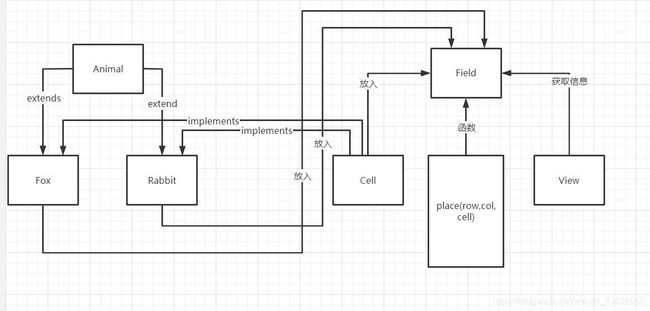
狐狸与兔子,代码解析
看懂代码从main函数开始
这是主类
package foxnrabbit;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import field.Field;
import field.View;
import field.Location;
import animal.Animal;
import animal.Fox;
import animal.Rabbit;
import cell.Cell;
public class FoxAndRabbit {
//成员变量
private Field theField;//Field变量,用来管理新的网格
private View theView;//继承自Jpanel的类,用来显示图形
/*------构造函数------*/
public FoxAndRabbit(int size) {
//创建网格
theField=new Field(size,size);
//遍历网格
for(int row=0;row<theField.getHeight();row++)
{
for(int col=0;col<theField.getWidth();col++)
{
double probability=Math.random();
//随机放入狐狸
if(probability<0.05)
{
theField.place(row,col,new Fox());
}
//随机放入兔子
else if(probability<0.15)
{
theField.place(row, col,new Rabbit());
}
}
}
/*------把theField加入到显示框------*/
theView=new View(theField);
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setResizable(false);
frame.setTitle("Cells");
frame.add(theView);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
/*------开始函数,传入的参数是程序要执行的次数------*/
public void satrt(int steps)
{
for (int i=0;i<steps;i++) {
step();
theView.repaint();//Java底层函数
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*------step()函数,每次更新表格- - - - - -*/
public void step() {
for(int row=0;row<theField.getHeight();row++)
{
for(int col=0;col<theField.getWidth();col++)
{
//获取所有Cell的对象变量
Cell cell=theField.get(row, col);
if(cell!=null)
{
//把管理的对象造型为Animal对象
Animal animal=(Animal)cell;
//年龄增长
animal.grow();
if(animal.isAlive())
{
//向周围移动
Location loc=animal.move(theField.getFreeNeighbour(row, col));
if(loc!=null) { theField.move(row,col,loc); }
//获取周围的兔子,储存进容器里面
Cell[] neighbour=theField.getNeighbour(row, col);
ArrayList<Animal> listRabbit=new ArrayList<Animal>();
for(Cell an:neighbour)
{//instanceof关键字,判断是不是某个类的实例
if(an instanceof Rabbit) { listRabbit.add((Rabbit)an); }
}
//吃掉兔子
if(!listRabbit.isEmpty()) //isEmpty()是ArrayList的函数,没有元素则返回true
{
//这里涉及到了多态,这个animal实际上是Fox的对象,调用的是Fox的feed()
//(animal本身是抽象类,自己不可能有对象的)
Animal fed=animal.feed(listRabbit);
//fed得到了兔子的对象之后,调用函数删除这个对象(被吃掉
if(fed!=null) { theField.remove((Cell)fed); }
}
//动物繁殖
Animal baby=animal.breed();
if(baby!=null) { theField.placeRandomAdj(row,col,(Cell)baby); }
}
else { theField.remove(row ,col); }
}
}
}
}
/*------看懂函数先从main函数开始------*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个30x30的网格
//走100步
FoxAndRabbit fr=new FoxAndRabbit(30);
fr.satrt(100);
}
}
view类
package field;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import cell.Cell;
public class View extends JPanel {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5258995676212660595L;
private static final int GRID_SIZE = 16;
//定义自己的变量
private Field theField;
//构造函数
public View(Field field) {
theField = field;
}
/**
* paint()函数,由于继承了JPanel类,该函数在对象初始化的会被自动调用
* drawLine()函数,前两个数是第一个点的坐标值,后两个数是第二个点的坐标值
* 该函数会先画一个与区域大小一样
* 然后会遍历整个区域,如果存在对象,给网格上色
*/
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
super.paint(g);//Invoked by Swing to draw components. 画出传入的图形
g.setColor(Color.gray);
for(int i=0;i<theField.getHeight();i++)
{
g.drawLine(0, i*GRID_SIZE, theField.getWidth()*GRID_SIZE, i*GRID_SIZE);
g.drawLine(i*GRID_SIZE, 0, i*GRID_SIZE, theField.getHeight()*GRID_SIZE);
}
//遍历传入的区域
for ( int row = 0; row<theField.getHeight(); row++ )
{
for ( int col = 0; col<theField.getWidth(); col++ )
{
//用细胞变量依次管理被遍历的 Cell对象
Cell cell = theField.get(row, col);
if ( cell != null ) //该区域有Cell的对象
{//调用draw函数 对象为传入的 g, x=1x16,y=1x16,y=2x16...
cell.draw(g, col*GRID_SIZE, row*GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE);
}
}
}
}
//这个函数我并没由找到他的作用说明,根据在细胞自动机里面的代码,写上就好了
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize() {
return new Dimension(theField.getWidth()*GRID_SIZE+1, theField.getHeight()*GRID_SIZE+1);
}
}
Field类
package field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.function.IntFunction;
import animal.Fox;
import animal.Rabbit;
import cell.Cell;
public class Field {
//测试代码
private static final Location[] adjacent= {
new Location(-1,-1),new Location(-1,0),new Location(-1,1),
new Location(0,-1),new Location(0,0),new Location(0,1),
new Location(1,-1),new Location(1,0),new Location(1,1)
};
//成员变量
private int height;
private int width;
private Cell[][] field;
//构造函数
public Field(int height, int width) {
this.height=height;
this.width=width;
field=new Cell[height][width];
}
public int getHeight() { return height; }
public int getWidth() { return width; }
/**
* place函数,
* 在Field类中,先定义Cell类型的变量ret
* Field的成员变量同时也是Cell类型的变量数组field[][],
* 让ret和field[row][col]管理同一个对象,此时ret管理的是null
* 让field[row][col]管理传入的细胞对象变量
* (不能实例化,但是可以管理实现了它的接口的Fox和Rabbit,
* 此时ret也会跟着管理这个对象
*/
public Cell place(int row, int col, Cell o) {
// Cell ret=field[row][col];
field[row][col]=o;
// return ret;
return field[row][col];//改写了这个函数,这样看条例更清晰
}
//获取当前对象
public Cell get(int row,int col) {
return field[row][col];
}
/**
*Field的getNeighbour()函数用于获取周围有对象的空格
*他要遍历周围所有的位置
*并且定义一个容器来储存Cell型变量(实际上可能是Fox或Rabbit的对象
*返回list长度的Cell变量数组
*/
public Cell[] getNeighbour(int row,int col) {
ArrayList<Cell> list=new ArrayList<Cell>();
for(int i=-1;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=-1;j<2;j++)
{
int r = row+i;
int c = col+j;
if ( r >-1 && r<height && c>-1 && c<width && !(r== row && c == col) )
{
list.add(field[r][c]);
}
}
}
return list.toArray(new Cell[list.size()]);
}
/**
*Field的getFreeNeighbour()函数用于获取周围没有管理对象的位置
*它会遍历周围所有的位置
*如果周围的位置是空的
*它就会用ArrayList把这些位置存到容器里面
*最后返回该数组长度的数组
*/
public Location[] getFreeNeighbour(int row,int col) {
ArrayList<Location> list=new ArrayList<Location>();
for(int i=-1;i<2;i++) {
for(int j=-1;j<2;j++)
{
int r=row+i;
int c=col+j;
//这里为什么不用排除掉自己呢,因为自己一定是有对象的
if(r>-1&&r<height&&c>-1&&c<width&&field[r][c]==null)
{
list.add(new Location(r,c));
}
}
}
return list.toArray( new Location[list.size()]);
}
/**
* 由于Animal的移动以后,当前loc的位置已经发生了变化
* 由发生变化的位置接管原来位置上面的对象
* 把原来位置上的对象清除
*/
public void move(int row, int col, Location loc) {
field[loc.getCol()][loc.getRow()]=field[row][col];
remove(row,col);
}
//删除对象,这个函数在FoxAndRabbit类里面被调用
public void remove(Cell cell) {
for(int row=0;row<height;row++)
{
for(int col=0;col<width;col++)
{
if(field[row][col]==cell) { field[row][col]=null; break; }
}
}
}
//删除对象,这个函数在类里面调用
public Cell remove(int row, int col) {
Cell ret=field[row][col];
field[row][col]=null;
return ret;
}
/**
*这个函数的作用把产生的小baby放入到随机一个格子里面去
*首先定义Location数组,接收周围没有对象的空格
*如果有空格,获取一个0到该数组长度之间的一个随机整数
*用该空格去管理传进来的baby(已经造型为Cell
*返回true
*这里的返回值我并不清楚它的作用
*/
public boolean placeRandomAdj(int row, int col, Cell baby) {
boolean ret=false;
Location[] FreeAdj=getFreeNeighbour(row, col);
if(FreeAdj.length>0)
{
int index=(int)(Math.random()*FreeAdj.length);
field[FreeAdj[index].getRow()][FreeAdj[index].getCol()]=baby;
ret=true;
}
return ret;
}
//清除所有对象
public void clear(){
for(int i=0;i<height;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<width;j++)
{
field[i][j]=null;
