深入理解 Golang: 网络编程
Go 中的 Epoll
关于计算机网络分层与 TCP 通信过程过程此处不再赘述。
- 考虑到 TCP 通信过程中各种复杂操作,包括三次握手,四次挥手等,多数操作系统都提供了
Socket作为 TCP 网络连接的抽象。 - Linux -> Internet domain socket -> SOCK_STREAM
- Linux 中 Socket 以 “文件描述符” FD 作为标识
在进行 Socket 通信时,服务端同时操作多个 Socket,此时便需要 IO 模型操作方案。:
- 阻塞 IO。传统 C/C++ 方案,同步读写 Socket(一个线程一个 Socket),线程陷入内核态,当读写成功后,切换回用户态继续执行。
- 非阻塞 IO。应用会不断自旋轮询,直到 Socket 可以读写,如果暂时无法收发数据,会返回错误。
- Epoll 多路复用。提供了事件列表,不需要查询各个 Socket。其注册多个 Socket 事件,调用 epoll ,当有事件发生则返回。
Epoll 是 Linux 下的 event poll,Windows 中为 IOCP, Mac 中为 kqueue。
在 Go 中,内部采用结合阻塞模型和多路复用的方法。在这里就不再是线程操作 Socket,而是 Goroutine 协程。每个协程关心一个 Socket 连接:
- 在底层使用操作系统的多路复用 IO。
- 在协程层次使用阻塞模型。
- 阻塞协程时,休眠协程。
我们知道,Go 是一个跨平台的语言,不同平台/操作系统下提供的 Epoll 实现不同,所以 Go 在 Epoll/IOCP/kqueue 上再独立了一层 epoll 抽象层,用于屏蔽各个系统的差异性,抽象各系统对多路复用器的实现。
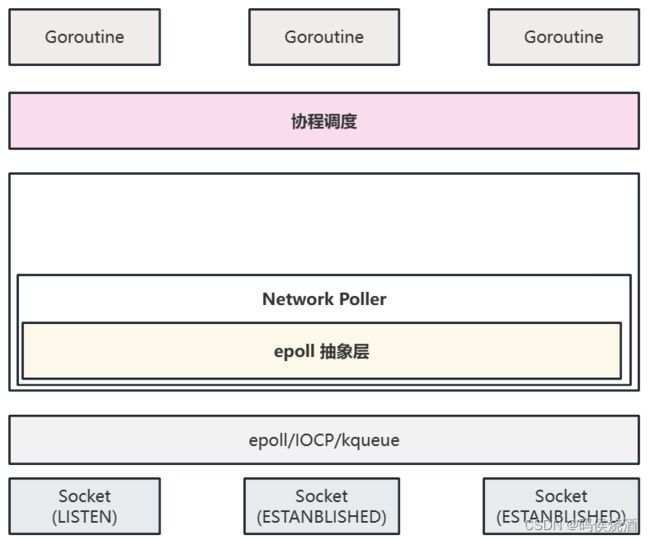
Go Network Poller 多路复用器的抽象,以 Linux 为例:
- Go Network Poller 对于多路复用器的抽象和适配
- epoll_create() -> netpollinit()
- epoll_ctl() -> netpollopen()
- epoll_wait() -> netpoll()
// Integrated network poller (platform-independent part).
// A particular implementation (epoll/kqueue/port/AIX/Windows)
// must define the following functions:
//
// func netpollinit()
// Initialize the poller. Only called once.
//
// func netpollopen(fd uintptr, pd *pollDesc) int32
// Arm edge-triggered notifications for fd. The pd argument is to pass
// back to netpollready when fd is ready. Return an errno value.
//
// func netpollclose(fd uintptr) int32
// Disable notifications for fd. Return an errno value.
//
// func netpoll(delta int64) gList
// Poll the network. If delta < 0, block indefinitely. If delta == 0,
// poll without blocking. If delta > 0, block for up to delta nanoseconds.
// Return a list of goroutines built by calling netpollready.
//
// func netpollBreak()
// Wake up the network poller, assumed to be blocked in netpoll.
//
// func netpollIsPollDescriptor(fd uintptr) bool
// Reports whether fd is a file descriptor used by the poller.
