输出:zhangsan \n lisi
4.1.2.2.2 配置Map数据
同上面的对象写法
4.1.2.2.3 配置数组(List、Set)数据
-
语法:
key:
- value1
- value2
或者:
key: [value1,value2]
-
示例代码:
-
city:
- beijing
- tianjin
- shanghai
- chongqing
#或者city: [beijing,tianjin,shanghai,chongqing]
#集合中的元素是对象形式
student:
- name: zhangsan
age: 18
score: 100
- name: lisi
age: 28
score: 88
- name: wangwu
age: 38
score: 90 -
注意:value1与之间的 - 之间存在一个空格
4.2 配置文件与配置类的属性映射方式
4.2.1 使用注解@Value映射
我们可以通过@Value注解将配置文件中的值映射到一个Spring管理的Bean的字段上
例如:
application.properties配置如下: