pytest合集(2)— 测试用例
一、编写测试用例
1、测试用例编写规范
- 测试文件名必须以“test_”开头或者以”_test”结尾
- 测试类命名以Test开头
- 测试方法必须以“test_”开头
- 测试用例包pakege必须要有__init__.py文件
- 使用assert断言
2、使用marker标记测试用例
跳过测试用例:skip,skipif
预期失败的用例:xfail
二、运行测试用例
在Pycharm中使用pytest运行测试用例有两种方式,分别是命令行模式和主函数模式。
1、Terminal终端(命令行模式)
语法糖:
pytest [options] [file_or_dir] [file_or_dir] [...]
在Pycharm中新建test_sample.py文件如下:
import pytest
def func(x):
return x + 1
def test_answer():
assert func(3) == 5
选中test_sample.py文件,鼠标右键Open in | Open in Terminal,打开在Terminal终端窗口,输入命令:pytest
(venv) C:\Users\057776\PycharmProjects\pytest-demo\testcases>pytest
================================== test session starts ===================================
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.8, pytest-6.2.3, py-1.10.0, pluggy-0.13.1
rootdir: C:\Users\057776\PycharmProjects\pytest-demo\testcases
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0, rerunfailures-9.1.1, assume-2.2.0, requests-mock-1.7.0
collected 1 itemtest_sample.py F [100%]
===================================== FAILURES =====================================
______________________________________ test_answer ______________________________________def test_answer():
> assert func(3) == 5
E assert 4 == 5
E + where 4 = func(3)test_sample.py:18: AssertionError
================================ short test summary info ================================
FAILED test_sample.py::test_answer - assert 4 == 5
=================================== 1 failed in 0.60s ===================================(venv) C:\Users\057776\PycharmProjects\pytest-demo\testcases>
说明:
pytest运行的时候会根据测试用例收集规则来收集测试用例并执行。
2、pytest.main方法(主函数模式)
pytest.main()方法可以作为我们自动化测试项目的测试用例执行入口。
修改上面的test_sample.py文件如下:
import pytest
# content of test_sample.py
def func(x):
return x + 1
def test_answer():
assert func(3) == 5
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
# pytest.main(['test_sample.py'])
# pytest.main(['-q','test_sample.py'])
说明:
- pytest.main() :无任何参数,会收集当前目录下所有的测试用例,相当于命令行模式下输入命令pytest。
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py']) :一个参数,执行指定文件test_sample.py的所有测试用例。
- pytest.main(['-q','test_sample.py']) :二个参数,参数-q表示安静模式, 不输出环境信息。
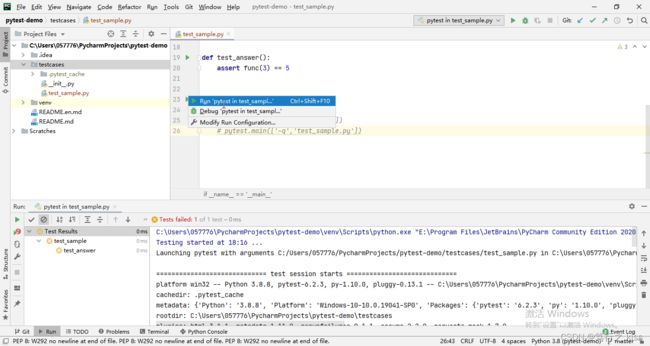
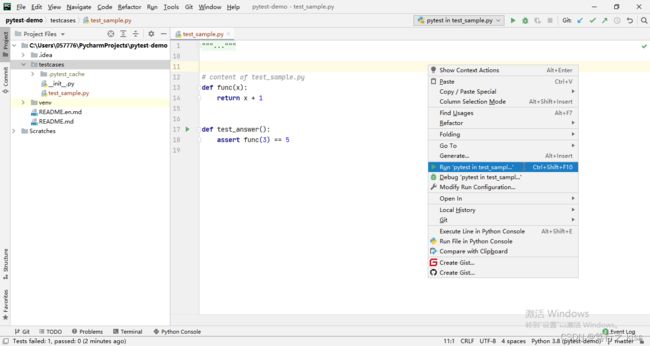
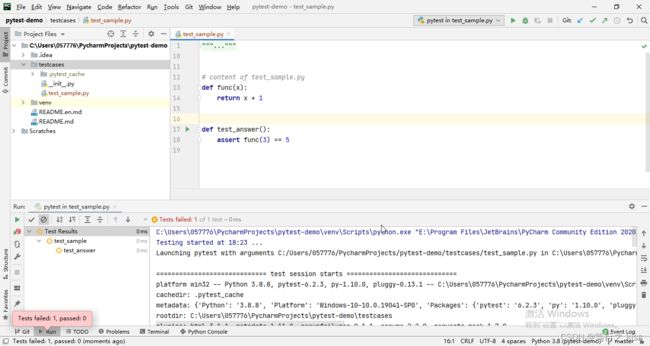
3、鼠标右键Run运行(测试运行器)
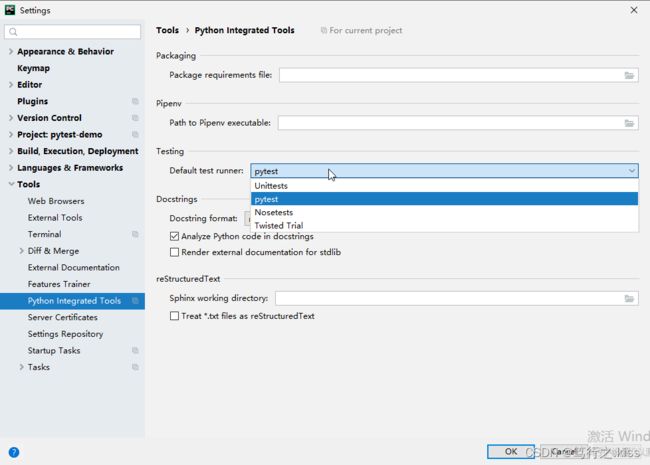
本地调试代码的时候,我们也可以通过配置默认的测试运行器,选择要运行的.py文件,鼠标右键Run运行。
File | Settings | Tools | Python Integrated Tools
说明:
这种方式可以直接使用pytest来运行指定的文件,方便调试。
4、测试用例收集规则
默认情况下,pytest会从当前目录及其子目录下所有以test_*.py或*_test.py文件中,收集以"test_"开头的测试函数。
Conventions for Python test discovery
pytestimplements the following standard test discovery:
If no arguments are specified then collection starts from testpaths (if configured) or the current directory. Alternatively, command line arguments can be used in any combination of directories, file names or node ids.
Recurse into directories, unless they match norecursedirs.
In those directories, search for
test_*.pyor*_test.pyfiles, imported by their test package name.From those files, collect test items:
testprefixed test functions or methods outside of class
testprefixed test functions or methods insideTestprefixed test classes (without an__init__method)For examples of how to customize your test discovery Changing standard (Python) test discovery.
Within Python modules,
pytestalso discovers tests using the standard unittest.TestCase subclassing technique.
说明:
(1)未指定参数,pytest会从当前目录及其子目录下所有以test_*.py或*_test.py文件中,收集以"test_"开头的函数。
(2)使用命令行参数来收集侧测试用例,命令行参数可以在目录、文件名或节点ID的任意组合中使用。
(3)读取pytest.ini配置文件。
(4)兼容unittest的测试用例。
5、运行结果标记符
- 点号,表示用例通过
- F 表示失败 Failure
- E 表示用例中存在异常 Error
- S 表示用例被跳过 Skip
- x 小写的 x 表示预期失败 xfail
- X 大写的 X 表示预期失败,但是通过了
6、.pytest_cache文件夹介绍
pytest运行测试用例后,会在当前执行脚本路径下生成.pytest_cache文件夹,即pytest缓存目录如下:
说明:将文件加入到.gitignore中之后,在pycharm中,该文件或文件夹的颜色变为黄色。
- lastfailed :上一次运行失败的测试用例。
- nodeids :上一次运行的所有测试用例(无论测试用例的执行结果通过还是失败)。
- stepwise :测试用例的路径。
- .gitignore :pytest测试框架 .pytest_cache的自带的 .gitignore 文件。
- CACHEDIR.TAG :pytest创建的缓存目录标签。
- README.md : .pytest_cache 文件夹介绍。
7、pytest.main()源码
def main(
args: Optional[Union[List[str], py.path.local]] = None,
plugins: Optional[Sequence[Union[str, _PluggyPlugin]]] = None,
) -> Union[int, ExitCode]:
"""Perform an in-process test run.
:param args: List of command line arguments.
:param plugins: List of plugin objects to be auto-registered during initialization.
:returns: An exit code.
