35.RocketMQ之Broker端消息存储文件详解
highlight: arduino-light
Broker端文件详解
dubbo的核心是spi,看懂了spi那么dubbo基本上也懂了。对于rmq来说,它的核心是broker,而broker的核心是commitlog、consumequeue、indexfile,而这些文件对应的最终都是MappedFile,那么搞明白了这个类,那么对于broker的存储这块也就很容易明白。
假如现在有个tyrant的主题,有4个messageQueue。
messageQueue 0、messageQueue 1位于broker1。
messageQueue 2、messageQueue 3位于broker2。
写入100条消息。每个队列是25条消息,那么broker1和broker2的commitLog各有50条消息。
现在有4个消费者在消费者组A消费消息:那么消费者组A在broker1和broker2消费的Queue各有2个。
也就是消费者组A消费所有的4个queue。
broker1:ConsumeQueue0 ConsumeQueue1
broker2:ConsumeQueue2 ConsumeQueue3每个ConsumeQueue记录的是对应的MessageQueue上消息的偏移量???
consumequeue文件采取定长设计,每一个条目共20个字节。
分别为在commitlog中的物理起始偏移量占8字节、4字节的消息长度、8字节tag hashcode。单个文件由30W个条目组成,可以像数组一样随机访问每一个条目,每个ConsumeQueue文件大小约5.72M。
打个比方MessageQueue0上消息的编号是1-25,共25条消息
那么在ConsumeQueue01上,一共有25个条目。
每一个条目共20个字节,分别为8字节的commitlog物理偏移量、4字节的消息长度、8字节tag hashcode。
假如
消费者组cosumerA中的A1去MessageQueue0消费了2条消息
消费者组cosumerA中的A2去MessageQueue1消费了3条消息
在Broker1的config文件下的consumerOffset.json存在以下记录
"tyrant@consumerA":{0:2,1:3}
代表的意思是tyrant主题下
queue0队列被consumerA组消费到了第2条消息,
queue1队列被consumerA组消费到了第3条消息,
消费者组cosumerA中的A3去MessageQueue2消费了2条消息
消费者组cosumerA中的A4去MessageQueue3消费了3条消息
在Broker2的config文件下的consumerOffset.json存在以下记录
"tyrant@ConsumerA":{2:2,3:3}
消费者组cosumerB中的B1去MessageQueue0消费了2条消息
消费者组cosumerB中的B2去MessageQueue1消费了3条消息
在Broker1的config文件下的consumerOffset.json
"tyrant@ConsumerB":{0:2,1:3}
消费者组cosumerB中的B3去MessageQueue2消费了2条消息
消费者组cosumerB中的B4去MessageQueue3消费了3条消息
在Broker2的config文件下的consumerOffset.json
"tyrant@ConsumerB":{2:2,3:3}如果现在消费者组cosumerA中的A1去消费MessageQueue0。
首先根据在Broker1的config文件下的consumerOffset.json中的记录
"tyrant\@ConsumerA":{0:2,1:3}
获取到了MessageQueue0的消费点位是0:2,也就是从MessageQueue0下标为2的地方开始消费。
什么意思呢?就是拿着2去计算读取偏移量然后去ConsumeQueue0中读取。
读取的起点是:2*20
读取的终点是:2*20 + 20
为什么呢?
因为1个条目是20字节,分别为8字节的commitlog物理偏移量、4字节的消息长度、8字节tag hashcode拿到了这个条目以后就可以拿到了当前条目对应的消息在CommitLog中的起始偏移量以及消息的长度。
先根据偏移量计算文件位置。然后根据偏移量在文件中读取消息长度个字节,就可以拿到我们要的消息了!
1.CommitLog
CommitLog ,消息存储文件,所有主题的消息都存储在 CommitLog 文件中。
我们知道,一台 Broker服务器有一个 CommitLog 文件组, RocketMQ 会将所有主题的消息存储在同一个文件中,这个文件中就存储着一条条Message,每条Message都会按照顺序写入。
也许有时候,你会希望看看这个 CommitLog 文件中,存储的内容到底长什么样子?
消息主体以及元数据的存储主体,存储Producer端写入的消息主体内容,消息内容不是定长的。
单个文件大小默认1G ,文件名长度为20位,左边补零,剩余为起始偏移量。
比如00000000000000000000代表了第一个文件,起始偏移量为0,文件大小为1G=1073741824;
当第一个文件写满了,第二个文件为00000000001073741824,起始偏移量为1073741824,以此类推。
消息主要是顺序写入日志文件,当文件满了,写入下一个文件;为什么commitLog是1个G呢?
这里需要注意的是,采用MappedByteBuffer这种内存映射的方式有几个限制,其中之一是一次只能映射1.5\~2G 的文件至用户态的虚拟内存,这也是为何RocketMQ默认设置单个CommitLog日志数据文件为1G的原因了。
MappedByteBuffer是DirectByteBuffer的子类
MappedByteBuffer使用的是mmap技术。MappedByteBuffer将文件映射为内存,也可能会被存储在虚拟内存里面,访问的时候通过缺页机制调进内存。
1.1消息发送
当然,我们需要先往 CommitLog 文件中写入一些内容,所以先来看一个消息发送的例子。 ```java package com.itheima.mq.rocketmq.base.producer;
import org.apache.rocketmq.client.producer.DefaultMQProducer;
import org.apache.rocketmq.client.producer.SendResult;
import org.apache.rocketmq.client.producer.SendStatus;
import org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.Message;
import org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.MessageQueue;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 发送同步消息
*/
public class SyncProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建消息生产者producer,并指定生产者组名
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("Producer");
//2.指定NameServer地址
producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
//3.启动producer
producer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
//4.创建消息对象,指定主题Topic、Tag和消息体
/**
* 参数一:消息主题Topic
* 参数二:消息Tag
* 参数三:消息内容
*/
Message msg = new Message("tyrant", "tyrant", ("Hello World 哈哈哈" + i +"-" + new Date().toString()).getBytes());
msg.setKeys("hello");
//5.发送消息
SendResult result = producer.send(msg);
//发送状态
SendStatus status = result.getSendStatus();
String msgId = result.getMsgId();
MessageQueue messageQueue = result.getMessageQueue();
System.out.println("结果:" + result );
System.out.println("状态:" + status);
System.out.println("messageQueue:" + messageQueue);
System.out.println("msgId:" + msgId);
//线程睡1秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
//6.关闭生产者producer
// producer.shutdown();
}
}``` 我们向10个不同的主题中发送消息,如果只有一台 Broker 机器,它们会保存到同一个 CommitLog 文件中。此时,这个文件的位置处于rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\config
1.2读取文件内容
这个文件我们不能直接打开,因为它是一个二进制文件,所以我们需要通过程序来读取它的字节数组。 java public static ByteBuffer read(String path)throws Exception{ File file = new File(path); FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file); byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)file.length()]; fin.read(bytes); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); return buffer; } 如上代码,可以通过传入文件的路径,读取该文件所有的内容。
为了方便下一步操作,我们把读取到的字节数组转换为 java.nio.ByteBuffer 对象。
1.3解析
在解析之前,我们需要弄明白两件事:
- 消息的格式,即一条消息包含哪些字段;
- 每个字段所占的字节大小。
在上面的图中,我们已经看到了消息的格式,包含了19个字段。
关于字节大小,有的是 4 字节,有的是 8 字节,我们不再一一赘述,直接看文件的消息单元存储结构。
文件的消息单元存储结构
| 顺序编号 | 字段简称 | 字段大小(字节) | 字段含义 | | ---- | -------------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | 1 | msgSize | 4 | 代表这个消息的大小即消息长度,使用物理偏移量作为起始位置,读取消息长度个字节,即为消息的内容 | | 2 | MAGICCODE | 4 | MAGICCODE = daa320a7 | | 3 | BODY CRC | 4 | 消息体BODY CRC 当broker重启recover时会校验 | | 4 | queueId | 4 | | | 5 | flag | 4 | | | 6 | QUEUEOFFSET | 8 | 这个值是个自增值不是真正的consume queue的偏移量,可以代表这个consumeQueue队列或者tranStateTable队列中消息的个数,若是非事务消息或者commit事务消息,可以通过这个值查找到consumeQueue中数据,QUEUEOFFSET * 20才是偏移地址;若是PREPARED或者Rollback事务,则可以通过该值从tranStateTable中查找数据 | | 7 | PHYSICALOFFSET | 8 | 代表消息在commitLog中的物理起始地址偏移量 | | 8 | SYSFLAG | 4 | 指明消息是事物事物状态等消息特征,二进制为四个字节从右往左数:当4个字节均为0(值为0)时表示非事务消息;当第1个字节为1(值为1)时表示表示消息是压缩的(Compressed);当第2个字节为1(值为2)表示多消息(MultiTags);当第3个字节为1(值为4)时表示prepared消息;当第4个字节为1(值为8)时表示commit消息;当第3/4个字节均为1时(值为12)时表示rollback消息;当第3/4个字节均为0时表示非事务消息; | | 9 | BORNTIMESTAMP | 8 | 消息产生端(producer)的时间戳 | | 10 | BORNHOST | 8 | 消息产生端(producer)地址(address:port) | | 11 | STORETIMESTAMP | 8 | 消息在broker存储时间 | | 12 | STOREHOSTADDRESS | 8 | 消息存储到broker的地址(address:port) | | 13 | RECONSUMETIMES | 8 | 消息被某个订阅组重新消费了几次(订阅组之间独立计数),因为重试消息发送到了topic名字为%retry%groupName的队列queueId=0的队列中去了,成功消费一次记录为0; | | 14 | PreparedTransaction Offset | 8 | 表示是prepared状态的事物消息 | | 15 | messagebodyLength | 4 | 消息体大小值 | | 16 | messagebody | bodyLength | 消息体内容 | | 17 | topicLength | 1 | topic名称内容大小 | | 18 | topic | topicLength | topic的内容值 | | 19 | propertiesLength | 2 | 属性值大小 | | 20 | properties | propertiesLength | propertiesLength大小的属性数据 |
所以在解析的时候我们只需要 ```java /** * commitlog 文件解析 * @param byteBuffer * @return * @throws Exception */ public static MessageExt decodeCommitLog(ByteBuffer byteBuffer)throws Exception {
MessageExt msgExt = new MessageExt();
// 1 TOTALSIZE 消息长度 4个字节
int storeSize = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setStoreSize(storeSize);
if (storeSize<=0){
return null;
}
// 2 MAGICCODE 4个字节
byteBuffer.getInt();
// 3 BODYCRC 4个字节
int bodyCRC = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setBodyCRC(bodyCRC);
// 4 QUEUEID 4个字节
int queueId = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setQueueId(queueId);
// 5 FLAG 4个字节
int flag = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setFlag(flag);
// 6 QUEUEOFFSET 8个字节
long queueOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setQueueOffset(queueOffset);