}
}
}
}
Location类
package field;
public class Location {
private int x;
private int y;
public Location(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getRow() {
return x;
}
public int getCol() {
return y;
}
}
Cell接口;
package cell;
import java.awt.Graphics;
public interface Cell {
void draw(Graphics g,int x,int y, int size);
}
Animal类
package animal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import field.Location;
public abstract class Animal {
//成员变量
private int ageLimit;
private int breedableAge;
private int age;
private boolean isAlive=true;
//构造函数,传入生命上限和可繁殖年龄
public Animal(int ageLimit, int breedableAge) {
this.ageLimit = ageLimit;
this.breedableAge = breedableAge;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
protected double getAgePercent() {
return (double)age/ageLimit;
}
// public abstract Animal breed();
/**
* 在之前的讨论中,我们用新的breed()函数,代替了原来的函数
* 这个函数做的事情是是到达了生育年龄
* 并且符合一定的几率
* 产生一个新的对象(Fox或者Rabbit
*/
public Animal breed()
{
Animal ret=null;
if(isBreedable()&&Math.random()<getValue())
{
ret=getAnimal();
}
return ret;
}
public abstract Animal getAnimal();
public abstract double getValue();
//生长函数
public void grow() {
age++;
if(age>=ageLimit)
{
die();
}
}
protected void die() {
isAlive=false;
}
public boolean isAlive() {
return isAlive;
}
protected boolean isBreedable()
{
return age>=breedableAge;
}
/**
* Animal的move()函数
* 传入Location的数组作为参数
* 如果传入的参数不为空,几率符合
* 由ret接管数组里面的一个随机位置对象
* 最后返回这个位置
*/
public Location move(Location[] freeAdj) {
Location ret=null;
if(freeAdj.length>0&&Math.random()<0.02) {
ret=freeAdj[(int)(Math.random()*freeAdj.length)];
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ""+age+":"+(isAlive?"live":"dead");
}
//让子类覆盖,实际这个函数并没有被调用
public Animal feed(ArrayList<Animal> neighbour) {
return null;
}
//吃掉兔子之后增加生命上限
protected void longerLife(int inc) {
ageLimit+=inc;
}
}
Fox类
package animal;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import cell.Cell;
public class Fox extends Animal implements Cell{
public Fox()
{
super(20,4);//生命上限20岁,生育年龄4岁
}
@Override
public void draw(Graphics g, int x, int y, int size) {
int alpha=(int)((1-getAgePercent())*255);
g.setColor(new Color(0,0,0,alpha));//用数字代表颜色,最后一个值是颜色深度,逐渐递减
g.fillRect(x, y, size, size);
}
//已经改写过的函数,增加可扩展性
@Override
public Animal breed() {
return super.breed();
}
@Override
public Animal getAnimal() {
return new Fox();
}
@Override
public double getValue() {
return 0.05;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Fox:"+super.toString();
}
/**
* Fox的feed()函数,他的参数是Animal的容器(周围的兔子
* 定义Animal类型的变量ret
* 在一定的几率下接收任意一个兔子
* 提高两个生命上限
* 返回这只兔子
*/
@Override
public Animal feed(ArrayList<Animal> neighbour) {
Animal ret=null;
if(Math.random()<0.2) {
ret=neighbour.get((int)(Math.random()*neighbour.size()));
longerLife(2);
}
return ret;
}
}
Rabbit类:
package animal;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import cell.Cell;
public class Rabbit extends Animal implements Cell {
public Rabbit() {
super(10,2);
}
@Override
public void draw(Graphics g, int x, int y, int size) {
int alpha=(int)((1-getAgePercent())*255);
g.setColor(new Color(255,0,0,alpha));
g.fillRect(x, y, size, size);
}
@Override
public Animal breed() {
return super.breed();
}
@Override
public Animal getAnimal() {
return new Rabbit();
}
@Override
public double getValue() {
return 0.12;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Rabbit"+super.toString();
}
}