golang程序启动流程详解
golang程序启动流程详解
环境
go1.16.5 linux/amd64
用例
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(42)
}
编译
-gcflags “-N -l”: 关闭优化和内联,方便调试跟踪
$ go build -gcflags "-N -l" -o hello hello.go
gdb跟踪执行流程
$ gdb hello
$ source /usr/lib/go/src/runtime/runtime-gdb.py # 加载Go运行时支持
预备知识:
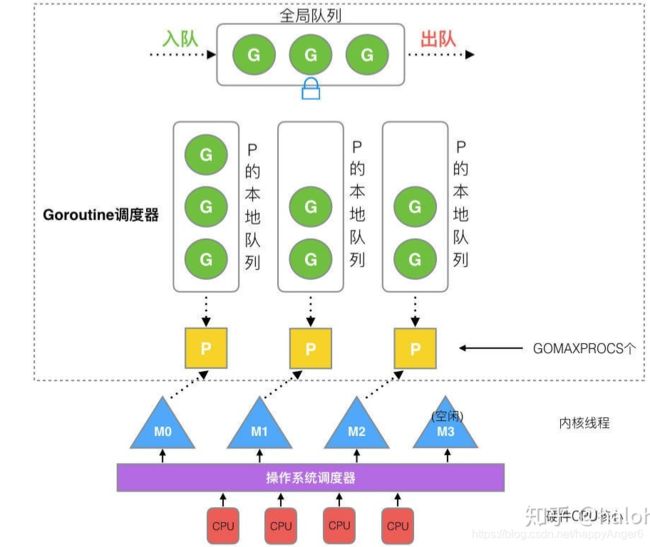
1. GMP调度模型
- Golang的调度器模型是"GMP"模型,P作为逻辑cpu的抽象,解决了竞争全局队列等问题.
- M是操作系统线程,M必须关联到某个P上,从P上获取工作goroutine
- 一个P可能有多个M,当某个M阻塞时.
2. runtime/proc.go中定义了一些重要的全局符号,下面分析启动流程会涉及这些符号:
var (
m0 m // 第一个m
g0 g // 第一个goroutine
mcache0 *mcache // m0的cache
raceprocctx0 uintptr // 用于竞争检测
)
- g0: 主线程上的第一个协程g0, g0拥有这个线程的系统栈,这个栈很大.g0还有创建新协程的职责,当我们调用go func创建新协程都会在g0的栈上执行.
- m0: 第一个工作线程,主线程
- mcache0: m0的cache
3. tls线程私有存储
每个线程的私有存储空间,golang主要用其来设置每个m当前正在运行的goroutine,这样可以快速获取到当前上下文的goroutine. 类似于linux内核中的current宏.
4. sched全局结构
golang使用一个全局schedt结构来控制全局调度(runtime2.go),里面主要的信息如全局运行队列,所有m,所有p的状态信息,系统监控sysmon等
var (
allm *m
gomaxprocs int32
ncpu int32
forcegc forcegcstate
sched schedt
newprocs int32
// allpLock protects P-less reads and size changes of allp, idlepMask,
// and timerpMask, and all writes to allp.
allpLock mutex
// len(allp) == gomaxprocs; may change at safe points, otherwise
// immutable.