// 7 PHYSICALOFFSET 8个字节
long physicOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setCommitLogOffset(physicOffset);
// 8 SYSFLAG 4个字节
int sysFlag = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setSysFlag(sysFlag);
// 9 BORNTIMESTAMP 8个字节
long bornTimeStamp = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setBornTimestamp(bornTimeStamp);
// 10 BORNHOST 4个字节
int bornhostIPLength = (sysFlag & MessageSysFlag.BORNHOST_V6_FLAG) == 0 ? 4 : 16;
byte[] bornHost = new byte[bornhostIPLength];
byteBuffer.get(bornHost, 0, bornhostIPLength);
int port = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setBornHost(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByAddress(bornHost), port));
// 11 STORETIMESTAMP 8个字节
long storeTimestamp = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setStoreTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
// 12 STOREHOST 4个字节
int storehostIPLength = (sysFlag & MessageSysFlag.STOREHOSTADDRESS_V6_FLAG) == 0 ? 4 : 16;
byte[] storeHost = new byte[storehostIPLength];
byteBuffer.get(storeHost, 0, storehostIPLength);
port = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setStoreHost(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByAddress(storeHost), port));
// 13 RECONSUMETIMES 4个字节
int reconsumeTimes = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setReconsumeTimes(reconsumeTimes);
// 14 Prepared Transaction Offset
long preparedTransactionOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setPreparedTransactionOffset(preparedTransactionOffset);
// 15 BODY
//偏移量指的是整个消息的偏移量,消息的具体内容要具体读取。
//BodyLength是4个字节,然后在读取BodyLength个字节就是body的长度
int bodyLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
if (bodyLen > 0) {
byte[] body = new byte[bodyLen];
byteBuffer.get(body);
msgExt.setBody(body);
}
// 16 TOPIC
byte topicLen = byteBuffer.get();
byte[] topic = new byte[(int) topicLen];
byteBuffer.get(topic);
msgExt.setTopic(new String(topic, CHARSET_UTF8));
// 17 properties
short propertiesLength = byteBuffer.getShort();
if (propertiesLength > 0) {
byte[] properties = new byte[propertiesLength];
byteBuffer.get(properties);
String propertiesString = new String(properties, CHARSET_UTF8);
Map map = string2messageProperties(propertiesString);
}
// 18
int msgIDLength = storehostIPLength + 4 + 8;
ByteBuffer byteBufferMsgId = ByteBuffer.allocate(msgIDLength);
String msgId = createMessageId(byteBufferMsgId, msgExt.getStoreHostBytes(), msgExt.getCommitLogOffset());
msgExt.setMsgId(msgId);
return msgExt;
} ```
1.4输出消息内容
```java import org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.MessageExt;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.MessageDecoder.*;
public class parseCommitLog {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "E:\study\5.rocketmq\rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\commitlog\00000000000000000000";
ByteBuffer buffer = read(filePath);
//读取指定的消息内容
//在debug中我们看到解析body时的position是84 消息长度是51
List messageList = new ArrayList<>();
byte[] useless = new byte[88];
buffer.get(useless);
byte[] bytes = new byte[51];
buffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println("主题:tyrant,消息:" + new String(bytes, "utf-8"));
buffer = read(filePath);
while (true) {
MessageExt message = decodeCommitLog(buffer);
if (message == null) {
break;
}
messageList.add(message);
}
for (MessageExt ms : messageList) {
System.out.println("主题:" + ms.getTopic() + ",消息:" +
new String(ms.getBody()) + ",队列ID:" + ms.getQueueId() + ",存储地址:" + ms.getStoreHost() + "总大小:" +
ms.getStoreSize() + ",偏移量:" +
ms.getCommitLogOffset() + "");
}
}
public static ByteBuffer read(String path) throws Exception {
File file = new File(path);
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
fin.read(bytes);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
return buffer;
}
/**
* commitlog 文件解析
*/
public static MessageExt decodeCommitLog(ByteBuffer byteBuffer) throws Exception {
MessageExt msgExt = new MessageExt();
// 1 TOTALSIZE
int storeSize = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setStoreSize(storeSize);
if (storeSize <= 0) {
return null;
}
// 2 MAGICCODE
byteBuffer.getInt();
// 3 BODYCRC
int bodyCRC = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setBodyCRC(bodyCRC);
// 4 QUEUEID
int queueId = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setQueueId(queueId);
// 5 FLAG
int flag = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setFlag(flag);
// 6 QUEUEOFFSET
long queueOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setQueueOffset(queueOffset);
// 7 PHYSICALOFFSET
long physicOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setCommitLogOffset(physicOffset);
// 8 SYSFLAG
int sysFlag = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setSysFlag(sysFlag);
// 9 BORNTIMESTAMP
