设备虚拟化基础 - PCI
目录
1. 配置空间概念和作用
2. 通过配置空间发现设备
3. Linux读取PCI配置空间接口
4. 内核中具体读取配置空间实例
5. Virtion设备自定义空间
6. Linux读取Capabilities List代码解析
1. 配置空间概念和作用
详细的定义可以参考PCI Spec的第六章《Configuration Space》中的描述,这里仅摘抄关键点
- 所有的PCI设备必须实现配置空间,配置空间的本质是一堆寄存器。
- 配置空间可以用来发现设备
- pci local bus spec规定的配置空间最大256字节,前64字节是spec中定义好的,称预定义空间,其中前16字节对所有类型的pci设备都相同(是指格式,而不其中具体的值),之后的空间格式因类型而不同,对前16字节空间,我称它为通用配置空间。
上面是摘自PCI3.0规范的配置空间,一共64字节,即预定义空间,其中前16字节对应通用配置空间。
预定义空间解析
vendor id:厂商ID,用来标识pci设备出自哪个厂商,这里是0x1af4,来自Red Hat。
device id:厂商下的产品ID,传统virtio-blk设备,这里是0x1001
revision id:厂商决定是否使用,设备版本ID,这里未使用
header type:pci设备类型,0x00(普通设备),0x01(pci bridge),0x02(CardBus bridge)。virtio是普通设备,这里是0x00
status: 描述pci设备状态的寄存器
其中有一位是Capabilities List,它是pci规范定义的附加空间标志位,Capabilities List的意义是允许在pci设备配置空间之后加上额外的寄存器,这些寄存器由Capability List组织起来,用来实现特定的功能,附加空间在64字节配置空间之后,最大不能超过256字节。以virtio-blk为例,它标记了这个位,因此在virtio-blk设备配置空间之后,还有一段空间用来实现virtio-blk的一些特有功能。1表示capabilities pointer字段(0x34)存放了附加寄存器组的起始地址。这里的地址表示附加空间在pci设备空间内的偏移。具体Capability List怎么理解本文后面分析。
2. 通过配置空间发现设备
发下设备需要确定两个事情:PCI设备地址,以及确定地址之后具体怎么通过该地址访问。
PCI设备地址 : 参考PCI规范3.2.2.3.2章节
设备地址可以通过Bus号,Device号,功能号和寄存器号唯一确定:
Linux内核中确定该地址可以通过宏:
/*
* Functions for accessing PCI base (first 256 bytes) and extended
* (4096 bytes per PCI function) configuration space with type 1
* accesses.
*/
#define PCI_CONF1_ADDRESS(bus, devfn, reg) \
(0x80000000 | ((reg & 0xF00) << 16) | (bus << 16) \
| (devfn << 8) | (reg & 0xFC))访问配置空间
- 配置空间寄存器偏移
PCI_CONF1_ADDRES宏确定了配置空间的基地址(Base Address),还要结合配置空间偏移具体访问具体的功能,比如访问配置空间的Command对应的offset:04h,Capabilities pointer偏移:0x34h。
- 端口访问
配置空间地址无法直接访问,需要通过特定的端口来访问:
CONFIG_ADDRESS(CF8h) : 将需要访问的配置空间地址设置到该端口
CONFIG_DATA(CFCh):从该端口读取配置空间的值。
3. Linux读取PCI配置空间接口
//参数dev : pci 设备
//where : 配置空间寄存器对应的偏移offset
int pci_read_config_byte(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u8 *val);
int pci_read_config_word(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u16 *val);
int pci_read_config_dword(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u32 *val);
int pci_write_config_byte(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u8 val);
int pci_write_config_word(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u16 val);
int pci_write_config_dword(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u32 val);上面API实现路径:drivers/pci/access.c
int pci_read_config_byte(const struct pci_dev *dev, int where, u8 *val)
{
if (pci_dev_is_disconnected(dev)) {
*val = ~0;
return PCIBIOS_DEVICE_NOT_FOUND;
}
return pci_bus_read_config_byte(dev->bus, dev->devfn, where, val);
}上面已pci_read_config_byte为例:我们知道要读取配置空间必须通过CONFIG_ADDRESS,地址需要bus number, device number, function number和offset,这些值通过dev和where获取,可以想象pci_bus_read_config_byte最终应该也是要调用out汇编指令访问CONFIG_DDRESS端口,层层跟进最终调用到如下函数:
arch/x86/pci/direct.c
#define PCI_CONF1_ADDRESS(bus, devfn, reg) \
(0x80000000 | ((reg & 0xF00) << 16) | (bus << 16) \
| (devfn << 8) | (reg & 0xFC))
static int pci_conf1_read(unsigned int seg, unsigned int bus,
unsigned int devfn, int reg, int len, u32 *value)
{
unsigned long flags;
if (seg || (bus > 255) || (devfn > 255) || (reg > 4095)) {
*value = -1;
return -EINVAL;
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&pci_config_lock, flags);
outl(PCI_CONF1_ADDRESS(bus, devfn, reg), 0xCF8);
switch (len) {
case 1:
*value = inb(0xCFC + (reg & 3));
break;
case 2:
*value = inw(0xCFC + (reg & 2));
break;
case 4:
*value = inl(0xCFC);
break;
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&pci_config_lock, flags);
return 0;
}4. Linux内核中具体读取配置空间实例
static void __iomem *map_capability(struct pci_dev *dev, int off,
size_t minlen,
u32 align,
u32 start, u32 size,
size_t *len)
{
u8 bar;
u32 offset, length;
void __iomem *p;
pci_read_config_byte(dev, off + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_cap,
bar),
&bar);
pci_read_config_dword(dev, off + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_cap, offset),
&offset);
pci_read_config_dword(dev, off + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_cap, length),
&length);
...
}这里off对应每个capbility的offset(具体怎么理解参见本文下面capbility相关章节),每个capbility用struct virtio_pci_cap结构体描述:
/* This is the PCI capability header: */
struct virtio_pci_cap {
__u8 cap_vndr; /* Generic PCI field: PCI_CAP_ID_VNDR */
__u8 cap_next; /* Generic PCI field: next ptr. */
__u8 cap_len; /* Generic PCI field: capability length */
__u8 cfg_type; /* Identifies the structure. */
__u8 bar; /* Where to find it. */
__u8 padding[3]; /* Pad to full dword. */
__le32 offset; /* Offset within bar. */
__le32 length; /* Length of the structure, in bytes. */
};5. Virtion设备自定义空间
每个PCI具有不同的功能和配置,所以除了64字节的预定义空间之外,每个PCI设备可以自定义配置空间,配置设备的能力,pci spec规范中有个很重要的Capabilities List概念,即设备的能力列表。有几个重要的问题:
5.1. 能力列表的位置(地址)
还记着预定义配置空间中有个Capability list么,这里面存储的就是能力列表的位置(offset)。
5.2 . 能力列表项格式
/* This is the PCI capability header: */
struct virtio_pci_cap {
__u8 cap_vndr; /* Generic PCI field: PCI_CAP_ID_VNDR */
__u8 cap_next; /* Generic PCI field: next ptr. */
__u8 cap_len; /* Generic PCI field: capability length */
__u8 cfg_type; /* Identifies the structure. */
__u8 bar; /* Where to find it. */
__u8 padding[3]; /* Pad to full dword. */
__le32 offset; /* Offset within bar. */
__le32 length; /* Length of the structure, in bytes. */
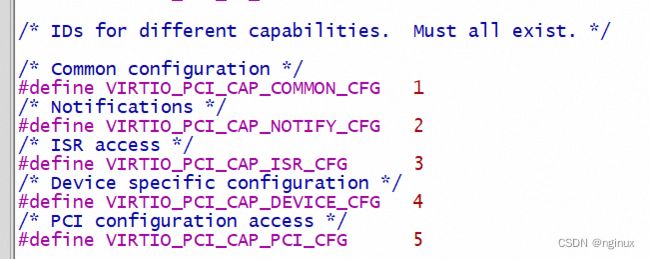
};vndr :capability类型,取值可参考pci spec H附录:
next:表示下一个capability在pci配置空间的位置
len:capability这个数据结构的长度
type : 取值范围如下
Capabilities List图示:
![]()
(引用自参考文章)
6. Linux读取Capabilities List代码解析
drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c:
/* the PCI probing function */
int virtio_pci_modern_probe(struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev)
{
struct pci_dev *pci_dev = vp_dev->pci_dev;
int err, common, isr, notify, device;
u32 notify_length;
u32 notify_offset;
check_offsets();
/* We only own devices >= 0x1000 and <= 0x107f: leave the rest. */
if (pci_dev->device < 0x1000 || pci_dev->device > 0x107f)
return -ENODEV;
if (pci_dev->device < 0x1040) {
/* Transitional devices: use the PCI subsystem device id as
* virtio device id, same as legacy driver always did.
