【Python】让 plotly 可视化更上一层:cufflinks 包
文章目录
- 一、导读
- 二、安装
- 三、使用方法
- 四、数据说明
- 五、折线图
- 六、散点图
- 七、气泡图
- 八、柱状图
- 九、箱型图box
- 十、直方图
- 十一、小提琴图
- 十二、热力图heatmap
- 十三、3d图
- 十四、散点矩阵图
- 十五、子图
一、导读
今天给大家推荐一个高级的可视化神器:cufflinks
学习过可视化库matplotlib和seaborn的朋友都知道:seaborn是matplotlib的高级封装。在这里我也告诉大家:cufflinks就是plotly的高级封装。
plotly的绘图已经够简洁和优雅,没有想到cufflinks更甚之。在这里用一句话形容cufflinks:
cufflinks之于plotly,犹如seaborn之于matplotlib
那到底什么是cufflinks呢?
cufflinks是一个基于Python的数据可视化库,它建立在Plotly库之上,为用户提供了一种简单而强大的方式来创建交互式的、美观的图表和可视化。它的设计旨在使绘图过程变得简单且具有灵活性,无需编写复杂的代码。
使用cufflinks可以轻松地将Pandas DataFrame和Series对象转换为交互式图表。它提供了与Pandas紧密集成的API,使数据可视化的过程变得直观且易于操作。通过几行简单的代码,就可以创建各种类型的图表,包括线图、柱状图、散点图、面积图、箱线图、热图等。
cufflinks还具有许多便捷的功能和选项,可让用户自定义图表的外观和样式。此外可以设置标题、轴标签、颜色、图例等,并通过拖动和缩放等交互式功能与图表进行互动。
此外,cufflinks还提供了简便的导出功能,可以将生成的图表保存为静态图像或动态HTML文件,以便与他人共享或嵌入到网页中。
二、安装
安装非常简单:
pip install cufflinks
建议用清华源加速:
pip install cufflinks -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
三、使用方法
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import cufflinks as cf
# 设置配置文件
# theme的7个选择项: 'ggplot', 'pearl', 'solar', 'space', 'white', 'polar', 'henanigans'
cf.set_config_file(world_readable=True, theme="pearl", offline=True)
%reload_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
查看cufflinks的帮助文档,目前cufflinks绘制的图形:
cf.help()
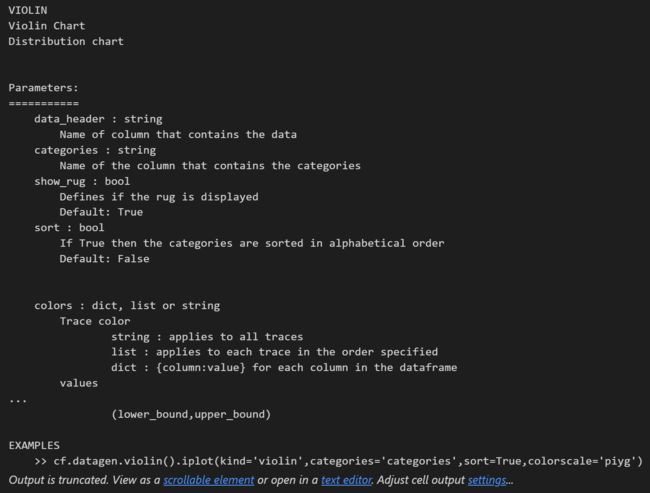
cf.help("violin")
DataFrame.Figure.iplot()
- DataFrame:pandas中的数据框
- Figure:指定图形,比如box、bar等
- iplot():参数设置
参数说明:
df.iplot(
kind='scatter',data=None,layout=None,filename='',sharing=None,
title='',xTitle='',yTitle='',zTitle='',theme=None,
colors=None,colorscale=None,fill=False,width=None,dash='solid',
mode='',interpolation='linear',symbol='circle',size=12,barmode='',
sortbars=False,bargap=None,bargroupgap=None,bins=None,histnorm='',
histfunc='count',orientation='v',boxpoints=False,annotations=None,keys=False,
bestfit=False,bestfit_colors=None,mean=False,mean_colors=None,categories='',
x='',y='',z='',text='',gridcolor=None,zerolinecolor=None,
margin=None,labels=None,values=None,secondary_y='',secondary_y_title='',
subplots=False,shape=None,error_x=None,error_y=None,error_type='data',
locations=None,lon=None,lat=None,asFrame=False,asDates=False,
asFigure=False,asImage=False,dimensions=None,asPlot=False,asUrl=False,online=None,**kwargs,
)
cufflinks的7大绘图主题风格:
cf.getThemes()
cf.colors.scales()
四、数据说明
我们使用sklearn自带的iris数据集:
from sklearn import datasets
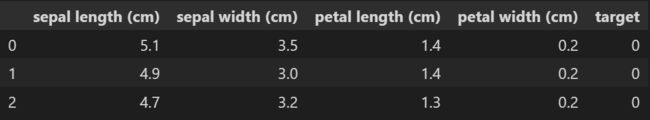
iris = datasets.load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data,columns=iris.feature_names)
df.head(3)
df["target"] = iris.target
df.head(3)
