Socket网络编程--Libev库学习(2)
这一小节讲各个观察器(Watcher)
在libev下面watcher相当于EventHandler这么一个概念,通常里面会绑定fd回调函数以及我们需要关注的事件。 然后一旦触发事件之后会触发我们使用的回调函数,回调函数参数通常有reactor,watcher以及触发的事件。这里不打算重复文档里面的watcher 相关的内容和对应的API,但是对于某些内容的话可能会提到并且附带一些注释。之前我们还是看看通用过程,这里使用TYPE区分不同类型watcher.
1 typedef void (*)(struct ev_loop *loop, ev_TYPE *watcher, int revents) callback; // callback都是这种类型 2 ev_init (ev_TYPE *watcher, callback); // 初始化watcher 3 ev_TYPE_set (ev_TYPE *watcher, [args]); // 设置watcher 4 ev_TYPE_init (ev_TYPE *watcher, callback, [args]); // 通常使用这个函数最方便,初始化和设置都在这里 5 ev_TYPE_start (loop, ev_TYPE *watcher); // 注册watcher 6 ev_TYPE_stop (loop, ev_TYPE *watcher); // 注销watcher 7 ev_set_priority (ev_TYPE *watcher, int priority); // 设置优先级 8 ev_feed_event (loop, ev_TYPE *watcher, int revents); // 这个做跨线程通知非常有用,相当于触发了某个事件。 9 bool ev_is_active (ev_TYPE *watcher); // watcher是否active. 10 bool ev_is_pending (ev_TYPE *watcher); // watcher是否pending. 11 int ev_clear_pending (loop, ev_TYPE *watcher); // 清除watcher pending状态并且返回事件
wacther的状态有下面这么几种:
(1) initialiased.调用init函数初始化
(2) active.调用start进行注册
(3) pending.已经触发事件但是没有处理
(4) inactive.调用stop注销。这个状态等同于initialised这个状态。
ev_io
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <ev.h> 5 6 7 static void stdin_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_io *w,int revents) 8 { 9 char str[1024]; 10 if(revents & EV_READ) 11 { 12 //stdin might have data for us 13 printf("有数据可读\n"); 14 scanf("%s",str); 15 ev_io_stop(loop,w); 16 } 17 else if(revents & EV_WRITE) 18 { 19 //stdout might have data for us 20 printf("有数据输出\n"); 21 //ev_break(loop,EVBREAK_ONE); 22 } 23 printf("water:%d\n",ev_is_active(w)); 24 } 25 26 int main(int argc,char **argv) 27 { 28 struct ev_loop * main_loop = ev_default_loop(0); 29 //这里的ev_default_loop可以使用ev_loop_new动态分配一个,然后使用ev_loop_destroy销毁。 30 //struct ev_loop * epoller = ev_loop_new(EVBACKEND_EPOLL | EVFLAG_NOENV); 31 //这里一般是使用EVBACKEND_EPOLL模型,同样的还有EVBACKEND_SELECT EVBACKEND_POLL EVBACKEND_KQUEUE EVBACKEND_DEVPOLL EVBACKEND_PORT 如果默认,那么ev会自动判断系统环境,选择最适合的模型,Linux一般为epoll bsd一般为kqueue什么的。 32 ev_io stdin_watcher; 33 ev_init(&stdin_watcher,stdin_callback); 34 ev_io_set(&stdin_watcher,STDIN_FILENO,EV_READ|EV_WRITE); 35 ev_io_start(main_loop,&stdin_watcher); 36 37 //ev_run(main_loop,EVRUN_ONCE); 38 39 //void ev_set_io_collect_interval (EV_P_ ev_tstamp interval);//这个是设置轮询的时间 40 //typedef double ev_tstamp 41 ev_set_io_collect_interval(main_loop,2.);//2秒 42 ev_run(main_loop,0); 43 //ev_is_active(ev_TYPE * watcher);//用于判断watcher是否为active 44 printf("main:%d\n",ev_is_active(&stdin_watcher)); 45 46 //initialiased.调用init函数初始化 47 //active.调用start进行注册 48 //pending.已经触发事件但是没有处理 49 //inactive.调用stop注销。这个状态等同于initialised这个状态 50 51 return 0; 52 }
ev_timer
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <ev.h> 5 6 static void three_second_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_timer *w,int revents) 7 { 8 //这是一个3秒触发的计时器 9 printf("3秒触发器\n"); 10 } 11 static void five_second_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_timer *w,int revents) 12 { 13 //这是一个5秒触发的计时器 14 printf("5秒触发器\n"); 15 } 16 static void the_second_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_timer *w,int revents) 17 { 18 //这是一个10秒触发的计时器 19 printf("10秒触发器\n"); 20 } 21 22 int main(int argc, char **args) 23 { 24 struct ev_loop * main_loop=ev_default_loop(0); 25 26 ev_timer mytimer_watcher3; 27 ev_timer mytimer_watcher5; 28 29 ev_init(&mytimer_watcher3,three_second_callback); 30 ev_timer_set(&mytimer_watcher3,3,0); 31 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher3); 32 ev_run(main_loop,0);//这个在ev_io上是一直判断的。