long bornTimeStamp = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setBornTimestamp(bornTimeStamp);
// 10 BORNHOST
int bornhostIPLength = 4;
byte[] bornHost = new byte[bornhostIPLength];
byteBuffer.get(bornHost, 0, bornhostIPLength);
int port = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setBornHost(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByAddress(bornHost), port));
// 11 STORETIMESTAMP
long storeTimestamp = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setStoreTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
// 12 STOREHOST
int storehostIPLength = (sysFlag & 20) == 0 ? 4 : 16;
byte[] storeHost = new byte[storehostIPLength];
byteBuffer.get(storeHost, 0, storehostIPLength);
port = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setStoreHost(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByAddress(storeHost), port));
// 13 RECONSUMETIMES
int reconsumeTimes = byteBuffer.getInt();
msgExt.setReconsumeTimes(reconsumeTimes);
// 14 Prepared Transaction Offset
long preparedTransactionOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();
msgExt.setPreparedTransactionOffset(preparedTransactionOffset);
// 15 BODY
int bodyLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
if (bodyLen > 0) {
byte[] body = new byte[bodyLen];
byteBuffer.get(body);
msgExt.setBody(body);
}
// 16 TOPIC
byte topicLen = byteBuffer.get();
byte[] topic = new byte[(int) topicLen];
byteBuffer.get(topic);
msgExt.setTopic(new String(topic, CHARSET_UTF8));
// 17 properties
short propertiesLength = byteBuffer.getShort();
if (propertiesLength > 0) {
byte[] properties = new byte[propertiesLength];
byteBuffer.get(properties);
String propertiesString = new String(properties, CHARSET_UTF8);
Map map = string2messageProperties(propertiesString);
}
int msgIDLength = storehostIPLength + 4 + 8;
ByteBuffer byteBufferMsgId = ByteBuffer.allocate(msgIDLength);
String msgId = createMessageId(byteBufferMsgId, msgExt.getStoreHostBytes(), msgExt.getCommitLogOffset());
msgExt.setMsgId(msgId);
return msgExt;
}
} ```
运行这段代码,我们就可以直接看到 CommitLog 文件中的内容:
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈0-Wed Mar 02 10:04:22 CST 2022
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈0-Wed Mar 02 10:04:22 CST 2022,队列ID:5,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:0
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈1-Wed Mar 02 10:04:25 CST 2022,队列ID:6,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:223
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈2-Wed Mar 02 10:04:26 CST 2022,队列ID:7,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:446
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈3-Wed Mar 02 10:04:27 CST 2022,队列ID:0,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:669
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈4-Wed Mar 02 10:04:28 CST 2022,队列ID:1,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:892
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈5-Wed Mar 02 10:04:29 CST 2022,队列ID:2,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:1115
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈6-Wed Mar 02 10:04:30 CST 2022,队列ID:3,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:1338
主题:tyrant,消息:Hello World 哈哈哈7-Wed Mar 02 10:04:31 CST 2022,队列ID:4,存储地址:/172.18.120.141:10911总大小:223,偏移量:1561CommitLog 文件中包含了主题Topic 和 消息所在的队列以及消息内容还有消息的broker所在的存储地址。
此时,我们再考虑另外一个问题:
CommitLog 文件保存了所有主题的消息,但我们消费时,更多的是订阅某一个主题进行消费。
RocketMQ 是怎么样进行高效的检索消息的呢 ?
2.ConsumeQueue
为了解决上面那个问题, RocketMQ 引入了 ConsumeQueue 消费队列文件。
在继续往下说 ConsumeQueue 之前,我们必须先了解到另外一个概念,即 MessageQueue 。
2.1MessageQueue
在发送消息的时候,要指定一个Topic。那么,在创建Topic的时候,有一个很重要的参数 MessageQueue 。
简单来说,就是你这个Topic对应了多少个队列,也就是几个 MessageQueue,默认是8个。
它的作用是数据分片。
比如我们的Topic里面有100条数据,该Topic默认是4个队列,那么每个队列中大约25条数据。
然后,这些 MessageQueue 是和 Broker 绑定在一起的,就是说每个 MessageQueue 都可能处于不同的 Broker 机器上,这取决于你的队列数量和Broker集群。
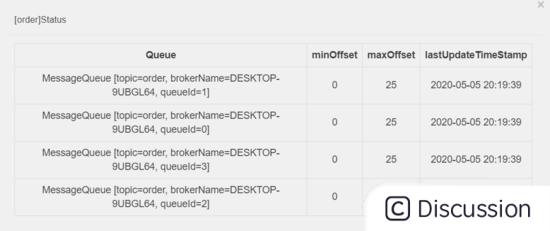
我们来看上面的图片,Topic名称为order的主题,一共有4个 MessageQueue ,每个里面都有25条数据。
因为在笔者的本地环境只有一个 Broker ,所以它们的 brokerName 都是指向同一台机器。
既然 MessageQueue 是多个,那么在消息发送的时候,势必要通过某种方式选择一个队列。
默认的情况下,就是通过轮询来获取一个消息队列。 java public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue() { int index = this.sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0) pos = 0; return this.messageQueueList.get(pos); } 当然, RocketMQ 还有一个故障延迟机制,在选择消息队列的时候会复杂一些,我们今天先不讨论。
消息持久化是RocketMq最核心的环节,它决定了生产者消息写入的吞吐量,决定了消息会不会丢失,消费者获取消息的吞吐量。 Broker的消息持久化依赖于两个文件CommitLog和ConsumeQueue。 当Broker收到一条消息后,首先会把该消息写入磁盘文件CommitLog,顺序写入哦。
CommitLog是很多磁盘文件,每个文件最多1GB,当一个文件写满之后,就新建一个。 现在我们的消息已经持久化在了磁盘上,但是有一个问题,当消费者要消费一条消息时,它怎么知道从CommitLog中具体获取哪个消息呢? 这时就用到另一个磁盘文件ConsumeQueue,在Broker中,每个MessageQueue都有一系列ConsumeQueue文件,如: \$HOME/store/consumequeue/{topic}/{queueid}/{filename}。
queueid就是对应MessageQueue,这个ConsumeQueue文件存储的就是一条消息在CommitLog中的偏移量,看到这里是不是有的懵逼,到底什么意思呢?
其实就是当Broker收到一条消息后,会把消息在CommitLog中的物理位置,也就是一个文件偏移量,记录在对应的MessageQueue的ConsumeQueue文件中。
所以MessageQueue和Topic一样是一个抽象的概念。
2.2ConsumeQueue:30w*20字节
ConsumerQueue消息消费队列是专门为消息订阅构建的索引文件,提高根据主题与消息队列检索消息的速度。
消息消费队列,引入的目的主要是提高消息消费的性能,由于RocketMQ是基于主题topic的订阅模式,消息消费是针对主题进行的,如果要遍历commitlog文件中根据topic检索消息是非常低效的。
Consumer即可根据ConsumeQueue来查找待消费的消息。
其中,ConsumeQueue(逻辑消费队列)作为消费消息的索引,保存了指定Topic下的队列消息在CommitLog中的起始物理偏移量offset,消息大小size和消息Tag的HashCode值。
consumequeue文件可以看成是基于topic的commitlog索引文件,故consumequeue文件夹的组织方式如下:topic/queue/file三层组织结构,具体存储路径为:\$HOME/store/consumequeue/{topic}/{queueId}/{fileName}。
同样consumequeue文件采取定长设计,每一个条目共20个字节,分别为8字节的commitlog物理偏移量、4字节的消息长度、8字节tag hashcode,单个文件由30W个条目组成,可以像数组一样随机访问每一个条目,每个ConsumeQueue文件大小约5.72M;
ConsumerQueue,它是为了高效检索主题消息的。
ConsumerQueue 也是一组组文件,它的位置在
E:\study\5.rocketmq\rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\storestore\consumequeue 。
该目录下面是以Topic命名的文件夹,再下一级是以 MessageQueue 队列ID命名的文件夹,最后才是一个或
多个文件。
order 是topic名称
1是队列id
00000000000000000000是具体文件名
rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\consumequeue\order
rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\consumequeue\order\1\00000000000000000000这样分层之后, RocketMQ 至少可以得到以下几个讯息:
- 先通过主题名称,可以定位到具体的文件夹;
- 然后根据消息队列ID找到具体的文件;
- 最后根据文件内容,找到具体的消息。
那么,这个文件里面存储的又是什么内容呢 ?
2.3解析ConsumerQueue文件
为了加速 ConsumerQueue 的检索速度和节省磁盘空间,文件中不会存储消息的全量消息。
其存储的格式如下:
同样的,我们先写一段代码,按照这个格式输出一下 ConsumerQueue 文件的内容。 ```java import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; //默认8个队列,往每个队列都写了一条消息 //在8个队列对应的consumequeue的文件中 //每个文件中的消息长度都是200 消息偏移量 = 文件名称 * 消息长度 //比如 1是200 2是 400 7是1400 0是1600 0 可以看作是8
//可以看出来队列的负载均衡
public class parseConsumeQueue {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
String path = "E:\study\5.rocketmq\rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\consumequeue\tyrant\5\00000000000000000000";
ByteBuffer buffer = read(path);
while (true){
long offset = buffer.getLong();
long size = buffer.getInt();
long code = buffer.getLong();
if (size==0){
break;
}
System.out.println("消息长度:"+size+" 消息偏移量:" +offset);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
public static ByteBuffer read(String path)throws Exception{
File file = new File(path);
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)file.length()];
fin.read(bytes);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);
return buffer;
}
}
/***
消息长度:223 消息偏移量:0
--------------------------
***/```
2.4通过ConsumeQueue查询消息
现在我们通过 ConsumerQueue 已经知道了消息的长度和偏移量,那么查找消息就比较容易了。 java public static MessageExt getMessageByOffset(ByteBuffer commitLog,long offset,int size) throws Exception { ByteBuffer slice = commitLog.slice(); slice.position((int)offset); slice.limit((int) (offset+size)); MessageExt message = CommitLogTest.decodeCommitLog(slice); return message; } 然后,我们可以依靠这种方法,来实现通过 ConsumerQueue 获取消息的具体内容。 ```java import org.apache.rocketmq.common.message.MessageExt;
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class getMessageByOffset {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//consumerqueue根目录
String consumerPath = "E:\study\5.rocketmq\rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\consumequeue";
//commitlog目录
String commitLogPath = "E:\study\5.rocketmq\rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\commitlog\00000000000000000000";
//读取commitlog文件内容
ByteBuffer commitLogBuffer = parseCommitLog.read(commitLogPath);
//遍历consumerqueue目录下的所有文件
//包含我们的tyrant主题下的8个队列
File file = new File(consumerPath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
//遍历:rocketmq-all-4.3.0-bin-release\bin\store\consumequeue\tyrant\0
for (File f:files) {
if (f.isDirectory()){
File[] listFiles = f.listFiles();
for (File queuePath:listFiles) {
//获取具体文件
String path = queuePath+"/00000000000000000000";
//读取consumerqueue文件内容
ByteBuffer buffer = parseCommitLog.read(path);
while (true){
//读取消息偏移量和消息长度
long offset = (int) buffer.getLong();
int size = buffer.getInt();
long code = buffer.getLong();