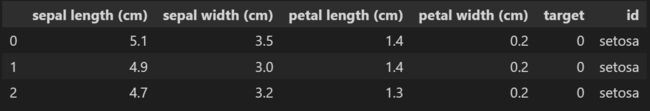
0:'setosa', 1:'versicolor', 2:'virginica'
df["id"] = df["target"].map({0:'setosa', 1:'versicolor', 2:'virginica'})
df.head(3)
五、折线图
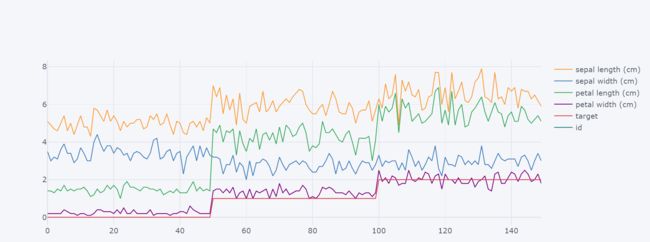
默认是折线图:
df.iplot()
# df.iplot(kind="scatter") # 等价
df.iplot(kind="scatter",fill=True)
六、散点图
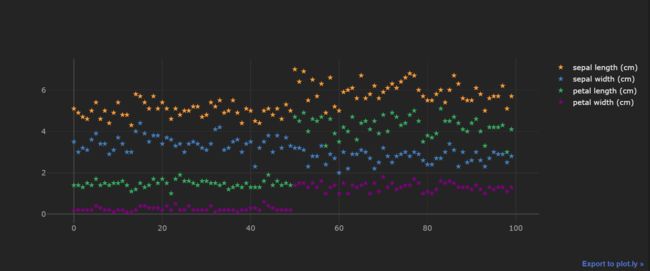
df.iloc[:100,:4].iplot(kind="scatter",
mode="markers", # 指定类型
# colors=["red","orange","blue","black"], # 颜色
size=7, # 大小
theme="henanigans", # 指定主题
symbol="star" # 散点形状;默认是圆点
)
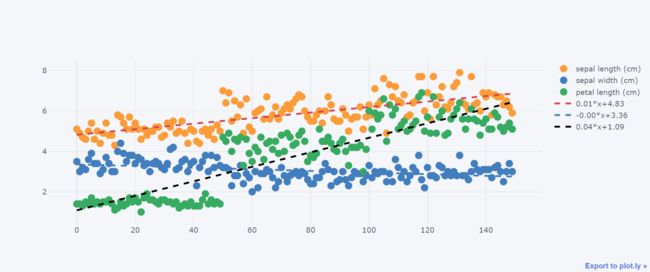
df.iloc[:,:3].iplot(kind="scatter",
mode="markers",
bestfit=True, # 拟合趋势
bestfit_colors=["red","blue","black"] # 拟合线颜色
)
七、气泡图
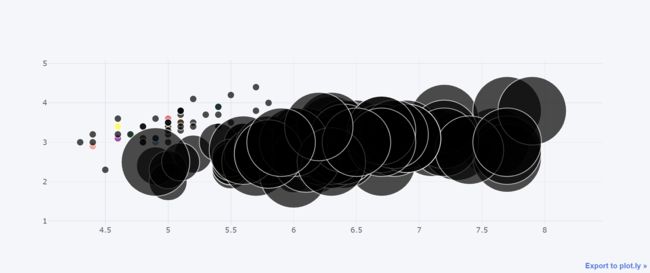
df.iplot(kind="bubble",x="sepal length (cm)",y="sepal width (cm)",size="target")
八、柱状图
df.head(20).iplot(kind="bar")
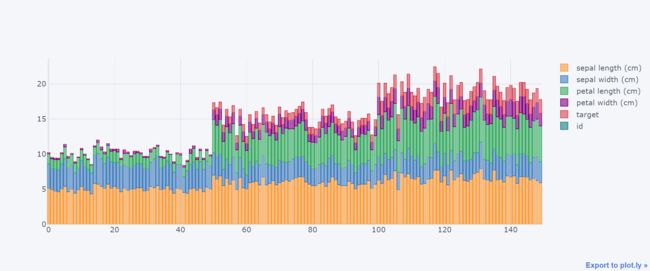
df.iplot(kind="bar", barmode="stack")
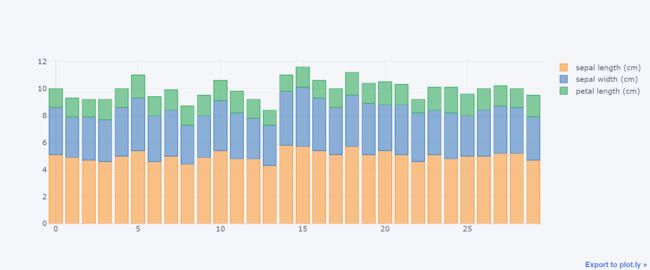
df.iloc[:30,:3].iplot(kind="bar", barmode="stack")
df.iloc[:20,:2].iplot(kind="barh", barmode="stack")

也可以通过参数orientation进行设置:v-垂直方向,h-水平方向
df.iloc[:20,:2].iplot(kind="bar",
barmode="stack",
orientation="h",
theme="space", # 指定主题
)
九、箱型图box
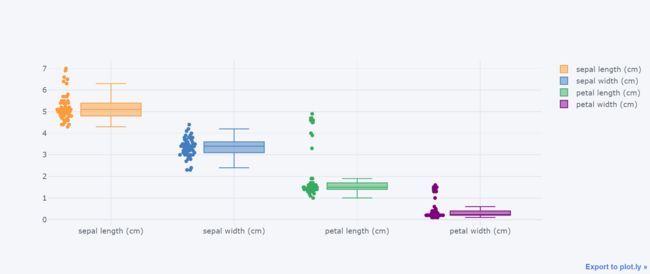
df.iloc[:60,:4].iplot(kind="box")
df.iloc[:60,:4].iplot(kind="box",boxpoints="all")
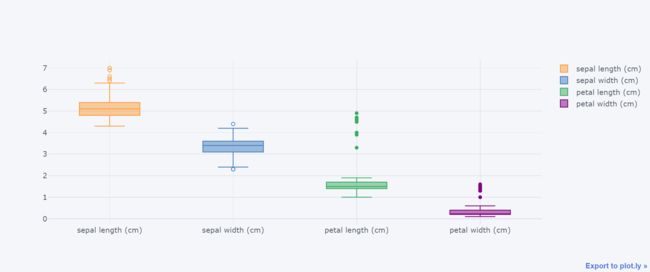
df.iloc[:60,:4].iplot(kind="box",boxpoints="outliers")
df.iloc[:60,:4].iplot(kind="box",boxpoints="suspectedoutliers")
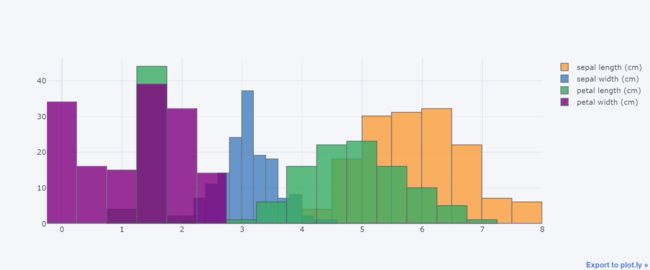
十、直方图
df.iloc[:,:4].iplot(kind="histogram")
十一、小提琴图
df.columns
Index(['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)',
'petal width (cm)', 'target', 'id'],
dtype='object')
df.iloc[:,:].iplot(kind="violin",data_header='sepal length (cm)')
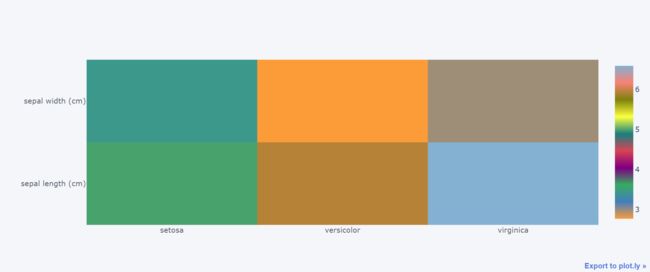
十二、热力图heatmap
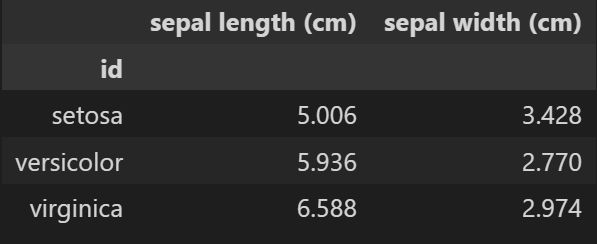
我们需要先生成透视表的数据:
data = pd.pivot_table(df,index="id",values=["sepal length (cm)","sepal width (cm)"])
data
data.iplot(kind="heatmap")
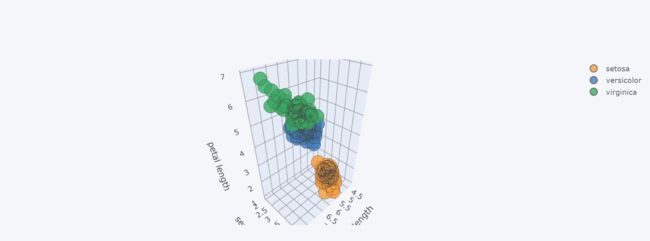
十三、3d图
df.iplot(kind="scatter3d",
x="sepal length (cm)", # 指定三个轴的数据
y="sepal width (cm)",
z="petal length (cm)",
categories="id",
xTitle="sepal length", # 指定3个轴的标题
yTitle="sepal width",
zTitle="petal length"
)
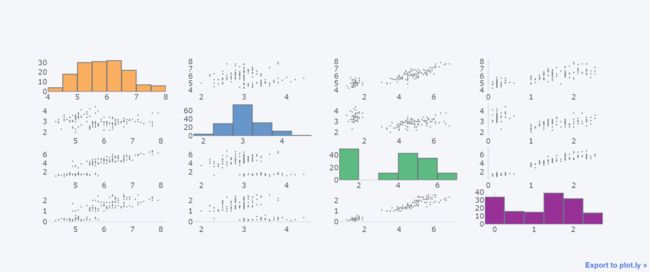
十四、散点矩阵图
df.iloc[:,:4].scatter_matrix()
十五、子图
df.iloc[:,:4].iplot(kind="bar",
barmode="stack", # 模式
title="绘制子图", # 标题
subplots=True, # 子图开始
shape=(2,2), # n行m列
shared_xaxes=True, # 是否共享x轴
vertical_spacing=0.08, # 垂直和水平间距
horizontal_spacing=0.05,
subplot_titles=True, # 开启子图名称
legend=False # 是否显示图例
)