基于Python的电影影片数据分析
摘 要
数据分析与可视化是当今数据分析的发展方向。大数据时代,数据资源具有海量特征。数据分析和可视化主要通过Python数据分析来实现。基于Python的数据分析可视化和技术实现是目前Python数据分析的主要目的,Python可以为数据分析可视化提供思路,在体现数据价值方面发挥着重要作用。因此,在研究数据分析、可视化的过程中,我们可以看到Python具有重要的应用价值。
BeautifulSoup 基于Python 的设计让您可以快速高效地抓取网站数据,Pandas 工具提供简单灵活的数据清理和分析,Python Matplotlib 工具包可以轻松将数据分析结果以图形方式可视化。在本文中,您将阅读Python中功能齐全的标准库,一个强大的第三方库请求,以编程方式使用Beautiful Soup和正则表达式从film.csv文件中读取电影信息数据,对读取的数据进行清理和组织,并使用Bar函数对节目电影的周平均票房输出(周平均票房代表该文件所包含的所有城市的整体周平均票房),Y轴代表以万元为单位的票房收入。 X 轴代表电影名称。通过Matplotlib 图形库,将数据结果以图形方式展示并分析得出相关结论。本论文的研究为培养学生的数据处理能力和可视化分析能力奠定了基础。
关键词:Python;爬虫;电影数据;数据分析;可视化
Movie data crawl and data analysis based on Python
XXXX
(XXXXXXXXXX,XX XXXXXX)
Abstract
Data analysis and visualization is the development direction of data analysis today.In the era of big data, data resources have massive characteristics.Data analysis and visualization are achieved primarily through Python data analysis.Python-based data analysis visualization and technical implementation are the main purpose of Python data analysis. Python can provide ideas for data analysis visualization and play an important role in reflecting the value of data.Therefore, in the process of studying data analysis and visualization, we can see that Python has an important application value.
BeautifulSoup’s Python-based design allows you to quickly and efficiently grab website data, Pandas tools provide simple and flexible data cleaning and analysis, and the Python Matplotlib toolkit can easily visualize data analysis results graphically.In this article, you will read the fully functional standard library in Python, a powerful third-party library request, programmatically read movie information from film.csv files using Beautiful Soup and regular expressions, clean and organize the read data, and use the Bar function to output the weekly average box office represents the overall weekly box office of all cities included in the file). The Y axis represents revenue in ten thousand yuan.The X-axis represents the movie name.Through the Matplotlib graphics library, the data results are graphically displayed and analyzed to draw relevant conclusions.The research in this paper lays the foundation for cultivating students’ data processing ability and visual analysis ability.
Key words: Python; crawler; movie data; data analysis; visualization
目 录
1绪论 1
1.1 选题背景及意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.2.1 爬虫技术概述 1
1.2.2 爬虫设计者面临的问题与反爬虫技术现状 3
2 相关理论及技术 6
2.1 robot协议对本设计的影响 6
2.2 爬虫 6
2.2.1 工作原理 6
2.2.2 工作流程 7
2.2.3 抓取策略 7
2.3 Python及Pycharm简介 8
2.4运行环境和系统结构 8
3 系统设计 9
3.1环境搭建 9
3.2设计思路 9
3.3 第三方类库的简介和安装 10
3.3.1 Scarpy简介及安装 10
3.3.2 Numpy简介及安装 11
3.3.3 Pandas简介及安装 11
3.3.4 JieBa简介及安装 12
3.3.5 WordCloud简介及安装 12
3.3.6 Matplotlib简介及安装 12
3.3.7 Pygal简介及安装 12
3.3.8 re简介 12
3.3.9 json简介 13
3.3.10 os简介 13
3.3.11 shutil简介 13
3.3.12 pathlib简介 13
3.3.13 random简介 13
3.3.14 math简介 14
3.3.15 PIL简介 14
3.4 Scrapy详解 14
3.4.1 架构介绍 14
3.4.2 数据流 15
4 电影基本数据爬取 17
4.1爬取 17
4.2数据分析 19
4.2.1评分星级 19
