基于docker的Hadoop集群下实现最小生成树的mapreduce程序
01.技术背景
在本文中,将为读者详细介绍如下内容:
- 如何部署基于docker的hadoop开发环境
- mapreduce的基本开发流程与基本知识
- java开发的一些基本知识
- 最小生成树算法相关的知识。
文章中假定您已经具有如下知识背景:
- 了解并掌握docker的相关操作开发过程中
- Linux相关的知识
- java的基本知识
- 算法相关的基本知识,如图、树等基本概念
在环境搭建与开发过程中,需要用到的资源如下:
- Hadoop 安装包
- Java Linux安装包
- Java 开发环境(本次使用的Idea)
02.重要说明:
后面有部分代码并没有放出来,主要是因为此学习过程是基于我当前学习的一们课程的大作业完成的。当前大作业还未上交,为避免造成协同现象,故暂时不放出代码,2022年9月1日后,一定会将剩余的代码补充完整。
1.基于Docker的Hadoop环境配置
1.1 拉取Ubuntu docker 映像
docker pull ubuntu1.2 安装java
1.2.1 下载java的安装包jdk-8u333-linux-x64.tar.gz
1.2.2 安装并配置java
启动docker并挂载目录到root根目录下:
进入docker并解压jdk安装包
配置java:
环境变量:
文件位置:/etc/profile
环境变量内容:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_333
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib:$JRE_HOME/lib:$CLASSPATH
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin:$PATH
export JRE_HOME=$JAVA_HOME/jre
运行测试:
注意:
此处可能需要 使用vim,具体安装参见本文 1.4 安装必要软件
1.3 安装hadoop
1.3.1 下载hadoop
hadoop下载地址(官方)
hadoop下载地址(清华源)
将hadoop解压并移到指定目录
tar -zxvf hadoop-3.1.3.tar.gz
mv hadoop-3.1.3 /usr/local/hadoop
1.4 安装必要软件
更换源并更新:
cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak
sed -i "s/archive.ubuntu.com/mirrors.aliyun.com/g" /etc/apt/sources.list
apt udpate1.4.1 vim
apt-get install vim1.4.2 ssh
apt-get install ssh配置ssh的免密登陆
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub >> .ssh/authorized_keys
echo "service ssh start" >> ~/.bashrc
1.5 配置hadoop
参考链接:
1.ubuntu基于docker搭建hadoop集群【史上最详细】_Looho_的博客-CSDN博客
2. 超详细的基于docker搭建hadoop集群_孤独之风。的博客-CSDN博客_docker搭建hadoop集群
1.5.1 配置hadoop运行环境变量
修改/etc/profile
配置 hadoop的环境变量
export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin
export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME
export HADOOP_LIBEXEC_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/libexec
export JAVA_LIBRARY_PATH=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native:$JAVA_LIBRARY_PATH
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop
export HDFS_DATANODE_USER=root
export HDFS_DATANODE_SECURE_USER=root
export HDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_USER=root
export HDFS_NAMENODE_USER=root
export YARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_USER=root
export YARN_NODEMANAGER_USER=root
1.5.2 配置hadoop配置文件
在修改完/etc/profile之后,运行如下命令,使刚才配置的环境变量生效,同时,切换到hadoop的配置文件夹下:
source /etc/profile
cd $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/主要修改以下5个文件:
1.hadoop-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_333
export HDFS_NAMENODE_USER=root
export HDFS_DATANODE_USER=root
export HDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_USER=root
export YARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_USER=root
export YARN_NODEMANAGER_USER=root2. core-site.xml,在后面添加如下配置:
fs.default.name
hdfs://h01:9000
hadoop.tmp.dir
/data/hadoop/tmp
3.配置 hdfs-site.xml,添加如下内容:
dfs.replication
2
dfs.namenode.name.dir
/data/hadoop/hdfs/name
dfs.namenode.data.dir
/data/hadoop/hdfs/data
此处需要建立几个文件夹:
mkdir /data/hadoop/tmp
mkdir /data/hadoop/hdfs
mkdir /data/hadoop/hdfs/name
mkdir /data/hadoop/hdfs/data
4.配置 mapred-site.xml,添加如下内容
mapreduce.framework.name
yarn
mapreduce.application.classpath
/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/lib/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/hdfs/lib/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/lib/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/*,
/opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/lib/*
5.配置yarn-site.xml,添加如下内容:
yarn.resourcemanager.hostname
h01
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services
mapreduce_shuffle
1.5.3 保存docker为新映像
命令:
docker commit -m "hadoop" eddd4e14c0b5 hadoop:docker需要根据自己实际进行修改:
1.6 配置hadoop 集群
1.6.1 配置docker
启动三个docker:
docker run -it -h h01 --name h01 -p 9870:9870 -p 8088:8088 hadoop /bin/bash
docker run -it -h h02 --name h02 hadoop /bin/bash
docker run -it -h h03 --name h03 hadoop /bin/bash
分别根据docker实际IP地址,修改/etc/hosts文件:
在三个docker中分别对另外两个docker进行ssh登陆,将ip写入known_hosts
1.6.2 配置集群
修改master节点上的配置目录下的workers文件,删除原先的localhsot,添加另外两个主机名。
1.6.3 启动集群
# 第一次第一次启动,务必要format一下namenode,后面再启动就不需要format了
hdfs namenode -format
# 启动集群
start-all.sh
1.6.4 查看各节点的状态
2.MapReduce 开发相关知识
2.1 开发流程
以mapreduce的经典案例wordcount为例,基本流程如下:
简易代码说明如下:
map代码:
reduce代码:
2.2 数据类型
2.2.1 常用的数据
//以下是常用的数据类型:
BooleanWritable //布尔型
ByteWritable
DoubleWritable
FloatWritable
IntWritable
LongWritable
Text //:使用UTF8格式存储我们的文本
NullWritable //当中key或者value为空时使用
2.2.2 常用数据类的基本操作
以IntWritable为例:
// 创建实例
IntWritable iKey = new IntWritable();
// 设置值
iKey.set(1);
//获取值
int key = iKey.get();2.3 java开发相关的基础
此处只介绍命令行下编译与运行相关的基础:
2.3.1. 编译 javac
linux下,javac在编译过程中,如果要使用classpath,是以" : " 为分割符的。
windows下,则是以 “;”为分割符的。
MENIFEST.MF文件的内容如下
如果在进行jar包生成的时候,如果不加MENIFEST.MF文件,在hadoop中运行的时候,需要指明主类的名称。
hadoop jar ./mst1.jar MyKruskalMST /input /outputt1
2.3.2 hadoop的常用命令
# 程序运行,如示例程序,路径一般在xx/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/
hadoop jar /opt/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount /input /wd_op
# 程序的命令行生成
javac *.java -cp /path1/xxx.jar:/path2/xxy.jar:$(hadoop classpath)
# 程序打包
jar -cvf Package_name.jar *.class
# hdfs 操作:
# 文件列表:
hadoop fs -ls path
# 文件删除
hadoop fs -rm path #在删除文件夹的过程中,需要添加 -r 选项
# 文件创建
hadoop fs -touch /path/filename
# 文件上传
hadoop fs -put local_file_path hdfs_file_path
# 文件下载
hadoop fs -get hdfs_file_path local_file_path
#集群停止
cd $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/
stop-all.sh
# 集群启动
cd $HADOOP_CONF_DIR
start-all.sh2.4 学习建议
水平有限,建议就不加了 ........................................
3. 最小生成树算法
3.1 最小生成树
一个连通图的生成树是一个极小的连通子图,它包含图中全部的n个顶点,但只有构成一棵树的n-1条边。
最小生成树,就是一个 带权图中边的权值和最小的生成树 ,最小是指边的权值之和小于或者等于其它生成树的边的权值之和。
3.2 常见的最小生成树算法
此处对两种算法进行简要的介绍,为后面的编程奠定一个基础,详细还需要进行专门的学习。
3.2.1Kruskal算法
克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal)是一种使用贪婪方法的最小生成树算法。 该算法初始将图视为森林,图中的每一个顶点视为一棵单独的树。 一棵树只与它的邻接顶点中权值最小且不违反最小生成树属性(不构成环)的树之间建立连边。
java实现:
程序摘自算法
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac KruskalMST.java
* Execution: java KruskalMST filename.txt
* Dependencies: EdgeWeightedGraph.java Edge.java Queue.java MinPQ.java
* UF.java In.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/tinyEWG.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/mediumEWG.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/largeEWG.txt
*
* Compute a minimum spanning forest using Kruskal's algorithm.
*
* % java KruskalMST tinyEWG.txt
* 0-7 0.16000
* 2-3 0.17000
* 1-7 0.19000
* 0-2 0.26000
* 5-7 0.28000
* 4-5 0.35000
* 6-2 0.40000
* 1.81000
*
* % java KruskalMST mediumEWG.txt
* 168-231 0.00268
* 151-208 0.00391
* 7-157 0.00516
* 122-205 0.00647
* 8-152 0.00702
* 156-219 0.00745
* 28-198 0.00775
* 38-126 0.00845
* 10-123 0.00886
* ...
* 10.46351
*
******************************************************************************/
package edu.princeton.cs.algs4;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* The {@code KruskalMST} class represents a data type for computing a
* minimum spanning tree in an edge-weighted graph.
* The edge weights can be positive, zero, or negative and need not
* be distinct. If the graph is not connected, it computes a minimum
* spanning forest, which is the union of minimum spanning trees
* in each connected component. The {@code weight()} method returns the
* weight of a minimum spanning tree and the {@code edges()} method
* returns its edges.
*
* This implementation uses Krusal's algorithm and the
* union-find data type.
* The constructor takes Θ(E log E) time in
* the worst case.
* Each instance method takes Θ(1) time.
* It uses Θ(E) extra space (not including the graph).
*
* This {@code weight()} method correctly computes the weight of the MST
* if all arithmetic performed is without floating-point rounding error
* or arithmetic overflow.
* This is the case if all edge weights are non-negative integers
* and the weight of the MST does not exceed 252.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 4.3 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
* For alternate implementations, see {@link LazyPrimMST}, {@link PrimMST},
* and {@link BoruvkaMST}.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class KruskalMST {
private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private double weight; // weight of MST
private Queue mst = new Queue(); // edges in MST
/**
* Compute a minimum spanning tree (or forest) of an edge-weighted graph.
* @param G the edge-weighted graph
*/
public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
// create array of edges, sorted by weight
Edge[] edges = new Edge[G.E()];
int t = 0;
for (Edge e: G.edges()) {
edges[t++] = e;
}
Arrays.sort(edges);
// run greedy algorithm
UF uf = new UF(G.V());
for (int i = 0; i < G.E() && mst.size() < G.V() - 1; i++) {
Edge e = edges[i];
int v = e.either();
int w = e.other(v);
// v-w does not create a cycle
if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) {
uf.union(v, w); // merge v and w components
mst.enqueue(e); // add edge e to mst
weight += e.weight();
}
}
// check optimality conditions
assert check(G);
}
/**
* Returns the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
* @return the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest) as
* an iterable of edges
*/
public Iterable edges() {
return mst;
}
/**
* Returns the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
* @return the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest)
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
// check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V)
private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
// check total weight
double total = 0.0;
for (Edge e : edges()) {
total += e.weight();
}
if (Math.abs(total - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", total, weight());
return false;
}
// check that it is acyclic
UF uf = new UF(G.V());
for (Edge e : edges()) {
int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) {
System.err.println("Not a forest");
return false;
}
uf.union(v, w);
}
// check that it is a spanning forest
for (Edge e : G.edges()) {
int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) {
System.err.println("Not a spanning forest");
return false;
}
}
// check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
for (Edge e : edges()) {
// all edges in MST except e
uf = new UF(G.V());
for (Edge f : mst) {
int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
if (f != e) uf.union(x, y);
}
// check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
for (Edge f : G.edges()) {
int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) {
if (f.weight() < e.weight()) {
System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code KruskalMST} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
KruskalMST mst = new KruskalMST(G);
for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
StdOut.println(e);
}
StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight());
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2002-2020, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
*
* Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
* Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
*
*
* algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
******************************************************************************/
测试程序:
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.EdgeWeightedGraph;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Edge;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.KruskalMST;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
class TestKruskalMST {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis();
File file =new File("mst_result.txt");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file.getAbsoluteFile());
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
KruskalMST mst = new KruskalMST(G);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
bw.write(e.toString()+"\n");
}
bw.write(String.format("%.5f\n", mst.weight()));
bw.close();
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
long costTime = (endtime - begintime);
StdOut.printf("constTime:"+costTime);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}生成与运行:
3.2.2 Prim算法
普里姆算法在找最小生成树时,将顶点分为两类,一类是在查找的过程中已经包含在生成树中的顶点(假设为 A 类),剩下的为另一类(假设为 B 类)。
对于给定的连通网,起始状态全部顶点都归为 B 类。在找最小生成树时,选定任意一个顶点作为起始点,并将之从 B 类移至 A 类;然后找出 B 类中到 A 类中的顶点之间权值最小的顶点,将之从 B 类移至 A 类,如此重复,直到 B 类中没有顶点为止。所走过的顶点和边就是该连通图的最小生成树。
编程实现:
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac PrimMST.java
* Execution: java PrimMST filename.txt
* Dependencies: EdgeWeightedGraph.java Edge.java Queue.java
* IndexMinPQ.java UF.java In.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/tinyEWG.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/mediumEWG.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/43mst/largeEWG.txt
*
* Compute a minimum spanning forest using Prim's algorithm.
*
* % java PrimMST tinyEWG.txt
* 1-7 0.19000
* 0-2 0.26000
* 2-3 0.17000
* 4-5 0.35000
* 5-7 0.28000
* 6-2 0.40000
* 0-7 0.16000
* 1.81000
*
* % java PrimMST mediumEWG.txt
* 1-72 0.06506
* 2-86 0.05980
* 3-67 0.09725
* 4-55 0.06425
* 5-102 0.03834
* 6-129 0.05363
* 7-157 0.00516
* ...
* 10.46351
*
* % java PrimMST largeEWG.txt
* ...
* 647.66307
*
******************************************************************************/
package edu.princeton.cs.algs4;
/**
* The {@code PrimMST} class represents a data type for computing a
* minimum spanning tree in an edge-weighted graph.
* The edge weights can be positive, zero, or negative and need not
* be distinct. If the graph is not connected, it computes a minimum
* spanning forest, which is the union of minimum spanning trees
* in each connected component. The {@code weight()} method returns the
* weight of a minimum spanning tree and the {@code edges()} method
* returns its edges.
*
* This implementation uses Prim's algorithm with an indexed
* binary heap.
* The constructor takes Θ(E log V) time in
* the worst case, where V is the number of
* vertices and E is the number of edges.
* Each instance method takes Θ(1) time.
* It uses Θ(V) extra space (not including the
* edge-weighted graph).
*
* This {@code weight()} method correctly computes the weight of the MST
* if all arithmetic performed is without floating-point rounding error
* or arithmetic overflow.
* This is the case if all edge weights are non-negative integers
* and the weight of the MST does not exceed 252.
*
* For additional documentation,
* see Section 4.3 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
* For alternate implementations, see {@link LazyPrimMST}, {@link KruskalMST},
* and {@link BoruvkaMST}.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class PrimMST {
private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private Edge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = shortest edge from tree vertex to non-tree vertex
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = weight of shortest such edge
private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = true if v on tree, false otherwise
private IndexMinPQ pq;
/**
* Compute a minimum spanning tree (or forest) of an edge-weighted graph.
* @param G the edge-weighted graph
*/
public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
edgeTo = new Edge[G.V()];
distTo = new double[G.V()];
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
pq = new IndexMinPQ(G.V());
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) // run from each vertex to find
if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v); // minimum spanning forest
// check optimality conditions
assert check(G);
}
// run Prim's algorithm in graph G, starting from vertex s
private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) {
distTo[s] = 0.0;
pq.insert(s, distTo[s]);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
scan(G, v);
}
}
// scan vertex v
private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
marked[v] = true;
for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.other(v);
if (marked[w]) continue; // v-w is obsolete edge
if (e.weight() < distTo[w]) {
distTo[w] = e.weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]);
else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
* @return the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest) as
* an iterable of edges
*/
public Iterable edges() {
Queue mst = new Queue();
for (int v = 0; v < edgeTo.length; v++) {
Edge e = edgeTo[v];
if (e != null) {
mst.enqueue(e);
}
}
return mst;
}
/**
* Returns the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
* @return the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest)
*/
public double weight() {
double weight = 0.0;
for (Edge e : edges())
weight += e.weight();
return weight;
}
// check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V)
private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
// check weight
double totalWeight = 0.0;
for (Edge e : edges()) {
totalWeight += e.weight();
}
if (Math.abs(totalWeight - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", totalWeight, weight());
return false;
}
// check that it is acyclic
UF uf = new UF(G.V());
for (Edge e : edges()) {
int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) {
System.err.println("Not a forest");
return false;
}
uf.union(v, w);
}
// check that it is a spanning forest
for (Edge e : G.edges()) {
int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) {
System.err.println("Not a spanning forest");
return false;
}
}
// check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
for (Edge e : edges()) {
// all edges in MST except e
uf = new UF(G.V());
for (Edge f : edges()) {
int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
if (f != e) uf.union(x, y);
}