但是这个触发器只会触发一次,不会每3秒触发一次。这是个问题。 33 34 ev_init(&mytimer_watcher5,five_second_callback); 35 ev_timer_set(&mytimer_watcher5,5,0); 36 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher5); 37 ev_run(main_loop,0); 38 39 40 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher3); 41 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher5); 42 ev_run(main_loop,0);//这里不会等待3,5秒,而是上一步后,直接输出,可见触发器只能用一次 43 44 ev_timer_set(&mytimer_watcher3,3,0); 45 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher3); 46 ev_timer_set(&mytimer_watcher5,5,0); 47 ev_timer_start(main_loop,&mytimer_watcher5); 48 ev_run(main_loop,0);//这里就会等待了,要重新set一遍 49 50 51 return 0; 52 }
运行的结果是在第3秒输出(3秒触发器),第8秒输出(5秒触发器)(3秒触发器)(5秒触发器),第11秒输出(3秒触发器),第13秒输出(5秒触发器)。
这个ev_timer居然不能重复,是不是没有解决办法呢?不是还有个ev_periodic这个可以实现周期性观察器。
ev_periodic
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <ev.h> 5 6 static void periodic_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_periodic * w, int revents) 7 { 8 printf("每3秒执行一次\n"); 9 //ev_break(loop,EVBREAK_ALL); 10 } 11 12 //ev_tstamp=double 13 static ev_tstamp periodic_scheduler_callback(ev_periodic *w,ev_tstamp now) 14 { 15 return now+3;//注意时间要加上个now,是一个绝对时间 16 } 17 18 int main(int argc, char **args) 19 { 20 struct ev_loop * main_loop=ev_default_loop(0); 21 22 ev_periodic periodic_watcher; 23 //下面这个是第3个参数为3 是一个表达式 24 ev_init(&periodic_watcher,periodic_callback); 25 ev_periodic_set(&periodic_watcher,0,3,0); 26 ev_periodic_start(main_loop,&periodic_watcher); 27 ev_run(main_loop,0); 28 29 //如果时间周期计算方式,不能通过一个表达式来表示,那么可以通过一个函数来表示,放在set的第4个参数 30 ev_init(&periodic_watcher,periodic_callback); 31 ev_periodic_set(&periodic_watcher,0,0,periodic_scheduler_callback); 32 ev_periodic_start(main_loop,&periodic_watcher); 33 ev_run(main_loop,0); 34 //注意上下两部分不能通过运行,要注释掉一个才可以看到效果 35 return 0; 36 }
ev_signal
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <signal.h> 5 #include <ev.h> 6 7 static void sigint_callback(struct ev_loop * loop,ev_signal *w,int revents) 8 { 9 if(revents & EV_SIGNAL)//用这个可以判断这次进来的是不是ev_signal 如果一个callback回调函数复用的话,就可以用这个来区分 10 { 11 printf("signal SIGINT\n"); 12 ev_break(loop, EVBREAK_ALL); 13 } 14 } 15 16 static void sigquit_callback(struct ev_loop * loop,ev_signal *w,int revents) 17 { 18 printf("signal SIGQUIT\n"); 19 ev_break(loop, EVBREAK_ALL); 20 } 21 22 int main(int argc, char **args) 23 { 24 struct ev_loop * main_loop=ev_default_loop(0); 25 26 ev_signal sigint_watcher; 27 ev_signal sigquit_watcher; 28 29 ev_init(&sigint_watcher,sigint_callback); 30 ev_signal_set(&sigint_watcher,SIGINT/*Other want to catch*/);//这里多个信号不能用或符号| 连接起来 31 ev_signal_start(main_loop,&sigint_watcher); 32 33 ev_init(&sigquit_watcher,sigquit_callback); 34 ev_signal_set(&sigquit_watcher,SIGQUIT/*Other want to catch*/); 35 ev_signal_start(main_loop,&sigquit_watcher); 36 37 ev_run(main_loop,0); 38 39 return 0; 40 }
运行程序,输入Ctrl-C或Ctrl-\都是可以捕获的。
ev_child
