java代码模型
李兴华讲师讲的几种java代码模型的总结。
- 1.简单java类
- 1.1简单java类的含义
- 1.2简单java类的开发原则
- 1.3简单java类的实现
2.对象比较
- 2.1对象比较的操作特点
- 2.2对象比较的简单实现
3.简单java类和数据表的映射
- 3.1单表
- 3.2一对一
- 3.3一对多
1.简单java类
1.1简单java类的含义
- 只包含基本属性,setter()、getter()方法和构造方法的类称为简单java类
1.2简单java类的开发原则
- 类名称必须可以明确的表示出一类的定义,如Person、Book;
- 类中的所有属性必须使用private属性进行封装,如private String name;
- 类中的所有属性都必须定义相应的setter()、getter()方法;
- 类中可以提供构造方法为属性进行初始化,但是不管提供了多少个构造方法,一定要保留一个无参构造函数;
- 类中不允许直接使用System.out.println()输出,所有的内容要返回给被调用出输出。
1.3简单java类的实现
- 实现要求:定义一个表示书本的类,这个类中包含书的编号、书名、作者、价格、出版社、类别,并且可以返回一本书的完整信息。
- 代码实现
class Book //书类
{
// 定义书的属性
private String ID; // 书编号
private String name; // 书名
private String author;// 作者
private double price; // 价格
private String press; // 出版社
private String kind; // 类别;
// 无参构造函数
public Book(){}
// 有参构造
public Book(String ID, String name, String author, double price, String press, String kind )
{
this.ID = ID;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.press = press;
this.kind = kind;
}
// ID的setter、gettter方法
public void setID(String ID)
{
this.ID = ID;
}
public String getID()
{
return this.ID;
}
// 书名name的setter、gettter方法
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return this.name;
}
// 作者author的setter、gettter方法
public void setAuthor(String author)
{
this.author = author;
}
public String getAuthor()
{
return this.author;
}
// 价格prtice的setter、gettter方法
public void setPrice(double price)
{
this.price = price;
}
public double getPrice()
{
return this.price;
}
// 出版社press的setter、gettter方法
public void setPress(String press)
{
this.press = press;
}
public String getPress()
{
return this.press;
}
// 类别kind的setter、gettter方法
public void setKind(String kind)
{
this.kind = kind;
}
public String getKind()
{
return this.kind;
}
public String getBookInfo() // 取得书的完整信息
{
return "书本信息:" + "\n" +
"编号:" + this.ID + "\n" +
"书名:" + this.name + "\n" +
"作者:" + this.author + "\n" +
"价格:" + this.price + "\n" +
"出版社:" + this.press + "\n" +
"类别:" + this.kind;
}
}测试类
public class TestDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Book book = new Book("001", "java核心技术精讲", "李兴华", 69.8, "清华大学出版社", "编程语言类");
System.out.println(book.getBookInfo());
}
}2.对象比较
对象比较是指:若两个对象的全部属性相同,则表示相等,否则不相同。对象比较操作在开发中最为重要的一种操作概念。
2.1对象比较的操作特点
- 本类接收自己的引用,而后与本类当前对象(this)进行比较
- 为避免NullPointorException异常的产生,首先应该增加一个null的判断
- 为防止浪费性能的情况出现(要判断的属性会多),可以增加地址数值的判断,因为相同对象的地址相同
- 之后进行属性的依次比较,如果属性全部相同返回true,否则返回false
2.2对象比较的简单实现
本次实现上述已经实现书籍简单java类对象的比较。
代码实现
public boolean compare(Book book)
{
if(book == null) // 比较对象为null,直接返回false
{
return false;
}
if(this == book) // 地址相同(同一个对象相比较),直接返回true
{
return true;
}
// 否则进行属性依次比较
if(this.ID.equals(book.ID) && this.name.equals(book.name)
&& this.author.equals(book.author) && this.price == book.price
&& this.press.equals(book.press) && this.kind.equals(book.kind))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}3.简单java类和数据表的映射
3.1单表
类和数据表的对应关系如下:
- 类中的属性 = 表的字段
- 类的名称 = 表的名称
- 类的一个实例化对象 = 数据表的一行记录
- 类的对象数组(链表) = 数据表的多行记录
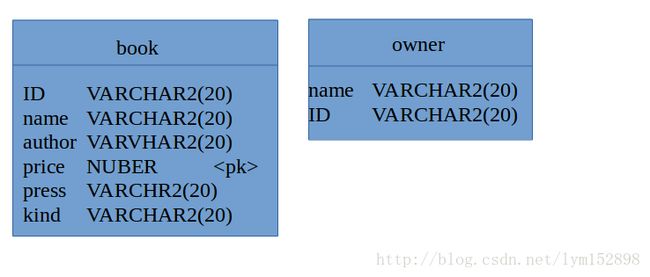
所以可以根据数据表写出简单java类。如下:将表book编写出Book简单类
3.2一对一
不妨假设现在有两张表,一张为表book,另一张为表owner,一对一关系表现为一个人拥有一本书,一本书对应一个拥有者。对这样关系的类可以按照以下步骤编写代码:
- 完成各自简单java类的定义
- 设置关联关系
其中表book已经编写成book简单类,下面将表owner编写成owner简单类。
class Owner // Owner类
{
// 定义私有属性
private String name;
private String ID;
// 无参构造函数
public Owner(){}
// 有参构造
public Owner(String name, String ID)
{
this.name = name;
this.ID = ID;
}
// name的setter和getter方法
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return this.name;
}
// ID的setter和getter方法
public void setID(String ID)
{
this.ID = ID;
}
public String getID()
{
return this.ID;
}
// 取得拥有者的全部信息
public String getOwnerInfo()
{
return "拥有者信息:" + "\n" +
"姓名:" + this.name + "\n" +
"ID:" + this.ID;
}
}测试类
public class TestDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Owner owner = new Owner("张三", "1204");
System.out.println(owner.getOwnerInfo());
}
}然后设置关联关系
由于一个读者拥有一本书,所以在类Owner中添加如下属性和操作方法
// class Owner
private Book book; // 拥有一本书
// book的setter和getter方法
public void setBook(Book book)
{
this.book = book;
}
// 返回book对象
public Book getBook()
{
return this.book;
}由于一本书由一个读者所拥有,所以在类Book中添加如下属性和操作方法
// class Book
private Owner owner;// 为一个读者所拥有
// owner 的setter和getter方法
public void setOwner(Owner owner)
{
this.owner = owner;
}
// 返回owner对象
public Owner getOwner()
{
return this.owner;
}至此,完成一对一关系的映射,测试代码
public class TestDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
// 配置关系
Owner owner = new Owner("张三", "012");
Book book = new Book("012","java核心技术精讲", "李兴华", 69.80, "清华大学出版社", "编程语言类");
// 一人拥有一本书
owner.setBook(book);
// 一本书为一个人所拥有
book.setOwner(owner);
// 取得关系
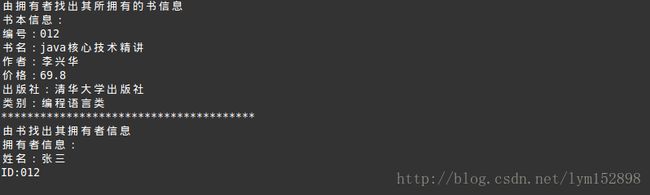
// 由拥有者找出其所拥有的书信息
System.out.println("由拥有者找出其所拥有的书信息");
System.out.println(owner.getBook().getBookInfo());
System.out.println("***************************************")
// 由书找出其拥有者信息
System.out.println("由书找出其拥有者信息");
System.out.println(book.getOwner().getOwnerInfo());
}
}3.3一对多
此类的关系同一对一的实现思路相同,可分为两个步骤实现
- 完成各自简单java类的实现
- 设置关联关系
类Book和类Owner在设置一对一关系时已经完成定义
设置关联关系
由于一个读者拥有多本书,所以在类Owner中添加如下属性和操作方法
// class Owner
private Book [] book; //一个读者拥有多本书
// 数组book的setter和getter方法
public void setBook(Book [] book)
{
this.book = book;
}
// 返回book对象数组
public Book [] getBook()
{
return book;
}由于一本书只由一个拥有者所拥有,所以与一对一关系一致,应在类Book中添加如下属性和操作方法
// class Book
private Owner owner;// 为一个读者所拥有
// owner 的setter和getter方法
public void setOwner(Owner owner)
{
this.owner = owner;
}
// 返回owner对象
public Owner getOwner()
{
return this.owner;
}至此,完成一对一关系的映射,测试代码
public class TestDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
// 配置关系
Owner owner = new Owner("张三", "012");
Book book1 = new Book("012","java核心技术精讲", "李兴华", 69.80, "清华大学出版社", "编程语言类");
Book book2 = new Book("013","数据库系统概论", "王珊", 39.60, "高等教育出版社", "编程语言类");
Book book3 = new Book("014","算法精解", "Kyle Loudon", 79.00, "机械工业出版社", "编程语言类");
Book [] book = new Book [] {book1, book2, book3};
// 一人拥有多本书
owner.setBook(book);
// 一本书为一个人所拥有
book1.setOwner(owner);
book2.setOwner(owner);
book3.setOwner(owner);
// 取得关系
// 由拥有者找出其所拥有的书信息
System.out.println("由拥有者找出其所拥有的书信息");
for(int i = 0; i < owner.getBook().length; i++)
{
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(owner.getBook()[i].getBookInfo());
}
System.out.println("***************************************")
// 由书找出其拥有者信息
System.out.println("由书找出其拥有者信息");
System.out.println(book1.getOwner().getOwnerInfo());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(book2.getOwner().getOwnerInfo());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(book3.getOwner().getOwnerInfo());
}
}