Vue全家桶(三):Vuex状态管理(State、Getters、Mutations、Actions)
目录
- Vuex
-
- 1. 理解Vuex
-
- 1.1 组件之间共享数据的方式
- 1.2 Vuex是什么
- 1.2 什么时候使用Vuex
- 1.3 Vuex的工作原理图
- 2 使用Vuex
-
- 2.1 搭建Vuex环境
- 2.2 Vuex基本使用
-
- 2.2.1 State
- 2.2.2 Getters
- 2.2.3 Mutations
- 2.2.4 Actions
- 2.2.5 Modules 模块化+命名空间
- 3 求和案例
-
- 3.1 使用纯vue编写
- 3.2 使用Vuex编写
-
- 3.2.1 原始写法
- 3.2.2 用mapXXX优化后
- 3.2.2 多组件共享数据
- 3.2.3 模块化优化后
- 4 求和案例2
-
- 4.1 props传递值
- 4.2 Vuex的state传递
- 4.3 Matuations来修改状态
- 4.4 Mutations带参数传递修改状态
- 5 多组件共享数据案例
Vuex
1. 理解Vuex
1.1 组件之间共享数据的方式
父向子传值:v-bind 属性绑定
子向父传值:v-on 事件绑定
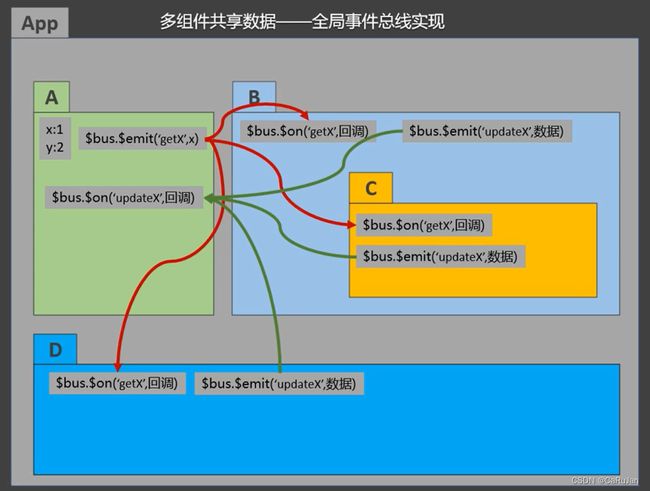
兄弟组件之间共享数据: EventBus(事件总线)
$on 接收数据的那个组件
$emit 发送数据的那个组件
1.2 Vuex是什么
1.概念: 专门在 Vue 中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个 Vue 插件,对 Vue 应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理 (读/写),也是一种组件间信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
Vuex Github: https://github.com/vuejs/vuex
1.2 什么时候使用Vuex
处理大量的需要在组件间传递的数据,直接定义一个全局的data属性保存就行了。
如果我们的页面比较简单,切记千万不要没事找事引入Vuex,我们使用Vuex是因为项目变得复杂之后,有很多数据需要在父组件、子组件和孙组件之间传递,处理起来很繁琐,于是就需要Vuex这样一个可以对这一部分数据进行统一管理的东西,也是响应式
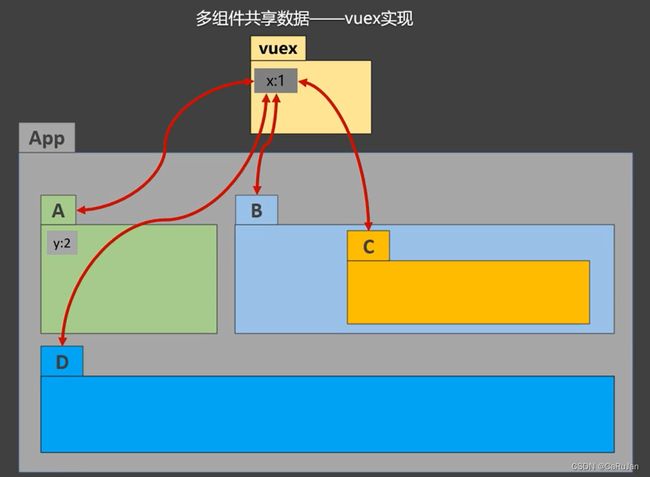
什么情况需要使用Vuex管理状态在多个组件间共享?
