10X空间转录组和单细胞转录组都在如火如荼的进行当中,单细胞提供了单个细胞的精度来研究组织,而空间转录组则是提供了细胞类型在组织中的具体位置,精度和空间位置几乎具有同等的研究价值,而两种技术上的联合分析正是优势互补的选择,而且也是一种挑战。目前联合分析的方法已经有了好几个,包括Seurat、scanpy等,但目前而言,利用的情况很少,今天我们来分享一下一种新的联合分析方法----cell2location。文献在这里Comprehensive mapping of tissue cell architecture via integrated single cell and spatial transcriptomics,今天我们的任务就是来参透这个方法,首先我们来分享文献。
Abstract
组织中细胞类型的空间位置从根本上塑造了细胞之间的相互作用和功能,but the high-throughput spatial mapping of complex tissues remains a challenge。We present сell2location, a principled and versatile Bayesian model(贝叶斯模型) that integrates single-cell and spatial transcriptomics to map cell types in situ in a comprehensive manner。在准确性和全面性的方面,cell2location的表现优异,In the mouse brain, we use a new paired single nucleus and spatial RNA-sequencing dataset to map dozens of cell types and identify tissue regions in an automated manner。We discover novel regional astrocyte subtypes including fine subpopulations in the thalamus and hypothalamus(新的发现)。In the human lymph node, we resolve spatially interlaced immune cell states and identify co-located groups of cells underlying tissue organisation.(细胞共定位)。我们在空间上绘制罕见的萌发前中心B细胞种群,并预测与干扰素反应相关的推定细胞相互作用。总之方法很好用。
这里我们需要注意的一点就是,贝叶斯模型,这个模型在建模的时候很常用,这里就不多介绍了,推荐大家看一本书《机器学习原理、算法与应用》,书中讲述了很多有关机器学习的算法和基础知识,有利于我们加深生信分析的算法原理。
Introduction
The cellular architecture of tissues, where distinct cell types are organized in space, underlies cell-cell communication, organ function and pathology.(组织是一个复杂的统一体)。Emerging spatial genomics technologies hold considerable promise for characterising tissue architecture, providing key opportunities to map resident cell types and cell signalling in situ, thereby helping guide in vitro tissue engineering efforts.(空间转录组的主要应用价值)。但是空间转录组仍然存在挑战,One reason is the enormous variation in tissue architecture across organs, ranging from the brain with hundreds of cell types found across discrete anatomical regions to immune organs with continuous cellular gradients and dynamically modified microenvironments。To create and map comprehensive tissue atlases, experimental and computational methods need to be aligned to cope with this variation and in particular, enable mapping numerous resident cell types across diverse and complex tissues in situ.(技术挑战)。
coupled single-cell and spatially resolved transcriptomics offer a scalable approach to address these challenges(单细胞和空间转录组的技术互补)。首先第一步要从解离的组织中识别各种细胞类型(单细胞转录组),然后匹配各个细胞类型的空间位置分布。目前的挑战是First, spatial RNA-seq measurements (i.e. locations) combine multiple cell types as array-based mRNA capture currently do not match cellular boundaries in tissues. Thus, each spatial position corresponds to either several cell types (Visium, Tomo-Seq) or fractions of multiple cell types (Slide-Seq, HDST). Second, spatial RNA-seq measurements are confounded by different sources of variation as 1) cell numbers vary across tissue positions, 2) different cells and cell types differ in total mRNA content, and 3) thin tissue sectioning captures variable fractions of each cell’s volume. Computational approaches need to appropriately model and account for all of these factors。
