ssm框架之SpringMVC:域共享数据
本篇主要聊的是在springmvc中的共享域传递数据的使用。如果对共享域可能不了解的话,可以看下前面聊servlet的时候,对共享域的详细描述,以及其作用和方法。传送阵
至于如何构建SpringMVC的环境,以及如何构建一个项目,可以看下前面的文章。传送阵
request共享域
通过 ServletAPI Request 域共享数据
这个前面说过,现在还是来一个实例演示一下:
重新创建了两个页面,两个页面内容如下:
index.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="SpringMVC结合thymeleaf">thyleaf没有效果h1>
<a th:href="@{/a}" >测试a>
body>
html>
sucess.html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<p th:text="${req}">p>
body>
html>
现在写一个控制类如下:
@Controller
public class controller {
@RequestMapping("/a")
public String test(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("req","我是request");
return "sucess";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String testindex(Model model){
return "index";
}
}
然后访问地址:http://localhost:8080/testSpringMVC_war/index
然后点击测试如下:
但是不太推荐这种方式。
通过ModelAndView 类(推荐)
@RequestMapping("/session")
public String testSession(HttpSession session) {
// public String testSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
// request.getSession().setAttribute("ses", "我是session");
session.setAttribute("ses", "我是session");
return "sucess";
}
这个是SpringMVC 官网推荐方式,不过可以看其名字就可以看出其有两个功能,model代表传递数据,view代表控制调整页面。
其实使用使用 ServletAPI Request 等方式本质还是框架帮忙生成ModelAndView 类,然后进行页面控制,这个后面具体看,先看ModelAndView如何使用。
然后再control类中添加方法:
@RequestMapping("/b")
public ModelAndView testB( ){
// 创建一个ModelAndView对象
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 设置模型数据将数据放入reqeuest中
modelAndView.addObject("req","通过ModeAndView是request");
// 设置视图名称,也就是跳转的页面
modelAndView.setViewName("sucess");
return modelAndView;
}
再index.html中添加:
<a th:href="@{/b}">测试Ba>
然后访问http://localhost:8080/testSpringMVC_war/index
点击测试B:
注意:使用modelAndView类,返回数据的话,那么映射方法必须返回modelAndView的对象。
通过model返回Reuest域共享数据(推荐)
前面说了ModelAndView中的model代表传递数据。那么自然可以单独使用model这个来作为传递数据来用。
还是老规矩进行代码演示
@RequestMapping("/c")
public String testC(Model model){
model.addAttribute("req","通过Model是request");
return "sucess";
}
然后index.html中添加一条:
<a th:href="@{/c}">测试Ca>
还是访问http://localhost:8080/testSpringMVC_war/index,然后点击测试C,结果如下:
通过ModelMap返回Reuest域共享数据
这个就不再演示结果了,因为与上面一样,所以只是写代码
在control中添加:
@RequestMapping("/d")
public String testD(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.addAttribute("req", "通过ModelMap是request");
return "sucess";
}
然后在index.index中添加
<a th:href="@{/d}">测试Da>
通过Map返回Reuest域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/e")
public String testE(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("req", "通过Map是request");
return "sucess";
}
<a th:href="@{/e}">测试Ea>
补充-- Model等几个到底为什么可以传递数据
再回答这个问题的生活,想要将如下操作
在control类中如下:
public class controller {
@RequestMapping("/a")
public String test(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("req", "我是request");
return "sucess";
}
@RequestMapping("/b")
public ModelAndView testB() {
// 创建一个ModelAndView对象
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 设置模型数据将数据放入reqeuest中
modelAndView.addObject("req", "通过ModeAndView是request");
// 设置视图名称,也就是跳转的页面
modelAndView.setViewName("sucess");
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/c")
public String testC(Model model) {
System.out.println("使用Model传递本质是-----"+model.getClass().getName());
model.addAttribute("req", "通过Model是request");
return "sucess";
}
@RequestMapping("/d")
public String testD(ModelMap modelMap) {
System.out.println("使用ModelMap传递本质是-----"+modelMap.getClass().getName());
modelMap.addAttribute("req", "通过ModelMap是request");
return "sucess";
}
@RequestMapping("/e")
public String testE(Map<String, Object> map){
System.out.println("使用Map传递本质是-----"+map.getClass().getName());
map.put("req", "通过Map是request");
return "sucess";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String testindex(Model model) {
return "index";
}
}
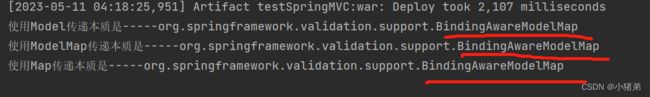
然后看一下后台输出了什么:
其实本质上都是类:
org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
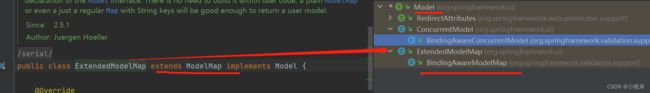
那就可以BindingAwareModelMap上面三个有关系,截图看一下:
而BindingAwareModelMap与map的关系,需要看游戏modelMap代码了
session共享域
这个直接如下即可:
@RequestMapping("/session")
// 可以通过HttpServletRequest得到session
// public String testSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
// request.getSession().setAttribute("ses", "我是session");
public String testSession(HttpSession session) {
session.setAttribute("ses", "我是session");
return "sucess";
}
当然sucess.html需要如下添加:
<p th:text="${session.ses}">p>
application"共享域
代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/application")
public String testApplication(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getServletContext().setAttribute("app", "我是application");
return "sucess";
}
然后再sucees.index添加:
<p th:text="${application.app}">p>