opencv 通过连通域得到外接矩形
本程序通过对图像二值化、连通域拆解,然后提取目标连通域的坐标及外接矩形参数,最终通过中心坐标为圆心,外接矩形的二分之一为半径进行画圆。
#include 原始图像:
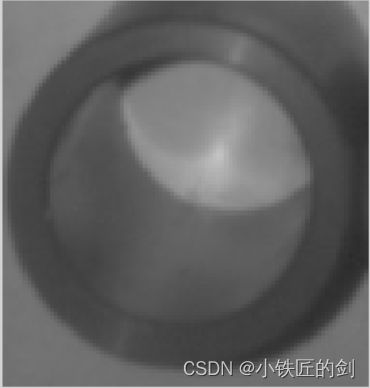
二值化后图像:

对连通域中背景(黑色)进行中心点、方框坐标提取并根据以上数据进行画圆:
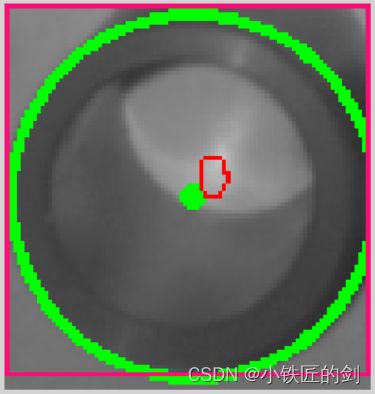
进一步的,对整幅图像提取ROI,然后进行提取目标中心。整幅图像如下:
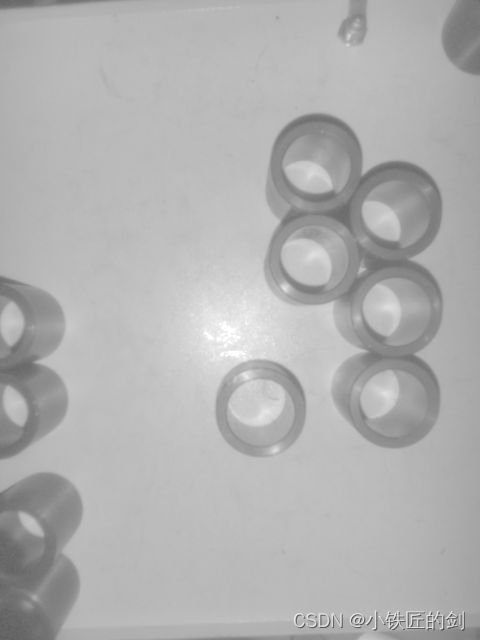

#include 目标识别效果如下:
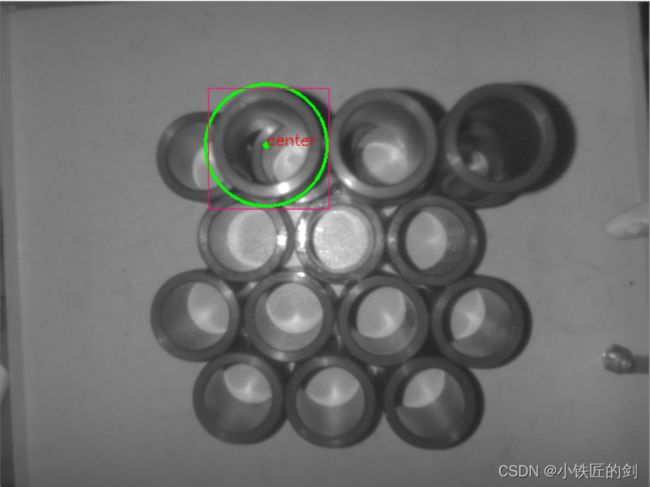

由于在本程序中只识别圆柱体,图像二值化后正好为背景图像,所以在画方框时只选择了背景连通域。即:
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++)
{
// 中心位置,
int center_x = centroids.at<double>(i, 0)+ roi_x;
int center_y = centroids.at<double>(i, 1)+ roi_y;
//矩形边框
int x = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_LEFT)+ roi_x;
int y = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_TOP) + roi_y;
int w = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_WIDTH);
int h = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_HEIGHT);
int area = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_AREA);
// 中心位置绘制
circle(img, Point(center_x, center_y), 2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);
//外接圆绘制
circle(img, Point(center_x, center_y), w/2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);
// 外接矩形
Rect rect(x, y, w, h);
rectangle(img, rect, colors[i], 1, 8, 0);
// putText(img, format("%d", i), Point(center_x, center_y),
putText(img, format("%s", "center"), Point(center_x, center_y),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
cout << "number: " << i << ",area: " << area << ",center_x: " << center_x << ",center_y: "<< center_y <<endl;
}
在实验室,可将变量i修改为number,提取不同连通域。即:
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
// 中心位置,
int center_x = centroids.at<double>(i, 0)+ roi_x;
int center_y = centroids.at<double>(i, 1)+ roi_y;
//矩形边框
int x = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_LEFT)+ roi_x;
int y = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_TOP) + roi_y;
int w = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_WIDTH);
int h = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_HEIGHT);
int area = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_AREA);
// 中心位置绘制
circle(img, Point(center_x, center_y), 2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);
//外接圆绘制
circle(img, Point(center_x, center_y), w/2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);
// 外接矩形
Rect rect(x, y, w, h);
rectangle(img, rect, colors[i], 1, 8, 0);
// putText(img, format("%d", i), Point(center_x, center_y),
putText(img, format("%s", "center"), Point(center_x, center_y),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
cout << "number: " << i << ",area: " << area << ",center_x: " << center_x << ",center_y: "<< center_y <<endl;
}
当然,该程序需要提前获取ROI的坐标,否则识别效果较差,该程序是一个探索结果,未必符合实际情况,再此提前说明。
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42722197/article/details/103826242