Python学习笔记-基于socket基础的http服务端程序
通过HTTP协议可以进行通信可以规范化的进行网络间通信。下面技术第一个http服务器小程序。简单的记录第一个试手程序。
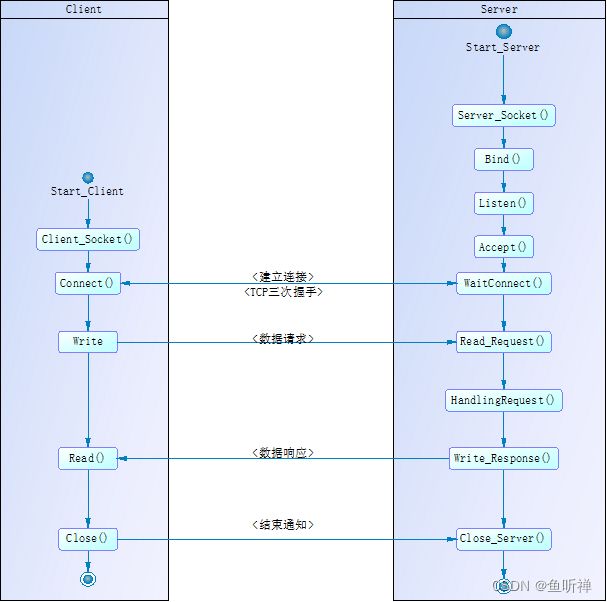
1.http通信的基本流程
整个流程对应四层网络架构:应用层、传输层、网络层、链路层。有的部分已经封装,不需要我们再行处理。
2.服务器程序设置
2.1 创建一个socket对象
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)第一个参数是指定IP协议,第二个参数用于指定通信方式。
官方构造函数解释如下:
def __init__(self, family=-1, type=-1, proto=-1, fileno=None):
# For user code address family and type values are IntEnum members, but
# for the underlying _socket.socket they're just integers. The
# constructor of _socket.socket converts the given argument to an
# integer automatically.
if fileno is None:
if family == -1:
family = AF_INET
if type == -1:
type = SOCK_STREAM
if proto == -1:
proto = 0
_socket.socket.__init__(self, family, type, proto, fileno)
self._io_refs = 0
self._closed = False基本参数信息如下:
| AF_INET = AddressFamily.AF_INET |
IPv4地址 |
| AF_INET6 = AddressFamily.AF_INET6 |
IPv6地址 |
| SOCK_STREAM = SocketKind.SOCK_STREAM |
基于TCP传输 |
| SOCK_DGRAM = SocketKind.SOCK_DGRAM |
基于UDP传输 |
2.2 绑定IP和端口
def bind(self, __address: _Address) -> None: ...
_Address: TypeAlias = tuple[Any, ...] | str | ReadableBuffer指定一个地址进行绑定。
通过元组的形式指定IP地址和端口号:
self.server_socket.bind(("", port))注意,需要使用元组型号的数据,第一个参数是IP地址,第二个参数是端口号,使用空字符串”“默认为本地IP地址:127.0.0.1。
2.3 启动监听
def listen(self, __backlog: int = ...) -> None: ...设置监听数量,即允许同时连接的最大客户端数量。
2.4 接收请求
def accept(self):
"""accept() -> (socket object, address info)
Wait for an incoming connection. Return a new socket
representing the connection, and the address of the client.
For IP sockets, the address info is a pair (hostaddr, port).
"""
fd, addr = self._accept()
sock = socket(self.family, self.type, self.proto, fileno=fd)
# Issue #7995: if no default timeout is set and the listening
# socket had a (non-zero) timeout, force the new socket in blocking
# mode to override platform-specific socket flags inheritance.
if getdefaulttimeout() is None and self.gettimeout():
sock.setblocking(True)
return sock, addr通过accept函数返回请求对象,返回两个参数,一个是请求的socket,一个是请求的地址信息。
client_socket, client_address = self.server_socket.accept()2.5 处理请求
处理请求就相当于字符串处理,解析报文,进行对应处理。
2.6 应答
def send(self, __data: ReadableBuffer, __flags: int = ...) -> int: ...通过send函数将bytes数据返回给客户端。
client_socket.send(bytes(response, "utf-8"))2.7 关闭socket
client_socket.close()关闭客户端的socket。
注意:此处关闭的是获取到的客户端socket,不是服务器的socket。
3. 示例代码
3.1 服务端代码
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
import socket
import re
import os
from multiprocessing import Process
HTML_ROOT_DIR = "./zero.staticserver/views"
class HTTPServer(object):
"""HTTP server"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""init"""
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
"""初始化socket,IPV4,TCP协议"""
def bind(self, port):
"""Binding port"""
self.server_socket.bind(("", port))
def start(self):
"""Start server"""
self.server_socket.listen(20) # 设置最大连接数20
print("Server started.Waitting to connect...")
while True:
# 接收的客户端连接信息
client_socket, client_address = self.server_socket.accept()
print("Client Connected. IP:{0},Port:{1}",
client_address[0], client_address[1])
process_client = Process(
target=self.handle_client, args=(client_socket,))
process_client.start()
client_socket.close()
def handle_client(self, client_socket: socket.socket):
"""handle of client"""
request_data = client_socket.recv(1024)
print("Request Data:", request_data)
print("********逐行输出请求数据*********")
request_lines = request_data.splitlines()
for line in request_lines:
print(line)
print("********解析报文*********")
request_start_line = request_lines[0]
str_request_start_line = request_start_line.decode("utf-8")
print(str_request_start_line)
filename = re.match(r"\w+ +(/[^ ]*) ", str_request_start_line).group(1)
print("File Name : {0}".format(filename))
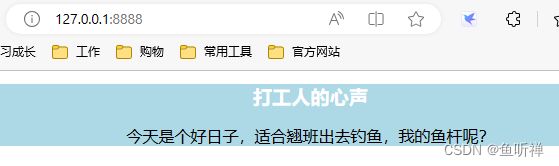
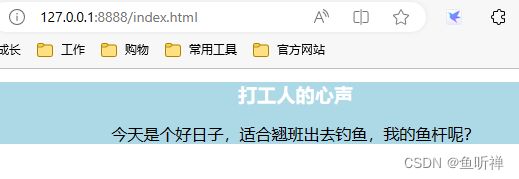
if filename == "/":
filename = "index.html"
print("root path : {0}".format(os.getcwd()))
try:
filepath = f"{HTML_ROOT_DIR}/{filename}"
file = open(filepath, "rb")
except IOError:
# 返回异常
response_start_line = "HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found"
response_headers = "Server:First server"
response_body = "The file is not found."
else:
# Read file data.
filedata = file.read()
file.close()
response_start_line = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
response_headers = "Server:First server"
response_body = filedata.decode("utf-8")
print("\r\n")
response = f"{response_start_line}\r\n{response_headers}\r\n\r\n{response_body}"
print("Response:\r\n{0}".format(response))
client_socket.send(bytes(response, "utf-8"))
# Close socket.
client_socket.close()
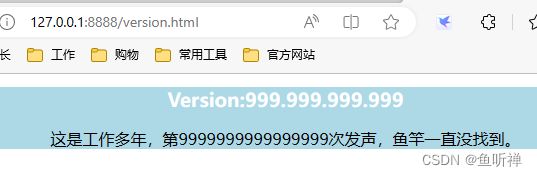
3.2 访问结果