allp []*p
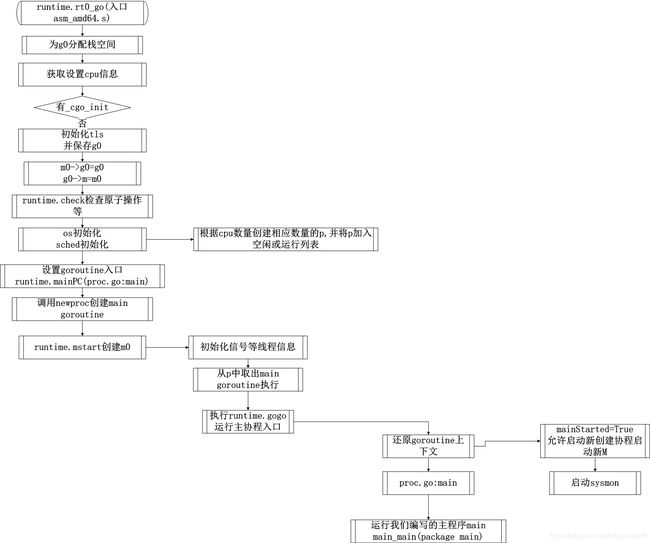
程序入口函数:
- 为g0分配栈空间
runtime.asm_amd64.s:89
TEXT runtime·rt0_go(SB),NOSPLIT,$0
// copy arguments forward on an even stack
MOVQ DI, AX // x64上使用rdi,rsi传递入参, di:argc si:argv
MOVQ SI, BX // argv
SUBQ $(4*8+7), SP // 开辟栈空间,用于存放argc, argv和两个局部变量
ANDQ $~15, SP //与~15& 保障SP 16字节对齐
MOVQ AX, 16(SP) // 存储argc, argv
MOVQ BX, 24(SP) //
MOVQ $runtime·g0(SB), DI // 将g0存储到DI寄存器
LEAQ (-64*1024+104)(SP), BX // 为g0开辟64kb栈空间
MOVQ BX, g_stackguard0(DI) // 将栈底地址保存到g0->stackguard0
MOVQ BX, g_stackguard1(DI)
MOVQ BX, (g_stack+stack_lo)(DI) // 将栈底保存到g0->stack->lo
MOVQ SP, (g_stack+stack_hi)(DI) // 将栈顶保存到g0->stack->hi
// 下面是g0的结构:
type g struct {
// Stack parameters.
// stack describes the actual stack memory: [stack.lo, stack.hi).
// stackguard0 is the stack pointer compared in the Go stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard normally, but can be StackPreempt to trigger a preemption.
// stackguard1 is the stack pointer compared in the C stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard on g0 and gsignal stacks.
// It is ~0 on other goroutine stacks, to trigger a call to morestackc (and crash).
stack stack // offset known to runtime/cgo
stackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblink
stackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink
- 获取cpu相关信息
// find out information about the processor we're on
MOVL $0, AX // 获取CPUID信息
CPUID
MOVL AX, SI // 我本机获取到的cpuid为0xd
CMPL AX, $0 //判断是否获取到了cpuid,成功
JE nocpuinfo
// 判断cpu的型号,并设置标志,如是否是intel.
// 主要是需要确定RDTSC的获取方式,即cpu时间戳计数器
CMPL BX, $0x756E6547 // "Genu" 正式版 o
JNE notintel
CMPL DX, $0x49656E69 // "ineI"
JNE notintel
CMPL CX, $0x6C65746E // "ntel"
JNE notintel
MOVB $1, runtime·isIntel(SB) //is inel
MOVB $1, runtime·lfenceBeforeRdtsc(SB) //
...
- 初始化tls,设置m->g0, g0->m,初始化sched信息
MOVQ _cgo_init(SB), AX // 查看是否有_cgo_init,如果有则需要调用,我们的例子中没有_cgo_init
TESTQ AX, AX
JZ needtls //设置tls
...
LEAQ runtime·m0+m_tls(SB), DI //获取m0中的tls结构
CALL runtime·settls(SB) // 调用sys_linux_amd64.s:658来设置tls, linux上设置tls主要是通过arch_pcrtl实现,设置当前线程的FS信息.
// store through it, to make sure it works
get_tls(BX) //下面代码主要测试tls是否正确工作.
MOVQ $0x123, g(BX)
MOVQ runtime·m0+m_tls(SB), AX
CMPQ AX, $0x123
JEQ 2(PC)
CALL runtime·abort(SB)
...
