String类1
String类
单个字符可以用char类型保存,多个字符组成的文本就需要保存在String对象中,String通常被称为字符串,一个对象最多占用4GB的文本类容。
- 声明字符串
1.字符串必须包含在“”中 例:”234”、”你好!”
2.声明字符串:String str;(声明变量必须初始化,否则会报错)
其中String 指该变量为字符串类型
Str 任意有效的变量名
String str = “你好!”;
- 创造字符串
Java中创建其他类对象,创建字符串对象,创建对象使用类的构造方法。
String的常用构造方法:
String(char a[])
Char a[] = {‘g’,’o’,’o’,’d’};
String s = new String(a);
等价于:String s = new String(“good”);- String(char a[], int offset, int length )该方法提取数组a的一部分创造一个字符串(数组对象,开始下标,字符串长度)
Char a[] = {‘s’,’t’,’u’,’e’,’n’,’t’};
String s = new String(a,2,4)
等价于:String s = new String(“uden”);- String(char[] value)该构造方法可分配一个新的String对象,使其表示字符数组参数中所有元素连接的结果
Char a[] = {‘s’,’t’,’u’,’d’,’e’,’n’,’t’}
String s = new String(a);
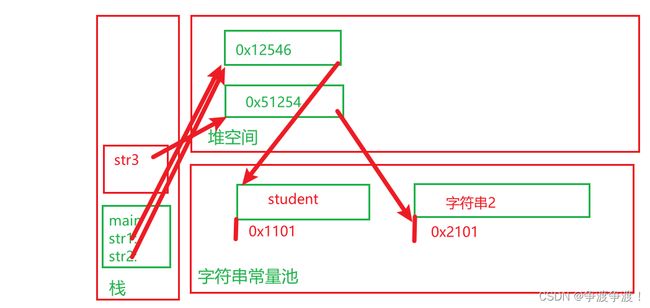
等价于:String s = new String(“student”);内存分析:
字符串内容保存在字符串常量池中;堆空间中储存字符串常量池相应内容的地址:内容相等时对象地址相同;字符串内容不相等时,自动添加到的字符串常量池中,并创建新的对象;
- 连接字符串;
1.连接多个字符串
使用“+”运算符可实现连接多个字符串功能,连接多个String对象并产生一个新的String对象。
Public class join{
Public static void main(Steing args[]){
String s1 = new String(“春风得意马蹄疾 ”);
String s2 = new String(“一日看尽长安花 “);
String s3 = s1 + s2;
System.out.println(s3);
}
}运行结果:春风得意马蹄疾
一日看尽长安花
2.连接其他数据类型
字符串与其他基本数据类型进行连接,会将其他数据类型的数据直接转换成字符串。
Public class join{
Public static void main(Steing args[]){
String s1 = new String(“春风得意马蹄疾 ”);
Int a= 1234567;
String s3 = s1 + a;
System.out.println(s1 + a);
System.out.println(s3);
}只要使用“+“运算符的一个操作数的字符串,编译器就会将另一个操作数转换成字符串形式。
- 获取字符串信息
- 获取字符串长度
使用String类的length()方法可获取声明的字符串对象的长度。
例:
String str = “We are student”;
Int len = str.length();- 字符串查找
String类提供两种查找字符串的方法indexOf()与lastIndexOf()方法。
indexOf(String s):返回字符串首次出现的索引位置。调用时,会从当前字符串开始位置查找S;例;
String str = “We are student”;
int size = str.indexOf(“a”);运行结果:size = 3