QML编程--学习Qt开发
QML编程--学习Qt开发
作者:老九—技术大黍
社交:知乎
公众号:老九学堂(新人有惊喜)
特别声明:原创不易,未经授权不得转载或抄袭,如需转载可联系笔者授权
前言
本讲义代码是使用Qt 6版本执行通过的,请大家放心使用。
什么是QML
我来参考翻译一下:
QML是一种Qt Meta-object Language的缩写。它是一种声明式编程语言,并且它是Qt框架的一个组成部分。QML的主要功能是让开发人员快速、便捷地开发出用户界面,这些界面包括了桌面应用、移动设备和嵌入式就用的界面。并且,QML还能够与JavaScript无缝整合一起开发使用,即在QML代码中可以直接使用JavaScript文件。
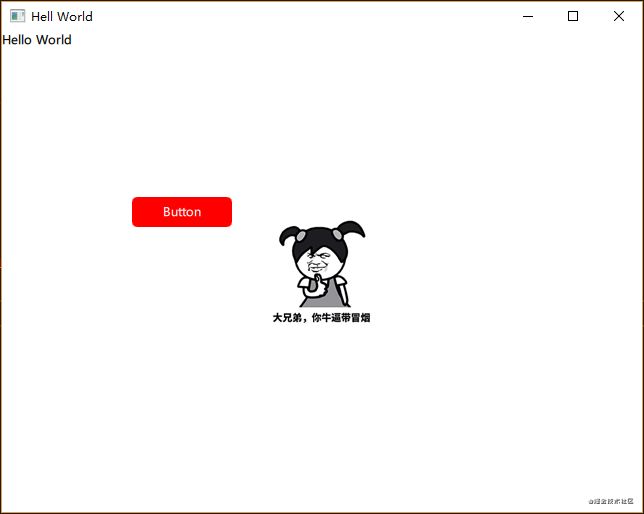
第一个Hello World
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
Window{
visible:true
width:640
height:480
title:qsTr("Hell World");
Rectangle {
width: 360
height: 360
Rectangle{
id: button1
width: 100
height: 30
color: "red"
radius: 5
anchors.centerIn:parent
Text{
id: buttonText
text:qsTr("Button")
color:"white"
anchors.centerIn:parent
}
MouseArea{
anchors.fill:parent
onClicked:{
buttonText.text = qsTr("Clicked");
buttonText.color = "black";
}
}
}
}
Text{
id:text1
text: qsTr("Hello World")
anchors.left:button1.right
}
Image{
source:"nb.png"
anchors.centerIn:parent
}
}运行效果
鼠标事件响应
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
Window{
visible:true
width:480
height:240
Rectangle{
anchors.fill:parent
color:"#4b7a4a"
MouseArea{
anchors.fill:parent
acceptedButtons: Qt.AllButtons
onClicked:{
console.log("Mouse Clicked.")
console.log("Mouse Location: <",mouseX,",",mouseY,">").
if ( mouse.button === Qt.RightButton )
parent.color = 'blue'
if ( mouse.button === Qt.LeftButton )
parent.color = 'red'
if ( mouse.button === Qt.MiddleButton )
parent.color = 'yellow'
}
onReleased: {
// print to console
console.log("Mouse Released.")
}
onDoubleClicked: {
// print to console
console.log("Mouse Double Clicked.")
}
}
}
}运行效果
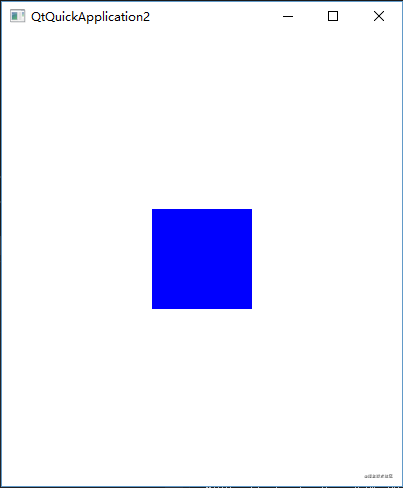
动画
演示代码
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
Window{
visible: true
width: 400
height: 640
Rectangle{
id: rect
anchors.centerIn: parent
height: 100
width: 100
color: "blue"
MouseArea{
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: na.running = true
}
NumberAnimation {
id: na //动画类型的ID
target: rect //动画运行的目标项
property: "height" //动画修改目标项的属性是什么
duration: 200 //动画执行时间长度
from: rect.height //动画属性的初始值
to: 200 //属性在动画执行后的最终值
}
}
}运行效果
我们点击蓝色方块后
在C++中创建自定义元素
QML有大量的可视化元素,如果只使用QML脚本语言,也是可以QML的可视化元素构建复杂的应用。我们可以基于这些标准件来构建界面 ,另外,我们还可以使用Canvas这种元素来创建自定义元素。除了不能构造触摸元素,QML其它界面元素都是可以构建的。
不过,QML脚本也不是万能的,虽然QML因为是什么OpenGL技术来实现界面高速绘制界面,因此我们可以使用QML实现两种自定义绘制元素:
- The traditional for Qt way using QPainter (QQuickPaintedItem). (传统的方式是使用QPainter/QQuickPaintedItem来绘制界面)
- The common QML way using QQuickItem and OpenGL functionality. (QML一般使用QQuickItem和OpenGL函数来绘制界面)
第一种方式似乎比较容易实现,并且QtQuick绘制的效率是比较慢的,因此,如果我们使用第二种方式绘制界面元素时,它们的运行效率会更快。
演示代码
QQuickCustomItem头文件
#pragma once
#include
/**
* 功能:创建一个自定义的类,实现QQuickItem类。用来演示自定义控件元素的实现
* 作者:技术大黍
*/
class QQuickCustomItem :
public QQuickItem
{
Q_OBJECT
Q_PROPERTY(QColor color READ color WRITE setColor NOTIFY colorChanged)
public:
QQuickCustomItem(QQuickItem* parent = Q_NULLPTR);
void paint(QPainter* painter);
protected:
QSGNode* updatePaintNode(QSGNode* oldNode, UpdatePaintNodeData* updatePaintNodeData);
QColor color() const;
void setColor(const QColor& color);
private:
QColor m_color;
bool m_needUpdate;
signals:
void colorChanged();
}; QQuickCustomItem源文件
#include "QQuickCustomItem.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
QQuickCustomItem::QQuickCustomItem(QQuickItem* parent /*= Q_NULLPTR*/)
:QQuickItem(parent),
m_color(Qt::red),
m_needUpdate(true)
{
setFlag(QQuickItem::ItemHasContents);
}
void QQuickCustomItem::paint(QPainter* painter)
{
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(width() / 2, 0);
path.lineTo(width(), height());
path.lineTo(0, height());
path.lineTo(width() / 2, 0);
painter->fillPath(path, m_color);
}
QSGNode* QQuickCustomItem::updatePaintNode(QSGNode* oldNode, UpdatePaintNodeData* updatePaintNodeData)
{
Q_UNUSED(updatePaintNodeData)
QSGGeometryNode* root = static_cast(oldNode);
if (!root) {
root = new QSGGeometryNode;
QSGGeometry* geometry = new QSGGeometry(QSGGeometry::defaultAttributes_Point2D(), 3);
geometry->setDrawingMode(6);
geometry->vertexDataAsPoint2D()[0].set(width() / 2, 0);
geometry->vertexDataAsPoint2D()[1].set(width(), height());
geometry->vertexDataAsPoint2D()[2].set(0, height());
root->setGeometry(geometry);
root->setFlag(QSGNode::OwnsGeometry);
root->setFlag(QSGNode::OwnsMaterial);
}
if (m_needUpdate) {
QSGFlatColorMaterial* material = new QSGFlatColorMaterial;
material->setColor(m_color);
root->setMaterial(material);
m_needUpdate = false;
}
return root;
}
QColor QQuickCustomItem::color() const
{
return m_color;
}
void QQuickCustomItem::setColor(const QColor& color)
{
if (m_color != color)
{
m_color = color;
m_needUpdate = true;
update();
colorChanged();
}
} main.qml文件
import QtQuick 2.3
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import main.qml 1.0
Window {
width: 800
height: 800
visible: true
Rectangle {
width: 200
height: 200
anchors.centerIn: parent
color: "lightgrey"
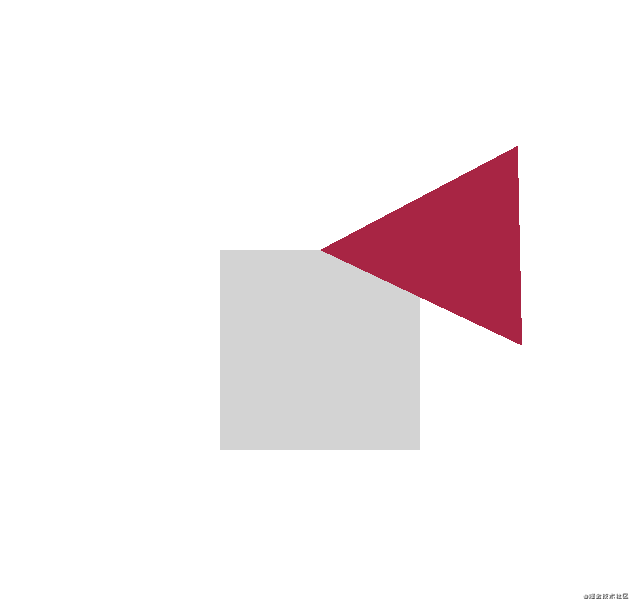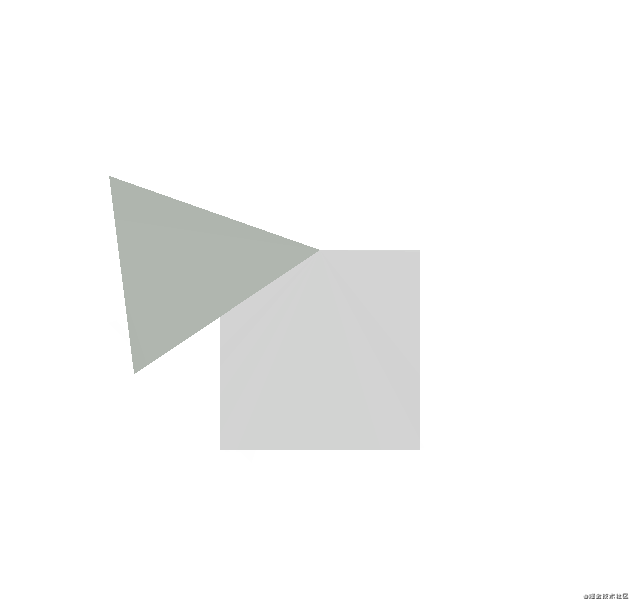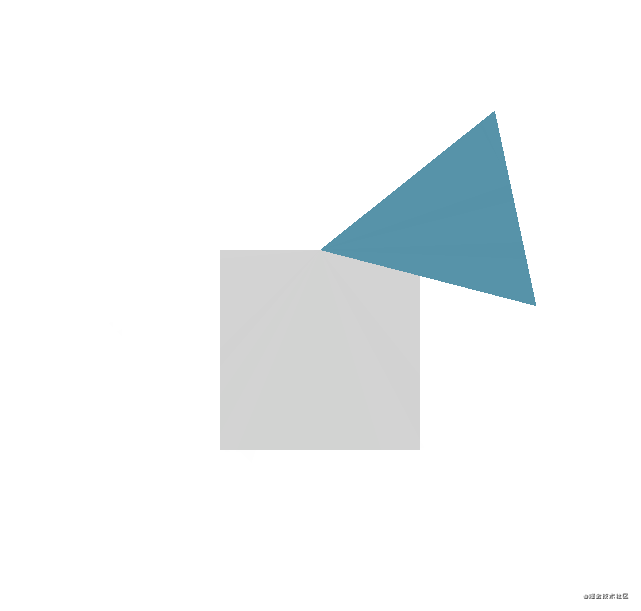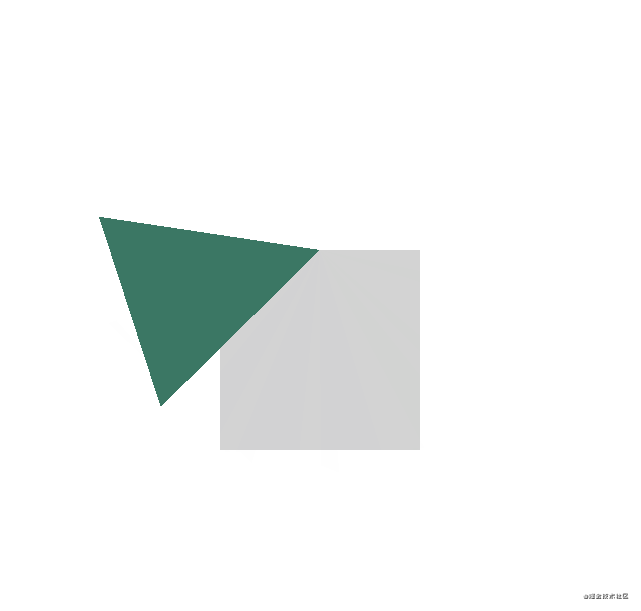
Triangle {
id: rect
width: 200
height: 200
transformOrigin: Item.Top
color: "green"
onColorChanged: console.log("color was changed");
PropertyAnimation on rotation {
from: 0
to: 360
duration: 5000
loops: Animation.Infinite
}
}
}
Timer {
interval: 1000
repeat: true
running: true
onTriggered: rect.color = Qt.rgba(Math.random(),Math.random(),Math.random(),1);
}
}main.cpp文件
#include
#include
#include "QQuickCustomItem.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#if defined(Q_OS_WIN)
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
#endif
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
// 老九学堂-技术大黍:使用自定义组件显示三角形动画
qmlRegisterType("main.qml", 1, 0, "Triangle");
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
if (engine.rootObjects().isEmpty())
return -1;
return app.exec();
} 运行效果
与C++整合
我们可以直接从C++创建QtQuick视图,并且还可以把C++定义的函数暴露给QML使用。
main.cpp文件
#include
#include
#include "QQuickCustomItem.h"
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#if defined(Q_OS_WIN)
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
#endif
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQuickView view;
view.setSource(QStringLiteral("main.qml"));
// Retrieving the QML context. This context allows us to expose data to the QML components
QQmlContext* rootContext = view.rootContext();
// Creating 2 new properties: the width and height of the view
rootContext->setContextProperty("WINDOW_WIDTH", 640);
rootContext->setContextProperty("WINDOW_HEIGHT", 360);
// Let's display the view
view.show();
return app.exec();
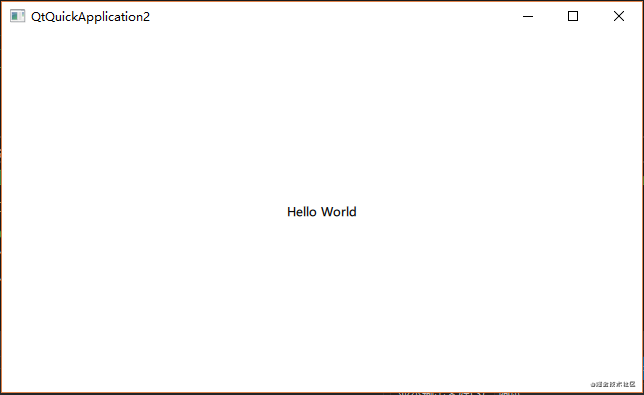
} main.qml文件
import QtQuick 2.3
Rectangle {
// We can now access the properties we defined from C++ from the whole QML file
width: WINDOW_WIDTH
height: WINDOW_HEIGHT
Text {
text: qsTr("Hello World")
anchors.centerIn: parent
}
}运行效果
Qt5版本更新
如果是Qt5.x版本,那么我们可以QQmlApplicationEngine类来替换QQuickView类来加载和呈现QML脚本。修改代码如下:
修改main.cpp
#include
#include
#include "QQuickCustomItem.h"
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#if defined(Q_OS_WIN)
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
#endif
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
QQmlContext* rootContext = engine.rootContext();
rootContext->setContextProperty("WINDOW_WIDTH", 640);
rootContext->setContextProperty("WINDOW_HEIGHT", 360);
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
return app.exec();
} 修改main.qml
import QtQuick 2.3
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
Window { // Must be this type to be loaded by QQmlApplicationEngine.
visible: true
width: WINDOW_WIDTH //Accessing global context declared in C++
height: WINDOW_HEIGHT //Accessing global context declared in C++
title: qsTr("Hello World")
Component.onCompleted: {
// We can access global context from within JavaScript too.
console.debug( "Width: " + WINDOW_WIDTH )
console.debug( "Height: " + WINDOW_HEIGHT )
}
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
Qt.quit();
}
}
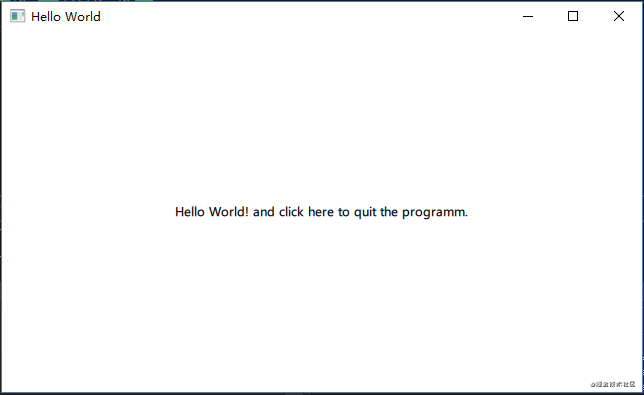
Text {
text: qsTr("Hello World! and click here to quit the programm.")
anchors.centerIn: parent
}
}运行效果
最后
记得给大黍❤️关注+点赞+收藏+评论+转发❤️
作者:老九学堂—技术大黍
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。