JDK定时线程池源码解读
最近在研究线程池的底层原理时,忽然想起来之前遇到的一个面试题:“你可以自己手写一个可定时的线程池吗?” 转念一想,spring的定时任务不就是干这个的吗?所以当时想的是采用Timer的方式去处理,面试官不是很满意,反问:“Timer的底层有了解过吗?”场面陷入尴尬,犹豫了一会儿,只能红着脸败下阵来。
JDK自带的线程池有四种,大家耳熟能详。其中固定长度、缓存以及单例的实现方案对比定时线程池较为简单,大家可以自行研究。本文主要分享记录帝都的雁在研究定时线程池源码时的一些思路和理解。
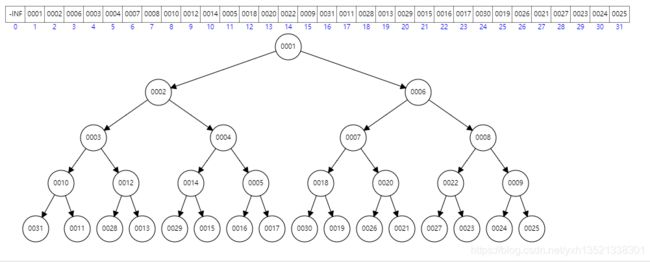
分享之前,需要脑补一些数据结构的知识。Java开发好几年了,最近才搞清楚,堆的数据结构,居然是个数组!我一直以为它是树状结构,但老牌程序猿的思维就是不一样,它利用数组存在下标,将堆的特性通过下标进行计算,得出其父子节点之间的关系。
一、堆的简单了解
堆,分为两种,小堆顶和大堆顶。
小堆顶,即自上而下遵循一个原则,上级永远不大于下级,而大堆顶刚好相反。
同时,堆的下标遵循原则: n为当前节点的下标,则
父节点: (n-1)/2
右子节点: 2n+1
左子节点: 2n-1
添加或删除元素时,通过这些关系来进行对堆进行换位操作,保证堆的稳定即可。
二、Executors.newScheduledThreadPool
JDK自带的创建定时任务的线程池,其参数只有一个,核心线程数。
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor则是ThreadPoolExecutor的一个子类,其封装调用了父类的构造(JDK自带的四个线程池都是这么玩的)。
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,new DelayedWorkQueue())可以看出,最大线程数为无界,所以阿里代码规范中提出,这个线程池可能会因为线程创建无上限而导致OOM,慎用。
DelayedWorkQueue则为它的队列,这也是本文要重点研究的对象,因为Timer也是沿用了DelayedWorkQueue的设计思想。
三、DelayedWorkQueue
DelayedWorkQueue是阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)的一个实现类,即存入队列时,存不进去就会使线程阻塞直到队列有空位,从队列取数据取不到时也会阻塞线程直到队列有数据。
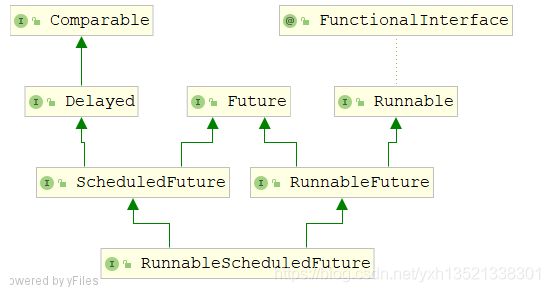
其内部维护了一个RunnableScheduledFuture的小堆顶,故其增删和扩容是严格遵循堆的原则
由类图可知,RunnableScheduledFuture是一个线程的任务,也遵循Future模式。
若有猿友对DelayedWorkQueue的增删感兴趣,可自行研究一下,本质上就是通过对数组下标指针指向关系的变动,实现对应元素的换位比较,使得更小的元素上升,更大的元素下沉。
四、执行定时任务的方法
定时任务线程池有两个执行定时任务的方法
1、scheduleAtFixedRate(任务,初始化延时时间,频率间隔,时间单位)
按照固定频率执行定时任务,线程池启动后,在经过初始化延时时间后,执行运行任务,不管任务是否执行完,都会在频率间隔的时间点定时去再次执行此任务。
2、scheduleWithFixedDelay(任务,初始化延时时间,任务间隔,时间单位)
按照固定频率执行定时任务,线程池启动后,在经过初始化延时时间后,执行运行任务,当任务执行结束后,间隔任务间隔的时间后,再次执行此任务。
五、定时任务是怎么做到按照频率执行呢?