4.2.2性别比例 21
4.2.3位置分布 22
4.2.4时评数量 25
4.2.5主要演员 27
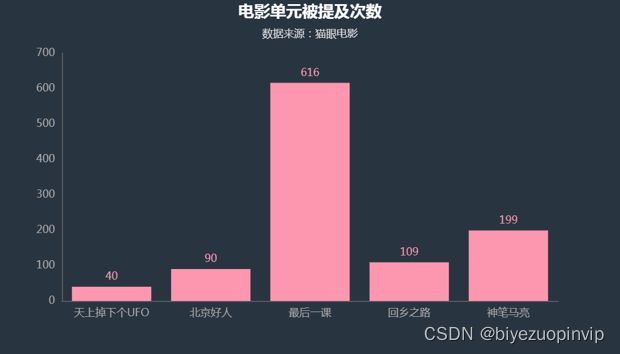
4.2.6电影单元 29
4.3词云展示 30
4.3.1整体词云 30
4.3.2热评词云 32
4.4小结 34
5 总结 35
致 谢 36
参考文献 37
数据分析
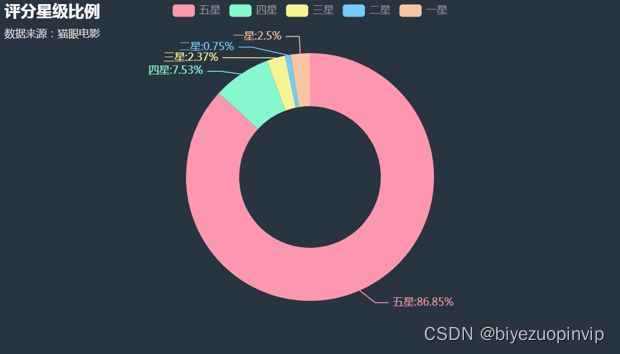
评分星级
首先,我们看一下爬取数据中每个评分星级的比例情况,主要实现代码如下:
评分星级
rates = []for s in df.iloc[:, 3]:
rates.append(s)
sx = [“五星”, “四星”, “三星”, “二星”, “一星”]
sy = [
str(rates.count(5.0) + rates.count(4.5)),
str(rates.count(4.0) + rates.count(3.5)),
str(rates.count(3.0) + rates.count(2.5)),
str(rates.count(2.0) + rates.count(1.5)),
str(rates.count(1.0) + rates.count(0.5))
]
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.CHALK, width=‘700px’, height=‘400px’))
.add(“”, list(zip(sx, sy)), radius=[“40%”, “70%”])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=“评分星级比例”, subtitle=“数据来源:猫眼电影”, pos_left = “left”))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter=“{b}:{d}%”, font_size=12))
).render_notebook()
效果如下:
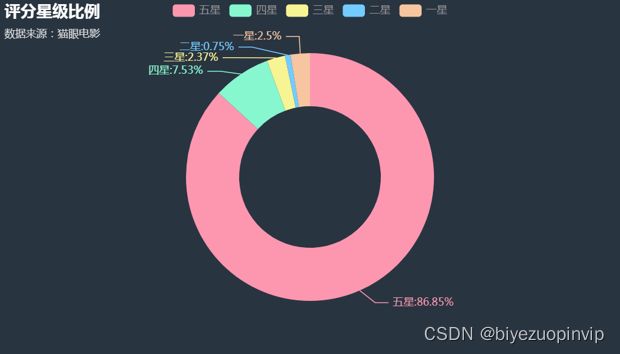
从图中我们可以看出:有接近 9 成的人给了该片 5 星,1、2、3 星总共占比只有 5% 左右,说明该片的质量得到了大部分人的认可。
性别比例
我们接着看评论人中的性别情况,主要实现代码如下:
性别比例
rates = []for s in df.iloc[:, 8]:
if s != 1 and s != 2:
s = 3
rates.append(s)
gx = [“男”, “女”, “未知”]
gy = [
rates.count(1),
rates.count(2),
rates.count(3)
]
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.CHALK, width=“700px”, height=“400px”))
.add(“”, list(zip(gx, gy)))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=“性别比例”, subtitle=“数据来源:猫眼电影”, pos_left = “left”))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter=“{b}:{d}%”, font_size=12))
).render_notebook()
效果如下:
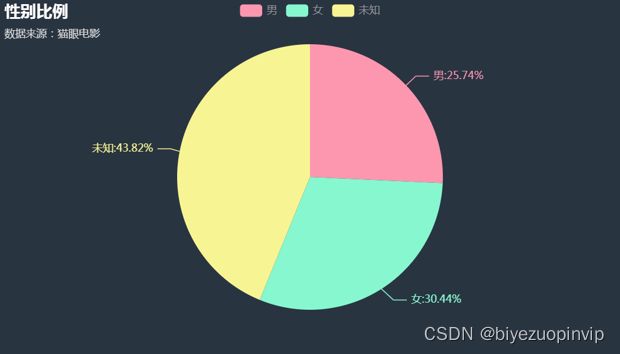
通过上图我们可以发现:大部分人是比较注重自己的隐私的,没有显示自己的性别,通过性别可见的数据,我们可以发现男人和女人在评论区的活跃程度比较接近,女人略高一些。
位置分布
我们再接着看评论人位置分布情况,先看下评论数量前 100 名的位置坐标情况,主要代码实现如下:
cities = []for city in df.iloc[:, 1]:
if city != “”:
cities.append(city)
data = Counter(cities).most_common(100)
gx1 = []
gy1 = []for c in data:
gx1.append(c[0])
gy1.append(c[1])
geo = Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width=“700px”, height=“400px”, theme=ThemeType.DARK, bg_color=“#404a59”))
(
geo.add_schema(maptype=“china”, itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color=“#323c48”, border_color=“#111”))
.add(“评论数量”, list(zip(gx1, gy1)))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(
toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts,
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=“位置分布地理坐标”, subtitle=“数据来源:猫眼电影”, pos_left = “left”),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=500, is_piecewise=True)
)
).render_notebook()
效果如下:
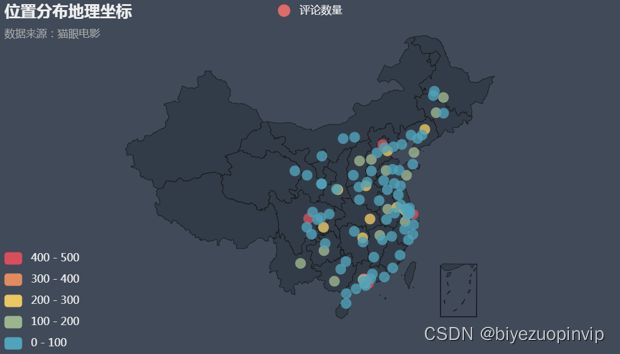
下面再通过柱状图来展示一下评论数量前 15 名的城市,主要代码实现如下:
data_top15 = Counter(cities).most_common(15)
gx2 = []
gy2 = []for c in data_top15:
gx2.append(c[0])
gy2.append(c[1])
(
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.CHALK, width=“700px”, height=“400px”))
.add_xaxis(gx2)
.add_yaxis(“”, gy2)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=“城市来源 TOP15”, subtitle=“数据来源:猫眼电影”, pos_left = “center”)
)
).render_notebook()
效果如下: