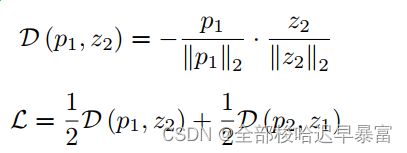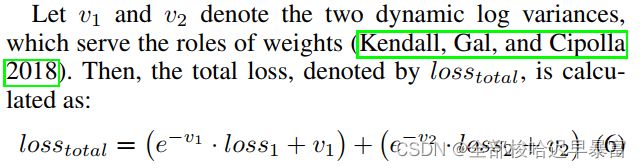几篇关于对比学习处理遥感图像的文章小结
一、背景
最近收集了几篇关于用对比学习处理遥感图像的文章。
二、对比学习做高光谱影像聚类
1. 文章连接:https://doi.org/ 10.3390/rs13214418
2. 文章摘要:
Hyperspectral image (HSI) clustering is a major challenge due to the redundant spectral information in HSIs. In this paper, we propose a novel deep subspace clustering method that extracts spatial–spectral features via contrastive learning. First, we construct positive and negative sample pairs through data augmentation. Then, the data pairs are projected into feature space using a CNN model. Contrastive learning is conducted by minimizing the distances of positive pairs and maximizing those of negative pairs. Finally, based on their features, spectral clustering is employed to obtain the final result. Experimental results gained over three HSI datasets demonstrate that our proposed method is superior to other state-of-the-art methods.
本文作者提出了一个深度子空间具类方法,该方法基于对比学习提取时空特征。首先构建正负样本。然后将数据投影到特征空间。通过最小化正样本之间的距离,最大化负样本之间的距离来实现对比学习。最后基于学习到的特征来做光谱聚类。
3. 文章介绍:
高光谱影像因为含有的冗余信息非常多,因此其分类一直精度较低,这一现象被称为Hughes现象。然而现实世界中的高光谱影像往往缺少标签数据,这对其分类研究带来了很大不便。
目前的高光谱图像主要分为两类方法,基于光谱的和基于空谱的。这些方法主要有两个步骤,即特征提取和传统聚类。
本文则基于对比学习,来做高光谱的聚类工作,具体而言,文章的贡献为:
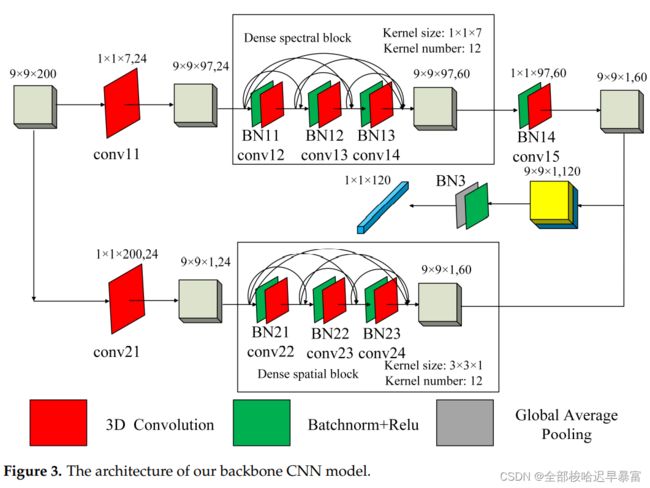
1. Inspired by DBMA and DBDA, we designed a double-branch dense spectral–spatial network for HSI clustering. These two branches can extract spectral and spatial features separately, avoiding the huge computation caused by multi-scale inputs. To reduce the computational load further, we remove the attention blocks in DBDA and DBMA. 本文设计了一个双分支浓缩的空谱网络来做高光谱影像分类。
2. We use contrastive learning to explore spatial–spectral information. We augment the image by removing the spectral information of some non-central pixels. Different methods of selecting pixels to remove spectral information can provide different augmented views of the HSI block. 使用对比学习来做表征空间-光谱信息。
3. The experimental results obtained over three publicly available HSI datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method compared to other state-of-the-art methods. 在三个高光谱数据集上的实验结果优于其他方法。
在使用对比学习对输入数据做变换的时候,为了保留输入数据的光谱信息,作者的变换方式选择为:
作者使用对比学习的模型结构为:
这里的CNN的结构都是一样的,而且是权值共享的,其具体的结构如下:
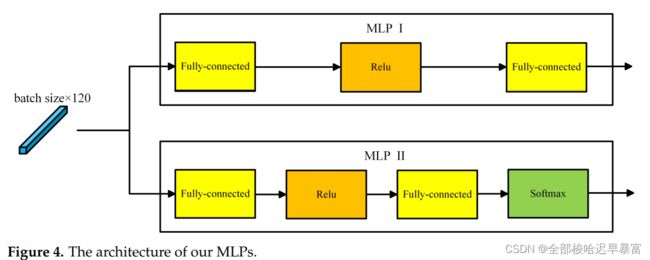
其中的MLP结构如下:
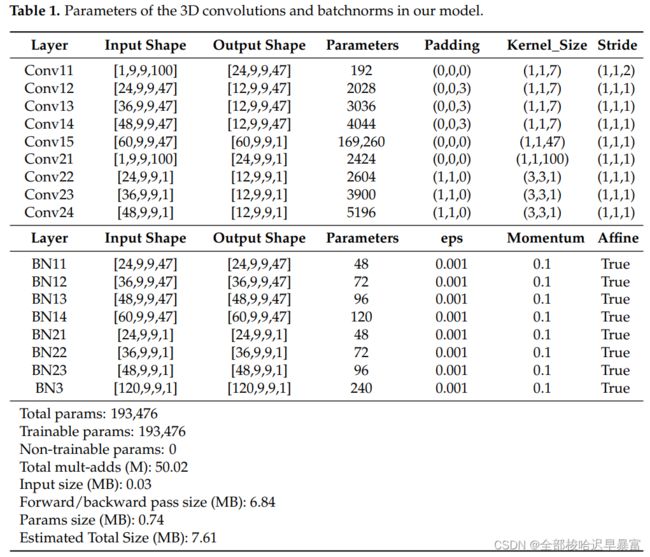
另外,在CNN中,作者使用的是3D卷积,因此每个卷积核的大小以及参数作者用表格列出:
三、对比学习寻找安第斯山脉南部的古村落
1. 文章连接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2112.06437v1.pdf
2. 文章摘要:
The detection of ancient settlements is a key focus in landscape archaeology. Traditionally, settlements were identified through pedestrian survey, as researchers physically traversed the landscape and recorded settlement locations. Recently the manual identification and labeling of ancient remains in satellite imagery have increased the scale of archaeological data collection, but the process remains tremendously time-consuming and arduous. The development of self-supervised learning (e.g., contrastive learning) offers a scalable learning scheme in locating archaeological sites using unlabeled satellite and historical aerial images. However, archaeology sites are only present in a very small proportion of the whole landscape, while the modern contrastive-supervised learning approach typically yield inferior performance on the highly balanced dataset, such as identifying sparsely localized ancient urbanization on a large area using satellite images. In this work, we propose a framework to solve this longtail problem. As opposed to the existing contrastive learning approaches that typically treat the labeled and unlabeled data separately, the proposed method reforms the learning paradigm under a semi-supervised setting to fully utilize the precious annotated data (<7% in our setting). Specifically, the highly unbalanced nature of the data is employed as the prior knowledge to form pseudo negative pairs by ranking the similarities between unannotated image patches and annotated anchor images. In this study, we used 95,358 unlabeled images and 5,830 labeled images to solve the problem of detecting ancient buildings from a long-tailed satellite image dataset. From the results, our semi-supervised contrastive learning model achieved a promising testing balanced accuracy of 79.0%, which is 3.8% improvement over state-of-theart approaches.