- 多个组件依赖于同一状态
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态
大型项目中组件很多,多个组件中共用的数据
例如:用户的登录状态、用户名称、头像、地理位置信息等
例如:商品的收藏、购物车中的物品。
例如:传递组件之间传递层次太多、不相关组件、公用组件
Vuex有点类似cookie和session,session是用于服务器端共享,cookie是用于浏览器的,Vuex是用于前端组件间共享
1.3 Vuex的工作原理图
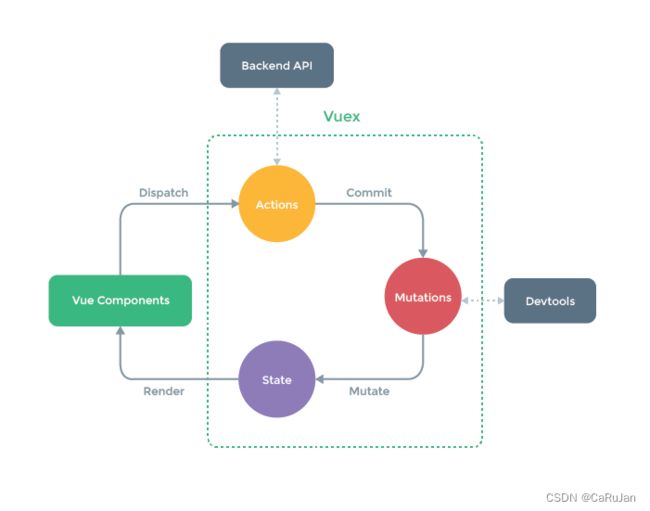
四个核心概念
Vuex 的四个核心概念分别是:
- The state tree:Vuex 使用单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。至此它便作为一个『唯一数据源(SSOT)』而存在。这也意味着,每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例。单状态树让我们能够直接地定位任一特定的状态片段,在调试的过程中也能轻易地取得整个当前应用状态的快照。
- Getters:用来从 store 获取 Vue 组件数据。
- Mutation:事件处理器用来驱动状态的变化。
- Actions:可以给组件使用的函数,以此用来驱动事件处理器 mutations
Vuex和简单的全局对象是不同的,当Vuex从store中读取状态值的时候,若状态发生了变化,那么相应的组件也会高效的更新。并且,改变store中状态的唯一途径就是提交commit mutations。这样便于我们跟踪每一次状态的变化。只要发生了状态的变化,一定伴随着mutation的提交。
2 使用Vuex
2.1 搭建Vuex环境
- 下载安装 Vuex
npm i vuex@3
npm i vuex是安装最新版本的Vuex
注意:
- Vue2中,要用Vuex的3版本
- Vue3中,要用Vuex的4版本
- 创建
src/store/index.js该文件用于创建Vuex中最为核心的store
写法一:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex) //应用Vuex
//创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {},
getters: {}, //里面定义方法,操作state方法
mutations: {}, // 操作数据State
actions: {}, //用于响应组件中的动作
modules: {},
})
写法二:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex) //应用Vuex
const actions = {} //用于响应组件中的动作
const mutations = {} // 操作数据State
const state = {}
const getters= {} //里面定义方法,操作state方法
const modules1 = {}
const modules2 = {}
//创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
modules: {
modules1,
modules2
}
})
2.2 Vuex基本使用
Vuex的基本使用
Vuex中一共有五个状态 State、Getter、Mutation、Action、Module
2.2.1 State
提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据统一放到store的state进行储存,相似与data
在vuex中state中定义数据,可以在任何组件中进行调用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
name:"张三",
age:12,
sex: '男',
count:0
},
})
读取
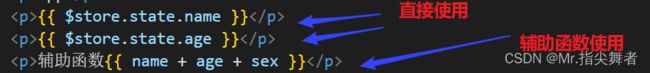
方法一:在标签中直接使用
<p>{{ $store.state.name }}p>
<p>{{ $store.state.age}}p>
方法二:
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
方法三:
从vuex中按需导入mapstate函数
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapState 函数
import { mapState } from "vuex";
通过刚才导入的 mapState 函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件的 computed 计算属性:
// 2. 将全局数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性
computed: {
// 对象写法
...mapState({name:'name', age:'age', sex:'sex'})
// 数组写法
...mapState(['name', 'age', 'sex'])
}
$store.dispatch('action中的方法名',数据)
//或是
$store.commit('mutations中的方法名',数据)
若没有网络请求或其他业务逻辑,组件中也可越过 actions,即不写 dispatch ,直接编
写commit
2.2.2 Getters
Getters 用于对 Store 中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据。
①Getters 可以对 Store 中已有的数据加工处理之后形成新的数据,类似 Vue 的计算属性。
②Store 中数据发生变化,Getters 的数据也会跟着变化。
具体操作类似于前几种
在Vuex中定义:
// 定义 Getters
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters: {
showNum: state => {
return '当前最新的数量是【'+ state.count * 10 +'】'
}
}
})
在组件中使用:
方法一:在标签中直接使用
<p>{{ $store.getter.name }}p>
<p>{{ $store.state.age}}p>
方法二:
this.$store.getters.名称
方法二:
从vuex中按需导入mapGetters 函数
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapGetters 函数,用于帮助映射 getters中的数据为当前组件的 computed 计算属性:
computed: {
//对象写法
...mapGetters({showNum:'showNum'})
//数组写法
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
}
2.2.3 Mutations
Mutations 用于变更 Store中 的数据。
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:
每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
① 只能通过 mutations 变更 Store 数据,不可以直接操作 Store 中的数据。
② 通过这种方式虽然操作起来稍微繁琐一些,但是可以集中监控所有数据的变化。
在Vuex中定义
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
name:"张三",
age:12,
sex: '男',
count:0
},
mutations: {
addCount(state, num) {
state.count += num
},
reduce(state){
state.count--
}
}
})
在组件中使用:
方法一:使用commit触发Mutations操作
// 触发mutations
methods: {
btn() {
// 触发 mutations 的第一种方式
this.$store.commit('addCount', 10) //每次加十
}
btn2() {
// 触发 mutations 的第一种方式
this.$store.commit('reduce')
}
}
方法二:使用辅助函数进行操作,具体方法同上
从vuex中按需导入mapMutations 函数
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapMutations 函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapMutations 函数,将需要的 mutations 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:
// 2. 将指定的 mutations 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 函数
methods: {
// 触发 mutations 的第二种方式 对象写法
...mapMutations({addCount: 'addCount', reduce:'reduce'}),
//或是
// 触发 mutations 的第二种方式 数组写法
...mapMutations(['addCount', 'reduce']),
btn() {
this.addCount(10) //每次加十
}
btn2() {
this.reduce()
}
}
2.2.4 Actions
Actions 用于处理异步任务。
如果通过异步操作变更数据,必须通过 Actions,而不能使用 Mutation,但是在 Actions 中还是要通过触发Mutation 的方式间接变更数据。
在Vuex中定义:
讲上面的操作改为异步操作
// 定义 Actions
export default new Vuex.Store({
// ...省略其他代码
mutations: {
//第一个参数是state,第二参数是传的参数
addCount(state, num) {
//state中的数据的改变会触发页面上对应数据的改变
state.count += num
},
reduce(state){
state.count--
}
},
// 异步操作
actions: {
asynReduce(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('reduce')
}, 1000)
},
//触发 actions 异步任务时携带参数,第一个参数是上下文对象,第二参数是传的参数
asynAdd(context, num) {
setTimeout(() => {
//会找到mutation对应的方法
context.commit('addCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
在组件中使用:
方法一:直接使用 dispatch触发Action函数
methods: {
btn() {
// 触发 actions 的第一种方式
this.$store.dispatch("asynAdd", 10)
}
btn2() {
// 触发 actions 的第一种方式
this.$store.dispatch("asynReduce")
}
}
方法二:使用辅助函数
从vuex中按需导入mapActions 函数
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapActions 函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapActions 函数,将需要的 actions 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:
// 2. 将指定的 actions 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 函数
methods: {
//对象写法
...mapActions({asynAdd:'asynAdd', asynReduce:'asynReduce'}),
//或是
//数组写法
...mapActions(['asynAdd', 'asynReduce']),
btn() {
this.asynAdd(10) //每次加十
}
btn2() {
this.asynReduce()
}
}
2.2.5 Modules 模块化+命名空间
-
目的:让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确
-
场景:当遇见大型项目时,数据量大,store就会显得很臃肿
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割: -
基本写法
写法一:
const countAbout = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
sum: 0,
name: 'zhangsan',
sex: 'man',
},
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
getters: {
bisSum(state){ return state.sum * 10}
}
const personAbout= {
namespaced: true,
state: {
personList: [{
id: '0001',
name: 'Lisi'
}]
},
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
getters: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countAbout,
personAbout
}
})
写法二:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countAbout:{
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
getters: { ... }
},
personAbout: {
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
getters: { ... }
}
}
})
默认情况下,模块内部的 action 和 mutation 仍然是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一个 action 或 mutation 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
- 开启命名空间后,组件中读取
state数据
//方法一:自己读取
this.$store.state.countAbout.sum
//方法二:借助mapState读取
...mapState('countAbout', ['sum', 'name', 'sex'])
- 开启命名空间后,组件中读取
getters数据
//方法一:自己读取
this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName']
//方法二:借助mapGetters读取
...mapGetters('countAbout', ['bisSum'])
- 开启命名空间后,组件中调用
commit
//方法一:自己commit
this.$store.commit('personAbout/addPerson', person)
//方法二:借助mapMutations读取
...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment: 'add', decrement: 'reduce'})
- 开启命名空间后,组件中调用
dispatch
//方法一:自己commit
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang', person)
//方法二:借助mapMutations读取
...mapActions('countAbout',{incrementOdd:'asyncAddOdd', incrementWait:'asyncAddWait'})
3 求和案例
3.1 使用纯vue编写
App.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<Count/>
div>
template>
<script>
import Countfrom './components/Count'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Count}
}
script>
<style>style>
Count.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>当前求和为:{{sum}}h1>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment">+button>
<button @click="decrement">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Count',
data() {
return {
n: 1,
sum: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.sum += this.n
},
decrement() {
this.sum -= this.n
},
incrementOdd() {
if (this.sum %2) {
this.sum += this.n
}
},
incrementWait() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.sum += this.n
}, 500);
}
}
}
script>
<style scoped>style>
3.2 使用Vuex编写
3.2.1 原始写法
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex) //应用Vuex
//创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
sum: 0,
name: 'zhangsan',
sex: 'man'
},
getters: {}, //里面定义方法,操作state方法
mutations: {
add(state, num) {
state.sum += num
},
reduce(state){
state.sum--
}
}, // 操作异步操作mutation
actions: {
asyncAddWait(context, num){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add', num)
},500)
},
asyncAddOdd(context, num){
if(context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit('add', num)
}
}
}, //用于响应组件中的动作
modules: {},
})
Count.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>当前求和为:{{$store.state.sum}}h1>
<h3>当前求和放大10倍:{{$store.getters.bigSum}}h3>
<h3>姓名:{{ $store.statename }},性别: {{ $store.statesex }}h3>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment">+button>
<button @click="decrement">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Count',
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
methods: {
//使用mutaion
increment() {this.$store.commit('add', this.n)},
decrement() { this.$store.commit('reduce')},
//使用Actions异步
incrementOdd() {this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddOdd', this.n)},
incrementWait() {this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddWait', this.n)}
}
}
script>
<style scoped>style>
3.2.2 用mapXXX优化后
Count.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>当前求和为:{{ sum }}h1>
<h3>当前求和放大10倍:{{bigSum}}h3>
<h3>姓名:{{ name }},性别: {{ sex }}h3>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
//借助mapSate和mapGetters生成计算属性
...mapState(['sum','name','sex']),
...mapGetters(['bigSum'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({increment: 'add', decrement: 'reduce'}),
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'asyncAddOdd', incrementWait:'asyncAddWait'})
//使用mutaion
//increment() {this.$store.commit('add', this.n)},
//decrement() { this.$store.commit('reduce')},
//使用Actions异步
//incrementOdd() {this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddOdd', this.n)},
//incrementWait() {this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddWait', this.n)}
}
}
script>
<style scoped>style>
3.2.2 多组件共享数据
<template>
<div class="container">
<Count/>
<Person/>
div>
template>
<script>
import Count from './components/Count'
import Person from './components/Person'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Count,Person}
}
script>
<style>style>
src/components/Count.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>当前求和为:{{ sum }}h1>
<h3>当前求和放大10倍:{{bigSum}}h3>
<h3>姓名:{{ name }},性别: {{ sex }}h3>
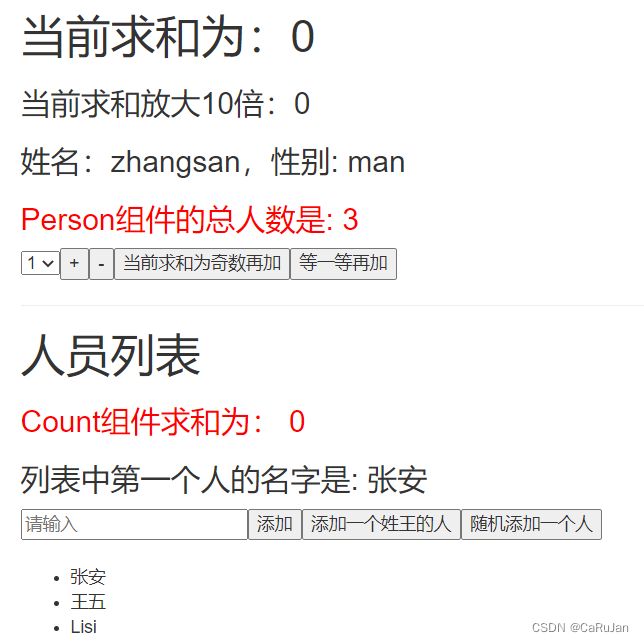
<h3 style="color:red">Person组件的总人数是: {{ personList.length }}h3>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
//借助mapSate和mapGetters生成计算属性
...mapState(['sum','name','sex','personList']),
...mapGetters(['bigSum'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({increment: 'add', decrement: 'reduce'}),
...mapActions({incrementOdd:'asyncAddOdd', incrementWait:'asyncAddWait'})
}
}
script>
<style scoped>style>
src/components/Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<hr>
<h1>人员列表h1>
<h3 style="color:red">Count组件求和为: {{ sum }}h3>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入" v-model="name">
<button @click="add">添加button>
<br><br>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in personList" :key="p.id">{{p.name}}li>
ul>
div>
template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: 'Person',
components: {},
props: {},
data() {
return {
name: ''
};
},
computed:{
...mapState(['personList', 'sum'])
},
methods: {
add() {
if(this.name === '') return
const personObj = {id: nanoid(), name: this.name}
this.$store.commit('addPerson', personObj)
this.name = ''
}
}
};
script>
<style scoped>style>
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex) //应用Vuex
//创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
sum: 0,
name: 'zhangsan',
sex: 'man',
personList: [{
id: '0001',
name: 'Lisi'
}]
},
//里面定义方法,操作state方法
getters: {
bigSum: state=>{
return state.sum * 10
}
},
// 操作异步操作mutation
mutations: {
add(state, num) {
state.sum += num
},
reduce(state){
state.sum--
},
addPerson(state, value) {
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
//用于响应组件中的动作
actions: {
asyncAddWait(context, num){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add', num)
},500)
},
asyncAddOdd(context, num){
if(context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit('add', num)
}
}
},
})
3.2.3 模块化优化后
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入Vuex
import countOptions from './count'
import personOptions from './person'
import count from './count'
Vue.use(Vuex) //应用Vuex
//创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countAbout: countOptions,
personAbout: personOptions
},
})
src/store/count.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
sum: 0,
name: 'zhangsan',
sex: 'man',
},
getters: {
bigSum(state){return state.sum * 10}
},
mutations: {
add(state, num) {
state.sum += num
},
reduce(state){
state.sum--
},
},
actions: {
asyncAddWait(context, num){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add', num)
},500)
},
asyncAddOdd(context, num){
if(context.state.sum % 2){
context.commit('add', num)
}
}
}
}
src/store/person.js
import axios from "axios"
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
personList: [{
id: '0001',
name: 'Lisi'
}]
},
getters: {
firstPersonName(state) {return state.personList[0].name}
},
mutations: {
addPerson(state, value) {
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
actions: {
addPersonWang(context, value) {
if(value.name.indexOf('王') === 0){
context.commit('addPerson', value)
}else {
alert('添加的人必须为王')
}
},
addPersonServer(context) {
axios.get('http://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social').then(
response => {
context.commit('addPerson', {id: nanoid(), name:response.data})
},
error => {
alert(error.message)
}
)
}
}
}
Count和Person的呈现了两种不同的写法,一个是用mapXXX的写法,一个是直接使用this.$store的写法
src/components/Count.vue
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>当前求和为:{{ sum }}h1>
<h3>当前求和放大10倍:{{bigSum}}h3>
<h3>姓名:{{ name }},性别: {{ sex }}h3>
<h3 style="color:red">Person组件的总人数是: {{ personList.length }}h3>
<select v-model.number="n">
<option value="1">1option>
<option value="2">2option>
<option value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
data() {
return {
n: 1
}
},
computed: {
//借助mapSate和mapGetters生成计算属性
...mapState('countAbout',['sum','name','sex']),
...mapState('personAbout', ['personList']),
...mapGetters('countAbout',['bigSum'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment: 'add', decrement: 'reduce'}),
...mapActions('countAbout',{incrementOdd:'asyncAddOdd', incrementWait:'asyncAddWait'})
}
}
script>
<style scoped>style>
src/components/Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<hr>
<h1>人员列表h1>
<h3 style="color:red">Count组件求和为: {{ sum }}h3>
<h3>列表中第一个人的名字是: {{ firstPersonName }}h3>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入" v-model="name">
<button @click="add">添加button>
<button @click="addWang">添加一个姓王的人button>
<button @click="addRandom">随机添加一个人button>
<br><br>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in personList" :key="p.id">{{p.name}}li>
ul>
div>
template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: 'Person',
components: {},
props: {},
data() {
return {
name: ''
};
},
computed:{
//直接读取的方法
personList() { return this.$store.state.personAbout.personList },
sum() { return this.$store.state.countAbout.sum },
firstPersonName() { return this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName'] }
},
methods: {
add() {
if(this.name === '') return
const personObj = {id: nanoid(), name: this.name}
this.$store.commit('personAbout/addPerson', personObj)
this.name = ''
},
addWang() {
if(this.name === '') return
const personObj = {id: nanoid(), name: this.name}
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang', personObj)
this.name = ''
},
addRandom() {
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonServer')
}
}
};
script>
<style scoped>
style>
4 求和案例2
4.1 props传递值
helloword子组件使用Home组件声明的变量,可采用之前学习的组件传递值的方法
Home组件
<template>
<div class="home">
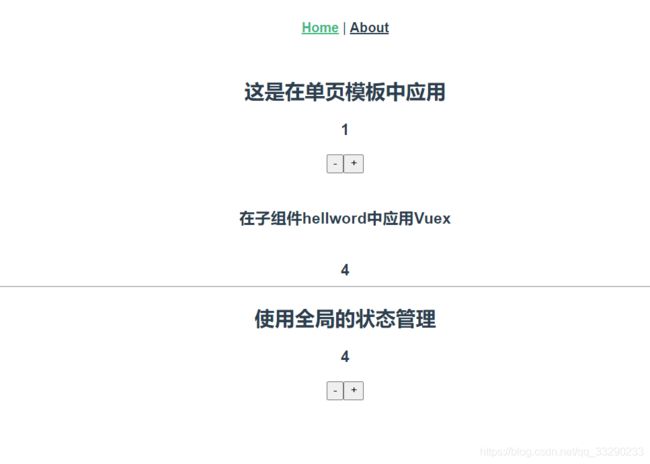
<h2>这是在单页模板中应用h2>
<h3>{{count}}h3>
<button @click="count--">-button>
<button @click="count++">+button>
<HelloWorld :count="count" msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
div>
template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
}
}
script>
helloword子组件
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}h1>
<h3>在子组件hellword中应用Home中的Datah3>
<h3>{{count}}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props: {
count: Number
}
}
script>
<style scoped lang="scss">
……
style>
效果
若About组件想要使用Home组件的count,通过组件传递的方式也可实现,就是有点麻烦,需要传递给中介App组件,App组件再传递给About组件。
4.2 Vuex的state传递
因此,在这里可采用Vuex,其配置文件在/store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
//任何地方都可使用这个状态管理
num: 0
},
mutations: { },
actions: {},
modules: {}
})
Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h2>使用全局的状态管理h2>
<h3>{{$store.state.num}}h3>
<button @click="$store.state.num--">-button>
<button @click="$store.state.num++">+button>
div>
template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
