【Zookeeper】使用Curator操作Zookeeper
简介
Curator 是 Apache ZooKeeper 的Java客户端库。
Zookeeper现有常见的Java API如:原生JavaAPI、Curator、ZkClient等。
添加依赖
org.apache.curator
curator-framework
4.0.0
org.apache.curator
curator-recipes
4.0.0
基本操作
创建连接
创建节点:create 持久 临时 顺序 数据
1. 基本创建 :create().forPath("")
2. 创建节点 带有数据:create().forPath("",data)
3. 设置节点的类型:create().withMode().forPath("",data)
4. 创建多级节点 /app1/p1 :create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath("",data)
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 10);// 尝试间隔时间,最大尝试次数
client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("localhost:2181") // 连接字符串。zk server 地址和端口 "192.168.149.135:2181,192.168.149.136:2181"
.sessionTimeoutMs(60 * 1000) // 会话超时时间 单位ms
.connectionTimeoutMs(15 * 1000) // 连接超时时间 单位ms
.retryPolicy(retryPolicy) // 重试策略
.namespace("itheima") // 根目录,后续的操作都在/itheima下进行
.build();
//开启连接
client.start();
//执行相关操作
.......
//关闭连接
if (client != null) {
client.close();
}
创建节点
不指定数据
//基本创建
//如果创建节点,没有指定数据,则默认将当前客户端的ip作为数据存储
String path = client.create().forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(path);
指定数据
//创建节点 带有数据
//如果创建节点,没有指定数据,则默认将当前客户端的ip作为数据存储
String path = client.create().forPath("/app2", "HelloWorld".getBytes());
System.out.println(path);
设置节点类型
//设置节点的类型(默认类型:持久化)
String path = client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/app3");// 创建临时节点
System.out.println(path);
节点可以分为四大类:
-
PERSISTENT 持久化节点
-
EPHEMERAL 临时节点,只在当前会话有效
-
PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL 持久化顺序节点
-
EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL 临时顺序节点
创建多级节点
//创建多级节点 /app1/p1
//creatingParentsIfNeeded():如果父节点不存在,则创建父节点
String path = client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath("/app4/p1");
System.out.println(path);
查询节点
查询节点:
1. 查询数据:get: getData().forPath()
2. 查询子节点: ls: getChildren().forPath()
3. 查询节点状态信息:ls -s:getData().storingStatIn(状态对象).forPath()
查询节点
//查询数据:get
byte[] data = client.getData().forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(new String(data));
查询子节点
// 查询子节点: ls
List<String> path = client.getChildren().forPath("/");
System.out.println(path);
查询状态信息
Stat status = new Stat();
System.out.println(status);
//查询节点状态信息:ls -s
client.getData().storingStatIn(status).forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(status);
Stat类导包:import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;该类封装好了状态信息,如下图所示。
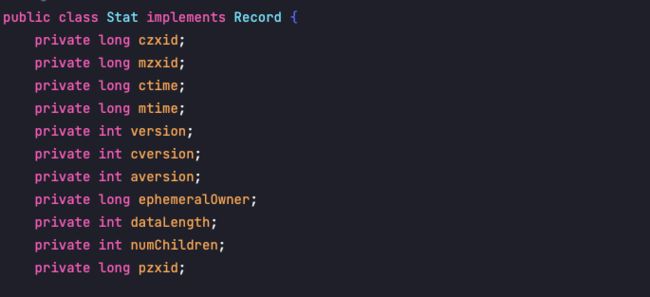
czxid:节点被创建的事务ID
ctime: 创建时间
mzxid: 最后一次被更新的事务ID
mtime: 修改时间
pzxid:子节点列表最后一次被更新的事务ID
cversion:子节点的版本号
dataversion:数据版本号
aclversion:权限版本号
ephemeralOwner:用于临时节点,代表临时节点的事务ID,如果为持久节点则为0
dataLength:节点存储的数据的长度
numChildren:当前节点的子节点个数
修改
修改数据
1. 基本修改数据:setData().forPath()
2. 根据版本修改: setData().withVersion().forPath()。 version 是通过查询出来的。目的就是为了让其他客户端或者线程不干扰我。
client.setData().forPath("/app1", "itcast".getBytes());
Stat status = new Stat();
//查询节点状态信息:ls -s
client.getData().storingStatIn(status).forPath("/app1");
int version = status.getVersion();
System.out.println(version);
client.setData().withVersion(version).forPath("/app1", "hehe".getBytes());
删除节点
删除节点: delete deleteall
1. 删除单个节点:delete().forPath("/app1");
2. 删除带有子节点的节点:delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/app1");
3. 必须成功的删除:为了防止网络抖动。本质就是重试。 client.delete().guaranteed().forPath("/app2");
4. 回调:inBackground
// 删除单个节点
client.delete().forPath("/app1");
//删除带有子节点的节点
client.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/app4");
//必须成功的删除
client.delete().guaranteed().forPath("/app2");
//回调
client.delete().guaranteed().inBackground(new BackgroundCallback(){
@Override
public void processResult(CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("我被删除了~");
System.out.println(event);
}
}).forPath("/app1");
Watch监听
Zookeeper允许用户在指定的事件桑拿注册Watcher,当一些特定的事件处罚时,Zookeeper服务端将通知感兴趣的客户端上,该机制是Zoookeeper实现分布式协调服务的重要特性。Zookeeper引入了Watcher机制来实现发布和订阅功能,能够让多个订阅者同时监听某个对象,当对象发生改变时会通知所有订阅者。
Curator引入了 Cache 来实现对 ZooKeeper 服务端事件的监听。提供了三种Watcher:
- NodeCache : 只是监听某一个特定的节点
- PathChildrenCache : 监控一个ZNode的子节点.
- TreeCache : 可以监控整个树上的所有节点,类似于PathChildrenCache和NodeCache的组合
//1. 创建NodeCache对象
final NodeCache nodeCache = new NodeCache(client,"/app1");
//2. 注册监听
nodeCache.getListenable().addListener(new NodeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void nodeChanged() throws Exception {
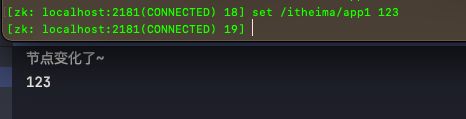
System.out.println("节点变化了~");
//获取修改节点后的数据
byte[] data = nodeCache.getCurrentData().getData();
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
});
//3. 开启监听.如果设置为true,则开启监听是,加载缓冲数据
nodeCache.start(true);
// 仅用于测试时方便查看
while (true){
}
演示 PathChildrenCache:监听某个节点的所有子节点们
//1.创建监听对象
PathChildrenCache pathChildrenCache = new PathChildrenCache(client,"/app2",true);
//2. 绑定监听器
pathChildrenCache.getListenable().addListener(new PathChildrenCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework client, PathChildrenCacheEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("子节点变化了~");
System.out.println(event);
//监听子节点的数据变更,并且拿到变更后的数据
//1.获取类型
PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type type = event.getType();
//2.判断类型是否是update
if(type.equals(PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type.CHILD_UPDATED)){
System.out.println("数据变了!!!");
byte[] data = event.getData().getData();
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
}
});
//3. 开启
pathChildrenCache.start();
演示 TreeCache:监听某个节点自己和所有子节点们
//1. 创建监听器
TreeCache treeCache = new TreeCache(client,"/app2");
//2. 注册监听
treeCache.getListenable().addListener(new TreeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework client, TreeCacheEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("节点变化了");
System.out.println(event);
}
});
//3. 开启
treeCache.start();
while (true){
}
参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M741137qY