// set the per-goroutine and per-mach "registers"
get_tls(BX)
LEAQ runtime·g0(SB), CX // 将g0保存到tls中
MOVQ CX, g(BX) // save g0 to tls
LEAQ runtime·m0(SB), AX // ax -->m0
// save m->g0 = g0
MOVQ CX, m_g0(AX) //将g0保存到m0中
// save m0 to g0->m
MOVQ AX, g_m(CX) // 将m0设置到g0中
CLD // convention is D is always left cleared
CALL runtime·check(SB) //runtime1.go:137 检查一些cas和原子操作工作是否正确
MOVL 16(SP), AX // 获取之前保存到栈中的argc, argv
MOVL AX, 0(SP)
MOVQ 24(SP), AX // copy argv
MOVQ AX, 8(SP)
CALL runtime·args(SB) //runtime1.go:61 设置argc, argv到全局变量runtime1.argc, runtime1.argv
CALL runtime·osinit(SB) //301 os初始化,根据cpu亲和性获取可用cpu个数,获取大页信息
CALL runtime·schedinit(SB) //600 sched初始化,这是一个go函数,先来看一下。
type m struct {
g0 *g // goroutine with scheduling stack
...
tls [6]uintptr // thread-local storage (for x86 extern register)
sched初始化
sched内容比较多,我们详细来看一下:
_g_ := getg() // 获取当前的goroutine, 之前已经保存在tls中了,getg就是从tls中获取
if raceenabled {
_g_.racectx, raceprocctx0 = raceinit()
}
sched.maxmcount = 10000 //设置最大m线程个数为10000
// The world starts stopped.
worldStopped()
stackinit() // 栈缓存初始化,golang运行时需要分配栈时优先使用缓存
mallocinit() // 内存管理初始化
fastrandinit() // must run before mcommoninit, 快速随机数初始化
mcommoninit(_g_.m, -1) // m初始化并将其放到全局allm链表中
cpuinit() // must run before alginit, cpu初始化
alginit() // maps must not be used before this call
modulesinit() // provides activeModules
typelinksinit() // uses maps, activeModules
itabsinit() // uses activeModules
sigsave(&_g_.m.sigmask) // 保存当前信号掩码到m
initSigmask = _g_.m.sigmask
goargs()
goenvs()
parsedebugvars()
gcinit() // 初始化gc
lock(&sched.lock)
sched.lastpoll = uint64(nanotime())
procs := ncpu
if n, ok := atoi32(gogetenv("GOMAXPROCS")); ok && n > 0 { //环境变量是否设置了GOMAXPROCS
procs = n
}
if procresize(procs) != nil { // 重新调整p的数量.
throw("unknown runnable goroutine during bootstrap")
}
unlock(&sched.lock)
// World is effectively started now, as P's can run.
worldStarted()
...
sched初始化就完成了,主要就是一些全局信息,包括内存,栈缓存,P的个数,gc等.
再回到汇编:
- 设置g0主协程入口函数runtime.mainPC,调用newproc创建协程
CALL runtime·schedinit(SB) //600
// create a new goroutine to start program
MOVQ $runtime·mainPC(SB), AX // 新goroutine的入口函数
PUSHQ AX // 压入栈中下面传递给newproc
PUSHQ $0 // arg size
CALL runtime·newproc(SB) // 创建新的p,这也是一个go函数,重点分析一下.