Here, we present cell2location, a principled and versatile Bayesian model for comprehensive mapping of cell types in spatial transcriptomic data.(我们关注的重点)Cell2location uses reference gene expression signatures of cell types derived from scRNA-seq to decompose multi-cell spatial transcriptomic data into cell type abundance maps(简单的原理与其他方法相同,算法有差异)。The model accurately maps complex tissues, including rare cell types and fine subtypes, and it identifies tissue regions and co-located cell types downstream in an automated manner(能够识别共定位的细胞类型,这个很重要)。下面是两个应用案例,证明这个方法好。
Result
(1)Cell2location: a Bayesian model for spatial mapping of cell types
Cell2location maps the spatial distribution of cell types by integrating single-cell RNAseq (scRNA-seq) and multi-cell spatial transcriptomic data from a given tissue。
从原理图上来看,单细胞作为参考,匹配细胞类型的空间位置,这个方向无可改变。
首先第一步:利用模型估计单细胞数据的细胞类型的表达特征。例如,通过使用常规聚类来识别细胞类型和亚群,然后估算平均聚类基因表达谱而获得的结果(如下图)
第二步:cell2location decomposes mRNA counts in spatial transcriptomic data using these reference signatures, thereby estimating the relative and absolute abundance of each cell type at each spatial location。(分解数据)。
Cell2location被实现为可解释的分层贝叶斯模型,thereby (1) providing principled means to account for model uncertainty, (2) accounting for linear dependencies in cell type abundances, (3) modelling differences in measurement sensitivity across technologies, and (4) accounting for unexplained/residual variation by employing a flexible count-based error model. Finally, (5) cell2location is computationally efficient, owing to variational approximate inference and GPU acceleration。(这些方法我们下一篇分享解析)。
To validate cell2location, we initially used simulated data that reflects diverse cell abundance and spatial patterns。(作者模拟了空间转录组数据)。
这里我们需要注意的是Jensen–Shannon divergence,也就是J-S散度,数学的内容我们下面讲解。
Briefly, we simulated a spatial transcriptomics dataset with 2,000 locations, based on reference cell-type annotations obtained from a mouse brain snRNA-seq reference dataset including 46 cell types,Multi-cell gene expression profiles at each location were derived by combining cells drawn from different reference cell types, using one of four cell abundance patterns with variable density and sparsity distribution that mimics the patterns observed in real data。然后运用cell2location进行分析,得到图中的结果。基本上有很高的相关性,但是这里有一个问题,那就是模拟的空间转录组数据是依据单细胞数据合并而来,一旦真正的空间转录组数据含有某些单细胞不存在的细胞类型(比如说技术壁垒,10X单细胞捕获中性粒细胞结果很差),那么预测的结果很可能出现错误,我们往后看看,是否作者提到这个问题。
Next, we compared cell2location to recently proposed alternative methods for the inference of relative cell-type abundance from spatial transcriptomics。一样的文献结果,自己的软件表现最好。并且该模型还产生了相对细胞类型丰度的更准确估计。
这里我们需要注意的是,PR曲线,这些数学上的问题我们下面讲解。
cell2location not only provides estimates of relative cell type fractions but additionally estimates absolute cell type abundance, which can be interpreted as the number of cells that express a reference cell type signature at a given location, which again were highly concordant with the simulated ground truth(估计细胞数量,这个也很重要)。
总之,these results support that cell2location can accurately estimate cell abundance across diverse cell types.
然后文章用了两个例子,运用该软见解决我们的联合分析问题。具体案例我们这里就不多说了,我们需要更多的是算法的原理。
我们首先解决一下J-S散度和PR曲线。
Jensen-Shannon divergence(J-S散度) is a method of measuring the similarity between two probability distributions。这个我们需要先知道一下KL散度。
KL散度又称为相对熵,信息散度,信息增益。KL散度是是两个概率分布P和Q 差别的非对称性的度量。 KL
散度是用来 度量使用基于Q的编码来编码来自P的样本平均所需的额外的位元数。 典型情况下,P表示数据的真实分布,Q表示数据的理论分布,模型分布,或P的近似分布。
定义如下:
因为对数函数是凸函数,所以 KL散度的值为非负数。
-
JS散度(Jensen-Shannon)
JS散度度量了两个概率分布的相似度,基于KL散度的变体,解决了KL散度非对称的问题。一般地,JS散度是对称的,其取值是0到1之间。定义如下:
图片.png
也就是图B 的结果。
PR曲线
相对于PR曲线,ROC曲线了解的更多一些,大家可以参考我关于ROC曲线的讲解深入理解R包AUcell对于分析单细胞的作用.
