RTC
文章目录
-
- 前言
- 驱动
- 应用程序
- 运行
前言
RTC(Real Time Clock,实时时钟)是个常用的外设,通过 RTC 我们可以知道日期和时间信息,因此在需要记录时间的场合就需要实时时钟。
可以使用专用的实时时钟芯片来完成此功能,如 DS1302,不过有些 SOC 内部就已经自带了 RTC 外设,比如 IMX6U。
RTC 本质上就是一个定时器,只要给它提供时钟,它就会一直运行。寄存器保存着秒数,直接读取寄存器值就知道过了多长时间了,一般以 1970 年 1 月 1 日为起点。
RTC 也是带有闹钟功能的,往相应寄存器写入值,当时钟值和闹钟值匹配时就会产生时钟中断。
驱动
step1:
内核启动打印
...
snvs_rtc 20cc000.snvs:snvs-rtc-lp: rtc core: registered 20cc000.snvs:snvs-r as rtc0
...
snvs_rtc 20cc000.snvs:snvs-rtc-lp: setting system clock to 2021-07-28 10:40:23 UTC (1627468823)
...
得知 rtc 的驱动为 20cc000.snvs
step2:
查看设备树
snvs: snvs@020cc000 {
compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon", "syscon", "simple-mfd";
reg = <0x020cc000 0x4000>;
snvs_rtc: snvs-rtc-lp {
compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp";
regmap = <&snvs>;
offset = <0x34>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 19 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>, <GIC_SPI 20 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
};
snvs_poweroff: snvs-poweroff {
compatible = "syscon-poweroff";
regmap = <&snvs>;
offset = <0x38>;
mask = <0x61>;
};
snvs_pwrkey: snvs-powerkey {
compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-pwrkey";
regmap = <&snvs>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 4 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
linux,keycode = <KEY_POWER>;
wakeup;
};
};
可知:rtc 是 snvs(Secure Non-Volatile Storage)的一个子功能,和其并列的还有 poweroff、pwrkey
目前我们只关注 snvs_rtc
snvs_rtc: snvs-rtc-lp {
compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp";
regmap = <&snvs>;
offset = <0x34>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 19 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>, <GIC_SPI 20 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
};
step3:
在 C 文件中搜索 "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp",用来找到驱动
// drivers/rtc/rtc-snvs.c
static const struct of_device_id snvs_dt_ids[] = {
{ .compatible = "fsl,sec-v4.0-mon-rtc-lp", },
{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, snvs_dt_ids);
进而找到对应的 probe() 函数
static struct platform_driver snvs_rtc_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "snvs_rtc",
.pm = SNVS_RTC_PM_OPS,
.of_match_table = snvs_dt_ids,
},
.probe = snvs_rtc_probe,
};
module_platform_driver(snvs_rtc_driver); // 疑问:为什么是平台总线?
step4:
分析驱动注册(初始化)流程
static int snvs_rtc_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct snvs_rtc_data *data;
struct resource *res;
int ret;
void __iomem *mmio;
data = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data)
return -ENOMEM;
data->regmap = syscon_regmap_lookup_by_phandle(pdev->dev.of_node, "regmap");
if (IS_ERR(data->regmap)) {
dev_warn(&pdev->dev, "snvs rtc: you use old dts file, please update it\n");
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
mmio = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res);
if (IS_ERR(mmio))
return PTR_ERR(mmio);
data->regmap = devm_regmap_init_mmio(&pdev->dev, mmio, &snvs_rtc_config);
} else {
data->offset = SNVS_LPREGISTER_OFFSET;
of_property_read_u32(pdev->dev.of_node, "offset", &data->offset);
}
if (!data->regmap) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't find snvs syscon\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
data->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
if (data->irq < 0)
return data->irq;
data->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "snvs-rtc");
if (IS_ERR(data->clk)) {
data->clk = NULL;
} else {
ret = clk_prepare_enable(data->clk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"Could not prepare or enable the snvs clock\n");
return ret;
}
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, data);
/* Initialize glitch detect */
regmap_write(data->regmap, data->offset + SNVS_LPPGDR, SNVS_LPPGDR_INIT);
/* Clear interrupt status */
regmap_write(data->regmap, data->offset + SNVS_LPSR, 0xffffffff);
/* Enable RTC */
snvs_rtc_enable(data, true);
device_init_wakeup(&pdev->dev, true);
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, data->irq, snvs_rtc_irq_handler,
IRQF_SHARED, "rtc alarm", &pdev->dev);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to request irq %d: %d\n",
data->irq, ret);
goto error_rtc_device_register;
}
data->rtc = devm_rtc_device_register(&pdev->dev, pdev->name,
&snvs_rtc_ops, THIS_MODULE); // 设备注册
if (IS_ERR(data->rtc)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(data->rtc);
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register rtc: %d\n", ret);
goto error_rtc_device_register;
}
return 0;
error_rtc_device_register:
if (data->clk)
clk_disable_unprepare(data->clk);
return ret;
}
step5:
先分析结构体
struct snvs_rtc_data {
struct rtc_device *rtc;
struct regmap *regmap;
int offset;
int irq; // 中断号,初始化过程中,register_irq()
struct clk *clk;
};
struct rtc_device
{
struct device dev;
struct module *owner;
int id;
char name[RTC_DEVICE_NAME_SIZE]; // 初始化过程中,肯定有个函数来对其进行赋值,猜测赋值 “rtc0”
const struct rtc_class_ops *ops; // file operations,行为核心
struct mutex ops_lock;
struct cdev char_dev;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long irq_data;
spinlock_t irq_lock;
wait_queue_head_t irq_queue;
struct fasync_struct *async_queue;
struct rtc_task *irq_task;
spinlock_t irq_task_lock;
int irq_freq;
int max_user_freq;
struct timerqueue_head timerqueue;
struct rtc_timer aie_timer;
struct rtc_timer uie_rtctimer;
struct hrtimer pie_timer; /* sub second exp, so needs hrtimer */
int pie_enabled;
struct work_struct irqwork;
/* Some hardware can't support UIE mode */
int uie_unsupported;
#ifdef CONFIG_RTC_INTF_DEV_UIE_EMUL
struct work_struct uie_task;
struct timer_list uie_timer;
/* Those fields are protected by rtc->irq_lock */
unsigned int oldsecs;
unsigned int uie_irq_active:1;
unsigned int stop_uie_polling:1;
unsigned int uie_task_active:1;
unsigned int uie_timer_active:1;
#endif
};
struct rtc_class_ops {
int (*open)(struct device *); // 打开
void (*release)(struct device *); // 关闭
int (*ioctl)(struct device *, unsigned int, unsigned long); // ioctl
int (*read_time)(struct device *, struct rtc_time *); // 读时间
int (*set_time)(struct device *, struct rtc_time *); // 设置时间
int (*read_alarm)(struct device *, struct rtc_wkalrm *); // 读闹钟时间
int (*set_alarm)(struct device *, struct rtc_wkalrm *); // 设置闹钟时间
int (*proc)(struct device *, struct seq_file *);
int (*set_mmss64)(struct device *, time64_t secs);
int (*set_mmss)(struct device *, unsigned long secs);
int (*read_callback)(struct device *, int data);
int (*alarm_irq_enable)(struct device *, unsigned int enabled);
};
static const struct file_operations rtc_dev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = rtc_dev_read,
.poll = rtc_dev_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = rtc_dev_ioctl, // case RTC_RD_TIME: rtc->ops->read_time(rtc->dev.parent, tm);
.open = rtc_dev_open, // rtc->ops->open()
.release = rtc_dev_release, // rtc->ops->release()
.fasync = rtc_dev_fasync,
};
关键函数
data->rtc = devm_rtc_device_register(&pdev->dev, pdev->name,
&snvs_rtc_ops, THIS_MODULE); // 设备注册
devm_rtc_device_register(,&snvs_rtc_ops,) // 设备注册
rtc_device_register()
rtc_dev_prepare()
cdev_init(&rtc->char_dev, &rtc_dev_fops);
驱动初始化的核心是上面这个函数 devm_rtc_device_register(),这个函数的核心是挂载 snvs_rtc_ops 和 rtc_dev_fops 这两个 operations。
其中 rtc_dev_fops 为 /dev/rtc0 对应的 operations,即在应用层对 /dev/rtc0 执行 open() 系统调用,则最终会执行 rtc_dev_open(),其它函数类似。
而 snvs_rtc_ops 是作为 RTC 功能实现的函数,作为 rtc_dev_fops 的 RTC 功能支撑。比如,应用层调用 open() 系统调用后,会调 file_operations 的 rtc_dev_open() 函数,而在这个函数里面又会去调用 RTC 功能的 snvs_rtc_ops 函数。
总结就是,file_operations 看名字带个 file 就知道,操作 /dev/rtc 文件,就会最终调用其 hook 函数。
而在 file_operations 的各个 hook 函数中,我们想要实现的是 RTC 功能,所以就要借助 RTC 相关的功能函数来完成任务,这些 RTC 的功能函数就是 snvs_rtc_ops。
open() --> rtc_dev_open() --> rtc->ops->open()
read() --> rtc_dev_read()
ioctl(fd, RTC_RD_TIME,) --> rtc_dev_ioctl: case RTC_RD_TIME: rtc->ops->read_time(); --> read_time()
close() --> rtc_dev_release() --> rtc->ops->release()
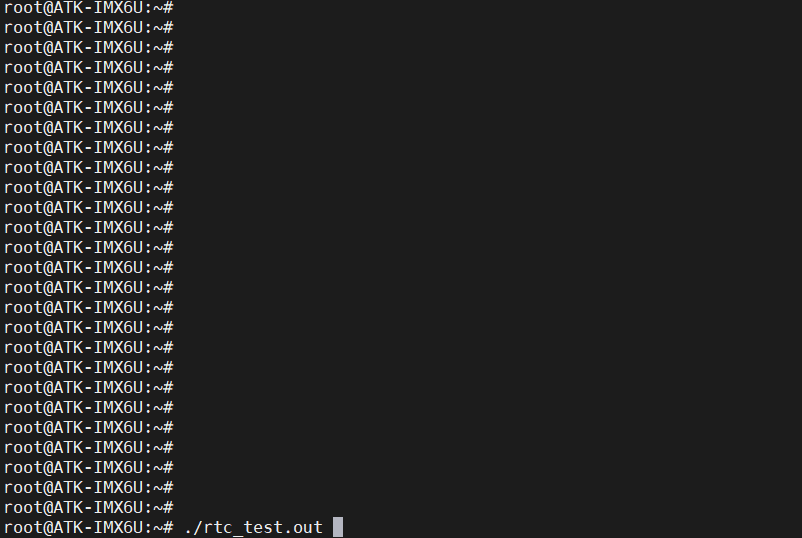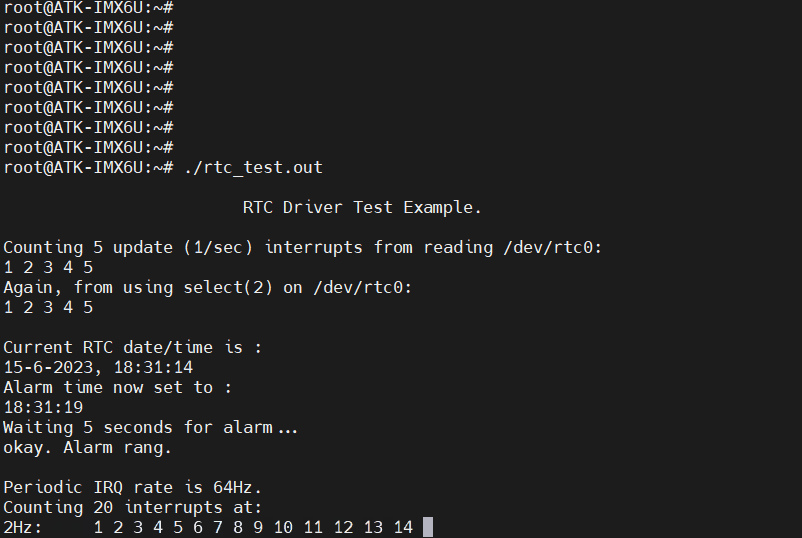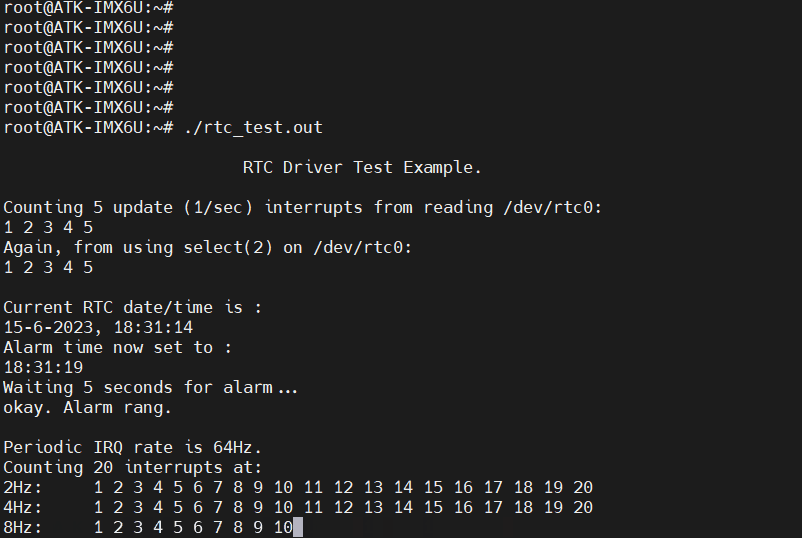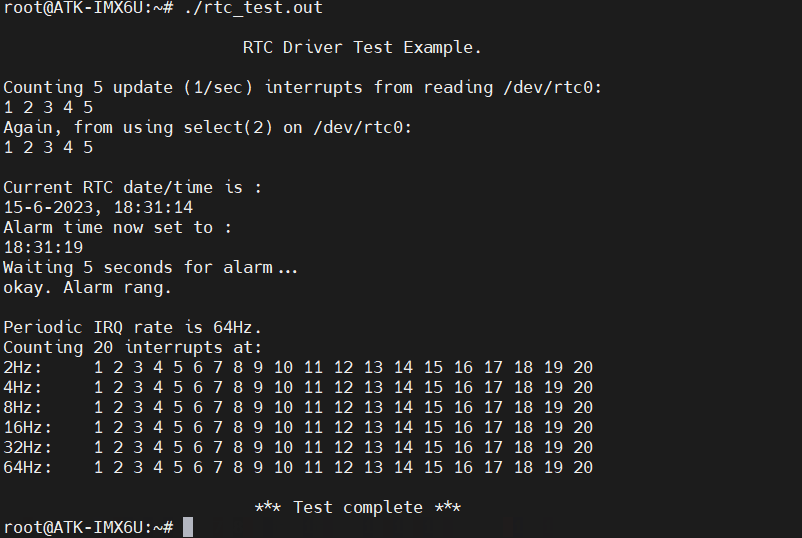
应用程序
rtc_test.c
#include Makefile
all:
arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc rtc_test.c -o rtc_test.out
install:
# cp rtc_test.out ~/tftp/
cp rtc_test.out ~/project/board/IMX6ULL/rootfs/home/root/
clean:
rm *.out
主要讲下 ioctl(fd, RTC_UIE_ON, 0),在应用程序调用 ioctl() 最终会执行驱动程序中的 rtc_dev_ioctl()。
内核中那么多 ioctl,怎么知道是要执行 rtc_dev_ioctl() 这个 ioctl 的呢,是根据 fd 匹配的。
在 rtc_dev_ioctl() 中解析 cmd,根据不同命令,执行不同操作,如读取时间、设置时间、中断使能和关闭等。
static long rtc_dev_ioctl(struct file *file,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int err = 0;
struct rtc_device *rtc = file->private_data;
const struct rtc_class_ops *ops = rtc->ops;
struct rtc_time tm;
struct rtc_wkalrm alarm;
void __user *uarg = (void __user *) arg;
err = mutex_lock_interruptible(&rtc->ops_lock);
if (err)
return err;
switch (cmd) {
case RTC_RD_TIME:
mutex_unlock(&rtc->ops_lock);
err = rtc_read_time(rtc, &tm);
if (err < 0)
return err;
if (copy_to_user(uarg, &tm, sizeof(tm)))
err = -EFAULT;
return err;
case RTC_SET_TIME:
mutex_unlock(&rtc->ops_lock);
if (copy_from_user(&tm, uarg, sizeof(tm)))
return -EFAULT;
return rtc_set_time(rtc, &tm);
case RTC_UIE_ON:
mutex_unlock(&rtc->ops_lock);
return rtc_update_irq_enable(rtc, 1);
case RTC_UIE_OFF:
mutex_unlock(&rtc->ops_lock);
return rtc_update_irq_enable(rtc, 0);
default:
/* Finally try the driver's ioctl interface */
if (ops->ioctl) {
err = ops->ioctl(rtc->dev.parent, cmd, arg);
if (err == -ENOIOCTLCMD)
err = -ENOTTY;
} else
err = -ENOTTY;
break;
}
done:
mutex_unlock(&rtc->ops_lock);
return err;
}