POPQ AX
POPQ AX
// start this M
CALL runtime·mstart(SB) //mstart loop
CALL runtime·abort(SB) // mstart should never return
RET
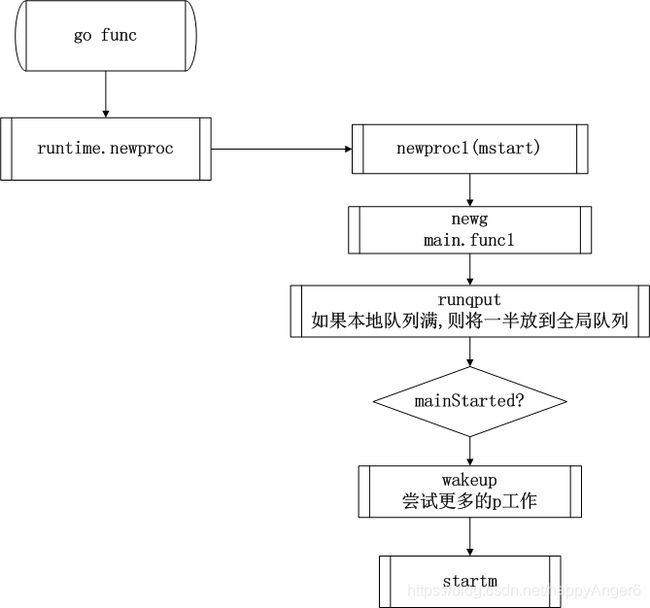
newproc:
- 创建主协程并将其放到p的本地队列中,systemstack函数表示在系统栈上执行goroutine的创建操作
argp := add(unsafe.Pointer(&fn), sys.PtrSize) // 获取argp
gp := getg() // 获取当前goroutine
pc := getcallerpc()
systemstack(func() { // 调用systemstack来执行
newg := newproc1(fn, argp, siz, gp, pc)
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr()
runqput(_p_, newg, true)
if mainStarted {
wakep()
}
})
systemstack
TEXT runtime·systemstack(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-8
MOVQ fn+0(FP), DI // DI = fn, 将要执行的函数指针放到rdi.
get_tls(CX) // 获取当前goroutine
MOVQ g(CX), AX // AX = g, g0
MOVQ g_m(AX), BX // BX = m, m0
CMPQ AX, m_gsignal(BX) //判断当前goroutine是否是用于处理信号的goroutine
JEQ noswitch
MOVQ m_g0(BX), DX // DX = g0
CMPQ AX, DX // 判断当前goroutine是否是当前栈的使用者
JEQ noswitch // 如果是则不需要切换栈, 这里明显是,因此直接跳转到noswitch
CMPQ AX, m_curg(BX)
JNE bad
noswitch:
// already on m stack; tail call the function
// Using a tail call here cleans up tracebacks since we won't stop
// at an intermediate systemstack.
MOVQ DI, DX
MOVQ 0(DI), DI // di是之前传递给systemstack的fn
JMP DI // 执行fn
systemstack(func() {
newg := newproc1(fn, argp, siz, gp, pc) //创建新goroutine执行fn
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr()
runqput(_p_, newg, true)
if mainStarted {
wakep()
}
})
newproc1:
newproc1的作用是为执行函数分配新的goroutine
func newproc1(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
_g_ := getg() // 获取当前g
if fn == nil {
_g_.m.throwing = -1 // do not dump full stacks
throw("go of nil func value")
}
acquirem() // 锁定m,禁止抢占
siz := narg
siz = (siz + 7) &^ 7
_p_ := _g_.m.p.ptr() // 获取当前的p
newg := gfget(_p_) // 查找是否有缓存的goroutine,这些goroutine是dead状态的,可以直接使用的.如果本地没有还会从全局查找,最后都没有才会真的申请新的goroutine
if newg == nil { // 当前没有可重复使用的缓存gorutine
newg = malg(_StackMin) // 申请新的goroutine
casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead) // 初始状态为Gdead.
allgadd(newg) // 将newg加入全局allg
}
/*为newg 准备栈和参数*/
totalSize := 4*sys.RegSize + uintptr(siz) + sys.MinFrameSize // extra space in case of reads slightly beyond frame
totalSize += -totalSize & (sys.SpAlign - 1) // align to spAlign
sp := newg.stack.hi - totalSize
spArg := sp
if usesLR {
// caller's LR
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = 0
prepGoExitFrame(sp)
spArg += sys.MinFrameSize
}
...
