.NetCore gRpc 客户端与服务端的单工通信Demo
文章目录
- .NetCore gRpc 客户端与服务端的单工通信Demo
-
- 服务端
-
- 方式一
- 方式二
- 客户端
- proto协议文件
-
- syntax = "proto3";
- import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
- service
- proto3与.netCore 的类型对应
- 日期和时间
- 可为 null 的类型
- 字节
- 小数
-
- 为 Protobuf 创建自定义 decimal 类型
- 集合
-
- 列表
- 字典
- 无结构的条件消息
-
- 任意
- Oneof
- “值”
.NetCore gRpc 客户端与服务端的单工通信Demo
服务端
方式一
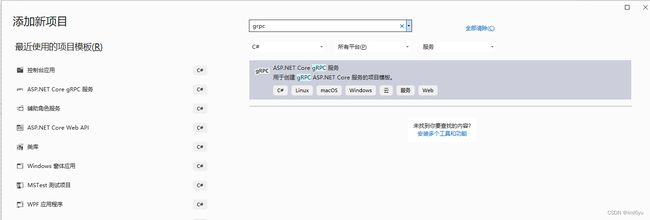
使用vs 2022(也可以是其他版本)创建一个grpc的服务,如下这样
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uipEG9Xu-1687172462785)(C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230619183828284.png)]
简单方便,创建项目后的目录结构如下图
- Protos:协议目录,里面是grpc的协议文件 默认是greet.proto
- Services:服务目录,对服务功能进行重写,默认文件是 GreeterService.cs
方式二
-
新建一个控制台程序,引入nuget包(版本根据实际情况确定)
-
新建一个Protos目录(当然也可以是其他的),新建一个文本文件命名为xxxxx.proto
-
编辑xxxx.proto文件(具体格式下面介绍)
-
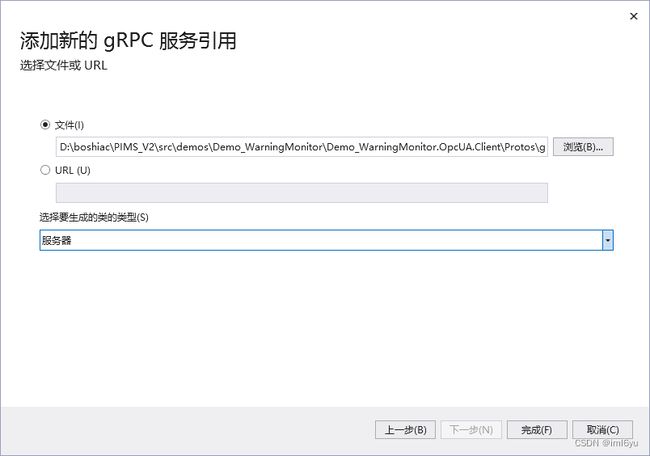
鼠标右键项目,添加–>服务引用–>gRPC–>选择文件(刚刚的那个proto文件)–>生成类型选择服务器,如下图
-
点击完成
-
新建一个Service.cs类,继承自生成的类后,重写处理方法(如果没有生成就先编译一下工程文件)
public class GreeterService : Greeter.GreeterBase { private readonly ILogger_logger; public GreeterService(ILogger logger) { _logger = logger; } public override Task SayHello(HelloRequest request, ServerCallContext context) { Console.WriteLine($"接收到请求!{request.Name}"); return Task.FromResult(new HelloReply { Message = "Hello " + request.Name }); } public override Task SayBye(Empty request, ServerCallContext context) { return base.SayBye(request, context); } } 注意命名空间
客户端
-
新建一个控制台
-
添加引用服务 grpc,选择客户端(具体操作和上面的生成服务端的类似)
-
代码如下
internal class Program { static async Task Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:6001"); var client = new Greeter.GreeterClient(channel); var response = await client.SayHelloAsync( new HelloRequest { Name = "张三 李四 王五" }); Console.WriteLine(response.Message); } }运行两个程序就可以了。
proto协议文件
https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto
上面的连接有详细说明,下面简单介绍一些基本使用
syntax = "proto3";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
option csharp_namespace = "Demo_WarningMonitor.OpcUA.Client";
package greet;
// The greeting service definition.
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply);
rpc SayBye(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings.
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
syntax = “proto3”;
声明协议语法是proto3
import “google/protobuf/empty.proto”;
导入一些默认的类型
service
定义一个服务,内部使用rpc关键字指定方法描述
proto3与.netCore 的类型对应
Protobuf 支持一系列本机标量值类型。 下表列出了全部本机标量值类型及其等效 C# 类型:
| Protobuf 类型 | C# 类型 |
|---|---|
double |
double |
float |
float |
int32 |
int |
int64 |
long |
uint32 |
uint |
uint64 |
ulong |
sint32 |
int |
sint64 |
long |
fixed32 |
uint |
fixed64 |
ulong |
sfixed32 |
int |
sfixed64 |
long |
bool |
bool |
string |
string |
bytes |
ByteString |
标量值始终具有默认值,并且该默认值不能设置为 null。 此约束包括 string 和 ByteString,它们都属于 C# 类。 string 默认为空字符串值,ByteString 默认为空字节值。 尝试将它们设置为 null 会引发错误。
可为 null 的包装器类型可用于支持 null 值。
日期和时间
本机标量类型不提供与 .NET 的 DateTimeOffset、DateTime 和 TimeSpan 等效的日期和时间值。 可使用 Protobuf 的一些“已知类型”扩展来指定这些类型。 这些扩展为受支持平台中的复杂字段类型提供代码生成和运行时支持。
下表显示日期和时间类型:
| .NET 类型 | Protobuf 已知类型 |
|---|---|
DateTimeOffset |
google.protobuf.Timestamp |
DateTime |
google.protobuf.Timestamp |
TimeSpan |
google.protobuf.Duration |
ProtoBuf复制
syntax = "proto3";
import "google/protobuf/duration.proto";
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
message Meeting {
string subject = 1;
google.protobuf.Timestamp start = 2;
google.protobuf.Duration duration = 3;
}
可为 null 的类型
C# 的 Protobuf 代码生成使用本机类型,如 int 表示 int32。 因此这些值始终包括在内,不能为 null。
对于需要显式 null 的值(例如在 C# 代码中使用 int?),Protobuf 的“已知类型”包括编译为可以为 null 的 C# 类型的包装器。 若要使用它们,请将 wrappers.proto 导入到 .proto 文件中,如以下代码所示:
ProtoBuf复制
syntax = "proto3";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
message Person {
// ...
google.protobuf.Int32Value age = 5;
}
wrappers.proto 类型不会在生成的属性中公开。 Protobuf 会自动将它们映射到 C# 消息中相应的可为 null 的 .NET 类型。 例如,google.protobuf.Int32Value 字段生成 int? 属性。 引用类型属性(如 string 和 ByteString )保持不变,但可以向它们分配 null,这不会引发错误。
下表完整列出了包装器类型以及它们的等效 C# 类型:
| C# 类型 | 已知类型包装器 |
|---|---|
bool? |
google.protobuf.BoolValue |
double? |
google.protobuf.DoubleValue |
float? |
google.protobuf.FloatValue |
int? |
google.protobuf.Int32Value |
long? |
google.protobuf.Int64Value |
uint? |
google.protobuf.UInt32Value |
ulong? |
google.protobuf.UInt64Value |
string |
google.protobuf.StringValue |
ByteString |
google.protobuf.BytesValue |
字节
Protobuf 支持标量值类型为 bytes 的二进制有效负载。 C# 中生成的属性使用 ByteString 作为属性类型。
使用 ByteString.CopyFrom(byte[] data) 从字节数组创建新实例:
var data = await File.ReadAllBytesAsync(path);
var payload = new PayloadResponse();
payload.Data = ByteString.CopyFrom(data);
使用 ByteString.Span 或 ByteString.Memory 直接访问 ByteString 数据。 或调用 ByteString.ToByteArray() 将实例转换回字节数组:
var payload = await client.GetPayload(new PayloadRequest());
await File.WriteAllBytesAsync(path, payload.Data.ToByteArray());
小数
Protobuf 本身不支持 .NET decimal 类型,只支持 double 和 float。 在 Protobuf 项目中,我们正在探讨这样一种可能性:将标准 decimal 类型添加到已知类型,并为支持它的语言和框架添加平台支持。 尚未实现任何内容。
可以创建消息定义来表示 decimal 类型,以便在 .NET 客户端和服务器之间实现安全序列化。 但其他平台上的开发人员必须了解所使用的格式,并能够实现自己对其的处理。
为 Protobuf 创建自定义 decimal 类型
ProtoBuf复制
package CustomTypes;
// Example: 12345.6789 -> { units = 12345, nanos = 678900000 }
message DecimalValue {
// Whole units part of the amount
int64 units = 1;
// Nano units of the amount (10^-9)
// Must be same sign as units
sfixed32 nanos = 2;
}
nanos 字段表示从 0.999_999_999 到 -0.999_999_999 的值。 例如,decimal 值 1.5m 将表示为 { units = 1, nanos = 500_000_000 }。 这就是此示例中的 nanos 字段使用 sfixed32 类型的原因:对于较大的值,其编码效率比 int32 更高。 如果 units 字段为负,则 nanos 字段也应为负。
集合
列表
Protobuf 中,在字段上使用 repeated 前缀关键字指定列表。 以下示例演示如何创建列表:
message Person {
// ...
repeated string roles = 8;
}
在生成的代码中,repeated 字段由 Google.Protobuf.Collections.RepeatedField 泛型类型表示。
public class Person
{
// ...
public RepeatedField<string> Roles { get; }
}
RepeatedField 可实现 IList。 因此你可使用 LINQ 查询,或者将其转换为数组或列表。 RepeatedField 属性没有公共 setter。 项应添加到现有集合中。
var person = new Person();
// Add one item.
person.Roles.Add("user");
// Add all items from another collection.
var roles = new [] { "admin", "manager" };
person.Roles.Add(roles);
字典
.NET IDictionary 类型在 Protobuf 中使用 map 表示。
message Person {
// ...
map attributes = 9;
}
在生成的 .NET 代码中,map 字段由 Google.Protobuf.Collections.MapField 泛型类型表示。 MapField 可实现 IDictionary。 与 repeated 属性一样,map 属性没有公共 setter。 项应添加到现有集合中。
var person = new Person();
// Add one item.
person.Attributes["created_by"] = "James";
// Add all items from another collection.
var attributes = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
["last_modified"] = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString()
};
person.Attributes.Add(attributes);
无结构的条件消息
Protobuf 是一种协定优先的消息传递格式。 构建应用时,必须在 .proto 文件中指定应用的消息,包括其字段和类型。 Protobuf 的协定优先设计非常适合强制执行消息内容,但可能会限制不需要严格协定的情况:
- 包含未知有效负载的消息。 例如,具有可以包含任何消息的字段的消息。
- 条件消息。 例如,从 gRPC 服务返回的消息可能是成功结果或错误结果。
- 动态值。 例如,具有包含非结构化值集合的字段的消息,类似于 JSON。
Protobuf 提供语言功能和类型来支持这些情况。
任意
利用 Any 类型,可以将消息作为嵌入类型使用,而无需 .proto 定义。 若要使用 Any 类型,请导入 any.proto。
import "google/protobuf/any.proto";
message Status {
string message = 1;
google.protobuf.Any detail = 2;
}
// Create a status with a Person message set to detail.
var status = new ErrorStatus();
status.Detail = Any.Pack(new Person { FirstName = "James" });
// Read Person message from detail.
if (status.Detail.Is(Person.Descriptor))
{
var person = status.Detail.Unpack<Person>();
// ...
}
Oneof
oneof 字段是一种语言特性。 编译器在生成消息类时处理 oneof 关键字。 使用 oneof 指定可能返回 Person 或 Error 的响应消息可能如下所示:
message Person {
// ...
}
message Error {
// ...
}
message ResponseMessage {
oneof result {
Error error = 1;
Person person = 2;
}
}
在整个消息声明中,oneof 集内的字段必须具有唯一的字段编号。
使用 oneof 时,生成的 C# 代码包括一个枚举,用于指定哪些字段已设置。 可以测试枚举来查找已设置的字段。 未设置的字段将返回 null 或默认值,而不是引发异常。
var response = await client.GetPersonAsync(new RequestMessage());
switch (response.ResultCase)
{
case ResponseMessage.ResultOneofCase.Person:
HandlePerson(response.Person);
break;
case ResponseMessage.ResultOneofCase.Error:
HandleError(response.Error);
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentException("Unexpected result.");
}
“值”
Value 类型表示动态类型的值。 它可以是 null、数字、字符串、布尔值、值字典 (Struct) 或值列表 (ValueList)。 Value 是一个 Protobuf 已知类型,它使用前面讨论的 oneof 功能。 若要使用 Value 类型,请导入 struct.proto。
import "google/protobuf/struct.proto";
message Status {
// ...
google.protobuf.Value data = 3;
}
// Create dynamic values.
var status = new Status();
status.Data = Value.ForStruct(new Struct
{
Fields =
{
["enabled"] = Value.ForBool(true),
["metadata"] = Value.ForList(
Value.ForString("value1"),
Value.ForString("value2"))
}
});
// Read dynamic values.
switch (status.Data.KindCase)
{
case Value.KindOneofCase.StructValue:
foreach (var field in status.Data.StructValue.Fields)
{
// Read struct fields...
}
break;
// ...
}
直接使用 Value 可能很冗长。 使用 Value 的替代方法是通过 Protobuf 的内置支持,将消息映射到 JSON。 Protobuf 的 JsonFormatter 和 JsonWriter 类型可用于任何 Protobuf 消息。 Value 特别适用于与 JSON 进行转换。
以下是与之前的代码等效的 JSON:
// Create dynamic values from JSON.
var status = new Status();
status.Data = Value.Parser.ParseJson(@"{
""enabled"": true,
""metadata"": [ ""value1"", ""value2"" ]
}");
// Convert dynamic values to JSON.
// JSON can be read with a library like System.Text.Json or Newtonsoft.Json
var json = JsonFormatter.Default.Format(status.Data);
var document = JsonDocument.Parse(json);
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/architecture/grpc-for-wcf-developers/migrate-duplex-services
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/grpc/protobuf?view=aspnetcore-7.0
https://blog.csdn.net/iml6yu/article/details/102948188?ops_request_misc=&request_id=45879ab70342436ea16723b29630d5e4&biz_id=&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2blogkoosearch~default-1-102948188-null-null.268v1control&utm_term=Grpc&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
https://blog.csdn.net/iml6yu/article/details/102959674?ops_request_misc=&request_id=45879ab70342436ea16723b29630d5e4&biz_id=&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2blogkoosearch~default-2-102959674-null-null.268v1control&utm_term=Grpc&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450