Spring 中声明式事务和编程式事务的使用
在 MySQL 中我们也学习了事务, 那么事务它到底是什么呢 ?
在数据库中, 事务是指一系列的操作被视为一个完整的、原子性的工作. 在进行复杂业务逻辑时, 可能出现多个 SQL 操作需要同时进行, 但是如果这些操作不是原子性的, 就会导致数据库的不一致性和完整性的问题.
比如常见的转账操作中, 张三给李四转账 100 元, 那么张三账户 -100, 李四账户 +100, 但资金转移过程由于出现某种错误, 导致张三钱扣了, 但李四却没收到钱. 因此为了保证数据的一致性和原子性, 我们需要使用事务来确保一组操作的原子性.
在 Spring 中, 提供了两种事务, 一种是编程式另一种是声明式来管理我们的事务
一. 编程式事务
编程式事务, 顾名思义是一种通过编写具体代码来实现事务管理的方式. 在编程式事务中, 开发人员需要手动编写代码来控制事务的开始、提交和回滚等操作.
下面就来演示一个编程式事务
1. 构建 Mapper 接口
我们需要操作的是数据库, 因此肯定是需要 Mybatis 的两个组件的 接口和接口的XML 实现.( 可以看我往期文章 )
@Mapper // 注意添加 Mapper 注解进行申明
public interface UserMapper {
int del(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
2. XML 接口功能实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 注意XXXMapper 的名称要对应 -->
<delete id="del" >
delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
3. 建立 service 调用链
遵循我们的标准分层协议, 数据库中的操作一般由 service 调用, 最终提供方法供外部使用
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public int del(Integer id) {
return userMapper.del(id);
}
}
4. 建立 controller 调用
外部通过控制器访问 service 调用链, 从而进行外部调用.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
// 编程式事务
@Autowired
private DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager; // 事务管理器
@Autowired
private TransactionDefinition transactionDefinition; // 定义事务属性
@RequestMapping("/del")
public int del(Integer id) {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = null;
int result = 0;
try {
// 1. 开启事务
// 传入 transactionDefinition 给事务管理器 transactionManager 创建一个 transactionStatus 事务
transactionStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
result = userService.del(id);
System.out.println("删除 : " + result + " 条数据");
// 2. 事务提交
transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 事务对象正常
if (transactionStatus != null) {
transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus); // 事务回滚
}
return 0;
}
return result;
}
}
可以看到, 这个代码里, 当我们访问路由方法时, 如果出现了异常主动进行回滚, 正常执行则提交事务.
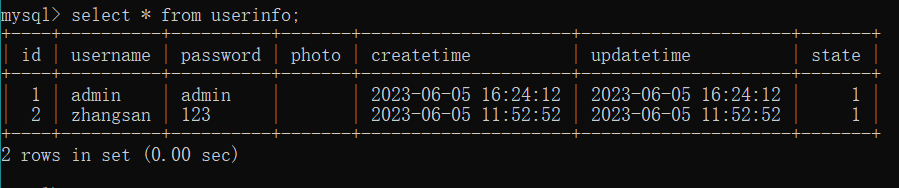
在 try 语句块中主动构建算数异常 : int a = 10 / 0; 加入到上述代码中, 执行路由方法观察是否进行回滚, 访问路由方法, 传入 id = 1

控制台显示我们已经删除了一条数据, 但我们预期的是发生异常后, 主动进行回滚, 数据库不被污染

可以看到, 异常后是成功的回滚了的.
这就是一个简单的编程式事务, 它非常的灵活, 而且也非常的受控, 但是它需要手写很多的事务代码, 因此存在可读性上会较差, 开发效率降低等问题.
二. 声明式事务
声明式事务是通过声明配置爱实现事务的管理方式. 在声明式事务中, 只需要在代码中通过添加事务注解或者 XML 配置文件中进行配置, 从而将事务管理交给框架来处理, 而无需手动编写大量的事务管理代码
1. 声明式事务的演示
声明式事务中最主要的就是 @Transactional 事务注解. 对于我们刚刚的删除操作, 同样可以用声明式事务来操作
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user2")
public class UserController2 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 该方法开启事务, 如果发生异常则进行事务回滚.
* 如果正常执行, 则提交事务
*/
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional
public int del(Integer id) {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
return userService.del(id);
}
}
service 层中
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
int result = userMapper.del(id);
return result;
}
}
UserMapper 中
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
int del(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
XMl 实现
<delete id="del" >
delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete>
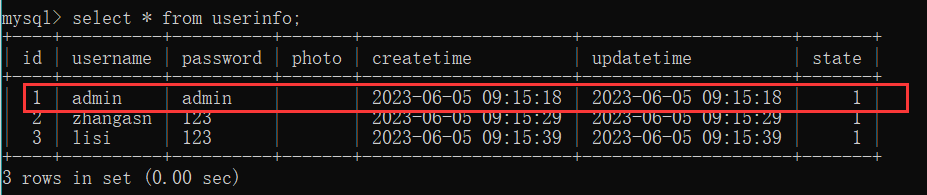
访问路由方法看其是否能够正常删除 id = 5 的用户
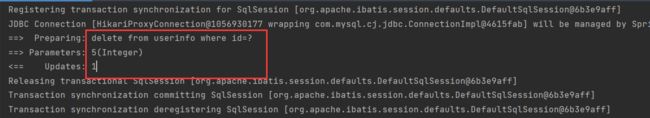
通过查看数据库, 可以看到它是正常的删除了的.
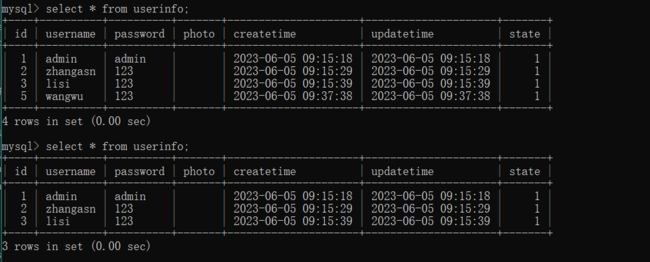
手动添加算数异常, 看我们的 @Transactional 事务注解 能否正常生效让其回滚. 此时传入 id = 1
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional
public int del(Integer id) {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0;
return result;
}
访问路由方法后, 控制台显示已经删除成功一条数据, 随后发生算数异常
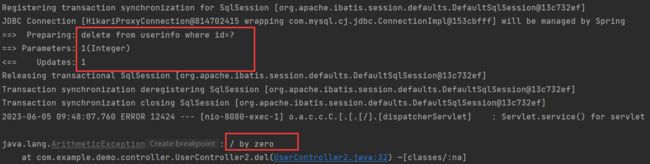
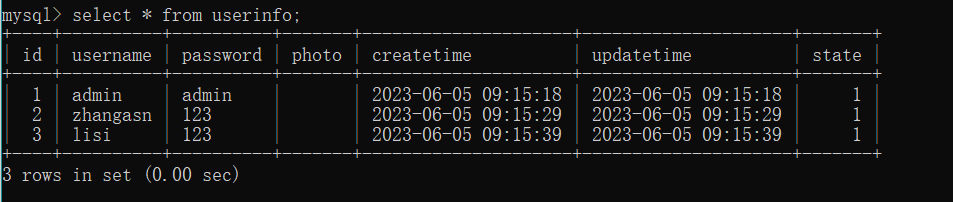
但是可以看到, 虽然在发生算数异常之前已经删除了 id = 1 的用户, 但是之后异常回滚并没有污染数据.
2. @Transactional 注解参数
| 参数 | 参数解释 |
|---|---|
| value | 当配置了多个事务管理器时, 使用该属性指定选择那个事务管理器 |
| transactionManager | 当配置了多个事务管理器时, 使用该属性指定选择那个事务管理器 |
| propagation | 事务的传播行为, 默认值为 Propagation.REQUIRED |
| isolation | 事务的隔离级别, 默认值为 Isolation.DEFAULT |
| timeout | 事务的超时时间, 默认值为 -1, 表示没有超时时间. |
| 当事务超过设定超时时间则自动进行事务回滚 | |
| readOnly | 指定事务是否为只读事务. 默认值为 false 不开启. |
| rollbackFor | 用于指定用于触发事务回滚的异常类型, 可以同时指定多个 |
| rollbackForClassName | 用于指定用于触发事务回滚的异常类型, 可以同时指定多个 |
| noRollbackFor | 触发指定异常则不会滚, 可以同时指定多个异常类型 |
| noRollbackForClassName | 触发指定异常则不会滚, 可以同时指定多个异常类型 |
3. @Transactional 注解失效场景
虽然 @Transactional 注解用起来非常的香, 不管是加在类上还是方法上都是可以使用的. 但是它却有着很多意想不到的 " 坑 " 等着我们
3.1 非 public 修饰符修饰
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional
int del(Integer id) {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0;
return result;
}
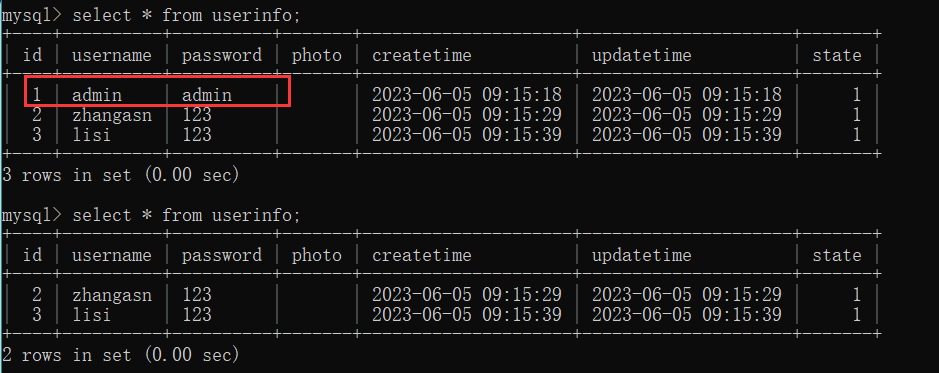
当我们不加 public 修饰符时, 普通的类中的方法默认访问权限是 default. 此时当我们再去访问这个路由方法时, 毋庸置疑它是会报错算数异常的.
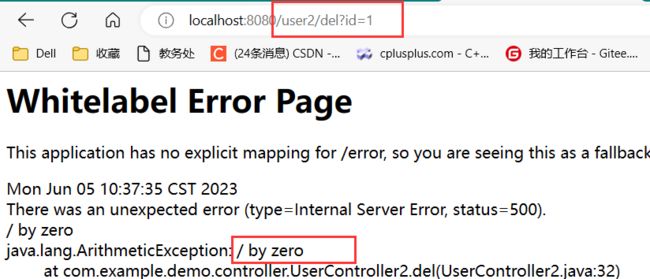
刚刚说的, @Transactional 事务注解在发生异常时会主动回滚事务, 然而上数据库中查询后惊奇的发现, 回滚失效了. 这是为什么 ?
**在 Spring 中, 事务的管理是通过 AOP( 里面的环绕通知来实现的 ), 当一个方法被代理后, Spring 就会在该方法执行前后插入一系列的 AOP 代码, 从而进行管理. **
我们知道, AOP 是通过动态代理的实现的, 因此当方法为非 public 修饰时, 它不能直接被调用也就无法被代理, 也就无法被拦截和增强, 那么它的事务管理也就失效了.
3.2 timeout 超时
设置事务的超时时间为 3 秒
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
return userService.del(id);
}
service 层中调用 del 方法是先休眠 5 秒
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
int result = userMapper.del(id);
// 休眠 5 秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
return result;
}
}
上面的代码可以看到, 写的是没有问题的, 没有异常出现, 此时去访问路由方法传入 id = 2, 预期超过了我们设置的超时时间, 它是会自动将事务进行回滚操作的.
当去访问这个路由方法时, 很明显是感觉到很慢的, 因为我们设置了休眠 5 秒