// check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
for (Edge f : G.edges()) {
int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) {
if (f.weight() < e.weight()) {
System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code PrimMST} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G);
for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
StdOut.println(e);
}
StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight());
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2002-2020, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
*
* Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
* Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
*
*
* algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
******************************************************************************/
测试程序:
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.EdgeWeightedGraph;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Edge;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.PrimMST;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
class TestPrimMST {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis();
File file =new File("mst_result.txt");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file.getAbsoluteFile());
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
bw.write(e.toString()+"\n");
}
bw.write(String.format("%.5f\n", mst.weight()));
bw.close();
long endtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
long costTime = (endtime - begintime);
StdOut.printf("constTime:"+costTime);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3.3 并查集
3.3.1 基本的概念
摘自:【算法与数据结构】—— 并查集_酱懵静的博客-CSDN博客_并查集
定义:
并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合的合并及查询问题(即所谓的并、查)。比如说,我们可以用并查集来判断一个森林中有几棵树、某个节点是否属于某棵树等。
主要构成:
并查集主要由一个整型数组pre[ ]和两个函数find( )、join( )构成。
数组 pre[ ] 记录了每个点的前驱节点是谁,函数 find(x) 用于查找指定节点 x 属于哪个集合,函数 join(x,y) 用于合并两个节点 x 和 y 。
作用:
并查集的主要作用是求连通分支数(如果一个图中所有点都存在可达关系(直接或间接相连),则此图的连通分支数为1;如果此图有两大子图各自全部可达,则此图的连通分支数为2……)
3.3.2 java实现
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac UF.java
* Execution: java UF < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
* Data files: https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/tinyUF.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/mediumUF.txt
* https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/largeUF.txt
*
* Weighted quick-union by rank with path compression by halving.
*
* % java UF < tinyUF.txt
* 4 3
* 3 8
* 6 5
* 9 4
* 2 1
* 5 0
* 7 2
* 6 1
* 2 components
*
******************************************************************************/
package edu.princeton.cs.algs4;
/**
* The {@code UF} class represents a union–find data type
* (also known as the disjoint-sets data type).
* It supports the classic union and find operations,
* along with a count operation that returns the total number
* of sets.
*
* The union–find data type models a collection of sets containing
* n elements, with each element in exactly one set.
* The elements are named 0 through n–1.
* Initially, there are n sets, with each element in its
* own set. The canonical element of a set
* (also known as the root, identifier,
* leader, or set representative)
* is one distinguished element in the set. Here is a summary of
* the operations:
*
* - find(p) returns the canonical element
* of the set containing p. The find operation
* returns the same value for two elements if and only if
* they are in the same set.
*
- union(p, q) merges the set
* containing element p with the set containing
* element q. That is, if p and q
* are in different sets, replace these two sets
* with a new set that is the union of the two.
*
- count() returns the number of sets.
*
*
* The canonical element of a set can change only when the set
* itself changes during a call to union—it cannot
* change during a call to either find or count.
*
* This implementation uses weighted quick union by rank
* with path compression by halving.
* The constructor takes Θ(n) time, where
* n is the number of elements.
* The union and find operations take
* Θ(log n) time in the worst case.
* The count operation takes Θ(1) time.
* Moreover, starting from an empty data structure with n sites,
* any intermixed sequence of m union and find
* operations takes O(m α(n)) time,
* where α(n) is the inverse of
* Ackermann's function.
*
* For alternative implementations of the same API, see
* {@link QuickUnionUF}, {@link QuickFindUF}, and {@link WeightedQuickUnionUF}.
* For additional documentation, see
* Section 1.5 of
* Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class UF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31)
private int count; // number of components
/**
* Initializes an empty union-find data structure with
* {@code n} elements {@code 0} through {@code n-1}.
* Initially, each element is in its own set.