探寻古村落是景观考古学的关键。一般多为步行调查,目前借助于遥感影像手动标记成为主流,但这种方法费时费力。对比学习提供了一种自监督的机制,可用无标签和历史数据来定位古遗址。然而古遗址只占整个景观的一小部分,而监督学习在高度平衡的数据集中表现效果较差,比如在大区域内识别古城镇。本文提出一种框架来解决这种长尾问题,不同于现有的对比学习方法将标签和非标签数据分开,本文所提出的方法改进了半监督设置下的范式,以充分利用少量的标注数据。具体的,将高度不平衡的自然影像数据作为先验,通过排序未标记数据和已标记数据之间的相似度,来构建伪的负样本对。
3. 文章内容:
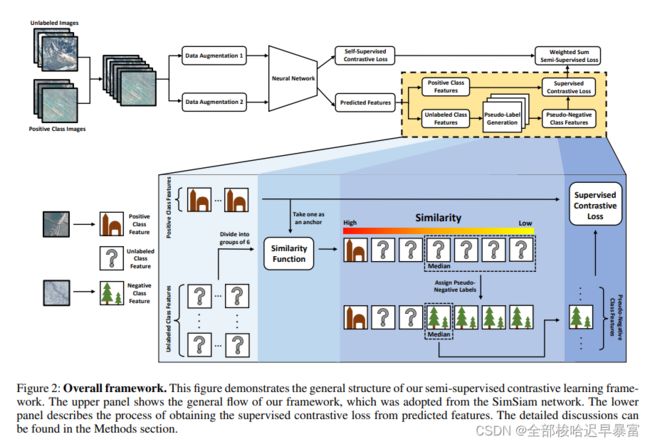
本文作者提出了一个自监督对比学习框架,来识别安第斯南部的古遗址。不同于一般自监督学习将标签和非标签数据分开建模的方法,本文使用了全局的端到端的半监督学习框架,使用高度不平衡的自然影像数据,通过排序未标记数据和已标记数据之间的相似度,来构建伪的负样本对。伪负样本被用于计算监督对比损失。
实验区域为安第斯南部,覆盖约4000km^2的面积,具体位置如下图:
影像来自于Worldview 2和Worldview 3,共有95358景未标记的数据和5830景标记的数据。总的来说,本文的主要贡献如下:
• We present a semi-supervised contrastive training framework that effectively learns from large-scale, sparsely annotated, and highly unbalanced remote sensing data.
• The highly unbalanced nature of the data is employed as the prior knowledge to form pseudo negative pairs by ranking the similarities between unannotated image patches and an-notated anchor images.
• To our knowledge, this is the first study that investigates semi-supervised contrastive learning in discovering ancient remains from aerial satellite images.
整个网络结构如下图所示,其中backbone选择的是simsiam:
伪标签合成:伪标签混合了一系列的未标记和正类别特征。首先对这一系列数据进行标准化,然后将它分为未标记的X特征和正类别的Y特征。再将X特征分为更小的子集,这里设置为16。从Y特征里面随机选择一个作为后续使用。
在每一次训练中,使用这个正类别特征,计算每个X特征子集里面特征和它的相似度。在未标记的影像中,具有中等相似度的则被用作伪标签。
文章最大的创新点在于提出了一个半监督对比学习策略。具体的说,我们在标准的余弦相似度损失里面加入了一个监督对比损失,核心部分的内容和simsiam一致:
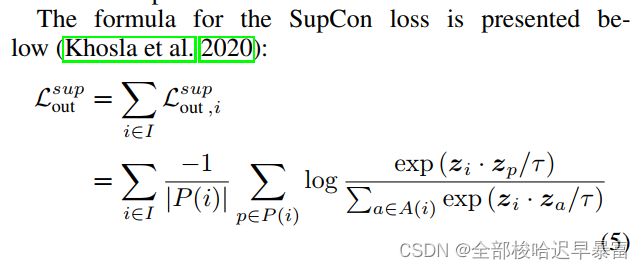
监督对比损失的定义如下:
模型的最终损失为两个损失之和: