详解.NET中的动态编译技术
代码的动态编译并执行是一个.NET平台提供给我们的很强大的工具用以灵活扩展(当然是面对内部开发人员)复杂而无法估算的逻辑,并通过一些额外的代码来扩展我们已有 的应用程序。这在很大程度上给我们提供了另外一种扩展的方式(当然这并不能算是严格意义上的扩展,但至少为我们提供了一种思路)。
动态代码执行可以应用在诸如模板生成,外加逻辑扩展等一些场合。一个简单的例子,为了网站那的响应速度,HTML静态页面往往是我们最好的选择,但基于数据驱动的网站往往又很难用静态页面实现,那么将动态页面生成html的工作或许就是一个很好的应用场合。另外,对于一些模板的套用,我们同样可以用它来做。另外这本身也是插件编写的方式。
最基本的动态编译
.Net为我们提供了很强大的支持来实现这一切我们可以去做的基础,主要应用的两个命名空间是:System.CodeDom.Compiler和Microsoft.CSharp或Microsoft.VisualBasic。另外还需要用到反射来动态执行你的代码。动态编译并执行代码的原理其实在于将提供的源代码交予CSharpCodeProvider来执行编译(其实和CSC没什么两样),如果没有任何编译错误,生成的IL代码会被编译成DLL存放于于内存并加载在某个应用程序域(默认为当前)内并通过反射的方式来调用其某个方法或者触发某个事件等。之所以说它是插件编写的一种方式也正是因为与此,我们可以通过预先定义好的借口来组织和扩展我们的程序并将其交还给主程序去触发。一个基本的动态编译并执行代码的步骤包括:
· 将要被编译和执行的代码读入并以字符串方式保存
· 声明CSharpCodeProvider对象实例
· 调用CSharpCodeProvider实例的CompileAssemblyFromSource方法编译
· 用反射生成被生成对象的实例(Assembly.CreateInstance)
· 调用其方法
以下代码片段包含了完整的编译和执行过程:
//get the code to compile
string strSourceCode = this.txtSource.Text;
// 1.Create a new CSharpCodePrivoder instance
CSharpCodeProvider objCSharpCodePrivoder = new CSharpCodeProvider();
// 2.Sets the runtime compiling parameters by crating a new CompilerParameters instance
CompilerParameters objCompilerParameters = new CompilerParameters();
objCompilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.dll");
objCompilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Windows.Forms.dll");
objCompilerParameters.GenerateInMemory = true;
// 3.CompilerResults: Complile the code snippet by calling a method from the provider
CompilerResults cr = objCSharpCodePrivoder. CompileAssemblyFromSource(objCompilerParameters, strSourceCode);
if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)
{
string strErrorMsg = cr.Errors.Count.ToString() + " Errors:";
for (int x = 0; x < cr.Errors.Count; x++)
{
strErrorMsg = strErrorMsg + "\r\nLine: " +
cr.Errors[x].Line.ToString() + " - " +
cr.Errors[x].ErrorText;
}
this.txtResult.Text = strErrorMsg;
MessageBox.Show("There were build erros, please modify your code.", "Compiling Error");
return;
}
// 4. Invoke the method by using Reflection
Assembly objAssembly = cr.CompiledAssembly;
object objClass = objAssembly.CreateInstance("Dynamicly.HelloWorld");
if (objClass == null)
{
this.txtResult.Text = "Error: " + "Couldn't load class.";
return;
}
object[] objCodeParms = new object[1];
objCodeParms[0] = "Allan.";
string strResult = (string)objClass.GetType().InvokeMember(
"GetTime", BindingFlags.InvokeMethod, null, objClass, objCodeParms);
this.txtResult.Text = strResult; |
需要解释的是,这里我们在传递编译参数时设置了GenerateInMemory为true,这表明生成的DLL会被加载在内存中(随后被默认引用入当前应用程序域)。在调用GetTime方法时我们需要加入参数,传递object类型的数组并通过Reflection的InvokeMember来调用。在创建生成的Assembly中的对象实例时,需要注意用到的命名空间是你输入代码的真实命名空间。以下是我们输入的测试代码(为了方便,所有的代码都在外部输入,动态执行时不做调整):
using System;
namespace Dynamicly
{
public class HelloWorld
{
public string GetTime(string strName)
{
return "Welcome " + strName + ", Check in at " + System.DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
} |
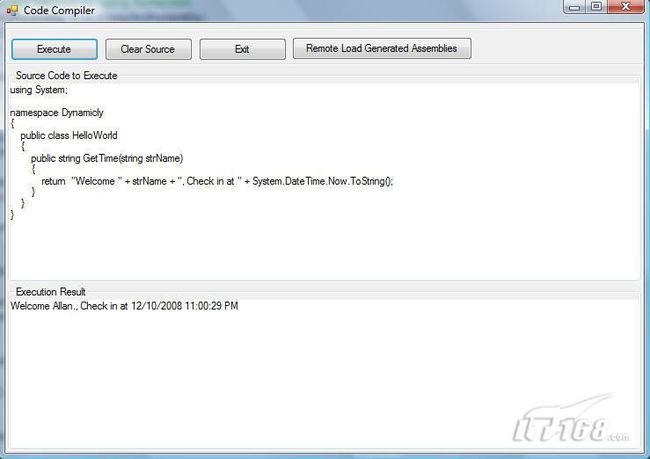
运行附件中提供的程序,可以很容易得到一下结果:
改进的执行过程
现在一切看起来很好,我们可以编译代码并把代码加载到当前应用程序域中来参与我们的活动,但你是否想过去卸载掉这段程序呢?更好的去控制程序呢?另外,当你运行这个程序很多遍的时候,你会发现占用内存很大,而且每次执行都会增大内存使用。是否需要来解决这个问题呢?当然需要,否则你会发现这个东西根本没用,我需要执行的一些大的应用会让我的服务器crzay,不堪重负而疯掉的。
要解决这个问题我们需要来了解一下应用程序域。.NET Application Domain是.NET提供的运行和承载一个活动的进程(Process)的容器,它将这个进程运行所需的代码和数据,隔离到一个小的范围内,称为Application Domain。当一个应用程序运行时,Application Domains将所有的程序集/组件集加载到当前的应用程序域中,并根据需要来调用。而对于动态生成的代码/程序集,我们看起来好像并没有办法去管理它。其实不然,我们可以用Application Domain提供的管理程序集的办法来动态加载和移除Assemblies来达到我们的提高性能的目的。具体怎么做呢,在前边的基础上增加以下步骤:
· 创建另外一个Application Domain
· 动态创建(编译)代码并保存到磁盘
· 创建一个公共的远程调用接口
· 创建远程调用接口的实例。并通过这个接口来访问其方法。
换句话来讲就是将对象加载到另外一个AppDomain中并通过远程调用的方法来调用。所谓远程调用其实也就是跨应用程序域调用,所以这个对象(动态代码)必须继承于MarshalByRefObject类。为了复用,这个接口被单独提到一个工程中,并提供一个工厂来简化每次的调用操作:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Reflection;
namespace RemoteAccess
{
/// Instance | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.CreateInstance;
public RemoteLoaderFactory() {}
public IRemoteInterface Create( string assemblyFile, string typeName, object[] constructArgs )
{
return (IRemoteInterface) Activator.CreateInstanceFrom(
assemblyFile, typeName, false, bfi, null, constructArgs,
null, null, null ).Unwrap();
}
}
}
|
接下来在原来基础上需要修改的是:
· 将编译成的DLL保存到磁盘中。
· 创建另外的AppDomain。
· 获得IRemoteInterface接口的引用。(将生成的DLL加载到额外的AppDomain)
· 调用InvokeMethod方法来远程调用。
· 可以通过AppDomain.Unload()方法卸载程序集。
以下是完整的代码,演示了如何应用这一方案。
//get the code to compile
string strSourceCode = this.txtSource.Text;
//1. Create an addtional AppDomain
AppDomainSetup objSetup = new AppDomainSetup();
objSetup.ApplicationBase = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
AppDomain objAppDomain = AppDomain.CreateDomain("MyAppDomain", null, objSetup);
// 1.Create a new CSharpCodePrivoder instance
CSharpCodeProvider objCSharpCodePrivoder = new CSharpCodeProvider();
// 2.Sets the runtime compiling parameters by crating a new CompilerParameters instance
CompilerParameters objCompilerParameters = new CompilerParameters();
objCompilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.dll");
objCompilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Windows.Forms.dll");
// Load the remote loader interface
objCompilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("RemoteAccess.dll");
// Load the resulting assembly into memory
objCompilerParameters.GenerateInMemory = false;
objCompilerParameters.OutputAssembly = "DynamicalCode.dll";
// 3.CompilerResults: Complile the code snippet by calling a method from the provider
CompilerResults cr = objCSharpCodePrivoder. CompileAssemblyFromSource(objCompilerParameters, strSourceCode);
if (cr.Errors.HasErrors)
{
string strErrorMsg = cr.Errors.Count.ToString() + " Errors:";
for (int x = 0; x < cr.Errors.Count; x++)
{
strErrorMsg = strErrorMsg + ""r"nLine: " +
cr.Errors[x].Line.ToString() + " - " +
cr.Errors[x].ErrorText;
}
this.txtResult.Text = strErrorMsg;
MessageBox.Show("There were build erros, please modify your code.", "Compiling Error");
return;
}
// 4. Invoke the method by using Reflection
RemoteLoaderFactory factory = (RemoteLoaderFactory)objAppDomain. CreateInstance("RemoteAccess","RemoteAccess.RemoteLoaderFactory").Unwrap();
// with help of factory, create a real 'LiveClass' instance
object objObject = factory.Create("DynamicalCode.dll", "Dynamicly.HelloWorld", null);
if (objObject == null)
{
this.txtResult.Text = "Error: " + "Couldn't load class.";
return;
}
// *** Cast object to remote interface, avoid loading type info
IRemoteInterface objRemote = (IRemoteInterface)objObject;
object[] objCodeParms = new object[1];
objCodeParms[0] = "Allan.";
string strResult = (string)objRemote.Invoke("GetTime", objCodeParms);
this.txtResult.Text = strResult;
//Dispose the objects and unload the generated DLLs.
objRemote = null;
AppDomain.Unload(objAppDomain);
System.IO.File.Delete("DynamicalCode.dll"); |
对于客户端的输入程序,我们需要继承于MarshalByRefObject类和IRemoteInterface接口,并添加对RemoteAccess程序集的引用。以下为输入:
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using RemoteAccess;
namespace Dynamicly
{
public class HelloWorld : MarshalByRefObject,IRemoteInterface
{
public object Invoke(string strMethod,object[] Parameters)
{
return this.GetType().InvokeMember(strMethod, BindingFlags. InvokeMethod,null,this,Parameters);
}
public string GetTime(string strName)
{
return "Welcome " + strName + ", Check in at " + System.DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
|