if (size==0){
break;
}
//根据偏移量和消息长度,在commitloh文件中读取消息内容
MessageExt message =
getMessageByOffset(commitLogBuffer,offset,size);
if (message!=null){
System.out.println
("消息主题:"+message.getTopic()+" MessageQueue:"+
message.getQueueId()+" 消息体:"
+new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static MessageExt getMessageByOffset(ByteBuffer commitLog, long offset, int size) throws Exception {
ByteBuffer slice = commitLog.slice();
slice.position((int)offset);
slice.limit((int) (offset+size));
MessageExt message = parseCommitLog.decodeCommitLog(slice);
return message;
}
}消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:0 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈3-Wed Mar 02 10:04:27 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:1 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈4-Wed Mar 02 10:04:28 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:2 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈5-Wed Mar 02 10:04:29 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:3 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈6-Wed Mar 02 10:04:30 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:4 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈7-Wed Mar 02 10:04:31 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:5 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈0-Wed Mar 02 10:04:22 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:6 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈1-Wed Mar 02 10:04:25 CST 2022
消息主题:tyrant MessageQueue:7 消息体:Hello World 哈哈哈2-Wed Mar 02 10:04:26 CST 2022```
2.5消费消息
消息消费的时候,其查找消息的过程也是差不多的。
值得注意的一点是:ConsumerQueue文件和 CommitLog 文件可能都是多个。
所以会有一个定位文件的过程。
假设某个消费者启动,获取在Broker1的config文件下的consumerOffset.json。
consumerOffset.json存在以下记录:"tyrant@consumerA":{0:2,1:3}
意思是
1.在主题tyrant下consumerA消费者组目前的消费进度是在queueId为0的队列上消费到了index为2的消息。
2.在主题tyrant下consumerA消费者组目前的消费进度是在queueId为1的队列上消费到了index为3的消息。
下次消费的时候要从
queueId为0的队列上从index为2的消息开始消费。
queueId为1的队列上从index为3的消息开始消费。假设我们现在分配的queueId是0,那么从index为2的消息开始消费。
我们来看源码:首先,根据消费进度2来查找对应的 ConsumerQueue ,获取其文件内容。 ```java public SelectMappedBufferResult getIndexBuffer(final long startIndex) { //ConsumerQueue文件大小 int mappedFileSize = this.mappedFileSize;
//根据startIndex=2,获取在consumerqueue文件里的起始偏移量 //CQSTOREUNITSIZE = 20; long offset = startIndex * CQSTOREUNITSIZE;
if (offset >= this.getMinLogicOffset()) {
//因为可能存在多个ConsumerQueue映射文件
//这里是返回具体的ConsumerQueue映射文件
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset(offset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
//返回文件里的某一块内容,这一块内容就是我们的消息在ConsumerQueue文件中
//保存的消息长度 偏移量 消息tag的hashcode
SelectMappedBufferResult result = mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer
((int) (offset % mappedFileSize));
return result;
}
}
return null;
}``` 拿到消息的消息长度 偏移量 消息tag的hashcode。
直接从CommitLog 文件根据偏移量和消息长度,获取消息即可。 java public SelectMappedBufferResult getMessage(final long offset, final int size) { //commitlog文件大小 int mappedFileSize = this.defaultMessageStore .getMessageStoreConfig() .getMappedFileSizeCommitLog(); //根据消息偏移量,定位到具体的commitlog文件 MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.findMappedFileByOffset (offset, offset == 0); if (mappedFile != null) { //根据消息偏移量和长度,获取消息内容 //offset % mappedFileSize = 8 % 10 = 8 int pos = (int) (offset % mappedFileSize); return mappedFile.selectMappedBuffer(pos, size); } return null; }
3.IndexFile
```java SendResult result = producer.send(msg); //发送状态 SendStatus status = result.getSendStatus(); String msgId = result.getMsgId(); MessageQueue messageQueue = result.getMessageQueue(); System.out.println("结果:" + result ); System.out.println("状态:" + status); System.out.println("messageQueue:" + messageQueue); System.out.println("msgId:" + msgId);