我们以scheduleAtFixedRate为例,查看它的源码。
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 将任务封装
ScheduledFutureTask sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
// 延时执行
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
} 在其内部源码中,任务被封装为ScheduledFutureTask,其为Runnable的一个实现类,我们可以先看看它的run方法。
public void run() {
boolean periodic = isPeriodic();
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic))
cancel(false);
else if (!periodic)
ScheduledFutureTask.super.run();
// ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset() 执行本次任务的业务代码
else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
// 任务续期
setNextRunTime();
// 任务重新投递
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}它会先通过ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset(),执行真正的任务代码(Callbale模式),然后重置自身的时间属性,更新为下次要执行的时间点,最后将任务再次投递至任务队列。
这是它重新投递定时任务的方法
void reExecutePeriodic(RunnableScheduledFuture task) {
if (canRunInCurrentRunState(true)) {
// 让任务添加至眼神队列的堆中
super.getQueue().add(task);
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(true) && remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
// 预热启动
ensurePrestart();
}
}先将任务放入延时阻塞队列的堆中,然后执行ensurePrestart()方法。到此我们再回到线程池执行定时任务方法内部
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
} 任务被封装好后,执行delayedExecute
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture task) {
if (isShutdown())
reject(task);
else {
super.getQueue().add(task);
if (isShutdown() &&
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
ensurePrestart();
}
}对比发现和ScheduledFutureTask内部的run几乎如出一辙,都是将任务加入队列并执行ensurePrestart。
void ensurePrestart() {
int wc = workerCountOf(ctl.get());
// 判断活跃线程数是否达到核心线程数
if (wc < corePoolSize)
addWorker(null, true);
else if (wc == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
ensurePrestart中则是先去判断当前线程池的活跃线程数量是否达到核心线程数,若未达到,则会将当前线程当做核心线程运行,使用完,放入线程池中。addWorker方法中,把提交的任务又封装为Worker对象,Worker也是Runnable的实现类
其run方法中通过AQS和Lock的方式在保证线程安全的情况下执行此次的延时任务。
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
// getTask()从延时队列中获取任务
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
// 本质上是在执行封装任务后的ScheduledFutureTask
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// Are workers subject to culling?
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
try {
// 从队列获取任务ScheduledFutureTask
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
六、总结流程
定时任务线程池在调用ThreadPoorExecutor的构造方法时,采用延时工作队列DelayedWorkQueue来当做自己存放任务的队列。
DelayedWorkQueue底层采用小堆顶实现,即内部的维护了RunnableScheduledFuture[],即time小的任务下标也小,会先被取出。
scheduleAtFixedRate执行时,将当前的任务封装为ScheduledFutureTask,ScheduledFutureTask内部维护了一个属性time,用于记录距离执行的时间戳;然后又被封装为RunnableScheduledFuture,作为参数传入delayedExecute方法。
delayedExecute()中将RunnableScheduledFuture任务放入DelayedWorkQueue队列中,然后执行ensurePrestart()方法。
ensurePrestart()判断当前线程池中活跃线程数量是否达到核心线程数,若未达到,则当前线程作为核心线程。之后调用addWorker(),增加工作的线程。
addWorker中任务被封装为Worker对象,Worker又是Runnbale的实现类。其run方法中通过getTask()从工作队列DelayedWorkQueue获取要执行的任务。然后执行task.run(),而此时的task为RunnableScheduledFuture封装的ScheduledFutureTask。
ScheduledFutureTask的run()中先调用ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()执行任务代码,再调用setNextRunTime()修改自身的time,将其时间延长至下次执行时间;然后调用reExecutePeriodic()将任务再次投递至改针对了中,同时调用ensurePrestart()回到第五步,实现定时循环的执行。
七、流程图
欢迎大家和帝都的雁积极互动,头脑交流会比个人埋头苦学更有效!共勉!
公众号:帝都的雁
![]()