*/
vp_dev->vdev.id.device = pci_dev->subsystem_device;
} else {
/* Modern devices: simply use PCI device id, but start from 0x1040. */
vp_dev->vdev.id.device = pci_dev->device - 0x1040;
}
vp_dev->vdev.id.vendor = pci_dev->subsystem_vendor;
/* check for a common config: if not, use legacy mode (bar 0). */
//遍历配置空间的Capabilities List列表,查找是否存在VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_COMMON_CFG这种
//Type类型的能力。
common = virtio_pci_find_capability(pci_dev, VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_COMMON_CFG,
IORESOURCE_IO | IORESOURCE_MEM,
&vp_dev->modern_bars);
if (!common) {
dev_info(&pci_dev->dev,
"virtio_pci: leaving for legacy driver\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
/* If common is there, these should be too... */
isr = virtio_pci_find_capability(pci_dev, VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_ISR_CFG,
IORESOURCE_IO | IORESOURCE_MEM,
&vp_dev->modern_bars);
notify = virtio_pci_find_capability(pci_dev, VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_NOTIFY_CFG,
IORESOURCE_IO | IORESOURCE_MEM,
&vp_dev->modern_bars);
if (!isr || !notify) {
dev_err(&pci_dev->dev,
"virtio_pci: missing capabilities %i/%i/%i\n",
common, isr, notify);
return -EINVAL;
}
err = dma_set_mask_and_coherent(&pci_dev->dev, DMA_BIT_MASK(64));
if (err)
err = dma_set_mask_and_coherent(&pci_dev->dev,
DMA_BIT_MASK(32));
if (err)
dev_warn(&pci_dev->dev, "Failed to enable 64-bit or 32-bit DMA. Trying to continue, but this might not work.\n");
/* Device capability is only mandatory for devices that have
* device-specific configuration.
*/
device = virtio_pci_find_capability(pci_dev, VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_DEVICE_CFG,
IORESOURCE_IO | IORESOURCE_MEM,
&vp_dev->modern_bars);
err = pci_request_selected_regions(pci_dev, vp_dev->modern_bars,
"virtio-pci-modern");
if (err)
return err;
err = -EINVAL;
vp_dev->common = map_capability(pci_dev, common,
sizeof(struct virtio_pci_common_cfg), 4,
0, sizeof(struct virtio_pci_common_cfg),
NULL);
if (!vp_dev->common)
goto err_map_common;
vp_dev->isr = map_capability(pci_dev, isr, sizeof(u8), 1,
0, 1,
NULL);
if (!vp_dev->isr)
goto err_map_isr;
/* Read notify_off_multiplier from config space. */
pci_read_config_dword(pci_dev,
notify + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_notify_cap,
notify_off_multiplier),
&vp_dev->notify_offset_multiplier);
/* Read notify length and offset from config space. */
pci_read_config_dword(pci_dev,
notify + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_notify_cap,
cap.length),
¬ify_length);
pci_read_config_dword(pci_dev,
notify + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_notify_cap,
cap.offset),
¬ify_offset);
/* We don't know how many VQs we'll map, ahead of the time.
* If notify length is small, map it all now.
* Otherwise, map each VQ individually later.
*/
if ((u64)notify_length + (notify_offset % PAGE_SIZE) <= PAGE_SIZE) {
vp_dev->notify_base = map_capability(pci_dev, notify, 2, 2,
0, notify_length,
&vp_dev->notify_len);
if (!vp_dev->notify_base)
goto err_map_notify;
} else {
vp_dev->notify_map_cap = notify;
}
/* Again, we don't know how much we should map, but PAGE_SIZE
* is more than enough for all existing devices.