//注意区分offsetMsgId 和 messageId 结果:SendResult [sendStatus=SENDOK, msgId=AC125FB467B414DAD5DC55CCCC480006, offsetMsgId=AC125FB400002A9F00000000001603A8, messageQueue=MessageQueue [topic=rnm, brokerName=broker-a, queueId=3], queueOffset=21] 状态:SENDOK messageQueue:MessageQueue [topic=rnm, brokerName=broker-a, queueId=3] msgId:AC125FB467B414DAD5DC55CCCC480006 ```
IndexFile索引文件提供了一种可以通过key或时间区间来查询消息的方法。
Index文件的存储位置是:$HOME \store\index${fileName}。
文件名fileName是以创建时的时间戳命名的。
固定的单个IndexFile文件大小约为400M,一个IndexFile可以保存 2000W个索引。
IndexFile的底层存储设计为在文件系统中实现HashMap结构。
故rocketmq的索引文件其底层实现为hash索引。
在上面的RocketMQ的消息存储整体架构图中可以看出,RocketMQ采用的是混合型的存储结构,即为单个Broker实例下所有的队列共用一个日志数据文件(即为CommitLog)来存储。
RocketMQ的混合型存储结构(多个Topic的消息实体内容都存储于一个CommitLog中)针对Producer和Consumer分别采用了数据和索引部分相分离的存储结构。
对于生产者只需要写入CommitLog和ConsumeQueue,对于消费者只要根据ConsumeQueue读取CommitLog。
Producer发送消息至Broker,然后Broker使用同步或者异步的方式对消息刷盘持久化,保存至CommitLog中。
只要消息被刷盘持久化至磁盘文件CommitLog中,那么Producer发送的消息就不会丢失。正因为如此,Consumer也就肯定有机会去消费这条消息。
当无法拉取到消息后,可以等下一次消息拉取,同时服务端也支持长轮询模式,如果一个消息拉取请求未拉取到消息,Broker允许等待15s的时间,只要这段时间内有新消息到达,将直接返回给消费端。
这里,RocketMQ的具体做法是,使用Broker端的后台服务线程—ReputMessageService不停地分发请求并异步构建ConsumeQueue(逻辑消费队列)和IndexFile(索引文件)数据。
上面我们看到了通过消息偏移量来查找消息的方式,但 RocketMQ 还提供了其他几种方式可以查询消息。
- 按照Message Key 查询:消息的key是业务开发同学在发送消息之前自行指定的,通常会把具有业务含义,区分度高的字段作为消息的key,如用户id,订单id等。
- 按照Unique Key查询: 除了业务开发同学明确的指定消息中的key,RocketMQ生产者客户端在发送发送消息之前,会自动生成一个UNIQ_KEY,设置到消息的属性中,从逻辑上唯一代表一条消息。
- 按照Message Id 查询:Message Id 是消息发送后,在Broker端生成的,其包含了Broker的地址,和在CommitLog中的偏移信息,并会将Message Id作为发送结果的一部分进行返回。Message Id中属于精确匹配,可以唯一定位一条消息,不需要使用哈希索引机制,查询效率更高。
- 通过时间区间查询,个人猜测是通过indexFile中的每个索引里的与第一条消息的差值字段去查询的。
在这里,Message Key和Unique Key 都是在消息发送之前,由客户端生成的。
Message msg = new Message("rnm", "tag", ("Hello World").getBytes());
//我们可以自己设置Message Key
msg.setKeys("hello");Message Id 是在 Broker 端存储消息的时候生成。
SendResult [
sendStatus=SEND_OK,
msgId=C0A801030D4B18B4AAC247DE4A0D0000,
offsetMsgId=C0A8010300002A9F000000000007BEE9,
messageQueue=MessageQueue [topic=TopicA, brokerName=broker-a, queueId=0],
queueOffset=0]RocketMQ有意弱化Unique Key与Message Id的区别,对外都称之为Message Id。在通过RocketMQ的命令行工具或管理平台进行查询时,二者可以通用。在根据Unique Key进行查询时,本身是有可能查询到多条消息的,但是查询工具会进行过滤,只会返回一条消息。种种情况导致很多RocketMQ的用户,并未能很好对二者进行区分。
msgIdRocketMQ生产者客户端在发送发送消息之前,会自动生成一个UNIQ_KEY,设置到消息的属性中,从逻辑上唯一代表一条消息。注意这里的命名虽然是msgId,但实际上其是Unique Key.
offsetMsgId:Broker返回的Message ID,在后文中,未进行特殊说明的情况下,Message ID总是表示offsetMsgId。
3.1通过OffsetMessageId查询
Message Id 总共 16 字节,包含消息存储主机地址(ip+端口号)和在 CommitLog 文件中的偏移量offset。
有源码为证: java /** * 创建消息ID * @param input * @param addr Broker服务器地址 * @param offset 正在存储的消息,在Commitlog中的偏移量 * @return */ public static String createMessageId(final ByteBuffer input, final ByteBuffer addr, final long offset) { input.flip(); int msgIDLength = addr.limit() == 8 ? 16 : 28; input.limit(msgIDLength); input.put(addr); input.putLong(offset); return UtilAll.bytes2string(input.array()); } 当我们根据 Message Id 向Broker查询消息时,首先会通过一个 decodeMessageId 方法,将Broker地址和消息的偏移量解析出来。 java public static MessageId decodeMessageId(final String msgId) throws Exception { SocketAddress address; long offset; int ipLength = msgId.length() == 32 ? 4 * 2 : 16 * 2; byte[] ip = UtilAll.string2bytes(msgId.substring(0, ipLength)); byte[] port = UtilAll.string2bytes(msgId.substring(ipLength, ipLength + 8)); ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(port); int portInt = bb.getInt(0); //解析出来Broker地址 address = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByAddress(ip), portInt); //偏移量 byte[] data = UtilAll.string2bytes(msgId.substring(ipLength + 8, ipLength + 8 + 16)); bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(data); offset = bb.getLong(0); return new MessageId(address, offset); } 所以通过 OffsetMessage Id 查询消息的时候,实际上还是直接从特定Broker上的 CommitLog 指定位置进行查询,属于精确查询。
//首先会根据偏移量在commitLog中读取4个字节
//这4个字节代表的是commitlog中消息的长度
SelectMappedBufferResult sbr = this.commitLog.getMessage(commitLogOffset, 4);
//消息的真正长度字节
int size = sbr.getByteBuffer().getInt();
//从指定偏移量读取size个字节
return this.commitLog.getMessage(commitLogOffset, size);3.2通过MessageKey和UniqueKey查询
但是如果通过 Message Key 和 Unique Key 查询的时候, RocketMQ 又是怎么做的呢?
通过index索引文件!