/*设置newg的sp, pc, g, startpc等 信息*/
newg.sched.sp = sp
newg.stktopsp = sp
newg.sched.pc = funcPC(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum // +PCQuantum so that previous instruction is in same function
newg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn)
newg.gopc = callerpc
newg.ancestors = saveAncestors(callergp)
newg.startpc = fn.fn
casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, _Grunnable) // 修改newg状态为runnable
if _p_.goidcache == _p_.goidcacheend {
// Sched.goidgen is the last allocated id,
// this batch must be [sched.goidgen+1, sched.goidgen+GoidCacheBatch].
// At startup sched.goidgen=0, so main goroutine receives goid=1.
_p_.goidcache = atomic.Xadd64(&sched.goidgen, _GoidCacheBatch)
_p_.goidcache -= _GoidCacheBatch - 1
_p_.goidcacheend = _p_.goidcache + _GoidCacheBatch
}
newg.goid = int64(_p_.goidcache) // 设置goroutie id.
_p_.goidcache++
...
创建好新的goroutine后,继续:
systemstack(func() {
newg := newproc1(fn, argp, siz, gp, pc) //创建新goroutine执行fn
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr() // 获取新routine的p.
runqput(_p_, newg, true) // 将新routine放入运行队列. 首先尝试放入本地队列,如果本地队列满则放入全局队列.本地队列最大256.
if mainStarted {
wakep()
}
})
新goroutine创建完成,再启动一个m,这个m目前是主线程,即m0
CALL runtime·newproc(SB)
POPQ AX
POPQ AX
// start this M
CALL runtime·mstart(SB) //调用mstart启动m
CALL runtime·abort(SB) // mstart should never return
RET
初始化m0,设置线程id
func minit() {
minitSignals() // 初始化信号处理,设置信号处理栈和掩码
// Cgo-created threads and the bootstrap m are missing a
// procid. We need this for asynchronous preemption and it's
// useful in debuggers.
getg().m.procid = uint64(gettid()) //设置m的procid,即线程id
}
- m0,g0都初始化完成后就开始执行主协程,这时通过汇编代码gogo执行主协程
TEXT runtime·gogo(SB), NOSPLIT, $16-8
MOVQ buf+0(FP), BX // gobuf
MOVQ gobuf_g(BX), DX
MOVQ 0(DX), CX // make sure g != nil
get_tls(CX)
MOVQ DX, g(CX)
MOVQ gobuf_sp(BX), SP // restore SP
MOVQ gobuf_ret(BX), AX
MOVQ gobuf_ctxt(BX), DX
MOVQ gobuf_bp(BX), BP
MOVQ $0, gobuf_sp(BX) // clear to help garbage collector
MOVQ $0, gobuf_ret(BX)
MOVQ $0, gobuf_ctxt(BX)
MOVQ $0, gobuf_bp(BX)
MOVQ gobuf_pc(BX), BX // 执行之前的runtime.mainPC,即主协程入口
JMP BX
- 执行主协程入口proc.go: main
主协程会启动sysmon线程进行监控,然后执行package main里我们实现的main函数
...
mainStarted = true // 设置main开始标志,这样才允许新协程启动新的M.
if GOARCH != "wasm" { // no threads on wasm yet, so no sysmon
// For runtime_syscall_doAllThreadsSyscall, we
// register sysmon is not ready for the world to be
// stopped.
atomic.Store(&sched.sysmonStarting, 1)
systemstack(func() {
newm(sysmon, nil, -1) // 启动sysmon
})
...
fn := main_main // 执行package main中主函数
fn()
上面就是一个go程序的启动流程,总结一下:
我们再来分析一下调用go func创建协程的流程
- go func关键字会被编译器转换为runtime.newproc调用创建新协程
- 新协程加入当前p的本地队列
- 如果本地队列已满,则批量将一半的goroutine放入全局队列
- 之前主协程已经设置了mainStarted标志,因此会调用wakeup尝试唤醒更多空闲的p来工作