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <sys/wait.h> 6 #include <ev.h> 7 8 static void child_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_child *w,int revents) 9 { 10 ev_child_stop(loop,w); 11 printf("Process %d exited with status %d\n",w->rpid,w->rstatus); 12 } 13 14 int main(int argc, char **args) 15 { 16 struct ev_loop * main_loop=ev_default_loop(0); 17 pid_t pid; 18 19 ev_child child_watcher; 20 21 pid=fork(); 22 if(pid<0) 23 { 24 printf("Fork Error\n"); 25 return -1; 26 } 27 else if(pid==0)//child 28 { 29 printf("child doing..\n"); 30 return 0; 31 } 32 else //father 33 { 34 sleep(2);//即使让子进程先执行,最后还是可以捕获到。 35 ev_init(&child_watcher,child_callback); 36 ev_child_set(&child_watcher,pid,0); 37 //ev_child_start(EV_DEFAULT_ &child_watcher); 38 ev_child_start(main_loop,&child_watcher); 39 ev_run(main_loop,0); 40 } 41 42 //waitpid(pid,0,0); 43 return 0; 44 }
上面的例子,主进程通过pid将子进程绑定到了child_callback事件中,当子进程挂掉后,主进程就能捕捉的信号,然后调用child_callback函数。
另一个测试场景:
1 主进程启动后启动一个子进程。
2 手动通过后台kill命令,kill掉子进程。
3 主进程收到信息,打印出提示。
上面代码第30行修改为while(1) ; 然后在第34行增加一行printf("pid:%d\n",pid); 然后运行,结果如下:
注意上面有些是命令,有些是输出的中间结果。这样看起来很乱,但是终端运行结果就是这样。第1、6行是命令。
ev_stat
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <ev.h> 6 7 static void stat_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_stat *w, int revents) 8 { 9 if(w->attr.st_nlink) 10 { 11 printf("The file size %ld\n",(long)w->attr.st_size); 12 } 13 else 14 { 15 printf("文件不存在\n"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 int main(int argc, char **args) 20 { 21 struct ev_loop *main_loop=ev_default_loop(0); 22 23 ev_stat stat_watcher; 24 ev_init(&stat_watcher,stat_callback); 25 ev_stat_set(&stat_watcher,"/home/myuser/hello.txt",0); 26 ev_stat_start(main_loop,&stat_watcher); 27 28 ev_run(main_loop,0); 29 return 0; 30 }
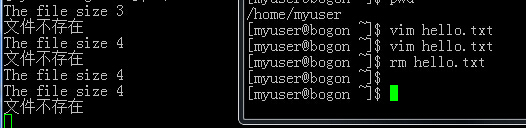
我们创建hello.txt这个文件,然后输入字符,然后保存,然后再打开,修改就这样。运行过程图
文件attr的其他属性。
文档原文:The previous attributes of the file. The callback gets invoked whenever C<prev> != C<attr>, or, more precisely, one or more of these members differ: C<st_dev>, C<st_ino>, C<st_mode>, C<st_nlink>, C<st_uid>, C<st_gid>, C<st_rdev>, C<st_size>, C<st_atime>, C<st_mtime>, C<st_ctime>
文档解释:如果以前的文件有一点修改,无论是什么属性,都将触发这个回调函数。这个attr文件在这里可以获取到的属性成员有
我们的stat_callback函数修改如下:
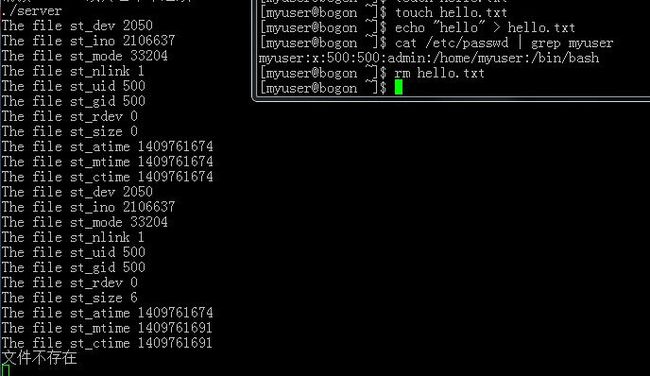
1 static void stat_callback(struct ev_loop *loop,ev_stat *w, int revents) 2 { 3 if(w->attr.st_nlink) 4 { 5 printf("The file st_dev %d\n",w->attr.st_dev); 6 printf("The file st_ino %d\n",w->attr.st_ino); 7 printf("The file st_mode %d\n",w->attr.st_mode); 8 printf("The file st_nlink %d\n",w->attr.st_nlink); 9 printf("The file st_uid %d\n",w->attr.st_uid); 10 printf("The file st_gid %d\n",w->attr.st_gid); 11 printf("The file st_rdev %d\n",w->attr.st_rdev); 12 printf("The file st_size %d\n",w->attr.st_size); 13 printf("The file st_atime %d\n",w->attr.st_atime); 14 printf("The file st_mtime %d\n",w->attr.st_mtime); 15 printf("The file st_ctime %d\n",w->attr.st_ctime); 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 printf("文件不存在\n"); 20 } 21 }
运行结果:
至于那些st_*的属性就不用说了,跟系统函数stat调用的返回结果是一样的。都是通用的。
这一节到这里就结束了,这一节了解了几个最主要的watcher了。除了上面的几个外,还有下面这几个 ev_idle ev_prepare/ev_check ev_embed ev_fork ev_cleanup ev_async .