*/
if (device) {
vp_dev->device = map_capability(pci_dev, device, 0, 4,
0, PAGE_SIZE,
&vp_dev->device_len);
if (!vp_dev->device)
goto err_map_device;
vp_dev->vdev.config = &virtio_pci_config_ops;
} else {
vp_dev->vdev.config = &virtio_pci_config_nodev_ops;
}
vp_dev->config_vector = vp_config_vector;
vp_dev->setup_vq = setup_vq;
vp_dev->del_vq = del_vq;
return 0;
...
return err;
}probe函数连续调用virtio_pci_find_capability通过遍历Capabilities List查找PCI设备是否存其第二个参数指定的能力,第二个参数对应virtio_pci_cap结构体中的cfg_type。
static inline int virtio_pci_find_capability(struct pci_dev *dev, u8 cfg_type,
u32 ioresource_types, int *bars)
{
int pos;
for (pos = pci_find_capability(dev, PCI_CAP_ID_VNDR);
pos > 0;
pos = pci_find_next_capability(dev, pos, PCI_CAP_ID_VNDR)) {
u8 type, bar;
pci_read_config_byte(dev, pos + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_cap,
cfg_type),
&type);
pci_read_config_byte(dev, pos + offsetof(struct virtio_pci_cap,
bar),
&bar);
/* Ignore structures with reserved BAR values */
if (bar > 0x5)
continue;
if (type == cfg_type) {
if (pci_resource_len(dev, bar) &&
pci_resource_flags(dev, bar) & ioresource_types) {
*bars |= (1 << bar);
return pos;
}
}
}
return 0;
}pci_find_capability :返回Capabilities List列表中的一个能力pos (配置空间的offset),其内部是通过配置空间的34h偏移处的Capabilities Pointer确定的。
/**
* pci_find_capability - query for devices' capabilities
* @dev: PCI device to query
* @cap: capability code
*
* Tell if a device supports a given PCI capability.
* Returns the address of the requested capability structure within the
* device's PCI configuration space or 0 in case the device does not
* support it. Possible values for @cap:
*
* %PCI_CAP_ID_PM Power Management
* %PCI_CAP_ID_AGP Accelerated Graphics Port
* %PCI_CAP_ID_VPD Vital Product Data
* %PCI_CAP_ID_SLOTID Slot Identification
* %PCI_CAP_ID_MSI Message Signalled Interrupts
* %PCI_CAP_ID_CHSWP CompactPCI HotSwap
* %PCI_CAP_ID_PCIX PCI-X
* %PCI_CAP_ID_EXP PCI Express
*/
int pci_find_capability(struct pci_dev *dev, int cap)
{
int pos;
//pos值是配置空间对应的Capabilities Pointer的offset,即0x34h
pos = __pci_bus_find_cap_start(dev->bus, dev->devfn, dev->hdr_type);
//如果开启了Capabilities List功能,__pci_find_nex_cap找到0x34H处对应的能力的pos
//如果是第一次查找,以5.2中图为例,__pci_find_next_cap返回的是第一个能力的pos 0x98
if (pos)
pos = __pci_find_next_cap(dev->bus, dev->devfn, pos, cap);
return pos;
}
static int __pci_bus_find_cap_start(struct pci_bus *bus,
unsigned int devfn, u8 hdr_type)
{
u16 status;
pci_bus_read_config_word(bus, devfn, PCI_STATUS, &status);
if (!(status & PCI_STATUS_CAP_LIST))
return 0;
switch (hdr_type) {
case PCI_HEADER_TYPE_NORMAL:
case PCI_HEADER_TYPE_BRIDGE:
return PCI_CAPABILITY_LIST; //宏的值为0x34h
case PCI_HEADER_TYPE_CARDBUS:
return PCI_CB_CAPABILITY_LIST;
}
return 0;
}
static int __pci_find_next_cap_ttl(struct pci_bus *bus, unsigned int devfn,
u8 pos, int cap, int *ttl)
{
u8 id;
u16 ent;
pci_bus_read_config_byte(bus, devfn, pos, &pos);
while ((*ttl)--) {
if (pos < 0x40)
break;
pos &= ~3;
pci_bus_read_config_word(bus, devfn, pos, &ent);
id = ent & 0xff;
if (id == 0xff)
break;
if (id == cap)
return pos;
pos = (ent >> 8);
}
return 0;
}参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/fouweng/article/details/62890979
VirtIO实现原理——PCI基础_virtio-pci_享乐主的博客-CSDN博客