SpringBoot配置文件
- 1、配置文件的作用
- 2、配置文件的格式
-
- 2.1、properties配置说明
-
- 读取配置文件
- 2.2、yml配置说明
-
- 读取yml配置文件
- value值加单双引号
- 配置对象
- 读取对象
- 配置&读取集合对象
- 3、properties Vs YAML/yml
1、配置文件的作用
Spring Boot的配置文件用于配置应用程序的行为和属性。它提供了一种灵活的方式,使开发人员可以根据需要来配置应用程序的各种属性,而无需修改代码。
配置文件的作用如下:
- 灵活性和可配置性: 通过配置文件,可以轻松更改应用程序的行为和属性,而无需重新编译和部署代码。这使得应用程序能够适应不同的环境和需求。
- 避免硬编码: 将应用程序的配置信息从代码中分离出来,使得代码更加清晰、可维护和可重用。通过修改配置文件而不是代码,可以更容易地进行配置调整和部署管理。
- 多环境支持: 可以针对不同的运行环境(如开发环境、测试环境、生产环境)使用不同的配置文件,以适应不同环境下的需求。这样可以在不同环境下灵活切换配置,减少了手动修改的工作量。
总之,Spring Boot的配置文件是配置应用程序行为和属性的重要途径,能够实现应用程序的灵活配置和多环境支持,提高了代码的可维护性和可扩展性。
2、配置文件的格式
SpringBoot配置文件主要分为两种,如下图:
默认是只有后缀为 .properties的文件
配置文件通常采用属性键值对的形式,可以使用不同的格式进行编写:
- **Properties文件:**使用
.properties作为文件扩展名,采用key=value的格式。 - **YAML文件:**使用
.yml或.yaml作为文件扩展名,采用缩进和冒号的结构化格式。
配置文件可以包含如下内容:
- 应用程序的基本配置属性:例如服务器端口号、数据库连接信息、日志级别、国际化配置等。这些属性可以根据实际需求进行自定义。
- Spring框架相关的配置属性:包括Spring MVC、Spring Data、Spring Security等模块的相关配置,如URL映射、数据源配置、安全认证配置等。
- 第三方库和组件的配置属性:许多第三方库和组件也提供了自己的配置属性,可以在配置文件中进行设置,以满足特定需求。
-
特殊声明:
properties和yml同时存在于一个项目中,如果配置文件出现了相同配置,优先以properties中的配置为主。比如properties和yml中都配置了server.port,那么这个时候会以properties中的配置为主。properties配置文件的优先级最高,但加载完properties文件会,也会加载yml的配置信息。
2.1、properties配置说明
properties 配置⽂件是最早期的配置⽂件格式,也是创建 Spring Boot 项⽬默认的配置⽂件。
基本语法:
Properties文件: 使用.properties作为文件扩展名,采用key=value的格式。
#配置项目端口号
server.port=8080
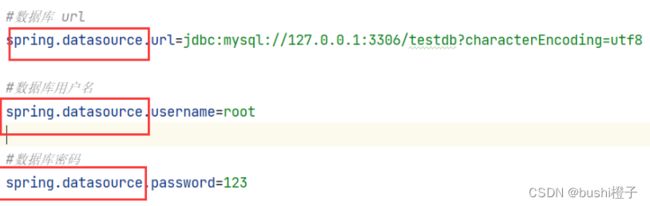
#数据库 url
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb?characterEncoding=utf8
#数据库用户名
spring.datasource.username=root
#数据库密码
spring.datasource.password=123
- 配置文件中使用
#来添加注释信息。
读取配置文件
在Spring Boot中,@Value 注解用于从配置文件中获取属性值,并将其注入到对应的变量中。该注解可以用于类的字段、方法的参数以及方法的返回值上。
@Value注解支持多种表达式,常见的有:
${property.key}:从配置文件中获取指定属性的值,支持SpEL表达式。${property.key:defaultValue}:在找不到属性值时,使用默认值。
使用@Value注解需要按照以下步骤进行操作:
- 在配置文件(如application.properties或application.yml)中定义属性的键值对。例如,在application.properties文件中定义了一个属性值:
#配置项目端口号
server.port=8080
- 在目标类中使用@Value注解来注入属性值。可以将@Value注解放置在字段上、方法的参数上或方法的返回值上,具体使用位置取决于你的需求。
- 字段注入:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
// ...
}
- 方法参数注入:
@Component
public class MyComponent {
private String port;
public MyComponent(@Value("${server.port}") String port){
this.port = port;
}
// ...
}
- 方法返回值注入:
//返回值注入
@Value("${server.port}")
public String set(String port){
return port;
}
// ...
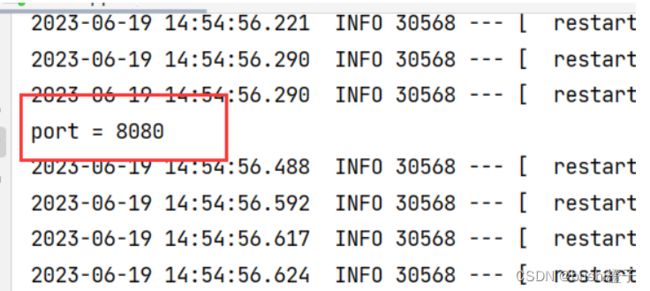
- 字段注入的运行结果:
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
// ...
@PostConstruct
public void doPostConstruct(){
System.out.println("port = " + this.port);
}
}
@@Component 在 Spring Boot 启动时候会注⼊到框架中,注⼊到框架中时会执⾏ @PostConstruct初始化⽅法,这个时候就能读取到配置信息了。
属性值会根据@Value注解中指定的表达式从配置文件中获取,并注入到相应的变量中。
综上所述:@Value注解是一个方便的工具,用于在Spring Boot应用中获取配置文件中的属性值并注入到相应的变量中,实现了属性值与代码的解耦。
properties缺点:代码冗余
2.2、yml配置说明
优点: 使用YML作为配置文件格式在Spring Boot中具有清晰易读、结构灵活、支持复杂数据类型和环境相关配置等优点。它是一种更现代、强大的配置选择,可以提高配置文件的可维护性和灵活性。
- 结构清晰、易读易写,语法与JSON语言类似。
- 支持更多的数据类型,可以简单表达清单(数组),散列表,标量等数据形态,使用空格符号缩进和大量依赖外观的特色,并减少了配置冗余。特别适合用来表达和编辑数据结构、各种配置文件。
- 支持更多的编程语言: 可以在JAVA,Golang,PHP。Python,Ruby,JavaScript,Perl中使用。
基本语法:
YAML文件: 使用.yml或.yaml作为文件扩展名,采用缩进和冒号的结构化格式。注意key和value之间使用英文冒号和空格组成的,其中空格不可省略,格式正确是有高亮显示的。

#配置项目端口号
server:
port: 8080
#数据库 url 用户名 用户密码
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb?characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: 123
yml配置多种类型,以及null
# 字符串
string:
value: hello
# 布尔值,true或false
boolean:
value: true
value1: false
# 整数
int:
value: 10
value1: 0b1010_0111_0100_1010_1110 # ⼆进制
# 浮点数
float:
value: 3.14159
value1: 314159e-5 # 科学计数法
# Null,~代表null
null:
value: ~
读取yml配置文件
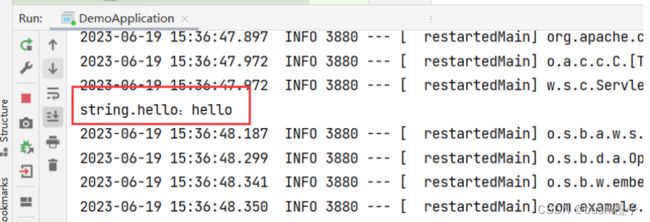
yml读取方式和properties方式相同,使用@Value注解即可:
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Value("${string.hello}")
private String hello;
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("string.hello:" + hello);
}
}
运行结果:
value值加单双引号
字符串默认不⽤加上单引号或者双引号,如果加英⽂的单双引号可以表示特殊的含义。
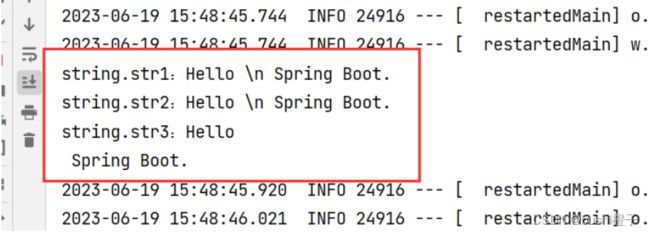
尝试在 application.yml 中配置如下信息:
string:
str1: Hello \n Spring Boot.
str2: 'Hello \n Spring Boot.'
str3: "Hello \n Spring Boot."
Component代码:
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Value("${string.str1}")
private String str1;
@Value("${string.str2}")
private String str2;
@Value("${string.str3}")
private String str3; @PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("string.str1:" + str1);
System.out.println("string.str2:" + str2);
System.out.println("string.str3:" + str3);
}
}
运行结果:
- 字符串默认可以不加单双引号。
- 单引号不会转义特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思。
- 双引号会转义特殊字符。
配置对象
student:
id: 1
name: lisi
或者使用行内写法:
student: {id: 1,name: lisi}
读取对象
使用@ConfigurationProperties 读取对象:
getter和setter方法不能省略
配置类具体实现:
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “student”)表示将以"student"为前缀的配置项绑定到此类中对应的属性上。student为配置文件里的student名字相对应,prefix可以省略。
- 确保配置类和配置文件中的前缀、命名、属性名的对应关系正确无误
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@Controller
public class StudentController {
//属性名与配置文件中的命名要对应
private int id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentController{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
调用类:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Controller
public class YAMLRead {
@Autowired
private StudentController studentController;
@PostConstruct
public void doPostConstruct(){
System.out.println(studentController);
}
}
在上述代码中,@Autowired注解用于将StudentController类自动注入到YAMLRead中,我们就可以使用StudentController类代表的Bean实例studentController对象了。
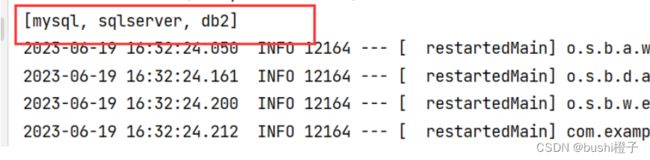
运行结果:
在上述代码中,@ConfigurationPropertiesScan注解用于扫描com.example.demo包下的所有@ConfigurationProperties注解,将它们转化为Java Bean对象。
配置&读取集合对象
读取集合和读取对象一些,使用@ConfigurationProperties 来读取的。prefix可以省略。
dbtypes:
name:
- mysql
- sqlserver
- db2
行内写法:
dbtypes: {name: [mysql,sqlserver,db2]}
配置类:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("dbtypes")
@Data
public class ListComponent {
private List<String> name;
}
-
@data注解:
-
在Spring Boot中,
@Data是一个Lombok注解,它可以自动生成Java类的一些常用方法,如getter、setter、equals、hashCode和toString。 -
使用
@Data注解可以简化代码编写,减少样板代码的冗余,并提高开发效率。 -
Getter和Setter:生成私有字段的公共getter和setter方法。
-
toString():生成包含对象属性值的字符串表示形式,方便输出日志或调试。
-
使用@Data注解时要确保已在项目的依赖中添加了Lombok库。在使用@Data注解后,编译器会自动为您生成相关的方法,无需手动编写这些常用方法。
调用类:
@Component
public class YAMLRead2 {
@Autowired
ListComponent listComponent;
@PostConstruct
public void dpPostConstruct(){
System.out.println(listComponent.getName());
}
}
运行结果:
3、properties Vs YAML/yml
- properties是以
key=value的形式配置键值类型。 - yml/yaml是以类似json格式的树形配置方式,yml层级之间用换行缩进的方式配置;key和value之间使用
“:”英文冒号加空格的方式设置,并且空格不可省。 - properties为早期并且是默认的配置文件格式,但其配置存在一定的冗余,而yml可以很好的解决冗余的问题。
- yml通用性更好,支持更多语言,如java,Go,Python等,如果是云服务器开发,可以使用一份配置文件作为java和Go的配置文件。
- yml支持更多的数据类型。
注释:
- properties文件支持以
“#”或“!”开头的行注释。 - YAML文件支持以
“#”作为行注释。
Spring Boot更多系统配置项 【官网链接】
Spring Boot读取配置文件的N种方法 【链接】