上诉所有方法的实现都在 %GOROOT/src/runtime/netpoll_epoll.go%
netpollinit() 新建多路复用器
- 新建 Epoll,不同系统对应不同的实现方式。
- 新建一个 Pipe 管道用于中断 Epoll。
- 将 “管道有数据到达” 事件注册到 Epoll 中。
func netpollinit() {
var errno uintptr
// 1. 新建 Epoll,不同系统对应不同的实现方式
epfd, errno = syscall.EpollCreate1(syscall.EPOLL_CLOEXEC)
if errno != 0 {
println("runtime: epollcreate failed with", errno)
throw("runtime: netpollinit failed")
}
// 用来中断 Epoll 的管道
r, w, errpipe := nonblockingPipe()
if errpipe != 0 {
println("runtime: pipe failed with", -errpipe)
throw("runtime: pipe failed")
}
// 3. 注册事件
ev := syscall.EpollEvent{
Events: syscall.EPOLLIN,
}
*(**uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.Data)) = &netpollBreakRd
errno = syscall.EpollCtl(epfd, syscall.EPOLL_CTL_ADD, r, &ev)
if errno != 0 {
println("runtime: epollctl failed with", errno)
throw("runtime: epollctl failed")
}
netpollBreakRd = uintptr(r)
netpollBreakWr = uintptr(w)
}
netpollopen() 插入事件
- 传入一个 Socket 的 FD 和
pollDesc指针。 pollDesc指针是 Socket 相关详细信息。pollDesc指针中记录了哪个协程在休眠等待此 Socket。- 将 Socket 的可读/可写/断开事件注册到 Epoll 中。
func netpollopen(fd uintptr, pd *pollDesc) uintptr {
var ev syscall.EpollEvent
// 事件类型
ev.Events = syscall.EPOLLIN | syscall.EPOLLOUT | syscall.EPOLLRDHUP | syscall.EPOLLET
*(**pollDesc)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.Data)) = pd
return syscall.EpollCtl(epfd, syscall.EPOLL_CTL_ADD, int32(fd), &ev)
}
netpoll() 查询事件
- 调用 EpollWait() 方法,查询有哪些事件发生
- 根据 Socket 相关的
pollDesc信息,返回哪些协程可以唤醒。
func netpoll(delay int64) gList {
// 1. 查询哪些事件发生
n, errno := syscall.EpollWait(epfd, events[:], int32(len(events)), waitms)
// ...
if errno != 0 {
if errno != _EINTR {
println("runtime: epollwait on fd", epfd, "failed with", errno)
throw("runtime: netpoll failed")
}
// If a timed sleep was interrupted, just return to
// recalculate how long we should sleep now.
if waitms > 0 {
return gList{}
}
goto retry
}
// 2. 根据 Socket 相关的 pollDesc 信息,返回哪些协程可以唤醒。
var toRun gList
for i := int32(0); i < n; i++ {
ev := events[i]
if ev.Events == 0 {
continue
}
if *(**uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.Data)) == &netpollBreakRd {
if ev.Events != syscall.EPOLLIN {
println("runtime: netpoll: break fd ready for", ev.Events)
throw("runtime: netpoll: break fd ready for something unexpected")
}
if delay != 0 {
var tmp [16]byte
read(int32(netpollBreakRd), noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&tmp[0])), int32(len(tmp)))
netpollWakeSig.Store(0)
}
continue
}
var mode int32
if ev.Events&(syscall.EPOLLIN|syscall.EPOLLRDHUP|syscall.EPOLLHUP|syscall.EPOLLERR) != 0 {
mode += 'r'
}
if ev.Events&(syscall.EPOLLOUT|syscall.EPOLLHUP|syscall.EPOLLERR) != 0 {
mode += 'w'
}
if mode != 0 {
pd := *(**pollDesc)(unsafe.Pointer(&ev.Data))
pd.setEventErr(ev.Events == syscall.EPOLLERR)
netpollready(&toRun, pd, mode)
}
}
// 协程列表
return toRun
}
Go Network Poller
Network Poller 初始化
- 初始化一个 Network Poller。
- 调用
netpollinit()新建多路复用器。
// %GOROOT%src/runtime/netpoll.go
func poll_runtime_pollServerInit() {
netpollGenericInit()
}
func netpollGenericInit() {
// 每个 Go 应用只初始化一次
if netpollInited.Load() == 0 {
lockInit(&netpollInitLock, lockRankNetpollInit)
lock(&netpollInitLock)
if netpollInited.Load() == 0 {
// 新建多路复用器
netpollinit()
netpollInited.Store(1)
}
unlock(&netpollInitLock)
}
}
关于 pollDesc,是 runtime 包对 Socket 的详细描述:
type pollDesc struct {
_ sys.NotInHeap
link *pollDesc // in pollcache, protected by pollcache.lock
fd uintptr // constant for pollDesc usage lifetime
atomicInfo atomic.Uint32 // atomic pollInfo
rg atomic.Uintptr // pdReady, pdWait, G waiting for read or pdNil
wg atomic.Uintptr // pdReady, pdWait, G waiting for write or pdNil
lock mutex // protects the following fields
closing bool
user uint32 // user settable cookie
rseq uintptr // protects from stale read timers
rt timer // read deadline timer (set if rt.f != nil)
rd int64 // read deadline (a nanotime in the future, -1 when expired)
wseq uintptr // protects from stale write timers
wt timer // write deadline timer
wd int64 // write deadline (a nanotime in the future, -1 when expired)
self *pollDesc // storage for indirect interface. See (*pollDesc).makeArg.
