线程的创建和使用(一)
1、线程
1.1、线程的概念
一个线程就是一个 "执行流". 每个线程之间都可以按照顺讯执行自己的代码. 多个线程之间 "同时" 执行着多份代码.
1.2、创建线程
方法一:继承Thread类
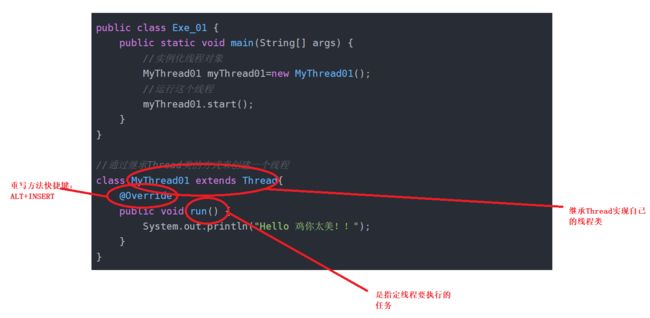
public class Exe_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程对象
MyThread01 myThread01=new MyThread01();
//运行这个线程
myThread01.start();
}
}
//通过继承Thread类的方式来创建一个线程
class MyThread01 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
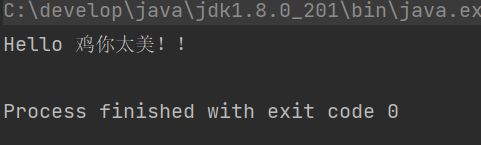
System.out.println("Hello 鸡你太美!!");
}
}运行结果:
观察线程调度:
public class Exe_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化线程对象
MyThread02 myThread02=new MyThread02();
//真正去操作系统中申请线程并参与CPU调度
myThread02.start();
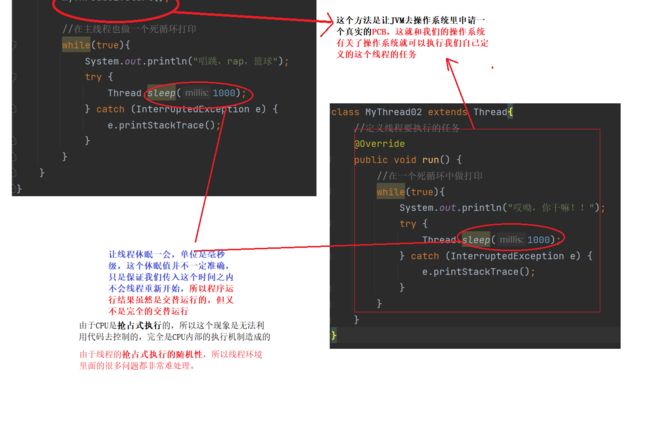
//在主线程也做一个死循环打印
while(true){
System.out.println("唱跳,rap,篮球");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class MyThread02 extends Thread{
//定义线程要执行的任务
@Override
public void run() {
//在一个死循环中做打印
while(true){
System.out.println("哎呦,你干嘛!!");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}运行结果:
方法二:实现Runnable接口
public class Exe_03 {
//通过实现Runnable的方式创建线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化自定义线程类
MyRunnable runnable=new MyRunnable();
//通过Thread的构造方法把Runnable作为参数传入
Thread thread=new Thread(runnable);
//启动线程才是真正意义上的创建系统线程,参与CPU调度
thread.start();
}
}
//实现Runnable接口
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
//定义线程要执行的任务
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
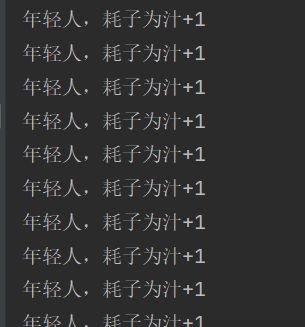
System.out.println("年轻人,耗子为汁+1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}运行结果:
由我来给大家利用线程制作一个蔡徐坤经典名场面
public class Exe_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//练习生任务
Runnable01 runnable01=new Runnable01();
//第一步给大家打个招呼
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable01);
t1.start();
//表演任务
Runnable02 runnable02=new Runnable02();
//第二步给介绍鸽鸽的特长
Thread t2=new Thread(runnable02);
t2.start();
//音乐走你
Runnable03 runnable03=new Runnable03();
//第三步showTime
Thread t3=new Thread(runnable03);
t3.start();
}
}
//创建Runnable类
//定义一个练习两年半练习生的任务
class Runnable01 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("全明星制作人们,大家好,我是一个练习时长两年半的个人练习生蔡徐坤");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//定义一个小黑子的任务
class Runnable02 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("喜欢唱、条、rap、篮球");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//点一首music送给鸽鸽
class Runnable03 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("music");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}运行结果:
通过Thread类的匿名内部类的方式创建线程
/*
通过Thread类的匿名内部类的方式创建线程
*/
public class Exe_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread=new Thread(){
public void run(){
while (true) {
System.out.println("通过创建Thread类的匿名内部类的方式创建线程");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
};
thread.start();
}
}运行结果:
通过创建实现了Runnable接口的匿名内部类的方式创建线程
/*
通过创建实现了Runnable接口的匿名内部类的方式创建线程
*/
public class Exe_06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 0;
while(true) {
System.out.println("通过创建实现了Runnable接口的匿名内部类的方式创建线程" + count++);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
//启动线程
thread.start();
}
}
对比:上面两种方法
继承Thread,直接使用this就表示当前线程的引用。
实现Runnable接口,this表示的是MyRunnbale的引用,需要使用Thread类来调用
3、通过lambda的方式创建线程
public class Exe_07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread=new Thread(()-> {
int count=0;
while(true){
count++;
System.out.println("通过lambda表达式的方式创建一个线程"+count);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
//启动线程
thread.start();
}
}
2、多线程的优势
多线程的优势--增加运行速度
多线程就是为了能够充分的利用CPU的资源,提升程序运行效率。
需求场景:
分别对两个变量做累加100亿次操作
一种是单线程执行,一种是两条线程并发操作。
/*多线程的优势-增加运行速度
分别对两个变量做100亿次累加操作
*/
public class Exe_08 {
private static long count=10_0000_0000l;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//串行方式
serial();
//并行方式
concurrency();
}
private static void concurrency() {
//记录开始时间
long begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建线程,在单个线程中执行对一个变量的累加
Thread t1=new Thread(()->{
long a=0l;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
a++;
}
});
Thread t2=new Thread(()->{
long b=0l;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
b++;
}
});
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
//等待
try {
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//记录结束时间
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
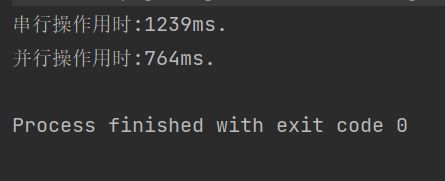
System.out.println("并行操作用时:"+(end-begin)+"ms.");
}
private static void serial(){
//记录开始时间
long begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
long a=0l;
//对变量进行累加
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
a++;
}
long b=0l;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
b++;
}
//累加完成之后记录结束时间
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("串行操作用时:"+(end-begin)+"ms.");
}
}运行结果:
结论:多线程的使用可以明显的提高程序的运行效率,充分利用CPU的资源。