数据库设计软件Power Designer详解教程(附源码)
版权声明
- 本文原创作者:谷哥的小弟
- 作者博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/lfdfhl
Power Designer概述
Power Designer 是美国Sybase公司的CASE工具集,利用Power Designer可分别从概念数据模型(Conceptual Data Model)和物理数据模型(Physical Data Model)两个层次对数据库进行设计。其中,概念数据模型描述的是独立于数据库管理系统(DBMS)的实体定义和实体关系定义;物理数据模型是在概念数据模型的基础上针对目标数据库管理系统的具体化。
Power Designer安装
请在Power Designer官方网站下载Power Designer并依据提示进行安装。在本教程中,我们将使用Power Designer 15展开数据库设计相关工作。
数据准备
在本节Power Designer使用教程中,我们准备三张表:学生表,教师表,班级表;各表字段信息如下:
学生表
| 字段名称 | 字段说明 |
|---|---|
| sid | 学生学号(主键) |
| sname | 学生姓名 |
| sage | 学生年龄 |
| sgender | 学生性别 |
| sclassid | 所属班级 |
教师表
| 字段名称 | 字段说明 |
|---|---|
| tid | 教师编号(主键) |
| tname | 教师姓名 |
| tage | 教师年龄 |
| tgender | 教师性别 |
班级表
| 字段名称 | 字段说明 |
|---|---|
| cid | 班级编号(主键) |
| cname | 班级名称 |
利用Power Designer设计概念数据模型
在此,详细介绍利用Power Designer设计概念数据模型。
第一步:创建概念模型
在Power Designer中依次点击File —> New Model —> Conceptual Data Model并设置Model name
![]()
第二步:打开Palette面板
依次点击Tools —> Customize Toolbars… —> Palette 打开Palette面板
![]()
第三步:创建标题
利用Palette面板中的Text工具创建文本,其内容为"学生教师班级数据模型"
第四步:创建实体Entity
利用Palette面板中的Entity工具创建3个实体
第五步:设置实体Entity
在此,以班级Entity为例详细介绍其设置过程。
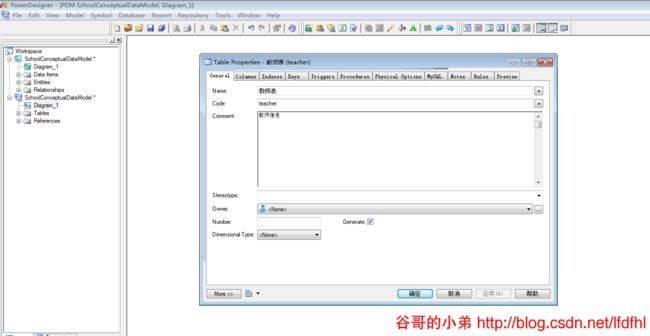
班级Entity
双击Entity为其设置基本信息。在该设置中Name用于描述表的,Code表示该实体在数据库中表的名字,Comment用于填写备注信息。
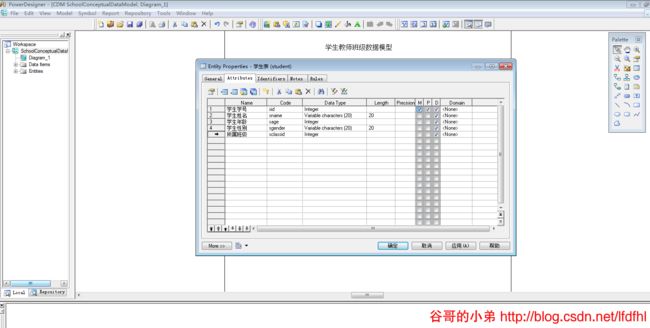
接下来,设置实体Entity的属性。在该设置中Name用于说明各字段含义;Code表示该字段在数据库表中的列名;Data Type表示数据类型;Length表示数据长度;Precision表示数据精度;M表示该属性是否为强制(Mandatory)的,即是否允许该列的值为空,选中表示不允许为空;P表示该属性是否为主标识符(Primary Identifier);D表示该属性是否在图形窗口中显示(Displayed)。
学生Entity
类似地,我们来完成学生Entity
教师Entity
类似地,我们来完成教师Entity
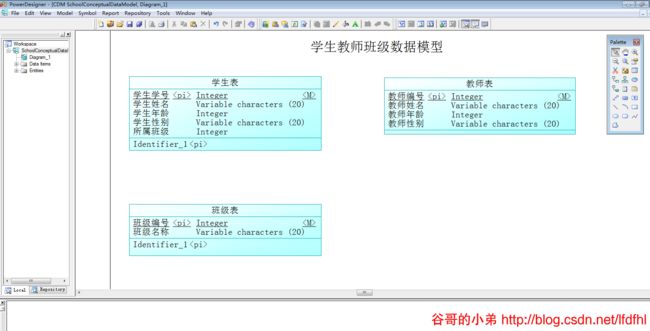
Entity总览
依次完成3个Entity后,图示如下:
第六步:设置实体Entity之间的关系
在此,以班级和学生之间一对多的关系为例进行介绍。
(1)、通过Palette面板中的Relationship工具为班级实体和学生实体添加联系
(2)、双击关系图标,在弹出的Relationship Properties对话框中设置实体之间的基本信息
(3)、在Relationship Properties对话框中点击Cardinalities设置实体之间的关系
设置实体间的各种关系,它们分别为:
- One-One选项,设置实体间的关系为一对一。
- One-Many选项,设置实体间的关系为一对多。
- Many-One选项,设置实体间的关系为多对一。
- Many-Many选项,设置实体间的关系为多对多。
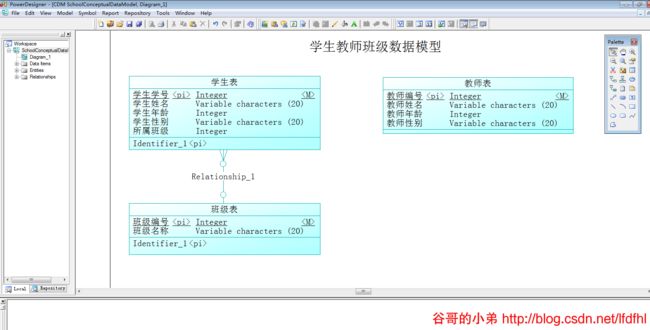
班级与学生的关系是一对多,所以在此选择One-Many选项
类似地,我们设置教师实体与学生实体之间的关系,图示如下:
教师与学生之间是多对多的关系,所以选择Many-Many选项。
利用Power Designer设计物理数据模型
当设计完概念数据模型后,利用Power Designer可非常容易地将概念数据模型(CDM)转换成物理数据模型(PDM)。
请在Power Designer中依次点击Tools —> Generate Physical Data Model。将DBMS设置为MySQL 5.0并将Name和Code修改为SchoolPhysicalDataModel再单击确定生产成了与MySQL匹配的物理数据模型。
观察该物理模型可看到,在从概念模型转到物理模型时自动将教师与学生的多对多关系拆解成了一对多。
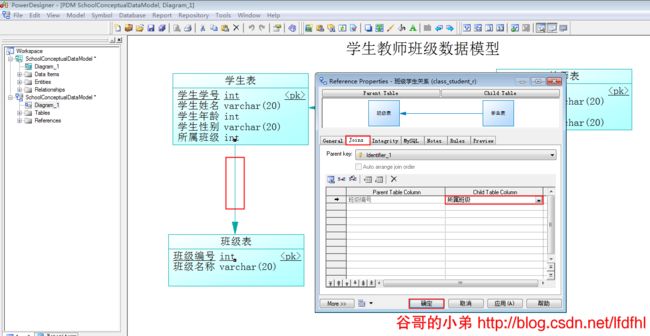
但是,我们发现:在学生表中自动生成了一个字段班级编号;并且,该字段作为了外键。这一点和我们的初衷有所差异;我们原本的想法是:将学生表里的字段所属班级作为外键。既然和原本的想法不同而且生成了多余的字段,那么我们可以对其进行修改。
1、双击学生表,删除生成的字段班级编号。
2、双击学生表与班级表之间的连线重新设置外键。
利用Power Designer创建数据库脚本
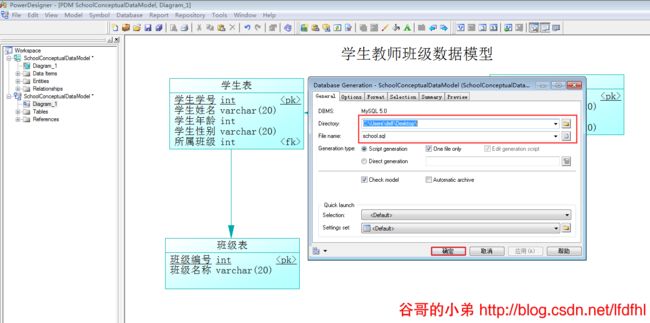
请在Power Designer中打开PDM,然后依次点击Database —> Generate Database。使用Directory和File name指定数据库脚本的存放路径及其保存后的文件名再单击确定。
最后,我们来查看由PDM生成的数据库脚本,代码如下:
/*==============================================================*/
/* DBMS name: MySQL 5.0 */
/* Created on: 2020/11/20 0:20:11 */
/*==============================================================*/
drop table if exists class;
drop table if exists student;
drop table if exists teacher;
drop table if exists teacher_student_r;
/*==============================================================*/
/* Table: class */
/*==============================================================*/
create table class
(
cid int not null,
cname varchar(20),
primary key (cid)
);
alter table class comment '班级信息';
/*==============================================================*/
/* Table: student */
/*==============================================================*/
create table student
(
sid int not null,
sname varchar(20),
sage int,
sgender varchar(20),
sclassid int,
primary key (sid)
);
alter table student comment '学生信息';
/*==============================================================*/
/* Table: teacher */
/*==============================================================*/
create table teacher
(
tid int not null,
tname varchar(20),
tage int,
tgender varchar(20),
primary key (tid)
);
alter table teacher comment '教师信息';
/*==============================================================*/
/* Table: teacher_student_r */
/*==============================================================*/
create table teacher_student_r
(
sid int not null,
tid int not null,
primary key (sid, tid)
);
alter table student add constraint FK_class_student_r foreign key (sclassid)
references class (cid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table teacher_student_r add constraint FK_teacher_student_r foreign key (sid)
references student (sid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table teacher_student_r add constraint FK_teacher_student_r foreign key (tid)
references teacher (tid) on delete restrict on update restrict;