ConsumerQueue 消息消费队列是专门为消息订阅构建的索引文件,提高根据主题与消息队列检索消息的速度。
另外,RocketMQ 引入Hash索引机制,为消息建立索引,它的键就是 Message Key 和 Unique Key 。
3.3构建Index索引
那么,我们先看看index索引文件的结构:
为了便于理解,我们还是以代码的方式,来解析这个文件。 ```java public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//index索引文件的路径
String path = "C:\Users\shiqizhen\store\index\20200506224547616";
ByteBuffer buffer = CommitLogTest.read(path);
//该索引文件中包含消息的最小存储时间
long beginTimestamp = buffer.getLong();
//该索引文件中包含消息的最大存储时间
long endTimestamp = buffer.getLong();
//该索引文件中包含消息的最小物理偏移量(commitlog文件偏移量)
long beginPhyOffset = buffer.getLong();
//该索引文件中包含消息的最大物理偏移量(commitlog文件偏移量)
long endPhyOffset = buffer.getLong();
//hashslot个数
int hashSlotCount = buffer.getInt();
//Index条目列表当前已使用的个数
int indexCount = buffer.getInt();
//500万个hash槽,每个槽占4个字节,存储的是index索引
for (int i=0;i<5000000;i++){
buffer.getInt();
}
//2000万个index条目 20字节
for (int j=0;j<20000000;j++){
//消息key的hashcode 4字节
int hashcode = buffer.getInt();
//消息对应的偏移量 8字节
long offset = buffer.getLong();
//消息存储时间和第一条消息的差值 4字节
int timedif = buffer.getInt();
//该条目的上一条记录的index索引 4字节
int pre_no = buffer.getInt();
}
System.out.println(buffer.position()==buffer.capacity());
}``` 我们看最后输出的结果为true,则证明解析的过程无误。
源码分析RocketMQ之消费队列、Index索引文件存储结构与存储机制
我们发送的消息体中,包含 Message Key 或 Unique Key ,那么就会给它们每一个都构建索引。
这里重点有两个:
- 根据消息Key计算Hash槽的位置。
- 根据Hash槽的数量和Index索引来计算Index条目的起始位置。
将当前 Index条目的索引值,写在Hash槽 absSlotPos 位置上。
将 Index条目的具体信息 (hashcode/消息偏移量/与第一条消息的时间差值/hash槽的值) ,从起始偏移量 absIndexPos 开始,顺序按字节写入。 ```java public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) { if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) { //计算key的hash int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key); //计算hash槽的坐标 与 500,0000取模 int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum; //获取slot的写入位置 int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEXHEADERSIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize; //获取旧的slot下的value int oldSlotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
//计算时间差值
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
//计算当前INDEX条目的起始偏移量
//IndexCount是全局自增AutomicInteger
//40字节 + 500万*4字节 + 当前index的数量 * index的大小
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
//依次写入
//hashcode=4字节
//commitLog消息偏移量=8字节
//时间戳=4字节
//hash槽的值=4字节
//共计20字节
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, oldSlotValue);
//将当前INDEX的下标写入HASH槽 注意这里是写入hash槽
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
return true;
}
return false;} //最后的结构就是:(hash槽的写入位置,index的下标) 根据 Message Key 或 Unique Key查询的时候。 0.假设下标为10的slot存的oldSlotvalue是20 1.根据key计算hash值=10 2.根据hash值=10和500万取模获取slot的下标位置即slotIndex=10 3.根据 40 + slotIndex * 4 计算slot写入的位置记做slotOffset=80 4.读取下标为slotIndex的slot的值,读取4字节也就是80-84,记做oldSlotvalue=20 5.计算当前条目的起始偏移量indexOffset:40字节 + 500万4字节 + indexCount * 20记做indexOffset indexCount是全局自增AutomicInteger 6.往indexOffset写入20字节 4字节的key的hashcode、 8字节的commitLog的物理偏移量、 4字节的消息存储时间和第一条消息的差值、 4字节的该slot的上一条记录的index索引下标oldSlotvalue=20 7.将当前key对应的slotIndex写入HASH槽 注意这里是写入hash槽也就是10写入哈希槽 原来的20被覆盖了。 哈希冲突解决办法: 1.第一条消息的slot的下标为1,index为20 2.第二条消息的slot的下标为1,index为30 3.第三条消息的slot的下标为1,index为40 存储结构是什么样的? 插入第1条数据:下标为1的槽里面记录是(1,20) 对应下标为20的index条目的上一条记录的index索引下标为0 即没有上一条,并且存储了第1条数据的key的hashcode、物理偏移量、消息存储时间和第一条消息的差值 插入第2条数据:下标为1的槽里面记录是(1,30) 下标为30的index条目的上一条记录的index索引下标为20 ,并且存储了第2条数据的key的hashcode、物理偏移量、消息存储时间和第一条消息的差值 插入第3条数据:下标为1的槽里面记录是(1,40) 下标为40的index条目的上一条记录的index索引下标为30 ,并且存储了第3条数据的key的hashcode、物理偏移量、消息存储时间和第一条消息的差值 现在假如查询第1条消息 根据key计算hash值 根据hash值和500万取模获取slot的下标位置即slotIndex 读取(40 + slotIndex4 ,40 + slotIndex*4 + 4) 获取到了第3条数据的索引是40, ``` 这样构建完Index索引之后,根据 Message Key 或 Unique Key 查询消息就简单了。
比如我们通过 RocketMQ 客户端工具,根据 Unique Key 来查询消息。
在 Broker 端,通过 Unique Key 来计算Hash槽的位置,从而找到Index索引数据。从Index索引中拿到消息的物理偏移量,最后根据消息物理偏移量,直接到 CommitLog 文件中去找就可以了。
上述设计,可以支持 hashcode 冲突,多个不同的key,相同的 hashcode,index 条目其实是一个逻辑链表的概念,因为每个index 条目的最后4个字节存放的就是上一个的位置。知道存了储结构,要检索 index文件就变的简单起来来,其实就根据 key 得到 hashcode,然后从最新的条目开始找,匹配时间戳是否有效(注意是commitlog存储时间与indexfile第一个条目的时间差,单位秒,如果commitlog存储时间减去indexfile第一个条目的时间等于),最后根据偏移量得到消息的物理地址(存放在commitlog文件中),然后就可以根据 commitlog 偏移量找到具体的消息,从而得到最终的key-value。