STL特性--LIST容器解析
- LIST概念
list是C++标准模版库(STL,Standard Template Library)中的部分内容。
list实现是一个双向链表,可以高效的进行插入删除,但不能够进行随机访问。
使用list容器之前必须加上头文件:#include《list》
list属于std命名域的内容,因此需要通过命名限定:using std::list;也可以直接使用全局的命名空间方式:using namespace std;
- LIST构造函数
LIST节点的定义:
template <typename Object> struct Node {
Object object;
Node<Object> *previous;//指向前一节点
Node<Object> *next;//指向后一节点
Node(const Object&obj) :object(obj), next(NULL),previous(NULL) {}
Node():next(NULL),previous(NULL){}
};
list双向链表的原理:
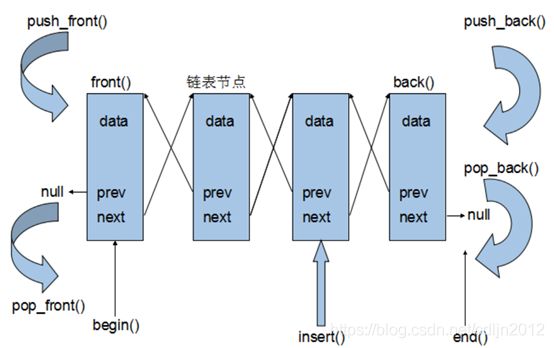
初始化:
list c0; //空链表
list c1(3); //建一个含三个默认值是0的元素的链表
list c2(5,2); //建一个含五个元素的链表,值都是2
list c4(c2); //建一个c2的copy链表
list c5(c1.begin(),c1.end()); c5含c1一个区域的元素[_First, _Last)。
- LIST成员函数
重载运算符:
operator==
operator!=
operator<
operator<=
operator>
operator>=
具体成员函数使用如下:
c.begin() 返回指向链表第一个元素的迭代器。
c.end() 返回指向链表最后一个元素之后的迭代器。
c.rbegin() 返回逆向链表的第一个元素,即c链表的最后一个数据。
c.rend() 返回逆向链表的最后一个元素的下一个位置,即c链表的第一个数据再往前的位置。
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
list<int>::iterator it;
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
list<int>::reverse_iterator it;
for(it = a1.rbegin();it!=a1.rend();it++){
cout << *it << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
c.assign(n,num) 将n个num拷贝赋值给链表c。
c.assign(beg,end) 将[beg,end)区间的元素拷贝赋值给链表c。
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
list<int> a1;
list<int>::iterator it;
a1.assign(2,10);
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.assign(a,a+5);
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
c.empty() 判断链表是否为空
c.front() 返回链表c的第一个元素。
c.back() 返回链表c的最后一个元素。
c.size() 返回链表c中实际元素的个数。
c.max_size() 返回链表c可能容纳的最大元素数量。
c.clear() 清除链表c中的所有元素。
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
if(!a1.empty()){
cout << "the first number is:" << a1.front() << endl;
cout << "the last number is:" << a1.back() << endl;
}
cout << a1.max_size() << endl;
a1.clear();
c.insert(pos,num) 在pos位置插入元素num。
c.insert(pos,n,num) 在pos位置插入n个元素num。
c.insert(pos,beg,end) 在pos位置插入区间为[beg,end)的元素。
c.erase(pos) 删除pos位置的元素。
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "insert before:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.insert(a1.begin(),0);
cout << "insert(pos,num) after:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.insert(a1.begin(),2,88);
cout << "insert(pos,n,num) after:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int arr[5] = {11,22,33,44,55};
a1.insert(a1.begin(),arr,arr+3);
cout << "insert(pos,beg,end) after:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
a1.erase(a1.begin());
cout << "erase after:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
c.push_back(num) 在末尾增加一个元素。
c.pop_back() 删除末尾的元素。
c.push_front(num) 在开始位置增加一个元素。
c.pop_front() 删除第一个元素。
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
a1.push_back(10);
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "push_back:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.pop_back();
cout << "pop_back:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.push_front(20);
cout << "push_front:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.pop_front();
cout << "pop_front:";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
resize(n) 从新定义链表的长度,超出原始长度部分用0代替,小于原始部分删除。
resize(n,num) 从新定义链表的长度,超出原始长度部分用num代替。
c1.swap(c2); 将c1和c2交换。
swap(c1,c2); 同上。
list<int> a1{1,2,3,4,5};
a1.resize(8);
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "resize(n):";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.resize(10, 10);
cout << "resize(n,num):";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
list<int>a2,a3;
a2.swap(a1);
cout << endl;
c1.merge(c2) 合并2个有序的链表并使之有序,从新放到c1里,释放c2。
c1.merge(c2,comp) 合并2个有序的链表并使之按照自定义规则排序之后从新放到c1中,释放c2。
list<int> a1{1,2,3},a2{4,5,6};
a1.merge(a2);
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "a1.merge(a2):";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a2.merge(a1,[](int n1,int n2){return n1>n2;});
cout << "a2.merge(a1,comp):";
for(it = a2.begin();it!=a2.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
c1.splice(c1.beg,c2) 将c2连接在c1的beg位置,释放c2
c1.splice(c1.beg,c2,c2.beg) 将c2的beg位置的元素连接到c1的beg位置,并且在c2中施放掉beg位置的元素
c1.splice(c1.beg,c2,c2.beg,c2.end) 将c2的[beg,end)位置的元素连接到c1的beg位置并且释放c2的[beg,end)位置的元素
remove(num) 删除链表中匹配num的元素。
remove_if(comp) 删除条件满足的元素,参数为自定义的回调函数。
list<int> a1{1,2,3},a2{4,5,6};
a1.splice(a1.begin(),a2,a2.begin(),a2.end());
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "a1.merge(a2):";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
reverse() 反转链表
unique() 删除相邻的元素
c.sort() 将链表排序,默认升序
c.sort(comp) 自定义回调函数实现自定义排序
list<int> a1{1,3,2,5,4};
a1.sort();
list<int>::iterator it;
cout << "sort():";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
a1.sort([](int n1,int n2){return n1>n2;});
cout << "sort(function point):";
for(it = a1.begin();it!=a1.end();it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;