前端到后端的参数传递问题(Axios+SpringMVC)
目录
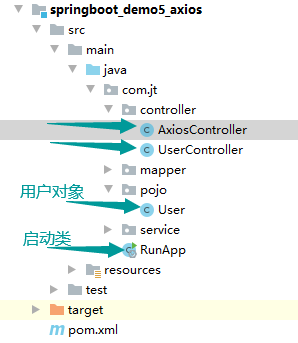
准备工作
项目结构
创建User类
创建UserController测试类
创建AxiosController测试类
参数传递的测试
单个参数的测试
编写测试方法
测试结果
多个参数的测试
编写测试方法
测试结果
对象参数的测试
编写测试方法
测试结果
restFul风格传递单个参数
编写测试代码
测试结果
restFul风格传递多个参数
编写测试代码
测试结果
Axios的简单使用
Axios传递简单参数
后端测试代码编写
前端测试代码编写
测试结果
Axios传递对象参数
后端测试代码编写
前端测试代码编写
测试结果
准备工作
项目结构
创建User类
package com.jt.pojo;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
@TableName("demo_user")
public class User implements Serializable {
//ID代表主键,不是id字段
@TableId(type=IdType.AUTO)//主键自增
//@TableField("name")//如果属性与字段同名(包括驼峰规则)注解可以省略
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
}
这里使用了lombok插件,可以不用手写get和set等方法.
创建UserController测试类
用于测试普通的参数传递方式与接收方式
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController//接收请求
@CrossOrigin//支持跨域
public class UserController {
}创建AxiosController测试类
用于测试使用Axios的参数传递方式与接收方式
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class AxiosController {
}参数传递的测试
单个参数的测试
编写测试方法
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/getById")
public String getById(Integer id){
return "单个参数的传递:"+id;
}
}
测试结果
注意传递的参数名要与方法的形参一致
多个参数的测试
编写测试方法
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class UserController {
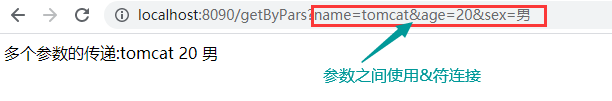
// URL: http://localhost:8090/getByPars?name=tomcat&age=20&sex=%E7%94%B7
@GetMapping("/getByPars")
public String getById(String name,Integer age,String sex){
return "多个参数的传递:"+name+" "+age+" "+sex;
}
}
测试结果
注意:参数位置的顺序是允许变化的
对象参数的测试
编写测试方法
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class UserController {
// URL: http://localhost:8090/user?name=mysql&age=18&sex=%E7%94%B7
@GetMapping("/user")
public User getById(User user){
return user;
}
}
测试结果
注意:参数位置的顺序是允许变化的
restFul风格传递单个参数
编写测试代码
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class UserController {
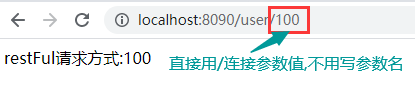
// URL: http://localhost:8090/user/100
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public String restFul(@PathVariable Integer id){
return "restFul请求方式:"+id;
}
}
测试结果
restFul风格传递多个参数
编写测试代码
package com.jt.controller;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class UserController {
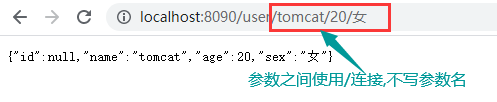
// URL: http://localhost:8090/user/tomcat/20/女
@GetMapping("user/{name}/{age}/{sex}")
public User restGetUser(User user){
return user;
}
}
测试结果
注意:参数位置的顺序不能改变,应与@getMapping参数的路径一致.
Axios的简单使用
Axios传递简单参数
后端测试代码编写
@GetMapping("/axios/getUserById")
public String getUserById(Integer id){
return "你好Axios入门: "+id;
}前端测试代码编写
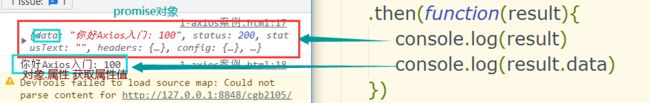
axios.get("http://localhost:8090/axios/getUserById?id=100")
.then(function(result){
console.log(result)
console.log(result.data)
})注意需先导入相关axios.js文件 。
测试结果
Axios传递对象参数
后端测试代码编写
@GetMapping("/axios/user/{name}/{age}")
public User restGetU(User user){
return user;
}多个参数传递可以封装为对象
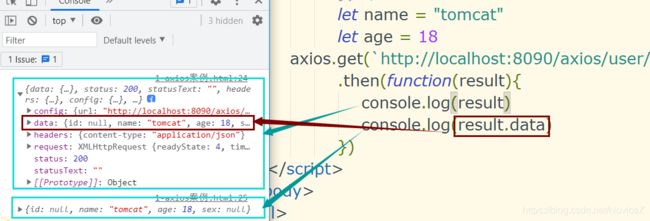
前端测试代码编写
let name = "tomcat"
let age = 18
axios.get(`http://localhost:8090/axios/user/${name}/${age}`)
.then(function(result){
console.log(result.data)
})注意这里的url信息使用了反引号包裹,即表示模版字符串,目的是优化参数,方便参数的传递,避免使用字符串连接符+号连接参数。
测试结果
Axios的get与post请求方式的传参区别
get方式
axios.get(url,{params: user})
.then(function(result){
console.log(result.data)
})post方式
post请求方式与get请求方式的区别是:post方式的第二个参数直接写传参对象user,而get方式的第二个参数的格式是{params: user},并且params是固定的,不能改变的.
get请求采用 axios.get(url, {params: 对象})
post请求采用 axios.post(url, 对象)
axios.post(url, user)
.then(function(result){
console.log(result.data)
})特别注意:使用post方式时,如果第二个参数为对象,后台对应方法的形参需要用到@RequestBody注解.
//定义axios基本请求路径,为Ajax请求添加前缀
axios.defaults.baseURL = "http://localhost:8090"
async insertUser(){
//解构赋值.post请求得到的结果是promise对象,对象里面的data使我们需要的数据
let {data: result} = await axios.post("/vue/insertUser",this.addUser)
} @PostMapping("insertUser")
private int insertUser(@RequestBody User user){
return userService.insertUser(user);
}一般都是JSON串处于前端与后端之间,所以前端到后端属于请求,后端想要得到对象,使用requestBody注解(form表单提交,参数可以直接转为对象,不需要注解).
前端得到后端的响应,要在后端先把对象转为JSON串,使用responseBody注解箭头函数
使用箭头函数x => x * x就相当于 function(x){return x*x}.
箭头函数作用:用于简化回调函数的写法
使用前提: 重复的 固定的可以简化
使用规则: 去掉function,在参数与方法体(小括号与大括号)之间加=>符号
如果回调函数参数只有一个,可以不要小括号
如果方法体的内容只有一个,可以不要大括号
使用箭头函数前:
axios.get(url)
.then(function(result) {
alert(result.data)
})使用箭头函数后:
axios.get(url)
.then(result =>
alert(result.data)
)