}
Network Poller 新增监听 Socket
- 在 pollCache 链表中分配一个 pollDesc。
- 初始化 pollDesc,rg,wg 都为 0。
- 调用
netpollopen()插入事件
func poll_runtime_pollOpen(fd uintptr) (*pollDesc, int) {
// 分配 pollDesc
pd := pollcache.alloc()
lock(&pd.lock)
wg := pd.wg.Load()
if wg != pdNil && wg != pdReady {
throw("runtime: blocked write on free polldesc")
}
rg := pd.rg.Load()
if rg != pdNil && rg != pdReady {
throw("runtime: blocked read on free polldesc")
}
// 初始化 pollDesc
pd.fd = fd
pd.closing = false
pd.setEventErr(false)
pd.rseq++
pd.rg.Store(pdNil)
pd.rd = 0
pd.wseq++
pd.wg.Store(pdNil)
pd.wd = 0
pd.self = pd
pd.publishInfo()
unlock(&pd.lock)
// 插入事件
errno := netpollopen(fd, pd)
if errno != 0 {
pollcache.free(pd)
return nil, int(errno)
}
return pd, 0
}
Network Poller 收发数据
- Socket 已经可读写时
- runtime 的
g0协程循环调用netpoll()方法。 - 发现 Socket 可读写时,给对应的
rg,wg置为 pdReady(1)。 - 协程调用
poll_runtime_pollWait()。 - 判断
rg或wg已置为 pdReady(1),返回 0。
- runtime 的
func poll_runtime_pollWait(pd *pollDesc, mode int) int {
// ...
// 判断 `rg` 或 `wg` 已置为 pdReady(1),返回 0。
for !netpollblock(pd, int32(mode), false) {
errcode = netpollcheckerr(pd, int32(mode))
if errcode != pollNoError {
return errcode
}
}
return pollNoError
}
- Socket 暂时无法读写时
Socket 通信
net 包中的 Socket 会被定义为一个 netFD 结构体:
type netFD struct {
// 最终指向的 runtime 中的 Socket 结构体
pfd poll.FD
family int
sotype int
isConnected bool // handshake completed or use of association with peer
net string
laddr Addr
raddr Addr
}
Server 端
以 TCP 协议为例:
net 的 net.Listen() 操作:
- 新建 Socket,并执行 bind 操作
- 新建一个
FD(net 包对 Socket 的详情描述)。 - 返回一个
TCPListener对象 - 将
TCPListener的FD信息加入监听。
func main() {
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8888")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
TCPListener 本质是一个 LISTEN 状态的 Scoket。
TCPListener.Accept() 操作:
- 直接调用 Socket 的
accept()。 - 如果失败,休眠等待新的连接。
- 将新的 Socket 包装成
TCPConn变量返回。 - 将
TCPConn的FD信息加入监听。
func main() {
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8888")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
conn, err := ln.Accept()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
}
TCPConn 本质是一个 ESTANBLISHED 状态的 Scoket。
TCPConn 收发数据
func main() {
// 1. 监听端口
ln, err1 := net.Listen("tcp", ":8888")
if err1 != nil {
panic(err1)
}
// 2. 建立连接
conn, err2 := ln.Accept()
if err2 != nil {
panic(err2)
}
defer conn.Close()
var recv [1024]byte
// 使用 bufio 标准库提供的缓冲区功能
send := bufio.NewReader(conn)
for {
// 3. 获取数据
_, err3 := conn.Read(recv[:])
if err3 != nil {
break
}
fmt.Printf("n: %v\n", string(recv[:]))
// 4. 发送数据
msg, err := send.ReadString('\n')
if strings.ToUpper(msg) == "Q" {
return
}
if err != nil {
return
}
_, err4 := conn.Write([]byte(msg))
if err4 != nil {
break
}
}
}
Client 端
func main() {
// 与服务端建立连接
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", ":8888")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
var recv [1024]byte
send := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
for {
s, _ := send.ReadString('\n')
if strings.ToUpper(s) == "Q" {
return
}
// 发送数据
_, err = conn.Write([]byte(s))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 接收数据
_, err := conn.Read(recv[:])
if err != nil {
break
}
fmt.Printf(":%v\n", string(recv[:]))
}
}
goroutine-per-connection style code
一个协程服务一个新的连接
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"net"
"strings"
)
func handleConnection(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close()
var recv [1024]byte
// 使用 bufio 标准库提供的缓冲区功能
send := bufio.NewReader(conn)
for {
// 3. 获取数据
_, err3 := conn.Read(recv[:])
if err3 != nil {
break
}
fmt.Printf("n: %v\n", string(recv[:]))
// 4. 发送数据
msg, err := send.ReadString('\n')
if strings.ToUpper(msg) == "Q" {
return
}
if err != nil {
return
}
_, err4 := conn.Write([]byte(msg))
if err4 != nil {
break
}
}
}
func main() {
// 1. 监听端口
ln, err1 := net.Listen("tcp", ":8888")
if err1 != nil {
panic(err1)
}
for {
// 2. 建立连接
conn, err2 := ln.Accept()
if err2 != nil {
panic(err2)
}
go handleConnection(conn)
}
}

