Java学习(11):Java实现图书馆书库管理系统
接上次博客:Java学习(10)多接口、接口的继承、抽象类和接口的区别、Object类【toString 、equals、hashcode】、接口实例 【compareTo、clone 】、浅拷贝和深拷贝、内部类_di-Dora的博客-CSDN博客
我们要想完成这个书库管理系统,首先应该理清楚它的底层逻辑。
我们一共写了三个包:
包1:book,它里面放了两个源文件,一个是Book,它代表了“Book”这个类,定义了相关的成员,代表了每本书的具体属性;一个是BookList,它可以被看作是一个书架,存放了我们拥有的图书的相关信息,可以对图书的信息进行查阅,还可以保存当前图书的数量。
包2:operation,它里面放了多个源文件,代表了可以对图书进行的一些相关操作,这些对象又都继承了一个接口IOPeration。
包3:user,针对不同的使用对象,该系统呈现的功能也会有所差异,所以这个包里面先实现了一个 User 作为父类,又实现了两个子类 NormalUser 和 AdminUser ,分别代表普通用户和管理员。
下面是这个系统的基础代码,我会通过注释在相关地方说明一些需要注意的知识点:
1、TestBook/src/Main.java
import book.BookList;
import user.AdminUser;
import user.NormalUser;
import user.User;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//可以利用返回值,的向上转型达到返回值的一致性
public static User login() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1---》管理员 0---》普通用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if(choice == 1) {
/*AdminUser adminUser = new AdminUser(name);
return adminUser;*/
return new AdminUser(name);
}else {
/*NormalUser normalUser = new NormalUser(name);
return normalUser;*/
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookList bookList = new BookList();
User user = login();
while (true) {
int choice = user.menu();
//user是哪个对象? choice是几? ---》 这些能够确定:我能够操作哪个对象的哪个方法。
//通过这两个变量可以确定之后,怎么联系起来
/*
* 1. 先让AdminUser和NormalUser存好各自对应的操作
* 2. 我们就可以通过不同对象的menu调用对象对应的操作了!
*/
user.doOperation(choice, bookList);
}
}
}2、TestBook/src/book
(1)、TestBook/src/book/Book.java
package book;
public class Book {
private String name;//书名
private String author;//作者
private int price;//价格
private String type;//类型
private boolean isBorrowed;//是否被借出 默认是false
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
//因为boolean isBorrowed 默认是false ,所以我们不需要在构造函数里面再写一遍
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
//实现我们自己的打印方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
((isBorrowed == true) ? " 该图书已经被借出":" 该图书未被借出")+
/*", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +*/
'}';
}
}(2)、TestBook/src/book/BookList.java
package book;
public class BookList {
private Book[] books = new Book[10];
private int usedSize;//这是一共计数器用来记录当前实际放的书的书目!
public BookList() {
//构造方法 来初始化成员
this.books[0] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",50," 中国古典名著 ");
this.books[1] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩",38," 中国古典名著 ");;
this.books[2] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",45," 中国古典名著 ");;
this.usedSize = 3;
}
//传入想要取得的图书的下标,得到图书
public Book getBook(int pos) {
return books[pos];
}
//传入想要放入的图书和放置的位置
public void setBooks(int pos,Book book) {
books[pos] = book;
}
public int getUsedSize() {
return usedSize;
}
public void setUsedSize(int usedSize) {
this.usedSize = usedSize;
}
}3、TestBook/src/operation
(1)、TestBook/src/operation/AddOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AddOperation implements IOPeration {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("新增图书!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入想要添加的书的书名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
//遍历整个书架,查看是否已经添加相同书籍
for(int n =0;n(2)、TestBook/src/operation/BorrowedOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BorrowedOperation implements IOPeration {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
System.out.println("这是本书库所有藏书");
for (int k = 0; k < currentSize; k++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(k);
System.out.println(book);
}
System.out.println("请输入想要借阅的书的书名:");
String nameborrow = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(nameborrow)) {
if(!book.isBorrowed()){
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
return;
}
else{
System.out.println("该图书已被借出,请重新选择!");
}
}
}
System.out.println("没有你想要借阅的书!");
}
}(3)、TestBook/src/operation/DelOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DelOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("这是本书库现有藏书");
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int k = 0; k < currentSize; k++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(k);
System.out.println(book);
}
System.out.println("请输入你想要删除的书的名字:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/*现在遍历书架,比对是否存在与输入字符串相同的书名
* 如果有,那么就把后一本数的信息前移,覆盖掉需要删除的书的信息
* */
String namedel = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(namedel)) {
for(int j=i+1;j我们可以再丰富一下这个代码:
public class DelOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
if(currentSize==0){
System.out.println("书架上现在没有书,无法删除书籍!");
return;
}
System.out.println("这是本书库现有藏书");
for (int k = 0; k < currentSize; k++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(k);
System.out.println(book);
}
System.out.println("请输入你想要删除的书的名字:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String namedel = scanner.nextLine();
//如果有这本书 就不能添加了
int index=-1;
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(namedel)) {
index=i;
break;
}
}
if(index==-1){
System.out.println("本书库没有这本书,无法删除!");
return;
}
for(int j=index;j(4)、TestBook/src/operation/ExitOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
public class ExitOperation implements IOPeration {
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("退出系统!");
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
bookList.setBooks(i,null);
}
bookList.setUsedSize(0);
System.exit(0);
}
}(5)、TestBook/src/operation/FindOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FindOperation implements IOPeration{
public void work(BookList bookList){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要查找的图书的书名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
/*一定不可以这么写!
* Book book = books[i];
* 记住!我们现在是在面向对象!
* */
if(book.getName().equals(name)) {
System.out.println("找到了你查找的书:");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("不好意思,本书库目前还未收藏该书!");
}
}
(6)、TestBook/src/operation/IOPeration.java
package operation;
import book.BookList;
public interface IOPeration {
void work(BookList bookList);//每个子类都要实现这个抽象的方法
}(7)、TestBook/src/operation/ReturnOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReturnOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
System.out.println("请输入你想要归还的图书的书名:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String nameborrow = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
if (book.getName().equals(nameborrow)) {
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还图书成功!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有你应该归还的书。");
}
}(8)、TestBook/src/operation/ShowOperation.java
package operation;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
public class ShowOperation implements IOPeration{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("这是本书库所有藏书");
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getBook(i);
//同样的,这里也不可以这样写:
//Book book = books[i];
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}3、TestBook/src/user
(1)、TestBook/src/user/User.java
package user;
import book.BookList;
import operation.IOPeration;
public abstract class User {
protected String name;//姓名
public IOPeration[] ioPerations;//这里我们采取的是先定义,后初始化的方式
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract int menu();
public void doOperation(int choice, BookList bookList) {
ioPerations[choice].work(bookList);
}
}(2)、TestBook/src/user/NormalUser.java
package user;
import operation.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.ioPerations = new IOPeration[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new BorrowedOperation(),
new ReturnOperation()
};
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("************************");
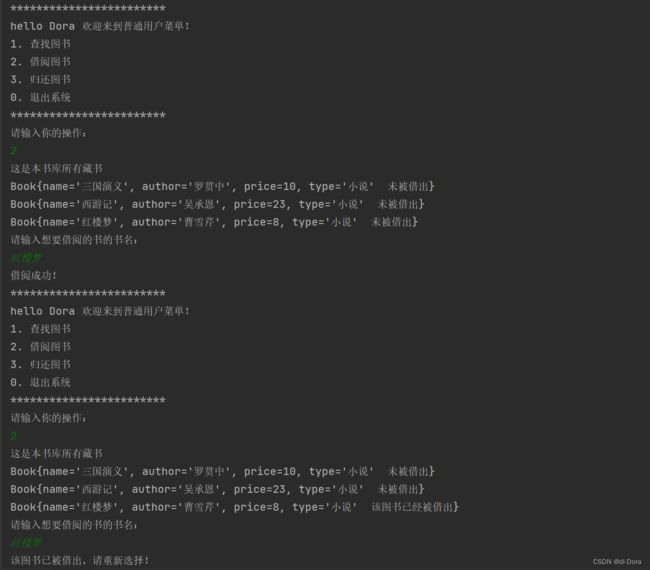
System.out.println("hello "+ this.name + " 欢迎来到普通用户菜单!");
System.out.println("1. 查找图书");
System.out.println("2. 借阅图书");
System.out.println("3. 归还图书");
System.out.println("0. 退出系统");
System.out.println("************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}(3)、TestBook/src/user/AdminUser.java
package user;
import operation.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdminUser extends User{
public AdminUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.ioPerations = new IOPeration[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new ShowOperation()
};
/*this.ioPerations = {
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new ShowOperation()
};*/
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("************************");
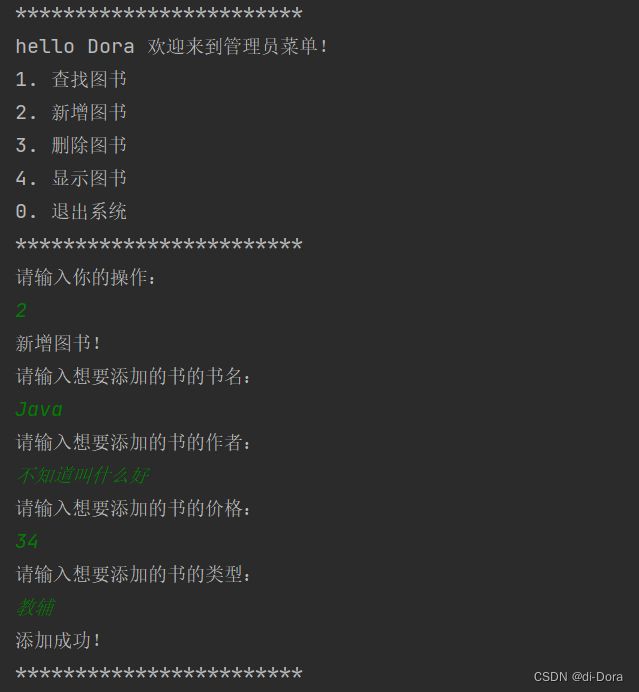
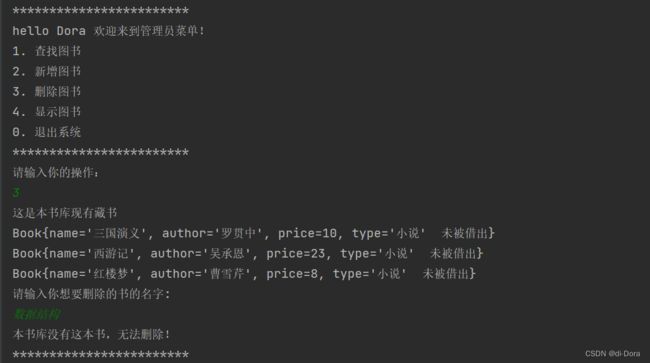
System.out.println("hello "+ this.name + " 欢迎来到管理员菜单!");
System.out.println("1. 查找图书");
System.out.println("2. 新增图书");
System.out.println("3. 删除图书");
System.out.println("4. 显示图书");
System.out.println("0. 退出系统");
System.out.println("************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}好了,写到这里,我们的书库管理系统就大功告成了(当然了,你也可以自己加一些新的功能)!
最后我们可以来看看这个系统的运行结果:
作为管理员:
作为普通用户: