redis设计与实现-Reactor模型的应用
1.概述
Redis没有使用第三方的libevent等网络库,而是基于Reactor模式自己开发了一个单线程的Reactor模型的事件处理模型。
称为文件事件处理器,其使用I/O多路复用,同时监听多个套接字,根据套接字执行的任务来为套接字关联不同的事件处理器。
Redis在主循环中统一处理文件事件和时间事件,信号事件则由专门的handler来处理。
2.实现
分为四个部分:套接字、I/O多路复用程序、文件事件派发器、事件处理器。
I/O多路复用程序会监听多个套接字,并将所有产生事件的套接字放到一个队列中,通过队列,每次一个套接字的方式向文件事件派发器传送套接字,相应的有事件处理器处理这些套接字。
当该套接字为事件所关联的事件处理器处理完毕之后,I/O多路复用程序才会继续向文件事件派发器传送下一个套接字。
图片参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/harvyxu/p/7499396.html
2.1 服务启动过程:
2.1.1 启动redisServer(redis.c/main),在main主线程中initServer:
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// 初始化服务器
initServerConfig();
// 如果服务器以 Sentinel 模式启动,那么进行 Sentinel 功能相关的初始化
// 并为要监视的主服务器创建一些相应的数据结构
if (server.sentinel_mode) {
initSentinelConfig();
initSentinel();
}
// 创建并初始化服务器数据结构
initServer();
// 省略加载rdb、aof文件等过程
// 运行事件处理器,一直到服务器关闭为止
aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep);
aeMain(server.el);
// 服务器关闭,停止事件循环
aeDeleteEventLoop(server.el);
}2.1.2 在redis.c/initServer中,初始化eventloop,并注册文件描述符事件和相关handler事件处理器:
// 初始化EventLoop
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+REDIS_EVENTLOOP_FDSET_INCR);
/* Create the serverCron() time event, that's our main way to process
* background operations. */
// 为 serverCron() 创建时间事件
if(aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
redisPanic("Can't create the serverCron time event.");
exit(1);
}
/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix
* domain sockets. */
// 为 TCP 连接关联连接应答(accept)处理器
// 用于接受并应答客户端的 connect() 调用
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
redisPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
// 为本地套接字关联应答处理器
if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event.");
/* Open the AOF file if needed. */
// 如果 AOF 持久化功能已经打开,那么打开或创建一个 AOF 文件
if (server.aof_state == REDIS_AOF_ON) {
server.aof_fd = open(server.aof_filename,
O_WRONLY|O_APPEND|O_CREAT,0644);
if (server.aof_fd == -1) {
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Can't open the append-only file: %s",
strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
}
2.1.3 轮训事件主循环(ae.c/aeMain):
/*
* 事件处理器的主循环
*/
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么运行它
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 开始处理事件
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
2.1.4 调度文件事件和时间事件的过程分为几个步骤(ae.c/aeProcessEvents):
(1)底层调用接口返回,将就绪事件拷贝到eventLoop->fired数组;
(2)遍历就绪数组,获取相关fd,进而获取fd对应的aeFileEvent : eventLoop->events[fd],从而得到相关handler;
/* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event
* (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed).
*
* 处理所有已到达的时间事件,以及所有已就绪的文件事件。
*
* Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event
* fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any).
*
* 如果不传入特殊 flags 的话,那么函数睡眠直到文件事件就绪,
* 或者下个时间事件到达(如果有的话)。
*
* If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns.
* 如果 flags 为 0 ,那么函数不作动作,直接返回。
*
* if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_ALL_EVENTS ,所有类型的事件都会被处理。
*
* if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_FILE_EVENTS ,那么处理文件事件。
*
* if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_TIME_EVENTS ,那么处理时间事件。
*
* if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all
* the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_DONT_WAIT ,
* 那么函数在处理完所有不许阻塞的事件之后,即刻返回。
*
* The function returns the number of events processed.
* 函数的返回值为已处理事件的数量
*/
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
/* Note that we want call select() even if there are no
* file events to process as long as we want to process time
* events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready
* to fire. */
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
// 获取最近的时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop);
if (shortest) {
// 如果时间事件存在的话
// 那么根据最近可执行时间事件和现在时间的时间差来决定文件事件的阻塞时间
long now_sec, now_ms;
/* Calculate the time missing for the nearest
* timer to fire. */
// 计算距今最近的时间事件还要多久才能达到
// 并将该时间距保存在 tv 结构中
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
tvp = &tv;
tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec;
if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) {
tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000;
tvp->tv_sec --;
} else {
tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000;
}
// 时间差小于 0 ,说明事件已经可以执行了,将秒和毫秒设为 0 (不阻塞)
if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0;
if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0;
} else {
// 执行到这一步,说明没有时间事件
// 那么根据 AE_DONT_WAIT 是否设置来决定是否阻塞,以及阻塞的时间长度
/* If we have to check for events but need to return
* ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout
* to zero */
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
// 设置文件事件不阻塞
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* Otherwise we can block */
// 文件事件可以阻塞直到有事件到达为止
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */
}
}
// 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由 tvp 决定
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 从已就绪数组中获取事件
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
// 读事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
// rfired 确保读/写事件只能执行其中一个
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
// 写事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
// 执行时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}2.2 相关数据结构
aeEventLoop, aeFileEvent, aeFiredEvent
图片参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/harvyxu/p/7499396.html
2.2.1 aeEventLoop,由ae.c/*aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize)初始化
events数组(已经注册的文件事件):是在服务启动的时候初始化
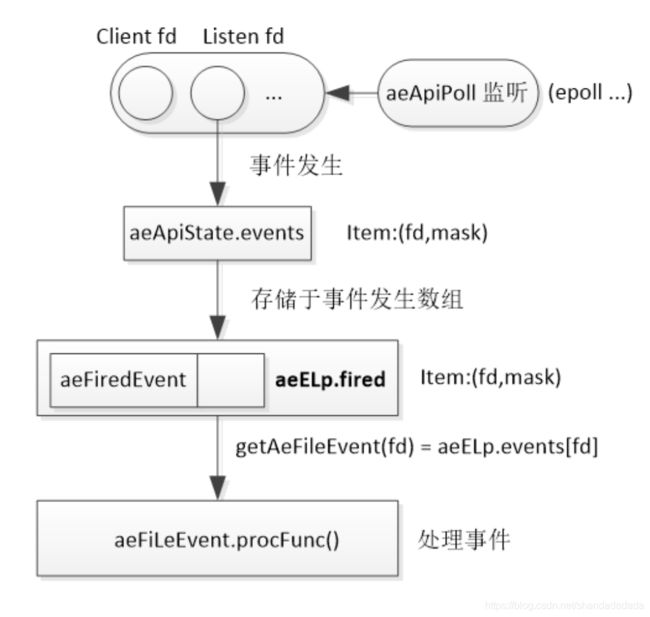
fired数组(已经就绪的文件事件):在aeApiPoll调用底层IO复用函数(如epoll)返回时,会将就绪事件从底层的就绪数组aeApiState.events拷贝到eventLoop->fired就绪数组中;通过aeFiredEvent中的fd可以找到对应的aeFileEvent,进而获取相关的handler处理器。
/* State of an event based program
*
* 事件处理器的状态
*/
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
// 目前已注册的最大描述符
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */
// 目前已追踪的最大描述符
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */
// 用于生成时间事件 id
long long timeEventNextId;
// 最后一次执行时间事件的时间
time_t lastTime; /* Used to detect system clock skew */
// 已注册的文件事件
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */
// 已就绪的文件事件
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */
// 时间事件
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead;
// 事件处理器的开关
int stop;
// 多路复用库的私有数据
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */
// 在处理事件前要执行的函数
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep;
} aeEventLoop;2.2.2 aeFiredEvent
/* A fired event
*
* 已就绪事件
*/
typedef struct aeFiredEvent {
// 已就绪文件描述符
int fd;
// 事件类型掩码,
// 值可以是 AE_READABLE 或 AE_WRITABLE
// 或者是两者的或
int mask;
} aeFiredEvent;2.2.3 aeFiredEvent
/* File event structure
*
* 文件事件结构
*/
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
// 监听事件类型掩码,
// 值可以是 AE_READABLE 或 AE_WRITABLE ,
// 或者 AE_READABLE | AE_WRITABLE
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */
// 读事件处理器
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
// 写事件处理器
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
// 多路复用库的私有数据
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;
3.总结
(1) 通过aeApiPoll监听用户感兴趣的事件;
(2) 当有文件事件发生时返回(此处不考虑时间事件),就绪事件将存储于底层的就绪数组aeApiState.events;
(3) 将就绪数组拷贝到aeEventLoop的就绪数组aeEventLoop.fired中;
(4)通过fd,在aeEventLoop的注册文件事件数组中找到aeFileEvent -- eventLoop->events[fd],最后调用相关回调函数,完成事件处理。
(5) epoll流程:
redis的定时任务是死循环+epoll_wait延时来实现的。其函数调用顺序是:
redis.c main 调用ae.c aeMain (死循环)
ae.c aeMain 调用 ae.c aeProcessEvents:
ae.c aeProcessEvents 调用 ae.c aeSearchNearestTimer(获取定时任务里下一个需要执行的任务)
ae.c aeProcessEvents 调用 ae_poll.c aeApiPoll(设置epoll_wait)
epoll_wait超时触发后,执行redis.c serverCron (由serverCron来调用各种具体的定时任务)