3.3 存在 try/catch 代码块
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional()
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = 0;
try {
result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0; // 设置异常
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
访问路由方法, 因为我设置了 catch, 因此将其进行了异常捕获, 页面未报错
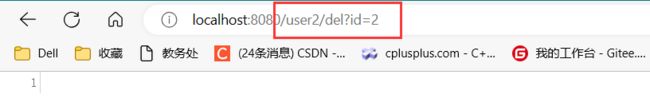
由于我没有对异常进行进一步处理, 在控制台中进行了报错, 预期在数据库中会进行回滚, 不会删除 id = 2 的用户

然而此时却看到 id = 2 的用户已经被删除了, 没有进行事务的回滚.
究其原因, 可以知道, @Transactional 注解是使用 AOP 中的环绕通知实现的. 环绕通知中, @ControllerAdvice 控制通知会监测整个框架中的异常. 但是由于我们主动将异常进行捕获了, 并没有交给框架去处理, 从而导致控制通知未检测到, 认为事务正常执行了, 也就不会进行回滚操作了.
对于这种情况下, 我们可以手动的进行回滚事务
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional()
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = 0;
try {
result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0; // 设置异常
} catch (Exception e) {
// 对异常主动事务回滚处理
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
}
return result;
}
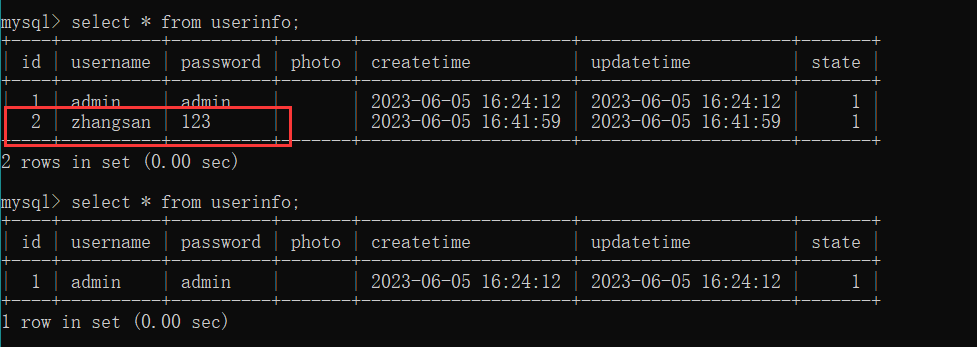
此时我们在尝试删除 id = 1 的用户, 控制台显示已经删除成功
可以看到, 由于对异常捕获后主动处理进行了回滚, 此时数据库中 id = 1 的用户还存在
除了主动回滚, 刚说到是由于控制监测没有监测到异常, 由于我们主动捕获但不做处理从而被吞噬了异常, 那么还可以将异常抛出去, 让它能够检测到异常从而主动进行回滚
@RequestMapping("del")
@Transactional
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = 0;
try {
result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0; // 设置异常
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
}
return result;
}

此时报错了, 但是主动抛出异常给框架去感知, 它感知到异常主动回滚了.
3.4 同一个类中调用类内部的 @Transactional 方法
@RequestMapping("/test")
public int test(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
return del(id);
}
/**
* 该方法开启事务, 如果发生异常则进行事务回滚.
* 如果正常执行, 则提交事务
*/
@RequestMapping("/del")
@Transactional
public int del(Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
if (id == null || id <= 0) return 0;
int result = 0;
result = userService.del(id);
int a = 10 / 0; // 设置异常
return result;
}
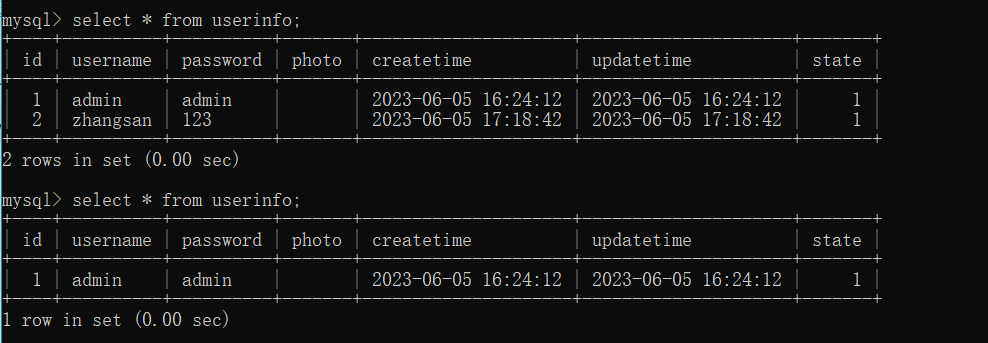
访问 user/test 方法时, 回去调用类里面的 del 方法, 该方法开启了事务, 并且有算数异常, 预期进行回滚不会删除数据

控制台显示删除成功, 但是由于出现异常, 预期该事务会主动进行回滚操作

上数据库中查看发现, 此时并没有进行回滚操作, 而执行了删除 id = 2 的操作.
3.5 不支持事务的数据库
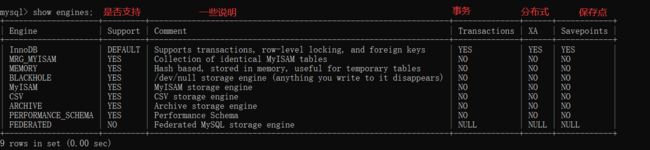
在 MySQL 它是支持很多引擎的, 但是有一些是不支持事务的. 具体的我们可以通过指令来查看有哪些引擎
show engines