而PR曲线
PR曲线实则是以precision(精准率)和recall(召回率)这两个为变量而做出的曲线,其中recall为横坐标,precision为纵坐标。
那么问题来了,什么是精准率?什么是召回率?这里先做一个解释。
在二分类问题中,分类器将一个实例的分类标记为是或否,可以用一个混淆矩阵来表示,如下图所示。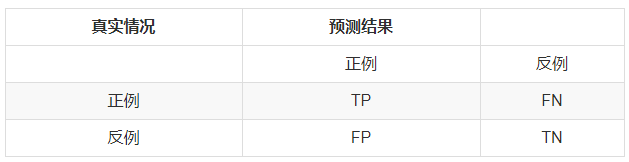 image
image注:把正例正确地分类为正例,表示为TP(true positive),把正例错误地分类为负例,表示为FN(false negative)。
把负例正确地分类为负例,表示为TN(true negative), 把负例错误地分类为正例,表示为FP(false positive)。
【举个栗子:A是只猫(正例),B是只仓鼠(负例),A在二分类中被划分为猫则为TP,被划分为仓鼠则为FN。B在二分类中被划分为仓鼠则为TN,被划分为猫则为。】
从混淆矩阵可以得出精准率与召回率:precision = TP/(TP + FP), recall = TP/(TP +FN)(注意:分子相同。)接下来补充一个重点:
一条PR曲线要对应一个阈值。通过选择合适的阈值,比如50%,对样本进行划分,概率大于50%的就认为是正例,小于50%的就是负例,从而计算相应的精准率和召回率。举个例子如下:(true这列表示正例或者负例,hyp这列表示阈值0.5的情况下,概率是否大于0.5)
 image
image那么根据这个表格我们可以计算:TP=6,FN=0,FP=2,TN=2。故recall=6/(6+0)=1,precison=6/(6+2)=0.75,那么得出坐标(1,0.75)。同理得到不同阈下的坐标,即可绘制出曲线。
PR曲线如下: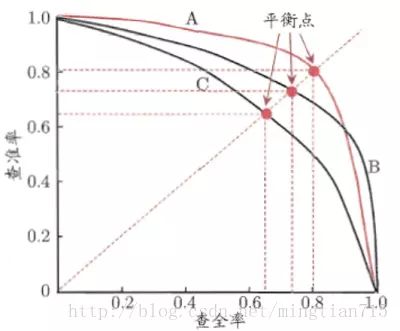 image
image如果一个学习器的P-R曲线被另一个学习器的P-R曲线完全包住,则可断言后者的性能优于前者,例如上面的A和B优于学习器C。但是A和B的性能无法直接判断,我们可以根据曲线下方的面积大小来进行比较,但更常用的是平衡点或者是F1值。平衡点(BEP)是P=R时的取值,如果这个值较大,则说明学习器的性能较好。而F1 = 2 * P * R /( P + R ),同样,F1值越大,我们可以认为该学习器的性能较好。
部分资料参考:二战周志华《机器学习》-PR曲线和ROC曲线
P-R曲线深入理解
两种曲线我们都需要了解一下,以免以后遇到不知道就尴尬了~~~
接下来我们来看cell2location的模型。
模型的简单介绍
For a complete derivation of the cell2location model, please see supplementary computational methods. Briefly, cell2location is a Bayesian model, which estimates absolute cell density of cell types by decomposing mRNA counts s,g of each gene = {1, . . , } at locations = {1, . . , } into a set of predefined reference signatures of cell types gf g.For 10X Visium data, this matrix can be directly obtained from the 10X SpaceRanger software and imported into data format used in a popular python package Scanpy(利用scanpy来读取10X分析数据,也可以联合Suerat进行分析)。ds,g should be fltered to a set of genes expressed in the single cell reference g f g.这个地方的处理在于单细胞与空间转录组映射的时候,表达基因的相同。cell2location的图表模型如下图:
Let G = {gf,g}, denote an F X G matrix of reference cell type signatures, which consist of F = {1,..., F} gene expression profiles Gf,: for g = {1,...,G} genes, representing average expression of each gene in each cell type in linear mRNA counts space (not log-space).This matrix needs to be provided to cell2location and can be estimated from scRNA-seq profles.这个地方我们可以看到,对各个细胞类型的基因表达求平均值来代表这个细胞类型。Cell2location models the elements of D as Negative Binomial distributed,这个地方稍微说一下负二项分布,
负二项分布是统计学上一种离散概率分布。满足以下条件的称为负二项分布:实验包含一系列独立的实验, 每个实验都有成功、失败两种结果,成功的概率是恒定的,实验持续到r次不成功,r为[正整数]。可以参考百度百科负二项分布,不过从这里开始,开始涉及到很深的数学只是背景,本人数学不会,但没有因此而骄傲过,所以希望有数学的大牛来分享一下内容。
最后展示一下分析的结果,
看起来相当不错。大家可以尝试。