}
script>
About.vue
<template>
<div class="about">
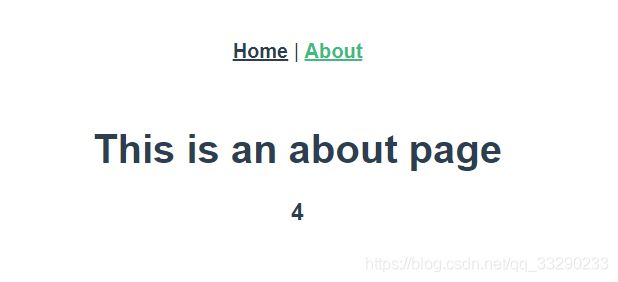
<h1>This is an about pageh1>
<h3>{{$store.state.num}}h3>
div>
template>
4.3 Matuations来修改状态
Vuex最好采用Matuations来修改状态,而不是通过组件的形式
index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
//任何地方都可使用这个状态管理
num: 0,
mnum: 0
},
mutations: {
//自动把state的参数传过来
sub(state) {
state.mnum--;
},
add(state) {
state.mnum++;
}
},
actions: { },
modules: {}
})
Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
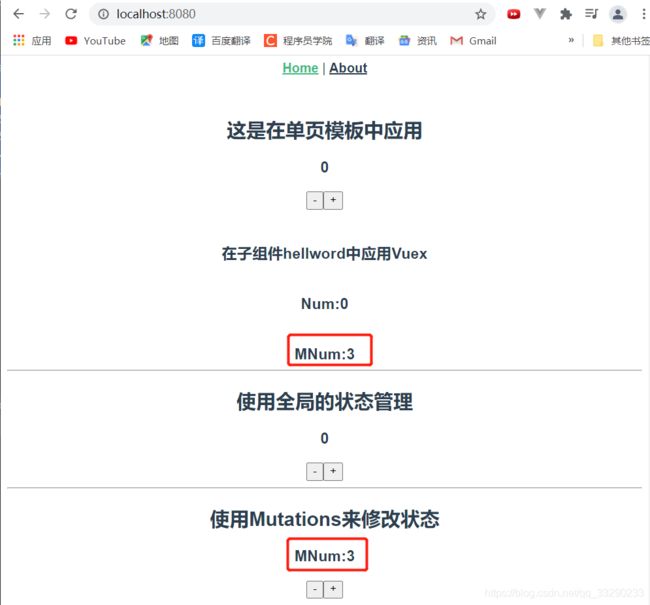
<h2>这是在单页模板中应用h2>
<h3>{{count}}h3>
<button @click="count--">-button>
<button @click="count++">+button>
<HelloWorld :count="count" msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
<hr>
<h2>使用全局的状态管理h2>
<h3>{{$store.state.num}}h3>
<button @click="$store.state.num--">-button>
<button @click="$store.state.num++">+button>
<hr>
<h2>使用Mutations来修改状态h2>
<h3>MNum:{{$store.state.mnum}}h3>
<button @click="sub1()">-button>
<button @click="add1()">+button>
div>
template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
add1() {
this.$store.commit('add')
},
sub1() {
this.$store.commit('sub')
},
}
}
script>
About.vue
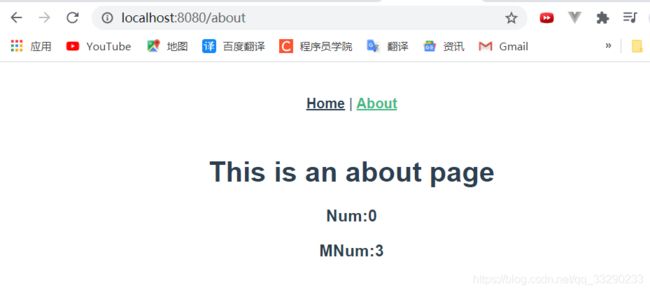
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1>This is an about pageh1>
<h3>Num:{{$store.state.num}}h3>
<h3>MNum:{{$store.state.mnum}}h3>
div>
template>
4.4 Mutations带参数传递修改状态
index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
//任何地方都可使用这个状态管理
num: 0,
mnum: 0
},
mutations: {
//自动把state的参数传过来
sub(state) {
state.mnum--;
},
add(state) {
state.mnum++;
},
//接收一个参数
sub2(state,count) {
console.log(count);
state.mnum-=count;
},
add2(state,count) {
console.log(count);
state.mnum+=count;
},
//接收多个参数
sub3(state,payload) {
console.log(payload);
state.mnum-=(payload.count+payload.num);
},
add3(state,payload) {
console.log(payload);
state.mnum+=(payload.count+payload.num);
}
},
actions: {},
modules: {}
})
Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<hr>
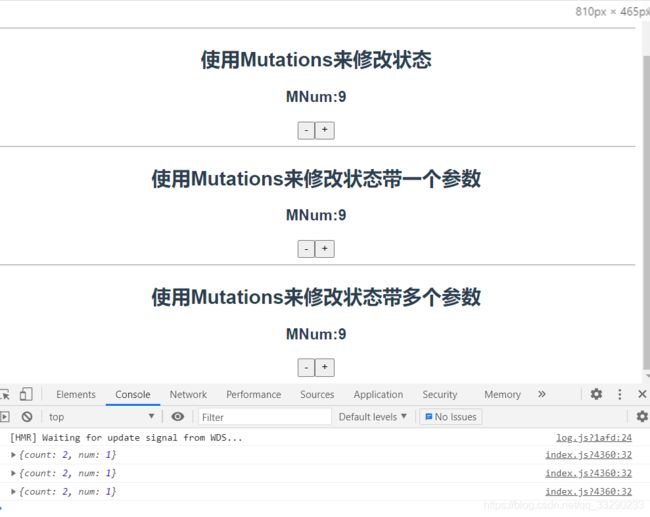
<h2>使用Mutations来修改状态h2>
<h3>MNum:{{$store.state.mnum}}h3>
<button @click="sub1()">-button>
<button @click="add1()">+button>
<hr>
<h2>使用Mutations来修改状态带一个参数h2>
<h3>MNum:{{$store.state.mnum}}h3>
<button @click="sub2()">-button>
<button @click="add2()">+button>
<hr>
<h2>使用Mutations来修改状态带多个参数h2>
<h3>MNum:{{$store.state.mnum}}h3>
<button @click="sub3()">-button>
<button @click="add3()">+button>
div>
template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
add1() {
this.$store.commit('add')
},
sub1() {
this.$store.commit('sub')
},
add2() {
let count = 2;
this.$store.commit('add2',count)
},
sub2() {
let count = 2;
this.$store.commit('sub2',count)
},
add3() {
let payload = {count:2, num:1}
this.$store.commit('add3',payload)
},
sub3() {
let payload = {count:2, num:1}
this.$store.commit('sub3',payload)
//等价于
//this.$store.commit({type:'sub3', payload})
}
}
}
script>