"""
main() 函数接受两个参数:
- args :命令行参数列表,和命令行模式运行时的参数相同,在列表 List 里以字符串 str 的形式,多参数以 “,” 隔开,也可以传入测试case的路径。
- plugins :为插件参数,初始化期间要自动注册的插件对象列表。
8、常见的命令行参数
- -h : 获取帮助信息
- -v : 输出详细信息
- -q : 输出简要信息
- -s : 显示 print 信息
- [-k EXPRESSION] : 仅运行与给定子字符串表达式匹配的测试,匹配不区分大小写。
- [-m MARKEXPR] : 执行 mark 标记的测试用例
- [-x, --exitfirst] : 遇到第一个 error 或 failed 的测试用例立即退出
- [--lf, --last-failed] : 重跑上次失败的 tests,如果没有失败就重跑全部
9、运行测试用例
运行所有测试:pytest
运行指定测试文件夹:pytest [命令行参数] [文件夹的绝对路径/相对路径]
运行指定测试文件:pytest [命令行参数] [文件名]
运行指定测试类:pytest [命令行参数] [文件名::测试类]
运行指定测试函数:pytest [命令行参数] [文件名::测试类::测试函数]
过滤测试用例:pytest -k EXPRESSION
第N个用例FAIL或者ERROR后,结束测试执行:pytest -x,pytest --maxfail=num
重新运行失败的测试用例,可以指定运行次数:pytest --reruns=RERUNS
并行测试:pytest-xdist 插件,pytest -n
三、测试用例执行顺序
pytest运行测试用例默认执行顺序是,文件之间按ASCLL码排序,文件里的测试用例从上往下执行。
1、使用钩子函数管理测试用例执行顺序
hook钩子函数需要放到conftest.py文件中。
# 管理收集到的测试用例执行顺序
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(session, config,items):
"""
called after collection is completed.
you can modify the ``items`` list
:param _pytest.main.Session session: the pytest session object
:param _pytest.config.Config config: pytest config object
:param List[_pytest.nodes.Item] items: list of item objects
"""
print("收集到的测试用例:%s"%items)
print("收集到的测试用例items:",type(items))
items.sort(key=lambda x: x.name)
print('调整后的测试用例执行顺序',items)
2、使用 pytest-ordering 插件管理测试用例执行顺序
注意:这个pytest插件已经不再维护了,只适用于python 3.6之前的版本。
官方文档:pytest-ordering: run your tests in order — pytest-ordering 0.4 documentation
使用方法如下:
(1)使用数字1,2,3...-3, -2(倒数第二), -1(最后)
import pytest
@pytest.mark.order2
def test_foo():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order1
def test_bar():
assert True
或者使用插件注册的run标签。
import pytest
@pytest.mark.run(order=-2)
def test_three():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run(order=-1)
def test_four():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
def test_two():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_one():
assert True
(2)使用英文单词 first,second,third...third_to_last(倒数第三), second-to-last(倒数第二), last(最后)
import pytest
@pytest.mark.second_to_last
def test_three():
assert True
@pytest.mark.last
def test_four():
assert True
@pytest.mark.second
def test_two():
assert True
@pytest.mark.first
def test_one():
assert True
或者使用插件注册的run标签。
import pytest
@pytest.mark.run('second-to-last')
def test_three():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run('last')
def test_four():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run('second')
def test_two():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run('first')
def test_one():
assert True
(3)使用逻辑函数,before ,after
import pytest
@pytest.mark.run(after='test_second')
def test_third():
assert True
def test_second():
assert True
@pytest.mark.run(before='test_second')
def test_first():
assert True
3、使用 pytest-order插件管理测试用例执行顺序
注意:
pytest-order 是 pytest-ordering 的升级版本。
适用于 Python 3.6 - 3.10;
对于除 Python 3.10 之外的所有版本,pytest 版本 >= 5.0.0;
对于 Python 3.10,pytest >= 6.2.4。
官网文档:pytest-order - a plugin to order test execution — pytest-order 1.0.1 documentation
使用方法:
(1)使用数字排序1,2,…,-2,-1
import pytest
@pytest.mark.order(-2)
def test_three():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order(index=-1)
def test_four():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order(index=2)
def test_two():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order(1)
def test_one():
assert True
(2)使用序数排序“first”、“second”、“second_to_last”、“last”
import pytest
@pytest.mark.order("second_to_last")
def test_three():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order("last")
def test_four():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order("second")
def test_two():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order("first")
def test_one():
assert True
说明,数字和序数的映射关系如下:
- “first”: 0
- “second”: 1
- “third”: 2
- “fourth”: 3
- “fifth”: 4
- “sixth”: 5
- “seventh”: 6
- “eighth”: 7
- “last”: -1
- “second_to_last”: -2
- “third_to_last”: -3
- “fourth_to_last”: -4
- “fifth_to_last”: -5
- “sixth_to_last”: -6
- “seventh_to_last”: -7
- “eighth_to_last”: -8
(3)逻辑排序before,after
import pytest
@pytest.mark.order(after="test_second")
def test_third():
assert True
def test_second():
assert True
@pytest.mark.order(before="test_second")
def test_first():
assert True
reference:
Get Started — pytest documentation