【boost搜索引擎】
实战项目:Boost搜索引擎
博主主页:桑榆非晚ᴷ
博主能力有限,如果有出错的地方希望大家不吝赐教
给自己打气:成功没有快车道,幸福没有高速路。所有的成功,都来自不倦地努力和奔跑,所有的幸福都来自平凡的奋斗和坚持✨
Boost 搜索引擎
- 实战项目:Boost搜索引擎
- 1.项目背景及项目目标
- 2.搜索引擎的相关宏观原理
- 3.搜索引擎技术栈和项目环境
- 4.正排索引 && 倒排索引 - 搜索引擎基本原理
- 5. 编写数据去标签与数据清理的模块 `Parser`
- 6. 编写建立索引的模块`Index`
- 7. 编写搜索引擎模块`Searcher `
- 8.编写搜索服务端`http_server.cc`
- 9. 编写前端模块
1.项目背景及项目目标
(1)在如今的信息时代下,市面上已经有了很多的公司有了自己的搜索引擎。比如最为知名的百度、搜狗、360搜索等搜索引擎。但是这些搜索引擎太过庞大,技术门槛太高,实现的资源成本也高,目前我们自主实现是不太可能的。我们可以自主实现一个站内搜索的搜索引擎,就比如我们经常使用的cplusplus.com网站,站内搜索的特点就是数据搜索更垂直,数据量更小。
(2)Boost作为C++的准标准库,在C++代码编写中使用频率很高,但是在官方的网站中,却没有站内搜索,并不便于用户的快速查找。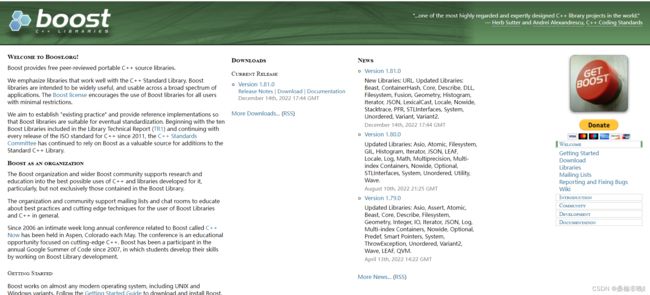
所以我们的项目boost搜索引擎,就是用来提供对boost官方库中资源的搜索服务的。
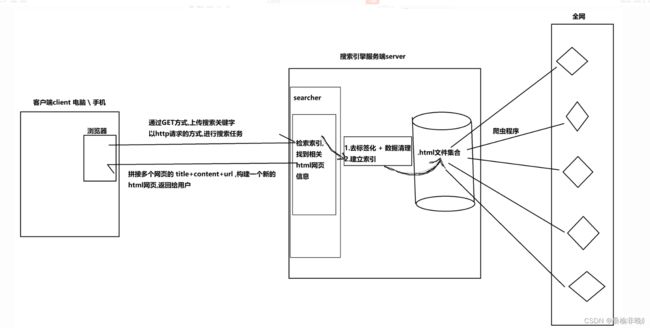
2.搜索引擎的相关宏观原理
(1)通过爬虫程序在全网中抓取相关的html网页信息,存至server服务器端的磁盘当中。
(2)对这些html文件,进行去标签化与数据清理,即只保留网页文件中的主要信息(title,content,url)。
(3)对去标签化清理后的数据,建立索引,方便我们进行后续的检索查找。
(4)客户端在浏览器中发起http请求,服务端在索引中检索到相关的html网页主要信息。
(5)拼接多个网页的(title+content+url)信息,构建出一个新html网页,返回给用户。
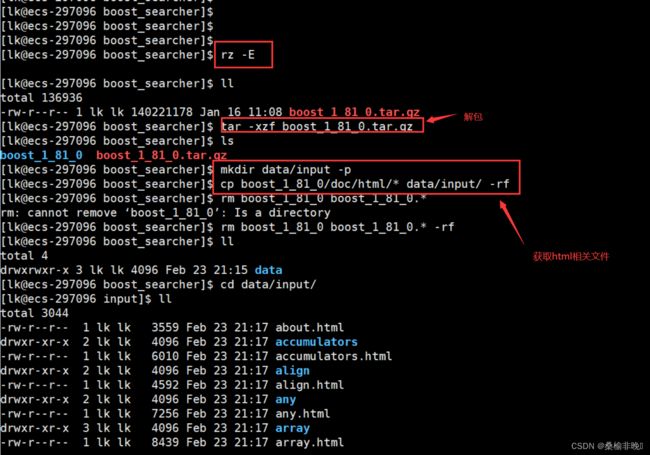
PS:爬虫程序,涉及法律,技术等因素限制,所以我们暂时只爬取一个boost库官方网站,且通过正规
渠道下载boost库的相关文件,我们这里使用的是boost_1_81_0版本。
boost库下载链接:https://boostorg.jfrog.io/artifactory/main/release/1.81.0/source/
我们项目里使用boost_1_81_0.tar.gz
3.搜索引擎技术栈和项目环境
- 技术栈:
C/C++、STL、 准标准库Boost、Jsoncpp、cppjieba、cpp-httplib 、HTML5,CSS,js,jQuery、Ajax - 项目环境:
Centos 7云服务器、vim/gcc(g++)/git/Makefile 、 VSCode
4.正排索引 && 倒排索引 - 搜索引擎基本原理
- 文档1:雷军买了四斤小米
- 文档2:雷军发布了小米手机
(1) 正排索引:根据文档ID找到文档内容
| 文档ID | 文档内容 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 雷军买了四斤小米 |
| 2 | 雷军发布了小米手机 |
(2) 文档分词:对目标文档进行分词(目的: 方便建立倒排索引与查找)
- 文档1[雷军买了四斤小米 ]: 雷军/买/四斤/小米/四斤小米
- 文档2[雷军发布了小米手机]:雷军/发布/小米/小米手机
PS:停止词如 “了” , “从” , “吗” , “the” , “a” 等,在我们分词的时候不纳入考虑范围。
(3) 倒排索引:根据文档内容,分词,整理不重复的各个关键字,对应联系到文档ID的方案
| 关键词(具有唯一性) | 文档ID,权重(weight) |
|---|---|
| 雷军 | 文档1、文档2 |
| 买 | 文档1 |
| 四斤 | 文档1 |
| 小米 | 文档1、文档2 |
| 四斤小米 | 文档1 |
| 发布 | 文档2 |
| 小米手机 | 文档2 |
(4) 模拟一次查找的过程:
用户输入 : 小米 -> 倒排索引中查找 -> 提取出文档ID{1,2} -> 根据正排索引
-> 找到文档内容 -> title+content+url 文档结果进行摘要 -> 构建响应结果
5. 编写数据去标签与数据清理的模块 Parser
(1) 获取相关boost资源,进入官网 https://www.boost.org 进行相应资源下载(我们以1.81.0为例)
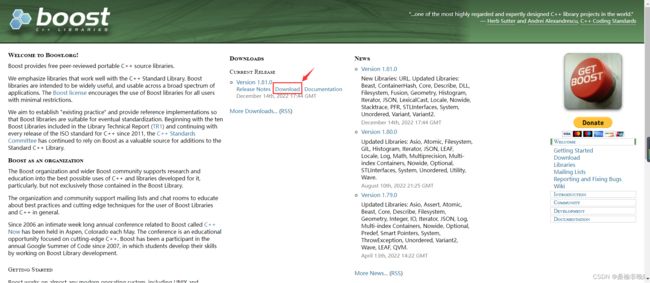
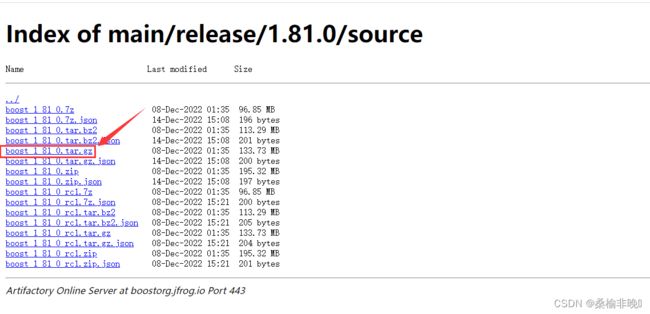
(2) Parser.cc代码框架
#include (3) EnumFile接口的实现:
要实现EnumFile接口,就是要在/data/input/文件夹下 , 提取每个html网页文件的路径名称。这时候就需要借助boost库中的接口来完成这一任务。
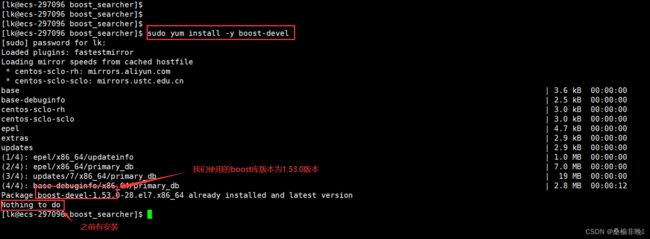
这里做一个区分,我们做站内搜索的版本是1.8.0 , 我们写代码要使用的boost库是1.53.0版本。

在云服务器中对boost库进行安装:sudo yum install -y boost-devel
EnumFile接口实现:
bool EnumFile(const std::string &src_path, std::vector<std::string> *files_list)
{
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
// 创建一个path对象
fs::path root_path(src_path);
// 判断路径是否存在,不存在就没有必要再往下走了
if(!fs::exists(root_path))
{
std::cerr << src_path << "not exists" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 定义一个空的迭代器,用来进行判断递归结束
fs::recursive_directory_iterator end;
for(fs::recursive_directory_iterator iter(root_path); iter != end; iter++)
{
// 判断是否是普通文件,html都是普通文件
if(!fs::is_regular_file(*iter))
{
continue;
}
// 判断文件路径的后缀是否符合要求
if(iter->path().extension() != ".html")
{
continue;
}
// std::cout << "debug: " << iter->path().string() << std::endl;
// 当程序执行的这里,说明当前的路径式合法的,以.html结束的普通网页文件
// 将所有带路径的html保存在files_list,方便后续进行文本分析
// iter->path()获取的还是path对象,我们需要的是string风格的带路径的文件名
files_list->push_back(iter->path().string());
}
return true;
}
ParseHtml接口实现:
bool ParseHtml(const std::vector<std::string> &files_list, std::vector<DocInfo_t> *results)
{
// files_list中存放的都是以.html结尾的文件名的路径
for(const std::string &file : files_list)
{
// 1.读取文件,Read()
std::string result; // 读取文件的内容放到result中
if(!ns_util::FileUtil::ReadFile(file, &result))
{
// 如果当前的.html文件读取失败,就不再进行解析,直接继续读取下一个.html文件
continue;
}
// typedef struct DocInfo
// {
// std::string title; // 文档标题
// std::string content; // 文档内容
// std::string url; // 该文档在官网中的url
// }DocInfo_t;
DocInfo_t doc;
// 2.解析指定文件,提取title
if(!ParseTitle(result, &doc.title))
{
continue;
}
// 3.解析指定文件,提取content
if(!ParseContent(result, &doc.content))
{
continue;
}
// 4.解析指定文件路径,构建url
if(!ParseUrl(file, &doc.url))
{
continue;
}
// done
results->push_back(std::move(doc));// bug:TODO 细节,本质会发生拷贝,效率可能比较低,所以使用c++11中的移动构造提高效率
}
return true;
}
ReadFile接口实现:
#pragma once
#include ParseTitle接口实现:
static bool ParseTitle(const std::string &result, std::string *title)
{
size_t begin = result.find(""</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin <span class="token operator">==</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>npos<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
size_t end <span class="token operator">=</span> result<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">find</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">" ");
if(end == std::string::npos)
{
return false;
}
begin += std::string(""</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin <span class="token operator">></span> end<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token operator">*</span>title <span class="token operator">=</span> result<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substr</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin<span class="token punctuation">,</span> end <span class="token operator">-</span> begin<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>ParseContent</strong>接口实现:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token keyword">static</span> <span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseContent</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>result<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>content<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 去标签,基于一个简易的状态机</span>
<span class="token keyword">enum</span> <span class="token class-name">status</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
LABLE<span class="token punctuation">,</span>
CONTENT
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">enum</span> <span class="token class-name">status</span> s <span class="token operator">=</span> LABLE<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">char</span> c <span class="token operator">:</span>result<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">switch</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">case</span> LABLE<span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'>'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
s <span class="token operator">=</span> CONTENT<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">case</span> CONTENT<span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'<'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
s <span class="token operator">=</span> LABLE<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">else</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 我们不想被保留原始文件中的\n,因为我们想用\n作为html解析之后文本的分隔符</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'\n'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
c <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token char">' '</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
content<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">default</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>ParseUrl</strong>接口实现:<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b721320a87c5470fa7a761202a0ecd0e.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b721320a87c5470fa7a761202a0ecd0e.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第15张图片" width="650" height="352" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token keyword">static</span> <span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseUrl</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>file_path<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>url<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 需要把官网的链接与本地链接进行拼接</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url_head <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// src_path = "data/input"</span>
<span class="token comment">// file_path = "data/input/*.html"</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url_tail <span class="token operator">=</span> file_path<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substr</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token operator">*</span>url <span class="token operator">=</span> url_head <span class="token operator">+</span> url_tail<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>SaveHtml</strong>接口实现:</p>
<p>把解析好的(去标签的)各个文件内容从<strong>std::vector<DocInfo_t> results</strong>以格式为title**\3<strong>content</strong>\3<strong>url\n写入到磁盘</strong>"data/raw_html/raw.txt"**文件中。</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">SaveHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>output<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">char</span> SEP <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token char">'\3'</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ofstream <span class="token function">out</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>output<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>out <span class="token operator">|</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>binary<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">is_open</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"open "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> output <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" failed!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 就可以进行文件的写入了</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> DocInfo_t <span class="token operator">&</span>item <span class="token operator">:</span> results<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string out_string<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> SEP<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> SEP<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> <span class="token char">'\n'</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">write</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>out_string<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">c_str</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> out_string<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">close</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p>如下图所示,这就是最终处理的结果,20代表行号,这一行由title\3content\3url\n组成,<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6933bdaeb69b4b2693ce3614d47629a8.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6933bdaeb69b4b2693ce3614d47629a8.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第16张图片" width="650" height="329" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>最终Parser.cc的代码内容:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><iostream></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><string></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><vector></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><boost/filesystem.hpp></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"util.hpp"</span></span>
<span class="token comment">// 是一个目录,下面放的是所有的html网页</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string src_path <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"data/input"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// </span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string output <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"data/raw_html/raw.txt"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">typedef</span> <span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">DocInfo</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string title<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档标题</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string content<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档内容</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 该文档在官网中的url</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// const & :输入</span>
<span class="token comment">// * : 输出</span>
<span class="token comment">// & : 输入输出</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">EnumFile</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">*</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">&</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">*</span>results<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">SaveHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>output<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> <span class="token function">main</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 创建一个用于保存文件名带路径的顺序容器vector</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> files_list<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 第一步:递归式的把每个html文件名带路径,保存到files_list,方便后期进行一个一个的文件进行读取</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">EnumFile</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"enum file name error!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 第二部:按照files_list读取每一个文件的内容,并进行解析</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> results<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">ParseHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"parse html error!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">2</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 第三步:把解析完毕的各个文件内容,写入到output,按照\3作为每个文档的分隔符</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">SaveHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> output<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"save html error!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">3</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">EnumFile</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">*</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">namespace</span> fs <span class="token operator">=</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>filesystem<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
fs<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>path <span class="token function">root_path</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 判断路径是否存在,不存在就没有必要再往下走了</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>fs<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">exists</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>root_path<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> src_path <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"not exists"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 定义一个空的迭代器,用来进行判断递归结束</span>
fs<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>recursive_directory_iterator end<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>fs<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>recursive_directory_iterator <span class="token function">iter</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>root_path<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> iter <span class="token operator">!=</span> end<span class="token punctuation">;</span> iter<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 判断是否是普通文件,html都是普通文件</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>fs<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">is_regular_file</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">*</span>iter<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 判断文件路径的后缀是否符合要求</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">path</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">extension</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">!=</span> <span class="token string">".html"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// std::cout << "debug: " << iter->path().string() << std::endl;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 当前的路径式合法的,以.html结束的普通网页文件</span>
<span class="token comment">// 将所有带路径的html保存在files_list,方便后续进行文本分析</span>
<span class="token comment">// iter->path()获取的还是path对象,我们需要的是string</span>
files_list<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">path</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">string</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> <span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseTitle</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>result<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>title<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
size_t begin <span class="token operator">=</span> result<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">find</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"<title>"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin <span class="token operator">==</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>npos<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
size_t end <span class="token operator">=</span> result<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">find</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">" ");
if(end == std::string::npos)
{
return false;
}
begin += std::string(""</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin <span class="token operator">></span> end<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token operator">*</span>title <span class="token operator">=</span> result<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substr</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>begin<span class="token punctuation">,</span> end <span class="token operator">-</span> begin<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> <span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseContent</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>result<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>content<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 去标签,基于一个简易的状态机</span>
<span class="token keyword">enum</span> <span class="token class-name">status</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
LABLE<span class="token punctuation">,</span>
CONTENT
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">enum</span> <span class="token class-name">status</span> s <span class="token operator">=</span> LABLE<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">char</span> c <span class="token operator">:</span>result<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">switch</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">case</span> LABLE<span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'>'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
s <span class="token operator">=</span> CONTENT<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">case</span> CONTENT<span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'<'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
s <span class="token operator">=</span> LABLE<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">else</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 我们不想被保留原始文件中的\n,因为我们想用\n作为html解析之后文本的分隔符</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token char">'\n'</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
c <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token char">' '</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
content<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>c<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">default</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token keyword">break</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> <span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseUrl</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>file_path<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>url<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url_head <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url_tail <span class="token operator">=</span> file_path<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substr</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>src_path<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token operator">*</span>url <span class="token operator">=</span> url_head <span class="token operator">+</span> url_tail<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">void</span> <span class="token function">ShowDoc</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> DocInfo_t <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"title: "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"content: "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"url: "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">ParseHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">&</span>files_list<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">*</span>results<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>file <span class="token operator">:</span> files_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.读取文件,Read()</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string result<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 读取文件的内容放到result中</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">FileUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">ReadFile</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>file<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>result<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
DocInfo_t doc<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.解析指定文件,提取title</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">ParseTitle</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>result<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 3.解析指定文件,提取content</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">ParseContent</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>result<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 4.解析指定文件路径,构建url</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span><span class="token function">ParseUrl</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>file<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// done </span>
results<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span><span class="token comment">// bug:TODO 细节,本质会发生拷贝,效率可能比较低</span>
<span class="token comment">// for debug</span>
<span class="token comment">// ShowDoc(doc);</span>
<span class="token comment">// break;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">SaveHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo_t<span class="token operator">></span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>output<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">char</span> SEP <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token char">'\3'</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ofstream <span class="token function">out</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>output<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>out <span class="token operator">|</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>binary<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">is_open</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"open "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> output <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" failed!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 就可以进行文件的写入了</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>item <span class="token operator">:</span> results<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string out_string<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> SEP<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> SEP<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out_string <span class="token operator">+=</span> <span class="token char">'\n'</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">write</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>out_string<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">c_str</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> out_string<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
out<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">close</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<h1>6. 编写建立索引的模块<code>Index</code></h1>
<p>(1) Index.hpp代码框架</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">pragma</span> <span class="token expression">once </span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><iostream></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><string></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><vector></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><unordered_map></span></span>
<span class="token keyword">namespace</span> ns_index
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 正排索引存储的基本信息,文档ID -> 文档信息</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">DocInfo</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string title<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档的标题</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string content<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档的内容</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 官网文档url</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档ID</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 倒排索引存储的基本信息 关键词 -> 文档ID,关键词权重weight</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">InvertedElem</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档Id</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string word<span class="token punctuation">;</span><span class="token comment">// 搜索关键词</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> weight<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 权重,后面详细解说</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 倒排拉链</span>
<span class="token keyword">typedef</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>InvertedElem<span class="token operator">></span> InvertedList<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">class</span> <span class="token class-name">Index</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">public</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token operator">~</span><span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 构建文档索引</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据去标签,格式化之后的文档,构建正排和倒排索引 </span>
<span class="token comment">// input = data/raw_html/raw.txt</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">BuildIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据doc_id找到文档内容</span>
DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据关键字获取倒排拉链</span>
InvertedList <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetInveretList</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token comment">// 正排索引的数据结果用数组,数组的下标就是文档id</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo<span class="token operator">></span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 倒排索引一定是一个关键字和一组(个)InvertedElem对应</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>unordered_map<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token punctuation">,</span> InvertedList<span class="token operator">></span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>BuildIndex</strong>接口:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">BuildIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ifstream <span class="token function">in</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>in <span class="token operator">|</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>binary<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>in<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">is_open</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"sorry, "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> input <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" open error"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string line<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> count <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">while</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">getline</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>in<span class="token punctuation">,</span> line<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span>doc <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">BuildForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>line<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 为啥还要返回正排节点</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"build "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> line <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" error"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// for debug</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token function">BuildInvertedIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">*</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
count<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>count <span class="token operator">%</span> <span class="token number">50</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"当前已经建立的索引文档: "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> count <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
in<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">close</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>BuildForwardIndex</strong>接口实现:</p>
<blockquote>
<p>切分字符串-boost库split函数使用</p>
<p>举例使用 : 一个例子带你了解boost::split分词使用</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><iostream></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><string></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><vector></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><boost/algorithm/string.hpp></span></span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string line <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"####################"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> <span class="token function">main</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string src_str <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"we may lose,we oftern lose,howervr,,,we never say die"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> results1<span class="token punctuation">,</span> results2<span class="token punctuation">,</span> results3<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string sep <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">","</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">split</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>results1<span class="token punctuation">,</span> src_str<span class="token punctuation">,</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">is_any_of</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">","</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>str <span class="token operator">:</span> results1<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> str <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> line <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">split</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>results2<span class="token punctuation">,</span> src_str<span class="token punctuation">,</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">is_any_of</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">","</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>token_compress_off<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>str <span class="token operator">:</span> results2<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> str <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> line <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">split</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>results3<span class="token punctuation">,</span> src_str<span class="token punctuation">,</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">is_any_of</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">","</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>token_compress_on<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>str <span class="token operator">:</span> results3<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> str <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> line <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/376160e8a4aa431fa7303f8e815bd112.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/376160e8a4aa431fa7303f8e815bd112.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第17张图片" width="650" height="275" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>可见boost::token_compress_off不会把boost::is_any_of(“字符串”)进行压缩,比如,上面按,进行分割字符串,它们三个之前会有两个空字符串也会被进行分割,分割后的空字符串push_back到std::vector< std::string>中。而boost::token_compress_on会把boost::is_any_of(“字符串”)进行压缩,压缩成一个,比如面的,就被压缩为一个,没有空字符串被push_back到std::vector< std::string >中。最后观察不带第四个参数,我们可以看到它的默认参数给的是boost::token_compress_off。</p>
<p>注意:编译时要指明要链接的库-lboost_system -lboost_filesystem</p>
<p><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9a2ab98a933044498386c801d3b9b572.jpg" alt="[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EeqTfDj5-1677335193533)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230225214948829.png)]" width="650" height="29"></p>
</blockquote>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp">DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">BuildForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>line<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.解析line,字符串切分</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string sep <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"\3"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> results<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">StringUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">Split</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>line<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> sep<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token number">3</span> <span class="token operator">!=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.字符串进行填充到Docinfo</span>
DocInfo doc<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">2</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 先进行保存id,在插入,对应的id就是当前doc在vector中的下标!</span>
<span class="token comment">// 3.插入到正排索引的vector</span>
forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>BuildInvertedIndex</strong>接口实现:</p>
<blockquote>
<p>Jieba库的安装和使用<br> 我们进入GitHub来获取cppjieba分词工具资源(链接如下)<br> cppjieba下载链接</p>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/40753214ea6f4e3eac4e9757a59c50bc.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/40753214ea6f4e3eac4e9757a59c50bc.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第18张图片" width="650" height="326" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/38275e6af801453d979649a6a9a6871e.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/38275e6af801453d979649a6a9a6871e.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第19张图片" width="650" height="128" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1875d930c8874c2096b154547579a283.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1875d930c8874c2096b154547579a283.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第20张图片" width="650" height="220" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