*
* @param n the number of elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}
*/
public UF(int n) {
if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
rank = new byte[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 0;
}
}
/**
* Returns the canonical element of the set containing element {@code p}.
*
* @param p an element
* @return the canonical element of the set containing {@code p}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= p < n}
*/
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression by halving
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
/**
* Returns the number of sets.
*
* @return the number of sets (between {@code 1} and {@code n})
*/
public int count() {
return count;
}
/**
* Returns true if the two elements are in the same set.
*
* @param p one element
* @param q the other element
* @return {@code true} if {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same set;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
* @deprecated Replace with two calls to {@link #find(int)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
/**
* Merges the set containing element {@code p} with the
* the set containing element {@code q}.
*
* @param p one element
* @param q the other element
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank
if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ;
else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP;
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
rank[rootP]++;
}
count--;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p) {
int n = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1));
}
}
/**
* Reads an integer {@code n} and a sequence of pairs of integers
* (between {@code 0} and {@code n-1}) from standard input, where each integer
* in the pair represents some element;
* if the elements are in different sets, merge the two sets
* and print the pair to standard output.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
UF uf = new UF(n);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.find(p) == uf.find(q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Copyright 2002-2020, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
*
* Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
* Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
*
*
* algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
******************************************************************************/
测试程序:
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*;
public class TestUF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
UF uf = new UF(n);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.find(p) == uf.find(q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}编译与运行:
4.hadoop 下实现最小生成树算法
以下是个人认识,可能对mapreduce认识不到位,同时,对java编程也不是非常熟悉,所以会存在一定的错误,仅做参考。
在hadoop 下,如果要使用基于并查集的生成树算法,需要对并查集进行一定的修改。首先,并查集使用固定的数组,其在实例化之前,需要知道数组的大小。在mapreduce中,如果map阶段的输入过程的文件开始阶段,设置图的边数与顶点数,如果对文件进行分割,则会导致后面的部分文件缺少这个数据而无法进行处理。我的解决方法:
将基于数组的并查集利用map与hashmap进行改造成一个动态并查集。
4.1 基于动态数组的并查集实现
代码如下 :
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
// A class to represent a disjoint set
class UnionFind
{
private Map parent = new HashMap<>();
// stores the depth of trees
private Map rank = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0;
}
测试代码如下 :
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*;
public class TestUF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
UF uf = new UF(n);
UnionFind huf = new UnionFind();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.find(p) != uf.find(q)){
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println("uf:"+p + " " + q);
}
if (huf.Find(p) != huf.Find(q)) {
huf.Union(p, q);
StdOut.println("huf" +p + " " + q);
}
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}4.2 mapreduce实现最小生成树求解
4.2.1 map
4.2.2 reduce
4.2.3 驱动程序
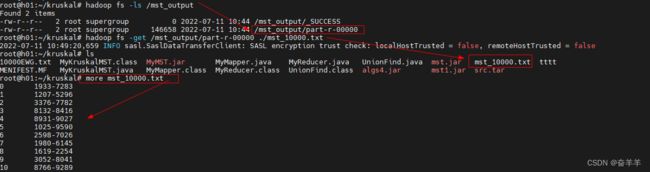
4.3 程序执行结果
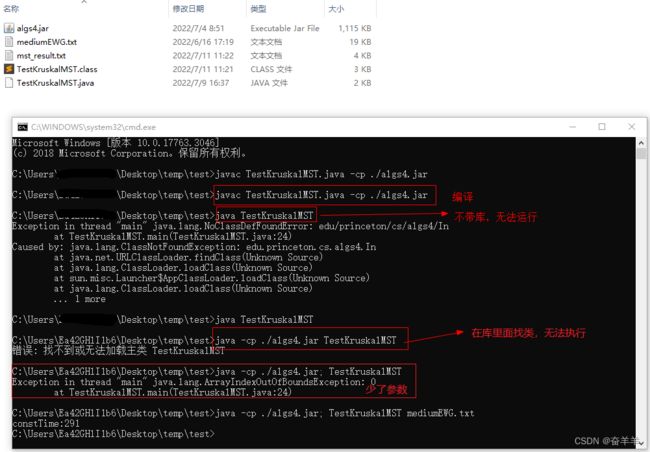
4.3.1 程序编译及运行过程
4.3.2 程序执行结果