</blockquote>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">BuildInvertedIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> DocInfo <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 负责记录title和content中关键词出现的次数</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">word_cnt</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> title_cnt <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> content_cnt <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 用来暂存词频的映射表 关键词->word_cnt</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>unordered_map<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token punctuation">,</span> word_cnt<span class="token operator">></span> word_map<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 使用jieba分词将title进行分词,分词结果保存到title_words中</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> title_words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">JiebaUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">CutString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>title_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string s <span class="token operator">:</span> title_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">to_lower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 将我们的分词进行统一转化为小写的</span>
word_map<span class="token punctuation">[</span>s<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>title_cnt<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 如果存在就获取,如果不存在就新建</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 使用jieba分词将content词结果保存到content_wrods中</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> content_words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">JiebaUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">CutString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>content_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string s <span class="token operator">:</span>content_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">to_lower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 将我们的分词进行统一转化为小写的</span>
word_map<span class="token punctuation">[</span>s<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>content_cnt<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">int</span> X <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">10</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">int</span> Y <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>word_pair <span class="token operator">:</span> word_map<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
InvertedElem item<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>word <span class="token operator">=</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>first<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight <span class="token operator">=</span> X <span class="token operator">*</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>second<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title_cnt <span class="token operator">+</span> Y <span class="token operator">*</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>second<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content_cnt<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 相关性</span>
InvertedList <span class="token operator">&</span>inverted_list <span class="token operator">=</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">[</span>word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>first<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 不理解,不存在就添加</span>
inverted_list<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>item<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>GetForwardIndex</strong>接口实现:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp">DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">>=</span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"doc_id out range, error!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>forward_index<span class="token punctuation">[</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><strong>GetInveretList</strong>接口实现:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp">InvertedList <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetInveretList</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">auto</span> iter <span class="token operator">=</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">find</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter <span class="token operator">==</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> word <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" have no InvertedList"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter<span class="token operator">-></span>second<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p>最终Index.hpp的代码内容(单例模式(懒汉模式)):</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">pragma</span> <span class="token expression">once </span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><iostream></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><string></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><vector></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><mutex></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><fstream></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><unordered_map></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"util.hpp"</span></span>
<span class="token keyword">namespace</span> ns_index
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">DocInfo</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string title<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string content<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string url<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 文档i:</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">InvertedElem</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string word<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> weight<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 倒排拉链</span>
<span class="token keyword">typedef</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>InvertedElem<span class="token operator">></span> InvertedList<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">class</span> <span class="token class-name">Index</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">public</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token operator">~</span><span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> Index<span class="token operator">*</span> <span class="token function">GetInstance</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> instance<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
mtx<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">lock</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> instance<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
instance <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token keyword">new</span> <span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
mtx<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">unlock</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> instance<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据doc_id找到文档内容</span>
DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">>=</span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"doc_id out range, error!"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>forward_index<span class="token punctuation">[</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据关键字获取倒排拉链</span>
InvertedList <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">GetInveretList</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">auto</span> iter <span class="token operator">=</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">find</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 有疑问</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter <span class="token operator">==</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> word <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" have no InvertedList"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter<span class="token operator">-></span>second<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 构建文档索引</span>
<span class="token comment">// 根据去标签,格式化之后的文档,构建正排和倒排索引 </span>
<span class="token comment">// data/raw_html/raw.txt</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">BuildIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token comment">// parse处理完毕的数据交给我</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ifstream <span class="token function">in</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>in <span class="token operator">|</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>ios<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>binary<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>in<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">is_open</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"sorry, "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> input <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" open error"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">false</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string line<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> count <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">while</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">getline</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>in<span class="token punctuation">,</span> line<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span>doc <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">BuildForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>line<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cerr <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"build "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> line <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">" error"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// for debug</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token function">BuildInvertedIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">*</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
count<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>count <span class="token operator">%</span> <span class="token number">50</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"当前已经建立的索引文档: "</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> count <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
in<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">close</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span><span class="token function">BuildForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>line<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.解析line,字符串切分</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string sep <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"\3"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> results<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">StringUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">Split</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>line<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>results<span class="token punctuation">,</span> sep<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token number">3</span> <span class="token operator">!=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.字符串进行填充到Docinfo</span>
DocInfo doc<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url <span class="token operator">=</span> results<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">2</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 先进行保存id,在插入,对应的id就是当前doc在vector中的下标!</span>
<span class="token comment">// 3.插入到正排索引的vector</span>
forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>forward_index<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">bool</span> <span class="token function">BuildInvertedIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> DocInfo <span class="token operator">&</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">word_cnt</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> title_cnt <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> content_cnt <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>unordered_map<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token punctuation">,</span> word_cnt<span class="token operator">></span> word_map<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 用来暂存词频的映射表</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> title_words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">JiebaUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">CutString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>title_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string s <span class="token operator">:</span> title_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">to_lower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 将我们的分词进行统一转化为小写的</span>
word_map<span class="token punctuation">[</span>s<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>title_cnt<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 如果存在就获取,如果不存在就新建</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> content_words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">JiebaUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">CutString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>content_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string s <span class="token operator">:</span>content_words<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">to_lower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>s<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 将我们的分词进行统一转化为小写的</span>
word_map<span class="token punctuation">[</span>s<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>content_cnt<span class="token operator">++</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">int</span> X <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">10</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">int</span> Y <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>word_pair <span class="token operator">:</span> word_map<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
InvertedElem item<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>word <span class="token operator">=</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>first<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight <span class="token operator">=</span> X <span class="token operator">*</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>second<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title_cnt <span class="token operator">+</span> Y <span class="token operator">*</span> word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>second<span class="token punctuation">.</span>content_cnt<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 相关性</span>
InvertedList <span class="token operator">&</span>inverted_list <span class="token operator">=</span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">[</span>word_pair<span class="token punctuation">.</span>first<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 不理解,不存在就添加</span>
inverted_list<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>item<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token boolean">true</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token comment">// 正排索引的数据结果用数组,数组的下标就是文档id</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>DocInfo<span class="token operator">></span> forward_index<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 倒排索引一定是一个关键字和一组(个)InvertedElem对应</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>unordered_map<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token punctuation">,</span> InvertedList<span class="token operator">></span> inverted_index<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token function">Index</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> Index<span class="token operator">&</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token keyword">delete</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
Index<span class="token operator">&</span> <span class="token keyword">operator</span><span class="token operator">=</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> Index<span class="token operator">&</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token keyword">delete</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> Index<span class="token operator">*</span> instance<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">static</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>mutex mtx<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
Index<span class="token operator">*</span> Index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>instance <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token keyword">nullptr</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>mutex Index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>mtx<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<h1>7. 编写搜索引擎模块<code>Searcher </code></h1>
<p>(1) searcher.hpp代码框架</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">pragma</span> <span class="token expression">once </span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"index.hpp"</span></span>
<span class="token keyword">namespace</span> ns_searcher
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">InvertedElemPrint</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> weight <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">class</span> <span class="token class-name">Searcher</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">public</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token function">Searcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token operator">~</span><span class="token function">Searcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">void</span> <span class="token function">InitSearcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span> input<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1. 获取或者创建index对象</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2. 根据index对象建立索引</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// query: 搜索关键词</span>
<span class="token comment">// json_string: 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结构</span>
<span class="token keyword">void</span> <span class="token function">Search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>query<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>json_string<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.[分词]: 对我们的query进行按照searcher的要求进行分词</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.[触发]: 就是根据分词的各个"词"进行index查找</span>
<span class="token comment">// 3.[合并排序]: 汇总查找结果,按照相关性进行降序排序</span>
<span class="token comment">// 4.[构建]: 根据查找出的结果,构建json串---jsoncpp--- 通过jsoncpp完成序列化和反序列化</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
ns_index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Index <span class="token operator">*</span>index<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 供系统进行查找的索引</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p>Jsoncpp库的引入与使用</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-Linux">Jsoncpp的下载:sudo yum install -y jsoncpp-devel
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8407f6480e4e4c6680977e33d736b29a.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8407f6480e4e4c6680977e33d736b29a.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第21张图片" width="650" height="140" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>对jsoncpp库的使用测试<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e5f15311e9b04205aa13615730ee4c71.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e5f15311e9b04205aa13615730ee4c71.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第22张图片" width="650" height="465" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1121d54363f74dda90dc7ce8912a4776.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1121d54363f74dda90dc7ce8912a4776.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第23张图片" width="650" height="238" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> 由于Jsoncpp是第三方库,所以编译是要指明要链接的库</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-Linux">g++ test.cc -ljsoncpp
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d995d8479ee049a0903f7768da6cd539.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d995d8479ee049a0903f7768da6cd539.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第24张图片" width="650" height="183" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c395deeb3a9e4b459ff17df280de40f9.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c395deeb3a9e4b459ff17df280de40f9.jpg" alt="[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TuUoWWwG-1677335193536)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230225222144492.png)]" width="650" height="79"></a></p>
<p>最终searcher.hpp的代码内容:</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">pragma</span> <span class="token expression">once </span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"index.hpp"</span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"util.hpp"</span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string"><algorithm></span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"jsoncpp/json/json.h"</span></span>
<span class="token keyword">namespace</span> ns_searcher
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">struct</span> <span class="token class-name">InvertedElemPrint</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span> doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> weight <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">class</span> <span class="token class-name">Searcher</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">public</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
<span class="token function">Searcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token operator">~</span><span class="token function">Searcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span><span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">void</span> <span class="token function">InitSearcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span> input<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1. 获取或者创建index对象</span>
index <span class="token operator">=</span> ns_index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">Index</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">GetInstance</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"获取单列成功..."</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2. 根据index对象建立索引</span>
index<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">BuildIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"建立正排和倒排索引成功..."</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// query: 搜索关键词</span>
<span class="token comment">// json_string: 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结构</span>
<span class="token keyword">void</span> <span class="token function">Search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>query<span class="token punctuation">,</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">*</span>json_string<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.[分词]: 对我们的query进行按照searcher的要求进行分词</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string<span class="token operator">></span> words<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_util<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token class-name">JiebaUtil</span><span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">CutString</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>query<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>words<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.[触发]: 就是根据分词的各个"词"进行index查找</span>
<span class="token comment">// ns_index::InvertedList inverted_list_all;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>vector<span class="token operator"><</span>InvertedElemPrint<span class="token operator">></span> inverted_list_all<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>unordered_map<span class="token operator"><</span><span class="token keyword">uint64_t</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> InvertedElemPrint<span class="token operator">></span> token_map<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string word <span class="token operator">:</span> words<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
boost<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">to_lower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
ns_index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>InvertedList <span class="token operator">*</span>inverted_list <span class="token operator">=</span> index<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">GetInveretList</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> inverted_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>elem<span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token operator">*</span>inverted_list<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>item <span class="token operator">=</span> token_map<span class="token punctuation">[</span>elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id <span class="token operator">=</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight <span class="token operator">+=</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>words<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> <span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>item<span class="token operator">:</span> token_map<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
inverted_list_all<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">push_back</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">move</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>second<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// 3.[合并排序]: 汇总查找结果,按照相关性进行降序排序</span>
<span class="token comment">// std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(),\
// [](const ns_index::InvertedElem &e1, const ns_index::InvertedElem &e2)\
// { return e1.weight > e2.weight; }); </span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">sort</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>inverted_list_all<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">begin</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> inverted_list_all<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>\
<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> InvertedElemPrint <span class="token operator">&</span>e1<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> InvertedElemPrint <span class="token operator">&</span>e2<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> e1<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight <span class="token operator">></span> e2<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 4.[构建]: 根据查找出的结果,构建json串---jsoncpp--- 通过jsoncpp完成序列化和反序列化</span>
Json<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Value root<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">auto</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>item <span class="token operator">:</span> inverted_list_all<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
ns_index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>DocInfo <span class="token operator">*</span>doc <span class="token operator">=</span> index<span class="token operator">-></span><span class="token function">GetForwardIndex</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">nullptr</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> doc<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">continue</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
Json<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Value elem<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
elem<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"title"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> doc<span class="token operator">-></span>title<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
elem<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"desc"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">GetDesc</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>doc<span class="token operator">-></span>content<span class="token punctuation">,</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>words<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// content是文档的去标签内容,但不是我们想要的,我们想要的只是其中的一部分 TODO</span>
elem<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"url"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> doc<span class="token operator">-></span>url<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// for debug</span>
elem<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"id"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token generic-function"><span class="token function">static_cast</span><span class="token generic class-name"><span class="token operator"><</span><span class="token keyword">int</span><span class="token operator">></span></span></span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>doc_id<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
elem<span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token string">"weight"</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span> <span class="token operator">=</span> item<span class="token punctuation">.</span>weight<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
root<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">append</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>elem<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">// Json::StyledWriter writer; // 方便调试</span>
Json<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>FastWriter writer<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token operator">*</span>json_string <span class="token operator">=</span> writer<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">write</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>root<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token function">GetDesc</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>content<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string <span class="token operator">&</span>word<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> size_t prev_step <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">50</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> size_t next_step <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">100</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// size_t pos = content.find(word); // 不能用这个找</span>
<span class="token comment">// if(pos == std::string::npos)</span>
<span class="token comment">// {</span>
<span class="token comment">// return "None1";</span>
<span class="token comment">// }</span>
<span class="token keyword">auto</span> iter <span class="token operator">=</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">begin</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> word<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">begin</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> word<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">int</span> x<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token keyword">int</span> y<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">tolower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>x<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">==</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">tolower</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>y<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>iter <span class="token operator">==</span> content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">end</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token string">"None1"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
size_t pos <span class="token operator">=</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span><span class="token function">distance</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">begin</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> iter<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
size_t start <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
size_t end <span class="token operator">=</span> content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">size</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token operator">-</span> <span class="token number">1</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 注意无符号数的相减</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>pos <span class="token operator">></span> start <span class="token operator">+</span> prev_step<span class="token punctuation">)</span> start <span class="token operator">=</span> pos <span class="token operator">-</span> prev_step<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>pos <span class="token operator">+</span> next_step <span class="token operator"><</span> end<span class="token punctuation">)</span> end <span class="token operator">=</span> pos <span class="token operator">+</span> next_step<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>start <span class="token operator">></span> end<span class="token punctuation">)</span> <span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token string">"None2"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string desc <span class="token operator">=</span> content<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">substr</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>start<span class="token punctuation">,</span> end <span class="token operator">-</span>start<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
desc <span class="token operator">+=</span> <span class="token string">"..."</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> desc<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">private</span><span class="token operator">:</span>
ns_index<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Index <span class="token operator">*</span>index<span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// 供系统进行查找的索引</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<h1>8.编写搜索服务端<code>http_server.cc</code></h1>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c399c596f6074e64ba968d9dd157bb18.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c399c596f6074e64ba968d9dd157bb18.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第25张图片" width="650" height="139" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>升级新版本gcc</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token comment">// 安装scl</span>
sudo yum install centos<span class="token operator">-</span>release<span class="token operator">-</span>scl scl<span class="token operator">-</span>uitls<span class="token operator">-</span>build
<span class="token comment">// 升级新版本gcc 7.0版本以上的gcc就没问题</span>
sudo yum install <span class="token operator">-</span>y devtoolset<span class="token operator">-</span><span class="token number">7</span><span class="token operator">-</span>gcc devtoolset<span class="token operator">-</span><span class="token number">7</span><span class="token operator">-</span>gcc<span class="token operator">-</span>c<span class="token operator">++</span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/56d87868f1ff4096bc497fb2b3c7f2e2.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/56d87868f1ff4096bc497fb2b3c7f2e2.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第26张图片" width="650" height="137" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token comment">// 启动scl更新gcc</span>
scl enable devtoolset<span class="token operator">-</span><span class="token number">7</span> bash
<span class="token comment">// (选做)配置自启动更新gcc</span>
vim <span class="token operator">~</span><span class="token operator">/</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span>bash_profile
<span class="token comment">// 在该文件的末尾放上语句 scl enable devtoolset-7 bash 即可 </span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3fa69d0e8e32422f889160984d64fc05.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3fa69d0e8e32422f889160984d64fc05.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第27张图片" width="650" height="430" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>安装cpp-httplib</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token comment">// cpp-httplib v0.7.15版本链接</span>
https<span class="token operator">:</span><span class="token comment">//gitee.com/liveever/cpp-httplib/tags?page=2</span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1372709289204e309c24a7a84b0138a1.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1372709289204e309c24a7a84b0138a1.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第28张图片" width="650" height="338" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> 把下载下来的cpp-httplib-v0.7.15.zip上传到Linux服务器上<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ba29b64951f74e3f83b63495d02ae24d.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ba29b64951f74e3f83b63495d02ae24d.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第29张图片" width="650" height="319" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>使用unzip指令对压缩包进行解压</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-c++">unzip cpp-httplib-v0.7.15.zip
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6687e161575b4f848f83da8f19b939da.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6687e161575b4f848f83da8f19b939da.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第30张图片" width="650" height="144" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/32a906886c59443199bec48b2a221dd2.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/32a906886c59443199bec48b2a221dd2.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第31张图片" width="650" height="260" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<p>测试cpp-httplib库</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"cpp-httplib/httplib.h"</span></span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> <span class="token function">main</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Server svr<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
svr<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">Get</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"/test"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Request <span class="token operator">&</span>req<span class="token punctuation">,</span> httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Response <span class="token operator">&</span>rsp<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
rsp<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">set_content</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"你好,这是一个测试!"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">"text/plain; charset=utf-8"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
svr<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">listen</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"0.0.0.0"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token number">8081</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/688ddb389a0f43809b1f87e1ff3a2116.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/688ddb389a0f43809b1f87e1ff3a2116.jpg" alt="[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Qluv1CEo-1677335193538)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230225115520487.png)]" width="650" height="79"></a><br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4226170b43af42cc975e4af90cba06d2.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4226170b43af42cc975e4af90cba06d2.jpg" alt="[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NVwi2pmi-1677335193539)(C:\Users\13916\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230225115545801.png)]" width="650" height="69"></a></p>
<p>http_server.cc代码框架</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-cpp"><span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"cpp-httplib/httplib.h"</span></span>
<span class="token macro property"><span class="token directive-hash">#</span><span class="token directive keyword">include</span> <span class="token string">"searcher.hpp"</span> </span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string root_path <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"./wwwroot"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">const</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string input <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token string">"data/raw_html/raw.txt"</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">int</span> <span class="token function">main</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
ns_searcher<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Searcher search<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
search<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">InitSearcher</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>input<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Server svr<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
svr<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">set_base_dir</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>root_path<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">c_str</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
svr<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">Get</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"/s"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token punctuation">[</span><span class="token operator">&</span>search<span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token keyword">const</span> httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Request <span class="token operator">&</span>req<span class="token punctuation">,</span> httplib<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>Response <span class="token operator">&</span>rsp<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span> <span class="token comment">// res.set_content("你好 世界!", "text/plain; charset=utf-8"); </span>
<span class="token keyword">if</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token operator">!</span>req<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">has_param</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"word"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
rsp<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">set_content</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"必须要有搜索关键字!"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">"text/plain; charset=utf-8"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string word <span class="token operator">=</span> req<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">get_param_value</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"word"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>cout <span class="token operator"><<</span> <span class="token string">"用户在搜索:"</span> <span class="token operator"><<</span> word <span class="token operator"><<</span> std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>endl<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
std<span class="token double-colon punctuation">::</span>string json_string<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
search<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">Search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>word<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token operator">&</span>json_string<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
rsp<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">set_content</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>json_string<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">"application/json"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
svr<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">listen</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"0.0.0.0"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token number">8081</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">return</span> <span class="token number">0</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</code></pre>
<p>http_server搜索端测试:<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/788f2340d7aa4f7bbbd3205fd45aa5b4.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/788f2340d7aa4f7bbbd3205fd45aa5b4.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第32张图片" width="650" height="335" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<h1>9. 编写前端模块</h1>
<p>前端基础说明:</p>
<blockquote>
<p>我们boost搜索引擎的主要代码(后端)已经完成,我们接下来简单介绍一下前端。</p>
<p>了解前端三大件:html , css , javascript(js)</p>
<p>html:是网页的骨骼 — 负责网页结构</p>
<p>css: 网页的皮肉 — 负责网页的美观</p>
<p>js:网页的灵魂 — 负责动态效果,以及前后端交互</p>
<p>前端学习网站推荐:http://www.w3school.com.cn</p>
</blockquote>
<p>编写前端代码工具选择及其安装<br> 我们使用Vscode连接云服务器进行前端代码的编写 , 下面我们安装Vscode并进行连接。</p>
<p>1.进入Vscode官方网站进行下载<br> https://code.visualstudio.com/</p>
<p>2.下载相关插件<br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8c0c5c369e014acb8169440543ae1249.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8c0c5c369e014acb8169440543ae1249.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第33张图片" width="650" height="310" style="border:1px solid black;"></a><br> <a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9d2b0832d1874f0b818f9033d2f4f870.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9d2b0832d1874f0b818f9033d2f4f870.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第34张图片" width="650" height="431" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
<blockquote>
<p>示例:</p>
<p>【1】安装好Remote - SSH之后 ,按F1打开输入对话框。</p>
<p>【2】输入remote-ssh</p>
<p>【3】ssh user_name@ip</p>
</blockquote>
<p>3 Html网页结构书写</p>
<pre><code class="prism language-html"><span class="token doctype"><span class="token punctuation"><!</span><span class="token doctype-tag">DOCTYPE</span> <span class="token name">html</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>html</span> <span class="token attr-name">lang</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>en<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>head</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>meta</span> <span class="token attr-name">charset</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>UTF-8<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>meta</span> <span class="token attr-name">http-equiv</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>X-UA-Compatible<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">content</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>IE=edge<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>meta</span> <span class="token attr-name">name</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>viewport<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">content</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>script</span> <span class="token attr-name">src</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-2.1.1.min.js<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token script"></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>script</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>title</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>Boost 搜索引擎<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>title</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>style</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token style"><span class="token language-css">
<span class="token comment">/* 去掉网页中所有的内外边距,html的盒子摘要 */</span>
<span class="token selector">*</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置外边距 */</span>
<span class="token property">margin</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 0<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置内边距 */</span>
<span class="token property">padding</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 0<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">body</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">height</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 100%<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 类选择器 .加类名 */</span>
<span class="token selector">.container</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 800px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">margin</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 0px auto<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">margin-top</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 15px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .search</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 100%<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">height</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 52px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .search input</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">float</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> left<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 600px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">height</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 50px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">border</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 1px solid black<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">border-right</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> none<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">padding-left</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 10px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">color</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> #ccc<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">font-size</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 15px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .search button</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">float</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> left<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 120px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">height</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 52px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">background</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> #4e6ef2<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">color</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> #FFF<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">font-size</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 19px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">font-family</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> Georgia<span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">'Times New Roman'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> Times<span class="token punctuation">,</span> serif<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">width</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 100%<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result .item</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">margin-top</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 15px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result .item a</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置为块级元素,单独站一行 */</span>
<span class="token property">display</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> block<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 去掉标题的下划线 */</span>
<span class="token property">text-decoration</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> none<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置字体大小 */</span>
<span class="token property">font-size</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 20px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置字体的颜色 */</span>
<span class="token property">color</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> #4e6ef2<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result .item a:hover</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 设置动态效果 */</span>
<span class="token property">text-decoration</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> underline<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result .item p</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">margin-top</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 5px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">font-size</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> 16px<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">font-family</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span><span class="token string">'Lucida Sans'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">'Lucida Sans Regular'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">'Lucida Grande'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> <span class="token string">'Lucida Sans Unicode'</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> Geneva<span class="token punctuation">,</span> Verdana<span class="token punctuation">,</span> sans-serif<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token selector">.container .result .item i</span> <span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token property">display</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> block<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">/* 取消url斜体 */</span>
<span class="token property">font-style</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> normal<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token property">color</span><span class="token punctuation">:</span> green<span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>style</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>head</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>body</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>container<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>search<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>input</span> <span class="token attr-name">type</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>text<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span> <span class="token attr-name">value</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>输入搜索关键字...<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>button</span> <span class="token special-attr"><span class="token attr-name">onclick</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span><span class="token value javascript language-javascript"><span class="token function">Search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span></span><span class="token punctuation">"</span></span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>搜索一下<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>button</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>div</span> <span class="token attr-name">class</span><span class="token attr-value"><span class="token punctuation attr-equals">=</span><span class="token punctuation">"</span>result<span class="token punctuation">"</span></span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token comment"><!-- 动态生成网页内容 --></span>
<span class="token comment"><!-- <div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>https://fanyi.baidu.com/translate?aldtype=16047&query=Memory+Management+Unit&keyfrom=baidu&smartresult=dict&lang=auto2zh#pt/zh/param</i>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>https://fanyi.baidu.com/translate?aldtype=16047&query=Memory+Management+Unit&keyfrom=baidu&smartresult=dict&lang=auto2zh#pt/zh/param</i>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>https://fanyi.baidu.com/translate?aldtype=16047&query=Memory+Management+Unit&keyfrom=baidu&smartresult=dict&lang=auto2zh#pt/zh/param</i>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>https://fanyi.baidu.com/translate?aldtype=16047&query=Memory+Management+Unit&keyfrom=baidu&smartresult=dict&lang=auto2zh#pt/zh/param</i>
</div>
<div class="item">
<a href="#">这是标题</a>
<p>这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要这是摘要</p>
<i>https://fanyi.baidu.com/translate?aldtype=16047&query=Memory+Management+Unit&keyfrom=baidu&smartresult=dict&lang=auto2zh#pt/zh/param</i>
</div> --></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>div</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"><</span>script</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span><span class="token script"><span class="token language-javascript">
<span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">Search</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 是浏览器的一个弹出框</span>
<span class="token comment">// alert("hello js");</span>
<span class="token comment">// 1.提取数据 JQuery $可以理解为JQuery的别称</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> query <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">".container .search input"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">val</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
console<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">log</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"query = "</span> <span class="token operator">+</span> query<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span> <span class="token comment">// console是浏览器的控制台,可以用它来查看js的数据</span>
<span class="token comment">// 2.发起http请求,ajax: 属于一个和后端进行数据交互的函数,JQuery中的</span>
$<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">ajax</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">type</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"GET"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">url</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"/s?word="</span> <span class="token operator">+</span> query<span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token function-variable function">success</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token keyword">function</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token parameter">data</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
console<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">log</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>data<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token function">BuildHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>data<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token keyword">function</span> <span class="token function">BuildHtml</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token parameter">data</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token comment">// 获取html中的result标签</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> result_lable <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">".container .result"</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token comment">// 清空历史搜索结果</span>
result_lable<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">empty</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">for</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span> <span class="token keyword">let</span> elem <span class="token keyword">of</span> data<span class="token punctuation">)</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
console<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">log</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
console<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">log</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> a_lable <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"<a>"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">text</span><span class="token operator">:</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>title<span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">href</span><span class="token operator">:</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url<span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">target</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"_blank"</span> <span class="token comment">// 跳转到新的网页</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> p_lable <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"<p>"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">text</span><span class="token operator">:</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>desc
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> i_lable <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"<i>"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token literal-property property">text</span><span class="token operator">:</span> elem<span class="token punctuation">.</span>url
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token keyword">let</span> div_lable <span class="token operator">=</span> <span class="token function">$</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span><span class="token string">"<div>"</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span>
<span class="token punctuation">{</span>
<span class="token keyword">class</span><span class="token operator">:</span> <span class="token string">"item"</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span><span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
a_lable<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">appendTo</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>div_lable<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
p_lable<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">appendTo</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>div_lable<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
i_lable<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">appendTo</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>div_lable<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
div_lable<span class="token punctuation">.</span><span class="token function">appendTo</span><span class="token punctuation">(</span>result_lable<span class="token punctuation">)</span><span class="token punctuation">;</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
<span class="token punctuation">}</span>
</span></span><span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>script</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>body</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
<span class="token tag"><span class="token tag"><span class="token punctuation"></</span>html</span><span class="token punctuation">></span></span>
</code></pre>
<p><a href="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2a4cd91954974a31aacd688f3aecf35a.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2a4cd91954974a31aacd688f3aecf35a.jpg" alt="【boost搜索引擎】_第35张图片" width="650" height="383" style="border:1px solid black;"></a></p>
</div>
</div>����������������
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!--PC和WAP自适应版-->
<div id="SOHUCS" sid="1670260658018541568"></div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/views/front/js/chanyan.js"></script>
<!-- 文章页-底部 动态广告位 -->
<div class="youdao-fixed-ad" id="detail_ad_bottom"></div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-3">
<div class="row" id="ad">
<!-- 文章页-右侧1 动态广告位 -->
<div id="right-1" class="col-lg-12 col-md-12 col-sm-4 col-xs-4 ad">
<div class="youdao-fixed-ad" id="detail_ad_1"> </div>
</div>
<!-- 文章页-右侧2 动态广告位 -->
<div id="right-2" class="col-lg-12 col-md-12 col-sm-4 col-xs-4 ad">
<div class="youdao-fixed-ad" id="detail_ad_2"></div>
</div>
<!-- 文章页-右侧3 动态广告位 -->
<div id="right-3" class="col-lg-12 col-md-12 col-sm-4 col-xs-4 ad">
<div class="youdao-fixed-ad" id="detail_ad_3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<h4 class="pt20 mb15 mt0 border-top">你可能感兴趣的:(实战项目,搜索引擎)</h4>
<div id="paradigm-article-related">
<div class="recommend-post mb30">
<ul class="widget-links">
<li><a href="/article/1835454543471669248.htm"
title="Java:爬虫框架" target="_blank">Java:爬虫框架</a>
<span class="text-muted">dingcho</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Java/1.htm">Java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/1.htm">爬虫</a>
<div>一、ApacheNutch2【参考地址】Nutch是一个开源Java实现的搜索引擎。它提供了我们运行自己的搜索引擎所需的全部工具。包括全文搜索和Web爬虫。Nutch致力于让每个人能很容易,同时花费很少就可以配置世界一流的Web搜索引擎.为了完成这一宏伟的目标,Nutch必须能够做到:每个月取几十亿网页为这些网页维护一个索引对索引文件进行每秒上千次的搜索提供高质量的搜索结果简单来说Nutch支持分</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835424412342513664.htm"
title="ChatGPT 高效学习套路揭秘:让知识获取事半功倍的秘诀" target="_blank">ChatGPT 高效学习套路揭秘:让知识获取事半功倍的秘诀</a>
<span class="text-muted">kkai人工智能</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/chatgpt/1.htm">chatgpt</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BA%BA%E5%B7%A5%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD/1.htm">人工智能</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0/1.htm">学习</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%AA%92%E4%BD%93/1.htm">媒体</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/ai/1.htm">ai</a>
<div>最近这段时间,AI热潮因ChatGPT的火爆再次掀起。如今,网上大部分内容都在调侃AI,但很少有人探讨如何正经使用ChatGPT做事情。作为一名靠搜索引擎和GitHub自学编程的开发者,第一次和ChatGPT深度交流后,我就确信:ChatGPT能够极大提高程序员学习新技术的效率。使用ChatGPT一个月后,我越发感受到它的颠覆性。因此,我想从工作和学习的角度,分享它的优势及我的一些使用技巧,而非娱</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835333267952332800.htm"
title="网站推广爬虫" target="_blank">网站推广爬虫</a>
<span class="text-muted">Bearjumpingcandy</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/1.htm">爬虫</a>
<div>网站推广爬虫是一种用于升网站曝光度和推广效果的工具。它通过自动化地访问和收集网站信息,从而实现对目标网站的广告、关键词、排名等数据进行分析和优化。以下是网站推广爬虫的一些介绍:数据收集:网站推广爬虫可以自动访问目标网站,并收集相关的数据,如网站流量、关键词排名、竞争对手信息等。这些数据可以帮助网站推广人员了解网站的现状和竞争环境,从而制定相应的推广策略。关键词优化:通过分析搜索引擎的关键词排名情况</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835305847157256192.htm"
title="Python OpenCV图像处理:从基础到高级的全方位指南" target="_blank">Python OpenCV图像处理:从基础到高级的全方位指南</a>
<span class="text-muted">极客代码</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%8E%A9%E8%BD%ACPython/1.htm">玩转Python</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80/1.htm">开发语言</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/python/1.htm">python</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/opencv/1.htm">opencv</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%9B%BE%E5%83%8F%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86/1.htm">图像处理</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E8%A7%86%E8%A7%89/1.htm">计算机视觉</a>
<div>目录第一部分:PythonOpenCV图像处理基础1.1OpenCV简介1.2PythonOpenCV安装1.3实战案例:图像显示与保存1.4注意事项第二部分:PythonOpenCV图像处理高级技巧2.1图像变换2.2图像增强2.3图像复原第三部分:PythonOpenCV图像处理实战项目3.1图像滤波3.2图像分割3.3图像特征提取第四部分:PythonOpenCV图像处理注意事项与优化策略4</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835262244313722880.htm"
title="SpringBoot整合ES搜索引擎 实现网站热搜词及热度计算" target="_blank">SpringBoot整合ES搜索引擎 实现网站热搜词及热度计算</a>
<span class="text-muted">码踏云端</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/springboot/1.htm">springboot</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Elasticsearch/1.htm">Elasticsearch</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/spring/1.htm">spring</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/boot/1.htm">boot</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/elasticsearch/1.htm">elasticsearch</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%90%8E%E7%AB%AF/1.htm">后端</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%83%AD%E6%90%9C%E8%AF%8D/1.htm">热搜词</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%83%AD%E5%BA%A6%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97/1.htm">热度计算</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a>
<div>博主简介:历代文学网(PC端可以访问:https://literature.sinhy.com/#/literature?__c=1000,移动端可微信小程序搜索“历代文学”)总架构师,15年工作经验,精通Java编程,高并发设计,Springboot和微服务,熟悉Linux,ESXI虚拟化以及云原生Docker和K8s,热衷于探索科技的边界,并将理论知识转化为实际应用。保持对新技术的好奇心,乐于</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835261105010733056.htm"
title="题解 | #完全数计算#不知道为什么没超时的暴力解法" target="_blank">题解 | #完全数计算#不知道为什么没超时的暴力解法</a>
<span class="text-muted">huaxinjiayou</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a>
<div>兄弟们,坚持就是胜利啊,找工作从去年秋招就开始找,到五月底才收到第一个offer星环的,然后六月初t咋六月了还有面试啊,有兄弟了解这个部门吗面完了家人们,纯纯kpi啊,上来就是一道题是打印多个字符串的华为接头人话术指南:欲投华为,必看此贴!引流华为招聘提前批【奖】这个夏天,和牛牛一起打卡刷题~Java面试实战项目25届本科找暑期实习的历程飞猪旅行运营岗面经百度视觉算法一面面经感谢牛友们,腾子pcg</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835077143051202560.htm"
title="网上商城项目总结报告" target="_blank">网上商城项目总结报告</a>
<span class="text-muted">WEB前端程序贵</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%89%8D%E7%AB%AF/1.htm">前端</a>
<div>网上商城项目总结报告1:掌握的知识通过网上商城这个实战项目的开发,不仅了解到了一个项目的业务逻辑,而且掌握了实现相关业务功能的方法。通过这个实战项目,了解到了模块化开发项目的基础结构的搭建,以及项目文件的管理方式。通过这个实战项目,运用封装的接口api文档实现了客户端服务器之间的交互知识。通过封装的axios实例对象与方法,向服务器请求数据,然后渲染页面。通过运用localStorage本地储存的</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1835056254905577472.htm"
title="2019.1.6" target="_blank">2019.1.6</a>
<span class="text-muted">root_restart</span>
<div>1.新版研学行程公众号推送及页面改动,以后继续尝试无logo版行程单方便转发,附带一篇研学政策解读2.百家号,头条号,搜狐号注册认证及审核,后续每天会在上面更新以往研学活动,增加搜索引擎中山大研学和雨滴教育的关联3.与鹿老师探讨研究方便代理的新宣传模式</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834946252899446784.htm"
title="只有一个诚字最重要(3.22)" target="_blank">只有一个诚字最重要(3.22)</a>
<span class="text-muted">胡同学的读书笔记</span>
<div>1人们会认为谷歌是搜索引擎。而事实上,谷歌是第一个以机器为主导的搜索引擎,这个分类在谷歌之前是不存在的,而你必须要认识到谷歌的这个秘密才能判断它与其他公司的不同之处。2如果我目前在一个公司,当大家不知道未来的路怎么走,过去的路也已经彻底放弃了,我会先把事实摆在所有人面前,然后让大家讨论,在争论的过程中产生一个纲领性的共识,让每个部门在大的纲领下去寻求一种变化,不再以增长和竞争为纲,而是转移到产品和</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834869224200302592.htm"
title="写出渗透测试信息收集详细流程" target="_blank">写出渗透测试信息收集详细流程</a>
<span class="text-muted">卿酌南烛_b805</span>
<div>一、扫描域名漏洞:域名漏洞扫描工具有AWVS、APPSCAN、Netspark、WebInspect、Nmap、Nessus、天镜、明鉴、WVSS、RSAS等。二、子域名探测:1、dns域传送漏洞2、搜索引擎查找(通过Google、bing、搜索c段)3、通过ssl证书查询网站:https://myssl.com/ssl.html和https://www.chinassl.net/ssltools</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834839242870714368.htm"
title="【ShuQiHere】快速排序(Quick Sort):揭开高效排序算法的神秘面纱" target="_blank">【ShuQiHere】快速排序(Quick Sort):揭开高效排序算法的神秘面纱</a>
<span class="text-muted">ShuQiHere</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/1.htm">排序算法</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/1.htm">算法</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84/1.htm">数据结构</a>
<div>【ShuQiHere】引言在计算机科学中,排序算法是我们日常编程不可或缺的一部分。无论是处理大量数据、优化搜索引擎,还是进行系统性能提升,排序算法都起到了至关重要的作用。在所有的排序算法中,快速排序(QuickSort)凭借其高效性和灵活的分治策略成为最受欢迎的排序算法之一。在这篇博客中,我们将深入探讨快速排序的原理、性能分析以及如何通过优化策略进一步提升其效率。1.什么是快速排序?(QuickS</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834815410797637632.htm"
title="海量数据查找最大K个值:数据结构与算法的选择" target="_blank">海量数据查找最大K个值:数据结构与算法的选择</a>
<span class="text-muted">星辰@Sea</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84/1.htm">数据结构</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Java/1.htm">Java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84/1.htm">数据结构</a>
<div>在处理大数据集时,经常需要找到数据集中最大的K个元素,这样的需求在很多领域都有广泛应用,例如推荐系统中寻找评分最高的K个商品、数据分析中找出最重要的K个特征、搜索引擎中找到排名前K的结果等等。面对海量数据,传统的排序方法可能不再适用,因为它们通常具有较高的时间复杂度。因此,选择合适的数据结构和算法对于提高效率至关重要。本文将详细介绍如何在海量数据集中查找最大的K个值,探讨不同的数据结构与算法选择,</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834743445248372736.htm"
title="全面解析MeiliSearch及其Go语言实现" target="_blank">全面解析MeiliSearch及其Go语言实现</a>
<span class="text-muted">寻找09之夏</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Meilisearch/1.htm">Meilisearch</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/golang/1.htm">golang</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80/1.htm">开发语言</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%90%8E%E7%AB%AF/1.htm">后端</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Meilisearch/1.htm">Meilisearch</a>
<div>前言随着互联网的发展和数字化进程的加速,无论是企业还是个人用户,都需要面对海量的信息。在这个背景下,搜索技术的重要性日益凸显。MeiliSearch是一款开源搜索引擎,它的出现为开发者提供了一个高效、灵活的选择。本文将从多个角度探讨MeiliSearch的特性、使用方法及其实现原理,并通过Go语言示例展示如何构建一个高性能的搜索系统。一、MeiliSearch特性MeiliSearch之所以受到欢</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834593431939280896.htm"
title="计算机毕业设计选题推荐-基于Python框架项目推荐(中)" target="_blank">计算机毕业设计选题推荐-基于Python框架项目推荐(中)</a>
<span class="text-muted">计算机毕设大佬</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Java%E6%AF%95%E8%AE%BE%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%A1%B9%E7%9B%AE/1.htm">Java毕设实战项目</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Python%E6%AF%95%E8%AE%BE%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%A1%B9%E7%9B%AE/1.htm">Python毕设实战项目</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB%2B%E5%A4%A7%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E6%AF%95%E8%AE%BE%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%A1%B9%E7%9B%AE/1.htm">爬虫+大数据毕设实战项目</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/python/1.htm">python</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E6%AF%95%E4%B8%9A%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1/1.htm">计算机毕业设计</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/django/1.htm">django</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E6%AF%95%E4%B8%9A%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E9%80%89%E9%A2%98/1.htm">计算机毕业设计如何选题</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/25%E5%B1%8A%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E6%AF%95%E4%B8%9A%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E9%80%89%E9%A2%98/1.htm">25届计算机毕业设计如何选题</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E6%AF%95%E4%B8%9A%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E9%80%89%E9%A2%98%E6%8E%A8%E8%8D%90/1.htm">计算机毕业设计选题推荐</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/24%E5%B1%8A%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E6%AF%95%E8%AE%BE%E9%80%89%E9%A2%98%E6%8E%A8%E8%8D%90/1.htm">24届计算机毕设选题推荐</a>
<div>博主介绍:✌十余年IT大项目实战经验、在某机构培训学员上千名、专注于本行业领域✌技术范围:Java实战项目、Python实战项目、微信小程序/安卓实战项目、爬虫+大数据实战项目、Nodejs实战项目、PHP实战项目、.NET实战项目、Golang实战项目。主要内容:系统功能设计、开题报告、任务书、系统功能实现、功能代码讲解、答辩PPT、文档编写、文档修改、文档降重、一对一辅导答辩。获取源码可以联系</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834586370551672832.htm"
title="面对信息茧房,我们如何破局?" target="_blank">面对信息茧房,我们如何破局?</a>
<span class="text-muted">听风便是雨_</span>
<div>当我们进入了互联网时代,信息的交互变得无比地便捷,当你需要什么样的信息,只需要在搜索引擎上输入,便可立马查询到你想要的结果,而且现在随着抖音、微博之类的应用APP的出现,我们本应从这些APP中获得更加丰富的知识或者信息,来开阔我们的眼界。但是事实上,我们仿佛没有获得预期的效果,更甚至于陷入更大的怪圈当中——缺乏耐心,不能容忍与自己想法不一样的他人建议,失去了与外界良好沟通的能力以及开拓自己的眼界的</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834524115801829376.htm"
title="opencv 之 实战项目 识别银行卡上的数字" target="_blank">opencv 之 实战项目 识别银行卡上的数字</a>
<span class="text-muted">SEVEN-YEARS</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/opencv/1.htm">opencv</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E8%A7%86%E8%A7%89/1.htm">计算机视觉</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BA%BA%E5%B7%A5%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD/1.htm">人工智能</a>
<div>OpenCV之实战项目:识别银行卡上的数字引言在日常生活中,银行卡的识别是一个常见的需求,特别是在金融领域。本实战项目旨在使用OpenCV库来识别银行卡上的数字。我们将通过模板匹配的方法,结合图像处理技术,来准确识别银行卡上的数字序列。项目准备本项目需要安装Python和OpenCV库。确保已经安装了必要的库,并准备好银行卡图像和数字模板图像。实验素材定义函数importcv2defsort_co</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834519838756794368.htm"
title="80%的人都知道的——内容营销" target="_blank">80%的人都知道的——内容营销</a>
<span class="text-muted">老泊</span>
<div>我们已经知道内容营销是依靠内容来进行营销,一起看一下内容营销的工作流吧。选题创作投放主要内容营销的选题类型-常青树:用户长时间关心的,比如房价,教育-热点:用户短时间关心的,比如八卦,实事二八原则常青树话题等等选题来源:访谈法:寻找目标用户尽可能一对一进行访谈,用户反馈的问题都可以成为你的选题来源数据法:利用搜索引擎获取内容选题。利用爬虫工具看看人们都比较关心哪些话题来作为选题基于时事的选题数据工</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834490616306823168.htm"
title="50.复盘变现之路" target="_blank">50.复盘变现之路</a>
<span class="text-muted">506小棉袄</span>
<div>1.昨天下载了头条,用搜索引擎找到了如何写文章。注册了一下。这一切其实都好简单,但是自己就是拖着没有做,而且还心安理得。现在在管理别人,于是用自己做到了才能教别人去做到来要求自己发现也不难。2.日更被我捡了起来。后面没有特殊情况,我会一直更下去。放弃一件事很容易,坚持自己喜欢的事也不会太难。3.今天完成了50关的最后一关,接下来就要挑战100关。想看看自己的极限在哪里。具体做法:1.每天早起一小时</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834455667604287488.htm"
title="NLP_jieba中文分词的常用模块" target="_blank">NLP_jieba中文分词的常用模块</a>
<span class="text-muted">Hiweir ·</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/NLP_jieba%E7%9A%84%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8/1.htm">NLP_jieba的使用</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%87%AA%E7%84%B6%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86/1.htm">自然语言处理</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87%E5%88%86%E8%AF%8D/1.htm">中文分词</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BA%BA%E5%B7%A5%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD/1.htm">人工智能</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/nlp/1.htm">nlp</a>
<div>1.jieba分词模式(1)精确模式:把句子最精确的切分开,比较适合文本分析.默认精确模式.(2)全模式:把句子中所有可能成词的词都扫描出来,cut_all=True,缺点:速度快,不能解决歧义(3)paddle:利用百度的paddlepaddle深度学习框架.简单来说就是使用百度提供的分词模型.use_paddle=True.(4)搜索引擎模式:在精确模式的基础上,对长词再进行切分,提高召回率,</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834285986738171904.htm"
title="Django:Python高级Web框架详解及参数设置" target="_blank">Django:Python高级Web框架详解及参数设置</a>
<span class="text-muted">零 度°</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/python/1.htm">python</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/python/1.htm">python</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/django/1.htm">django</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%89%8D%E7%AB%AF/1.htm">前端</a>
<div>Django是一个高级的PythonWeb框架,它鼓励快速开发和简洁实用的设计。Django遵循MVC设计模式,提供了一套完整的解决方案,用于构建复杂的、数据库驱动的网站。Django的主要特点自动管理数据库:通过ORM(对象关系映射)自动管理数据库。自动生成站点地图:支持搜索引擎优化(SEO)。用户身份认证:内置用户认证系统。中间件支持:强大的中间件支持,可以处理请求和响应。跨站请求伪造(CSR</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834086585994407936.htm"
title="实战项目:俄罗斯方块(七)" target="_blank">实战项目:俄罗斯方块(七)</a>
<span class="text-muted">小珑也要变强</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80/1.htm">开发语言</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/c%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80/1.htm">c语言</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%89%A9%E8%81%94%E7%BD%91/1.htm">物联网</a>
<div>文章目录自我介绍图形存储及输出设置类型设计图形输出代码设计要实现的结果展示user_global.c(全局变量的C文件)user_print.huser_print.cmain.c你的点赞评论就是对博主最大的鼓励当然喜欢的小伙伴可以:点赞+关注+评论+收藏(一键四连)哦~自我介绍 Hello,大家好,我是小珑也要变强(也是小珑),我是易编程·终身成长社群的一名“创始团队·嘉宾”和“内容共创官”,</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1834079519187759104.htm"
title="ES(Elasticsearch)常用的函数" target="_blank">ES(Elasticsearch)常用的函数</a>
<span class="text-muted">遨游在知识的海洋里无法自拔</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a>
<div>Elasticsearch(简称ES)是一个开源的搜索引擎,广泛用于全文搜索、分析和数据可视化。以下是一些常用的Elasticsearch函数和操作:索引操作创建索引PUT/index_name删除索引DELETE/index_name查看索引GET/index_name文档操作插入文档POST/index_name/_doc/{"field":"value"}获取文档GET/index_name</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833991422127206400.htm"
title="HTML 图片" target="_blank">HTML 图片</a>
<span class="text-muted">一壶浊酒..</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%89%8D%E7%AB%AF%E5%BC%80%E5%8F%91/1.htm">前端开发</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/html/1.htm">html</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%89%8D%E7%AB%AF/1.htm">前端</a>
<div>在HTML中,我们可以使用img标签来显示一张图片。对于img标签,我们只需要掌握它的三个属性:src、alt和title。alt属性用于描述图片,这个描述文字是给搜索引擎看的,并且当图片无法显示时,页面会显示alt中的文字。title属性也用于描述图片,不过这个描述文字是给用户看的,并且当鼠标指针移到图片上时,会显示title中的文字。colspan属性body{background-color</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833970134469931008.htm"
title="生信学习Day-1" target="_blank">生信学习Day-1</a>
<span class="text-muted">GJJDr</span>
<div>1.如何学习2.怎样解决学习中遇到的问题?a.第一步:搜索:首选-谷歌,其次-必应,大神级的搜索引擎:虫部落快搜。专业教程-搜狗微信、搜狗知乎、、githubb.第二步:如果你的问题不知该如何搜索,可在微信群中与小组成员讨论c.第三步:正确的提问3.如何搭建高效的学习平台a.效率软件:(1)浏览器-chrome浏览器简洁高效无广告,可以添加插件,比如”沙拉查词”(自行搜索),可以即时翻译。(2)电</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833913498179039232.htm"
title="2024年最全软件测试面试常见问题【含答案】_软件测试面试常见问题及答案,优秀软件测试程序员必知必会的网络基础" target="_blank">2024年最全软件测试面试常见问题【含答案】_软件测试面试常见问题及答案,优秀软件测试程序员必知必会的网络基础</a>
<span class="text-muted">2401_84563179</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%91%98/1.htm">程序员</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95/1.htm">面试</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C/1.htm">网络</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%81%8C%E5%9C%BA%E5%92%8C%E5%8F%91%E5%B1%95/1.htm">职场和发展</a>
<div>既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上软件测试知识点,真正体系化!由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以戳这里获取4、如何保障测试质量?面试官考察:1、你对质量的认知;2、你的过往经验中是如何来保障测试质量的。参考以</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833838084278546432.htm"
title="优质素材的六个搜索技巧" target="_blank">优质素材的六个搜索技巧</a>
<span class="text-muted">老李大李和小李</span>
<div>一是要有耐心哦耐心不但是搜索的技巧而且是前提的、必要的。没有耐心进行搜索就不会有大量的好的输入。二是多关键词这个就像我们在搜索引擎中使用的方法,输入关键词反复搜索就会发现好多有用的而且是我们未知的知识。三是多渠道我们要利用各种搜索引擎和各种方式包括读书、和人聊天的方法来搜集资料。四是多维度至少要从三方面着手~文字、图片、视频。五是精准搜索有了前面做的功课,我们要对主题和材料进行凝炼~取其精华去除无</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833814523505635328.htm"
title="2025毕业设计指南:如何用Hadoop构建超市进货推荐系统?大数据分析助力精准采购" target="_blank">2025毕业设计指南:如何用Hadoop构建超市进货推荐系统?大数据分析助力精准采购</a>
<span class="text-muted">计算机编程指导师</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Java%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%9B%86/1.htm">Java实战集</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Python%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%9B%86/1.htm">Python实战集</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%A4%A7%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98%E9%9B%86/1.htm">大数据实战集</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%AF%BE%E7%A8%8B%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1/1.htm">课程设计</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/hadoop/1.htm">hadoop</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/1.htm">数据分析</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/spring/1.htm">spring</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/boot/1.htm">boot</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%BF%9B%E8%B4%A7/1.htm">进货</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/python/1.htm">python</a>
<div>✍✍计算机编程指导师⭐⭐个人介绍:自己非常喜欢研究技术问题!专业做Java、Python、小程序、安卓、大数据、爬虫、Golang、大屏等实战项目。⛽⛽实战项目:有源码或者技术上的问题欢迎在评论区一起讨论交流!⚡⚡Java实战|SpringBoot/SSMPython实战项目|Django微信小程序/安卓实战项目大数据实战项目⚡⚡文末获取源码文章目录⚡⚡文末获取源码基于hadoop的超市进货推荐系</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833758804395782144.htm"
title="什么是黑链?什么是黑帽?什么是明链?" target="_blank">什么是黑链?什么是黑帽?什么是明链?</a>
<span class="text-muted">倔强的小蚁云Zt</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C/1.htm">网络</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93/1.htm">数据库</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/tcp%2Fip/1.htm">tcp/ip</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E8%BF%90%E7%BB%B4/1.htm">运维</a>
<div>什么是黑链?什么是黑帽?什么是明链?黑链有哪几种表示方式!怎样预防黑链?首先我们说下黑链定义:黑链是SEO黑帽手法中相当普遍的一种手段,笼统地说,它就是指一些人用非正常的手段获取的其它网站的反向链接,最常见的黑链就是通过各种网站程序漏洞获取搜索引擎权重或者PR较高的网站的WEBSHELL,进而在被黑网站上链接自己的网站。黑链的写法黑链文本黑链标签被放在一个隐藏的div中。用户在浏览器中是无法看到的</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833756276794945536.htm"
title="精准剖析白帽SEO和黑帽SEO的区别" target="_blank">精准剖析白帽SEO和黑帽SEO的区别</a>
<span class="text-muted">heimaoxuexi</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E9%BB%91%E5%B8%BDseo/1.htm">黑帽seo</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E9%BB%91%E5%B8%BD/1.htm">黑帽</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/seo/1.htm">seo</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E9%BB%91%E5%B8%BDseo%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF/1.htm">黑帽seo技术</a>
<div>我们都知道,SEO就是搜索引擎优化,是对网站进行内部及外部的不断调整优化,改进网站在搜索引擎中的关键词自然排名,获得更多流量。而SEO又分为白帽SEO和黑帽SEO,SEO中的黑帽SEO技术http://www.heimaolianmeng.com。根据做网站的实战经验,分享一下自己对于白帽SEO和黑帽SEO的见解。一、白帽SEO1、符合用户体验原理就是指我们网站上做的任何内容、任何图片以及任何网站</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1833565266987020288.htm"
title="这可能是全网最详细的 Spring Cloud OAuth2 单点登录使用教程了,妈妈再也不用担心我被面试官吊打了!" target="_blank">这可能是全网最详细的 Spring Cloud OAuth2 单点登录使用教程了,妈妈再也不用担心我被面试官吊打了!</a>
<span class="text-muted">2401_84558091</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%91%98/1.htm">程序员</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95/1.htm">面试</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0/1.htm">学习</a>
<div>最后对于很多Java工程师而言,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,不成体系的学习效果低效漫长且无助。整理的这些资料希望对Java开发的朋友们有所参考以及少走弯路,本文的重点是你有没有收获与成长,其余的都不重要,希望读者们能谨记这一点。再分享一波我的Java面试真题+视频学习详解+技能进阶书籍本文已被CODING开源项目:【一线大厂Java面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+最新讲解视频+实战项目源码】收</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/53.htm"
title="二分查找排序算法" target="_blank">二分查找排序算法</a>
<span class="text-muted">周凡杨</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BA%8C%E5%88%86%E6%9F%A5%E6%89%BE/1.htm">二分查找</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F/1.htm">排序</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/1.htm">算法</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%8A%98%E5%8D%8A/1.htm">折半</a>
<div> 一:概念 二分查找又称
折半查找(
折半搜索/
二分搜索),优点是比较次数少,查找速度快,平均性能好;其缺点是要求待查表为有序表,且插入删除困难。因此,折半查找方法适用于不经常变动而 查找频繁的有序列表。首先,假设表中元素是按升序排列,将表中间位置记录的关键字与查找关键字比较,如果两者相等,则查找成功;否则利用中间位置记录将表 分成前、后两个子表,如果中间位置记录的关键字大于查找关键字,则进一步</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/180.htm"
title="java中的BigDecimal" target="_blank">java中的BigDecimal</a>
<span class="text-muted">bijian1013</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/BigDecimal/1.htm">BigDecimal</a>
<div> 在项目开发过程中出现精度丢失问题,查资料用BigDecimal解决,并发现如下这篇BigDecimal的解决问题的思路和方法很值得学习,特转载。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ugg/article/de</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/307.htm"
title="Shell echo命令详解" target="_blank">Shell echo命令详解</a>
<span class="text-muted">daizj</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/echo/1.htm">echo</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/shell/1.htm">shell</a>
<div>Shell echo命令
Shell 的 echo 指令与 PHP 的 echo 指令类似,都是用于字符串的输出。命令格式:
echo string
您可以使用echo实现更复杂的输出格式控制。 1.显示普通字符串:
echo "It is a test"
这里的双引号完全可以省略,以下命令与上面实例效果一致:
echo Itis a test 2.显示转义</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/434.htm"
title="Oracle DBA 简单操作" target="_blank">Oracle DBA 简单操作</a>
<span class="text-muted">周凡杨</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/oracle+dba+sql/1.htm">oracle dba sql</a>
<div> --执行次数多的SQL
select sql_text,executions from (
select sql_text,executions from v$sqlarea order by executions desc
) where rownum<81;
&nb</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/561.htm"
title="画图重绘" target="_blank">画图重绘</a>
<span class="text-muted">朱辉辉33</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%B8%B8%E6%88%8F/1.htm">游戏</a>
<div> 我第一次接触重绘是编写五子棋小游戏的时候,因为游戏里的棋盘是用线绘制的,而这些东西并不在系统自带的重绘里,所以在移动窗体时,棋盘并不会重绘出来。所以我们要重写系统的重绘方法。
在重写系统重绘方法时,我们要注意一定要调用父类的重绘方法,即加上super.paint(g),因为如果不调用父类的重绘方式,重写后会把父类的重绘覆盖掉,而父类的重绘方法是绘制画布,这样就导致我们</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/688.htm"
title="线程之初体验" target="_blank">线程之初体验</a>
<span class="text-muted">西蜀石兰</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B/1.htm">线程</a>
<div>一直觉得多线程是学Java的一个分水岭,懂多线程才算入门。
之前看《编程思想》的多线程章节,看的云里雾里,知道线程类有哪几个方法,却依旧不知道线程到底是什么?书上都写线程是进程的模块,共享线程的资源,可是这跟多线程编程有毛线的关系,呜呜。。。
线程其实也是用户自定义的任务,不要过多的强调线程的属性,而忽略了线程最基本的属性。
你可以在线程类的run()方法中定义自己的任务,就跟正常的Ja</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/815.htm"
title="linux集群互相免登陆配置" target="_blank">linux集群互相免登陆配置</a>
<span class="text-muted">林鹤霄</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/linux/1.htm">linux</a>
<div>配置ssh免登陆
1、生成秘钥和公钥 ssh-keygen -t rsa
2、提示让你输入,什么都不输,三次回车之后会在~下面的.ssh文件夹中多出两个文件id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub
其中id_rsa为秘钥,id_rsa.pub为公钥,使用公钥加密的数据只有私钥才能对这些数据解密 c</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/942.htm"
title="mysql : Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction" target="_blank">mysql : Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction</a>
<span class="text-muted">aigo</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/mysql/1.htm">mysql</a>
<div>原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/freeliver54/archive/2010/09/30/1839042.html
原因是你使用的InnoDB 表类型的时候,
默认参数:innodb_lock_wait_timeout设置锁等待的时间是50s,
因为有的锁等待超过了这个时间,所以抱错.
你可以把这个时间加长,或者优化存储</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1069.htm"
title="Socket编程 基本的聊天实现。" target="_blank">Socket编程 基本的聊天实现。</a>
<span class="text-muted">alleni123</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/socket/1.htm">socket</a>
<div>public class Server
{
//用来存储所有连接上来的客户
private List<ServerThread> clients;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Server s = new Server();
s.startServer(9988);
}
publi</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1196.htm"
title="多线程监听器事件模式(一个简单的例子)" target="_blank">多线程监听器事件模式(一个简单的例子)</a>
<span class="text-muted">百合不是茶</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B/1.htm">线程</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E7%9B%91%E5%90%AC%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F/1.htm">监听模式</a>
<div>
多线程的事件监听器模式
监听器时间模式经常与多线程使用,在多线程中如何知道我的线程正在执行那什么内容,可以通过时间监听器模式得到
创建多线程的事件监听器模式 思路:
1, 创建线程并启动,在创建线程的位置设置一个标记
2,创建队</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1323.htm"
title="spring InitializingBean接口" target="_blank">spring InitializingBean接口</a>
<span class="text-muted">bijian1013</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/spring/1.htm">spring</a>
<div>spring的事务的TransactionTemplate,其源码如下:
public class TransactionTemplate extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionOperations, InitializingBean{
...
}
TransactionTemplate继承了DefaultT</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1450.htm"
title="Oracle中询表的权限被授予给了哪些用户" target="_blank">Oracle中询表的权限被授予给了哪些用户</a>
<span class="text-muted">bijian1013</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/oracle/1.htm">oracle</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%BA%93/1.htm">数据库</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90/1.htm">权限</a>
<div> Oracle查询表将权限赋给了哪些用户的SQL,以备查用。
select t.table_name as "表名",
t.grantee as "被授权的属组",
t.owner as "对象所在的属组"</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1577.htm"
title="【Struts2五】Struts2 参数传值" target="_blank">【Struts2五】Struts2 参数传值</a>
<span class="text-muted">bit1129</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/struts2/1.htm">struts2</a>
<div>Struts2中参数传值的3种情况
1.请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上
2.Action将值传递到转发的视图上
3.Action将值传递到重定向的视图上
一、请求参数绑定到Action的实例字段上以及Action将值传递到转发的视图上
Struts可以自动将请求URL中的请求参数或者表单提交的参数绑定到Action定义的实例字段上,绑定的规则使用ognl表达式语言</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1704.htm"
title="【Kafka十四】关于auto.offset.reset[Q/A]" target="_blank">【Kafka十四】关于auto.offset.reset[Q/A]</a>
<span class="text-muted">bit1129</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/kafka/1.htm">kafka</a>
<div>I got serveral questions about auto.offset.reset. This configuration parameter governs how consumer read the message from Kafka when there is no initial offset in ZooKeeper or </div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1831.htm"
title="nginx gzip压缩配置" target="_blank">nginx gzip压缩配置</a>
<span class="text-muted">ronin47</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/nginx+gzip+%E5%8E%8B%E7%BC%A9%E8%8C%83%E4%BE%8B/1.htm">nginx gzip 压缩范例</a>
<div>nginx gzip压缩配置 更多
0
nginx
gzip
配置
随着nginx的发展,越来越多的网站使用nginx,因此nginx的优化变得越来越重要,今天我们来看看nginx的gzip压缩到底是怎么压缩的呢?
gzip(GNU-ZIP)是一种压缩技术。经过gzip压缩后页面大小可以变为原来的30%甚至更小,这样,用</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/1958.htm"
title="java-13.输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点" target="_blank">java-13.输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点</a>
<span class="text-muted">bylijinnan</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a>
<div>two cursors.
Make the first cursor go K steps first.
/*
* 第 13 题:题目:输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点
*/
public void displayKthItemsBackWard(ListNode head,int k){
ListNode p1=head,p2=head;
</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2085.htm"
title="Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate queryForObject" target="_blank">Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate queryForObject</a>
<span class="text-muted">bylijinnan</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/spring/1.htm">spring</a>
<div>JdbcTemplate中有两个可能会混淆的queryForObject方法:
1.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, Class requiredType)
2.
Object queryForObject(String sql, Object[] args, RowMapper rowMapper)
第1个方法是只查</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2212.htm"
title="[冰川时代]在冰川时代,我们需要什么样的技术?" target="_blank">[冰川时代]在冰川时代,我们需要什么样的技术?</a>
<span class="text-muted">comsci</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF/1.htm">技术</a>
<div>
看美国那边的气候情况....我有个感觉...是不是要进入小冰期了?
那么在小冰期里面...我们的户外活动肯定会出现很多问题...在室内呆着的情况会非常多...怎么在室内呆着而不发闷...怎么用最低的电力保证室内的温度.....这都需要技术手段...
&nb</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2339.htm"
title="js 获取浏览器型号" target="_blank">js 获取浏览器型号</a>
<span class="text-muted">cuityang</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/js/1.htm">js</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%B5%8F%E8%A7%88%E5%99%A8/1.htm">浏览器</a>
<div>根据浏览器获取iphone和apk的下载地址
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" content="text/html"/>
<meta name=</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2466.htm"
title="C# socks5详解 转" target="_blank">C# socks5详解 转</a>
<span class="text-muted">dalan_123</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/socket/1.htm">socket</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/C%23/1.htm">C#</a>
<div>http://www.cnblogs.com/zhujiechang/archive/2008/10/21/1316308.html 这里主要讲的是用.NET实现基于Socket5下面的代理协议进行客户端的通讯,Socket4的实现是类似的,注意的事,这里不是讲用C#实现一个代理服务器,因为实现一个代理服务器需要实现很多协议,头大,而且现在市面上有很多现成的代理服务器用,性能又好,</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2593.htm"
title="运维 Centos问题汇总" target="_blank">运维 Centos问题汇总</a>
<span class="text-muted">dcj3sjt126com</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BA%91%E4%B8%BB%E6%9C%BA/1.htm">云主机</a>
<div>一、sh 脚本不执行的原因
sh脚本不执行的原因 只有2个
1.权限不够
2.sh脚本里路径没写完整。
二、解决You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
修改/usr/share/logwatch/default.conf/logwatch.conf配置文件
MailTo =
MailFrom
三、查询连接数</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2720.htm"
title="Yii防注入攻击笔记" target="_blank">Yii防注入攻击笔记</a>
<span class="text-muted">dcj3sjt126com</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/sql/1.htm">sql</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/WEB%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8/1.htm">WEB安全</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/yii/1.htm">yii</a>
<div>网站表单有注入漏洞须对所有用户输入的内容进行个过滤和检查,可以使用正则表达式或者直接输入字符判断,大部分是只允许输入字母和数字的,其它字符度不允许;对于内容复杂表单的内容,应该对html和script的符号进行转义替换:尤其是<,>,',"",&这几个符号 这里有个转义对照表:
http://blog.csdn.net/xinzhu1990/articl</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2847.htm"
title="MongoDB简介[一]" target="_blank">MongoDB简介[一]</a>
<span class="text-muted">eksliang</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/mongodb/1.htm">mongodb</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/MongoDB%E7%AE%80%E4%BB%8B/1.htm">MongoDB简介</a>
<div>MongoDB简介
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2173288 1.1易于使用
MongoDB是一个面向文档的数据库,而不是关系型数据库。与关系型数据库相比,面向文档的数据库不再有行的概念,取而代之的是更为灵活的“文档”模型。
另外,不</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/2974.htm"
title="zookeeper windows 入门安装和测试" target="_blank">zookeeper windows 入门安装和测试</a>
<span class="text-muted">greemranqq</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/zookeeper/1.htm">zookeeper</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85/1.htm">安装</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%88%86%E5%B8%83%E5%BC%8F/1.htm">分布式</a>
<div>一、序言
以下是我对zookeeper 的一些理解: zookeeper 作为一个服务注册信息存储的管理工具,好吧,这样说得很抽象,我们举个“栗子”。
栗子1号:
假设我是一家KTV的老板,我同时拥有5家KTV,我肯定得时刻监视</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3101.htm"
title="Spring之使用事务缘由(2-注解实现)" target="_blank">Spring之使用事务缘由(2-注解实现)</a>
<span class="text-muted">ihuning</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/spring/1.htm">spring</a>
<div>
Spring事务注解实现
1. 依赖包:
1.1 spring包:
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3228.htm"
title="iOS App Launch Option" target="_blank">iOS App Launch Option</a>
<span class="text-muted">啸笑天</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/option/1.htm">option</a>
<div>iOS 程序启动时总会调用application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:,其中第二个参数launchOptions为NSDictionary类型的对象,里面存储有此程序启动的原因。
launchOptions中的可能键值见UIApplication Class Reference的Launch Options Keys节 。
1、若用户直接</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3355.htm"
title="jdk与jre的区别(_)" target="_blank">jdk与jre的区别(_)</a>
<span class="text-muted">macroli</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/java/1.htm">java</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/jvm/1.htm">jvm</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/jdk/1.htm">jdk</a>
<div>简单的说JDK是面向开发人员使用的SDK,它提供了Java的开发环境和运行环境。SDK是Software Development Kit 一般指软件开发包,可以包括函数库、编译程序等。
JDK就是Java Development Kit JRE是Java Runtime Enviroment是指Java的运行环境,是面向Java程序的使用者,而不是开发者。 如果安装了JDK,会发同你</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3482.htm"
title="Updates were rejected because the tip of your current branch is behind" target="_blank">Updates were rejected because the tip of your current branch is behind</a>
<span class="text-muted">qiaolevip</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E6%B0%B8%E6%97%A0%E6%AD%A2%E5%A2%83/1.htm">学习永无止境</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E6%AF%8F%E5%A4%A9%E8%BF%9B%E6%AD%A5%E4%B8%80%E7%82%B9%E7%82%B9/1.htm">每天进步一点点</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/%E4%BC%97%E8%A7%82%E5%8D%83%E8%B1%A1/1.htm">众观千象</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/git/1.htm">git</a>
<div>$ git push joe prod-2295-1
To git@git.dianrong.com:joe.le/dr-frontend.git
! [rejected] prod-2295-1 -> prod-2295-1 (non-fast-forward)
error: failed to push some refs to 'git@git.dianron</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3609.htm"
title="[一起学Hive]之十四-Hive的元数据表结构详解" target="_blank">[一起学Hive]之十四-Hive的元数据表结构详解</a>
<span class="text-muted">superlxw1234</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/hive/1.htm">hive</a><a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/hive%E5%85%83%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84/1.htm">hive元数据结构</a>
<div>关键字:Hive元数据、Hive元数据表结构
之前在 “[一起学Hive]之一–Hive概述,Hive是什么”中介绍过,Hive自己维护了一套元数据,用户通过HQL查询时候,Hive首先需要结合元数据,将HQL翻译成MapReduce去执行。
本文介绍一下Hive元数据中重要的一些表结构及用途,以Hive0.13为例。
文章最后面,会以一个示例来全面了解一下,</div>
</li>
<li><a href="/article/3736.htm"
title="Spring 3.2.14,4.1.7,4.2.RC2发布" target="_blank">Spring 3.2.14,4.1.7,4.2.RC2发布</a>
<span class="text-muted">wiselyman</span>
<a class="tag" taget="_blank" href="/search/Spring+3/1.htm">Spring 3</a>
<div>
Spring 3.2.14、4.1.7及4.2.RC2于6月30日发布。
其中Spring 3.2.1是一个维护版本(维护周期到2016-12-31截止),后续会继续根据需求和bug发布维护版本。此时,Spring官方强烈建议升级Spring框架至4.1.7 或者将要发布的4.2 。
其中Spring 4.1.7主要包含这些更新内容。 </div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div class="container">
<div class="indexes">
<strong>按字母分类:</strong>
<a href="/tags/A/1.htm" target="_blank">A</a><a href="/tags/B/1.htm" target="_blank">B</a><a href="/tags/C/1.htm" target="_blank">C</a><a
href="/tags/D/1.htm" target="_blank">D</a><a href="/tags/E/1.htm" target="_blank">E</a><a href="/tags/F/1.htm" target="_blank">F</a><a
href="/tags/G/1.htm" target="_blank">G</a><a href="/tags/H/1.htm" target="_blank">H</a><a href="/tags/I/1.htm" target="_blank">I</a><a
href="/tags/J/1.htm" target="_blank">J</a><a href="/tags/K/1.htm" target="_blank">K</a><a href="/tags/L/1.htm" target="_blank">L</a><a
href="/tags/M/1.htm" target="_blank">M</a><a href="/tags/N/1.htm" target="_blank">N</a><a href="/tags/O/1.htm" target="_blank">O</a><a
href="/tags/P/1.htm" target="_blank">P</a><a href="/tags/Q/1.htm" target="_blank">Q</a><a href="/tags/R/1.htm" target="_blank">R</a><a
href="/tags/S/1.htm" target="_blank">S</a><a href="/tags/T/1.htm" target="_blank">T</a><a href="/tags/U/1.htm" target="_blank">U</a><a
href="/tags/V/1.htm" target="_blank">V</a><a href="/tags/W/1.htm" target="_blank">W</a><a href="/tags/X/1.htm" target="_blank">X</a><a
href="/tags/Y/1.htm" target="_blank">Y</a><a href="/tags/Z/1.htm" target="_blank">Z</a><a href="/tags/0/1.htm" target="_blank">其他</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<footer id="footer" class="mb30 mt30">
<div class="container">
<div class="footBglm">
<a target="_blank" href="/">首页</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="/custom/about.htm">关于我们</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="/search/Java/1.htm">站内搜索</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="/sitemap.txt">Sitemap</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="/custom/delete.htm">侵权投诉</a>
</div>
<div class="copyright">版权所有 IT知识库 CopyRight © 2000-2050 E-COM-NET.COM , All Rights Reserved.
<!-- <a href="https://beian.miit.gov.cn/" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">京ICP备09083238号</a><br>-->
</div>
</div>
</footer>
<!-- 代码高亮 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/syntaxhighlighter/scripts/shCore.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/syntaxhighlighter/scripts/shLegacy.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/syntaxhighlighter/scripts/shAutoloader.js"></script>
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="/static/syntaxhighlighter/styles/shCoreDefault.css"/>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/syntaxhighlighter/src/my_start_1.js"></script>
</body>
</html>